30: Skull Foramina and Cranial Nerves
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
fissure
opening between 2 bones (articulation)
foramen
hole within a bone
canal
elongated passageway, has its own foramen on each end
meatus
air filled passageways
What is the name of cranial n. III, and what innervation is it?
oculomotor n.
GSE and GVE
GSE
general somatic efferent (motor)
GSA
general somatic afferent (sensory)
GVE
general visceral efferent (parasympathetic)
What is the name of cranial n. IV, and what innervation is it?
trochlear n.
GSE
What is the name of cranial n. VI, and what innervation is it?
abducens n.
GSE
What is the name of cranial n. II, and what innervation is it?
optic n.
special afferent
What is the name of cranial n. I, and what innervation is it?
olfactory n.
special afferent
What is the name of cranial n. VII, and what innervation is it?
facial n.
GSE, GSA, GVE, special afferent
What is the name of cranial n. IX, and what innervation is it?
glossopharyngeal n.
GSA, GSE, GVE, special afferent
What is the name of cranial n. V, and what innervation is it?
trigeminal n.
GSA
What is the name of cranial n. VIII, and what innervation is it?
vestibulocochlear n.
special afferent
What is the name of cranial n. X, and what innervation is it?
vagus n.
GVE, GSE, GSA, special afferent
What is the name of cranial n. XI, and what innervation is it?
accessory n.
GSE
What is the name of cranial n. XII, and what innervation is it?
hypoglossal n.
GSE
The trigeminal nerve has 3 branches. What are they, and what is their innervation?
V1- GSA
V2- GSA
V3- GSA and GSE
Why is it important to know the skull and mandible foramen?
nerve blocks
The foramen magnum is the passageway for what structures?
spinal cord
meninges
vessels
The muscular tubercles are located between what structures? What is their function?
basilar portion of occipital bone and basisphenoid bone
point of insertion of the longus capitis mm.
The vertebral arteries converge in the skull to form what structure? Where?
basilar a.
basilar part of occipital bone
The hypoglossal canal is the passageway for what nerve? What does this nerve innervate?
CN XII (hypoglossal n.)
motor to the tongue
The tympana-occipital fissure is a passageway for what structure(s)?
CN IX (glossopharyngeal n.)
CN X (vagus n.)
CN XI (accessory n.)
internal carotid a.
sympathetic nn.
What attaches to the tentorial process? Where isthmus process located?
dura matter attaches and extends down between cerebellum and cerebrum
between the brain hemispheres and cerebellum
The zygomatic process is a process of what bone? What bone does it articulate, and what structure does it form?
temporal bone
zygomatic bone
zygomatic arch
What 2 structures form the bony processes of the temporomandibular joint?
mandibular fossa and condylar process
What fossa conjoins with the condylar process of the mandible?
mandibular fossa
The mandibular process is the site of articulation with what bone? What joint does this form?
condylar process of the mandible
temporomandibular joint
The internal petrosal portion of the temporal bone provides what canal, meatus, fossa, and foramen?
canal for trigeminal n. (CN V)
internal acoustic meatus
cerebellar fossa
jugular foramen
The apex of the petrosal portion of the temporal bone is directed in what direction?
rostrally
The internal acoustic meatus houses what structures?
facial n. (CV VII)
vestibulocochlear n. (CN VIII)
The cerebellar fossa houses what structure?
parafollicular lobe of cerebellum
The jugular foramen houses what structures?
CN IX, X, and XI
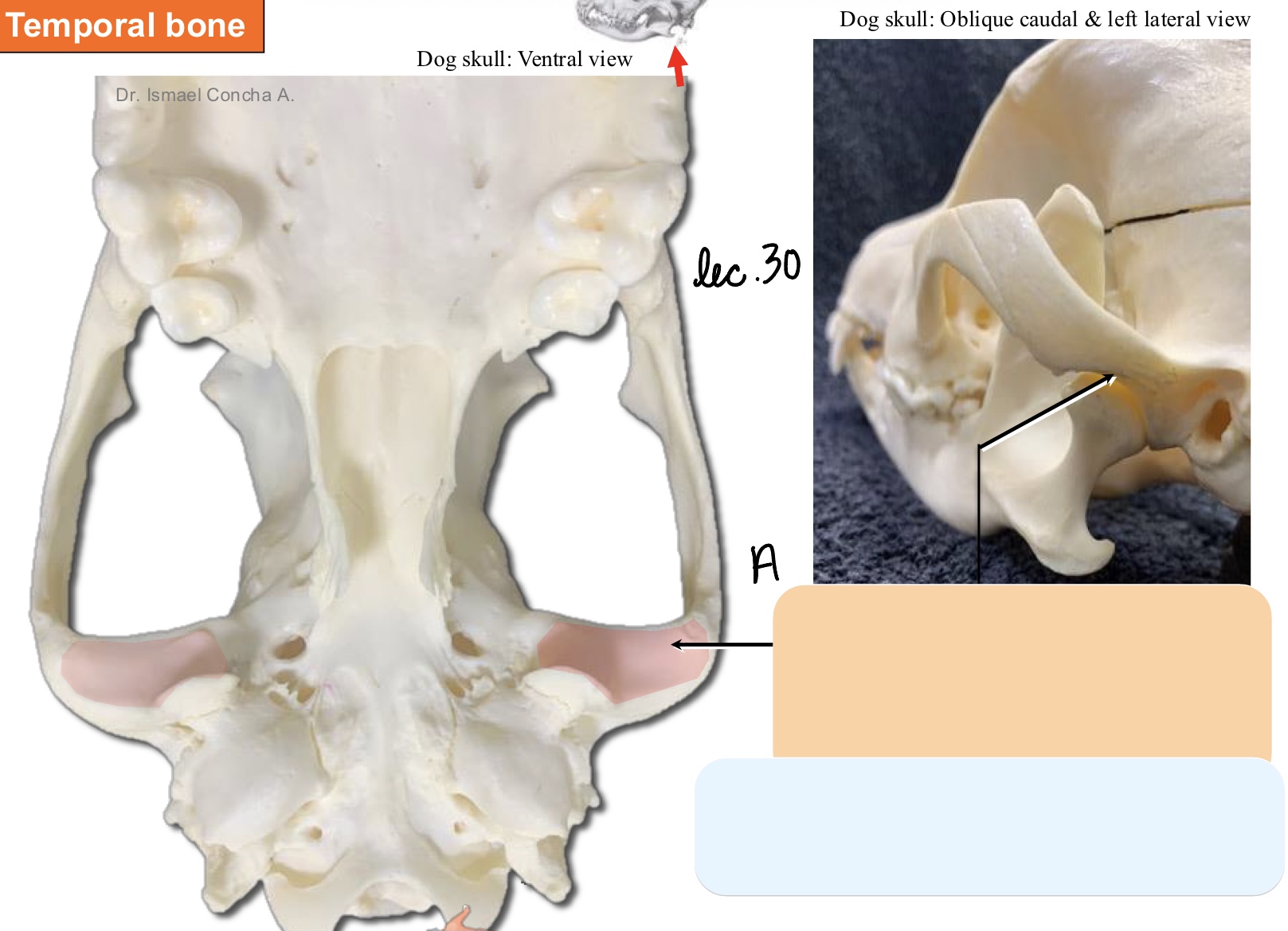
The external petrosal portion of the temporal bone has what process and foramen?
mastoid process
stylomastoid foramen
What is the significance of the mastoid process?
point of insertion of some neck muscles
What structures pass through the stylomastoid foramen?
facial n. (CN VII)
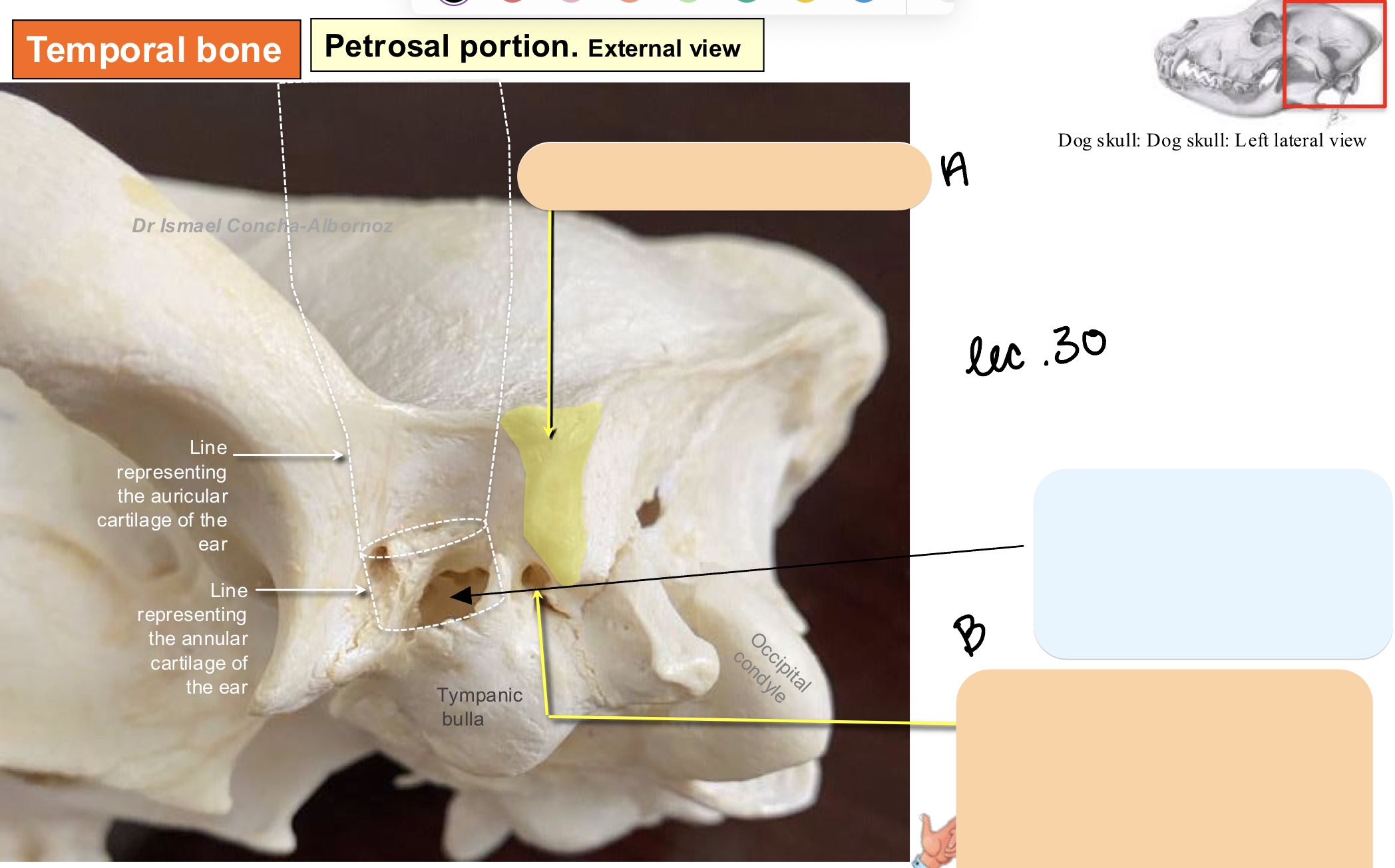
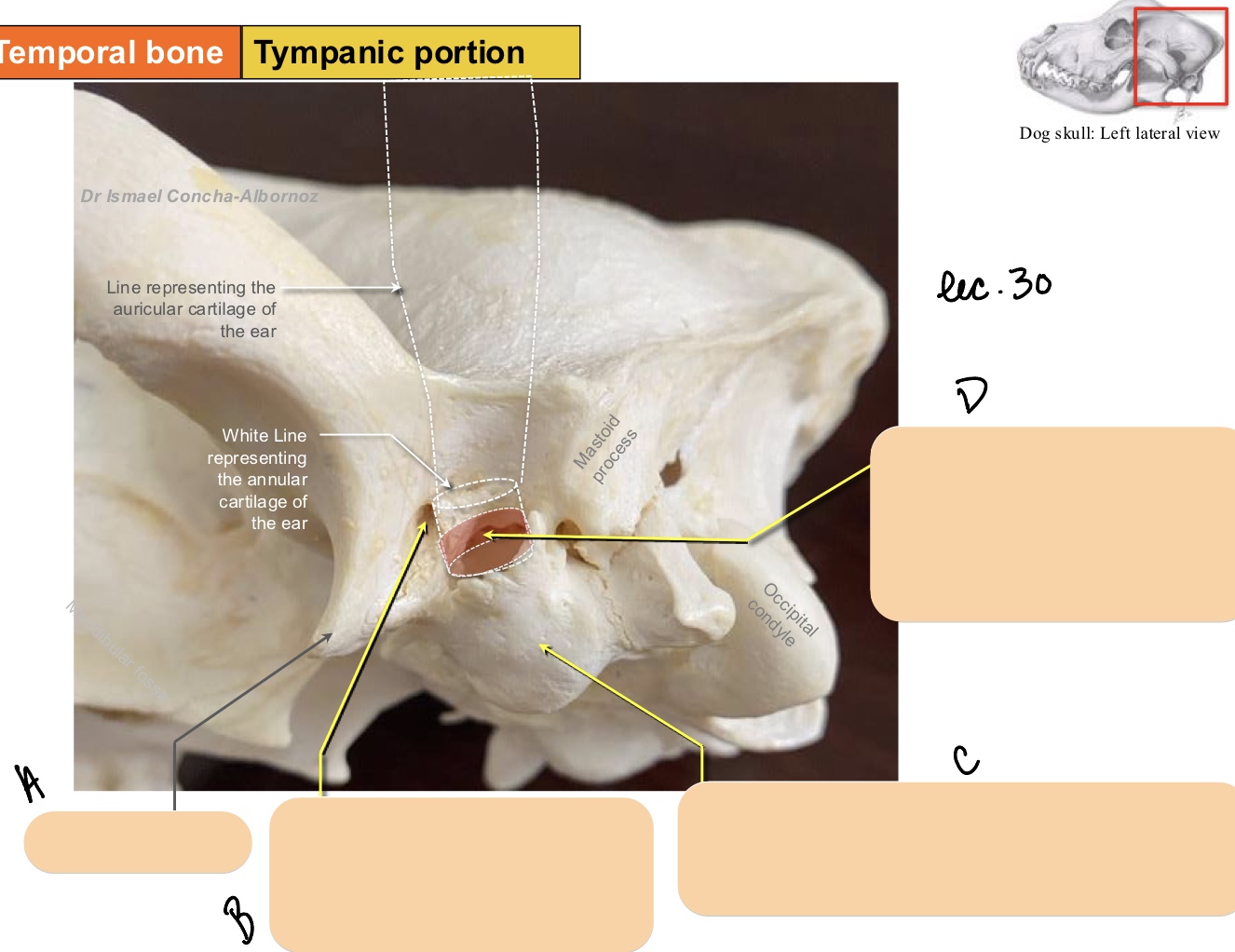
The tympanic portion of the temporal bone is contains a bulla, meatus, and foramen. What are they?
tympanic bulla
external acoustic meatus
retroarticular foramen
The retroarticular foramen provides passage for what structure?
retroarticular vein
tympanic bulla
hemispherical bony structure, encapsulates air-filled, ventral expansion of middle ear cavity
The external acoustic meatus leads into what area? What is this structure?
cavity of the middle ear
short, bony canal where the tympanic membrane attaches
What structure serves as the landmark between the middle and external ear?
external acoustic meatus
The basisphenoid bone contains a fissure, 4 foramen, a fossa, and a tiny prominence. What are they?
orbital fissure
round, oval, caudal alar, and rostral alar foramen
hypophyseal fossa
dorsum sellae
The orbital fissure allows passage of what structures?
oculomotor n. (CN III)
trochlear n. (CN IV)
abducens n. (CN VI)
ophthalmic n. (CN V-1)
The trigeminal nerve has 3 branches. What are they?
ophthalmic n. (CN V-1)
maxillary n. (CN V-2)
mandibular n. (CN V-3)
The round foramen allows passage of what structure?
maxillary n. (CN V-2)
The oval foramen allows passage of what structure?
mandibular n. (CN V-3)
The hypophyseal fossa houses what structure? In what depression is it located?
hypophysis (pituitary gland)
sella turcica
What is the name of the caudal-most bony prominence of the sella turcica?
dorsum sellae
The caudal alar foramen allows passage for what structure?
maxillary a.
The rostral alar foramen allows passage for what structures?
maxillary n.
maxillary a.
The alar canal is located between what two foramen?
caudal alar and rostral alar foramen
The presphenoid bone contains what structures?
optic canals
chiasmatic groove
The optic canals allow passage of what structure?
optic n. (CN II)
chiasmatic groove
bony groove for optic chiasm
corresponds to the optic nn. crossover
What structure forms the rostral part of the temporal fossa?
temporal surface/face
What structure forms the medial surface of the orbit?
orbital part of the frontal bone
The frontal bone is what type of bone? What does this mean?
pneumatic bone
it contains air filled spaces or sinuses connected with the nasal cavity
How many sinuses are there normally in the frontal bone? The cavity of some of these (particularly the most rostral) are occupied by what?
3
ectoturbinate bone structures (part of ethmoid bone)
ectoturbinate
bony formations from the ethmoidal bone located in the most rostral areas of the frontal sinus
What structures make up the nasal septum?
perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone
nasal septum cartilage
vomer
The vomer articulates with what structures?
perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone
nasal septum cartilage
cribriform plate
bony wall between the cranial and nasal cavities
The cribriform plate allows passage of what structures?
olfactory nn. (CN I)
vomeronasal nn.
The lacrimal bone contains what fossa?
fossa for the lacrimal sac
The maxilla contains 2 foramen with a canal in-between, as well as a fossa and two more foramen. What are their names?
infraorbital foramen
maxillary foramen
infraorbital canal
pterygopalatine fossa
sphenopalatine foramen
caudal palatine foramen
The infraorbital canal is located between what two foramen?
infraorbital foramen
maxillary foramen
The infraorbital foramen allows passage of what structures?
branches of the maxillary n. (CN V-2)
The maxillary foramen allows passage of what structures? In what view can it not be seen?
maxillary n. (CN V-2)
lateral
Where can the infraorbital foramen be accessed?
through buccal vestibule, at level of 3rd and 4th superior premolars
sphenopalatine foramen
communication between the pterygopalatine fossa and nasal cavity
vessels and nerves toward nasal conchae and its mucosa
caudal palatine foramen
communication between pterygopalatine fossa and hard palate
vessels and nerves toward hard palate bones and mucosa
Both the sphenopalatine and caudal palatine foramen allow passage of what structures?
branches of maxillary n. (CN V-2)
The palatine portion of the maxilla contains a process and two foramen. What are they?
palatine process of maxilla
major palatine foramen
minor palatine foramen
The major palatine foramen allows passage for what structures?
branch of maxillary n. (CN V-2)
vessels and nerves toward the hard palate mucosa
The minor palatine foramen allows passage for what structures? Where is it normally located?
branch of maxillary n. (CN V-2)
vessels and nerves toward rheumatoid arthritis hard palate mucosa
between maxilla and palatine bones
The palatine bone contains one foramen and 2 laminate. What are their names?
minor palatine foramen
horizontal laminate of palatine bone
perpendicular laminate of palatine bone
The mandible contains a canal in between 2 foramen. What are their names?
mandibular canal
mandibular foramen
mental foramina
The mandibular foramen is the caudal opening of what canal? What passes through here?
mandibular canal
branch of mandibular n. (CN V-3)
The mental foramina is the rostral opening of what canal? What passes through here?
mandibular canal
branches of mandibular n. (CN V-3)
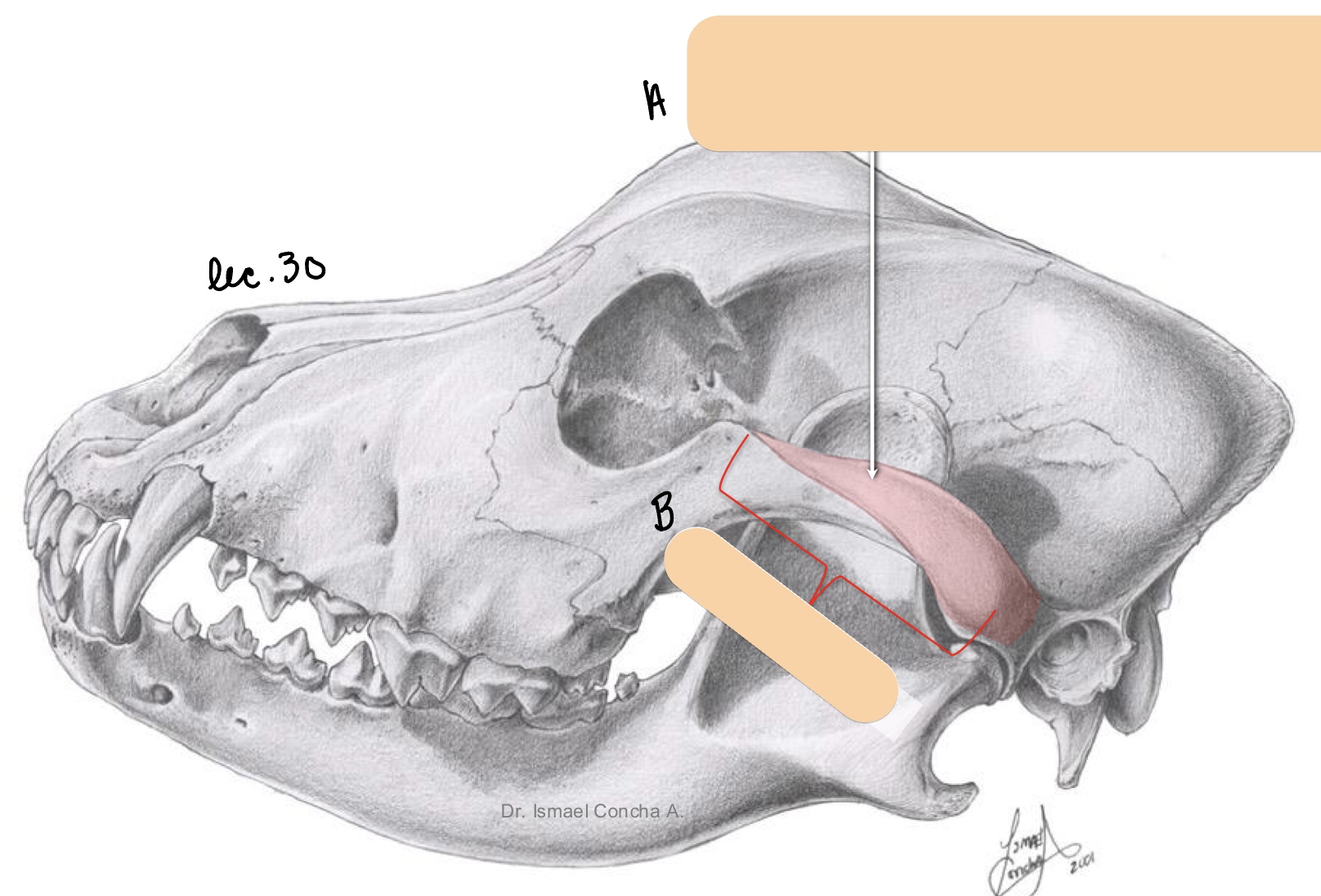
Name the structure(s) indicated by a and b.
zygomatic process
zygomatic arch
Name the structure(s) indicated by a.
mandibular fossa
Name the structure(s) indicated by a and b.
mastoid process
stylomastoid foramen
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, c, and d.
retroarticular process
retroarticular foramen
tympanic bulla
external acoustic meatus
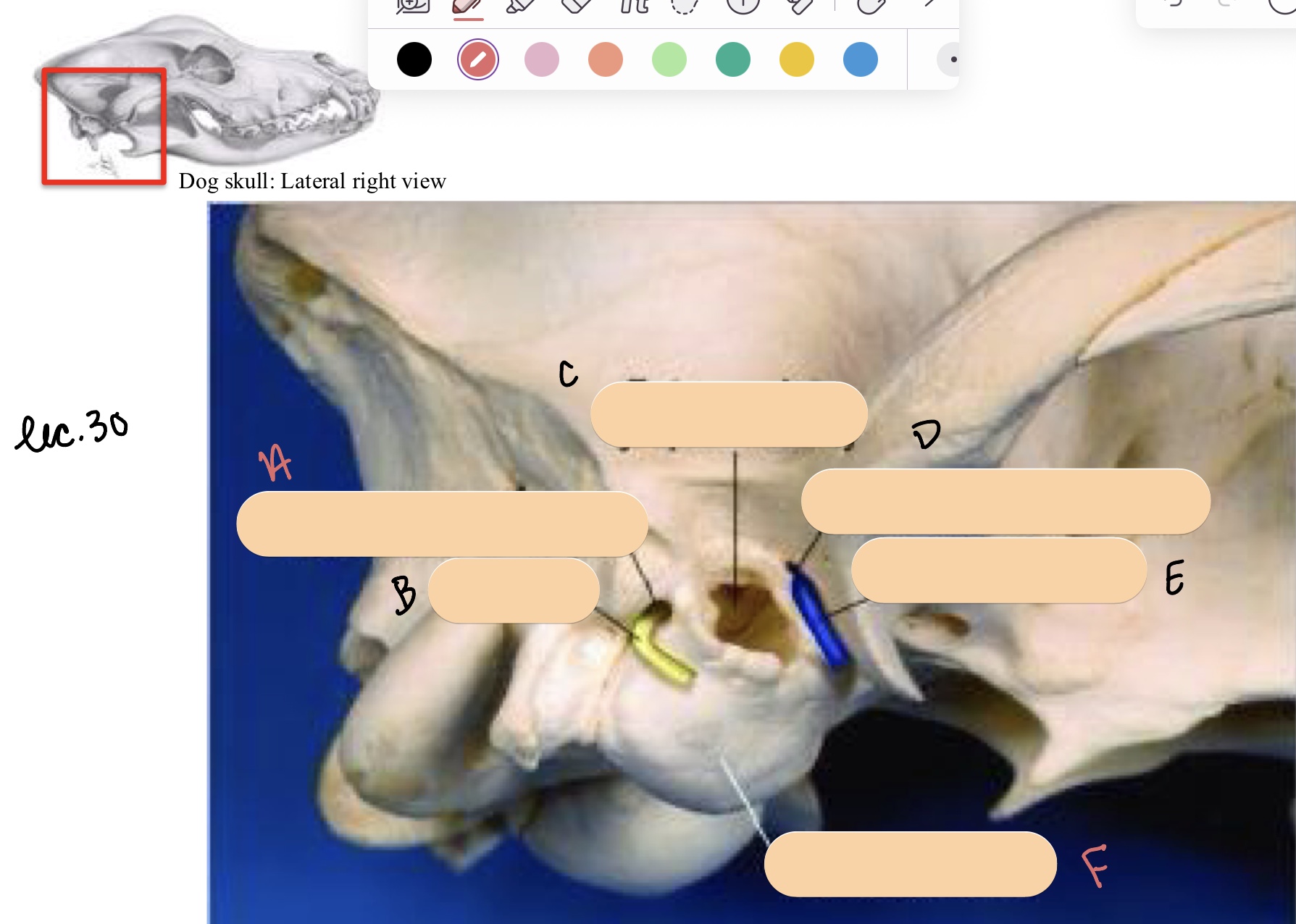
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
stylomastoid foramen
facial n.
entrance into tympanic cavity
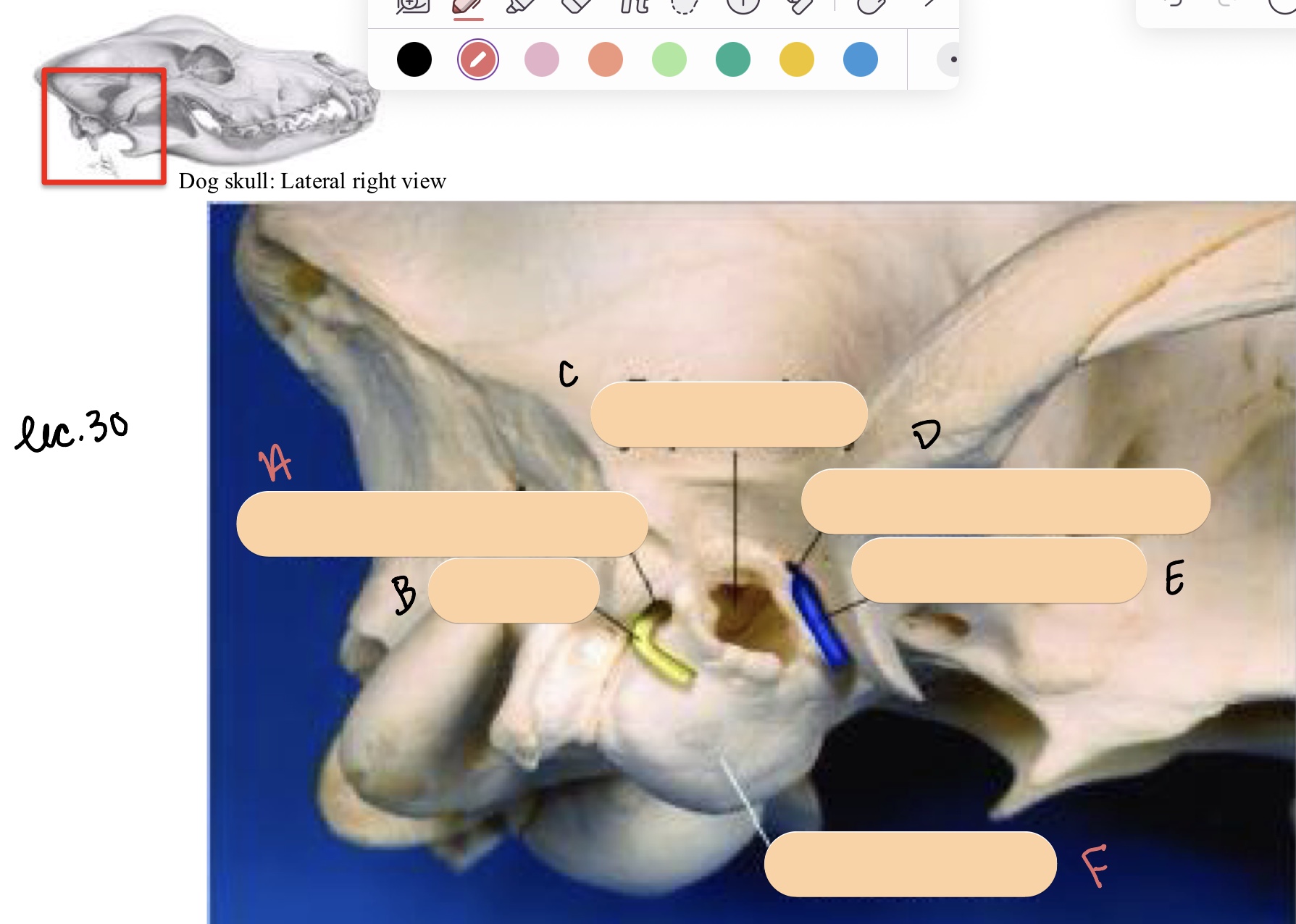
Name the structure(s) indicated by d, e, and f.
retroarticular foramen
retroarticular v.
tympanic bulla
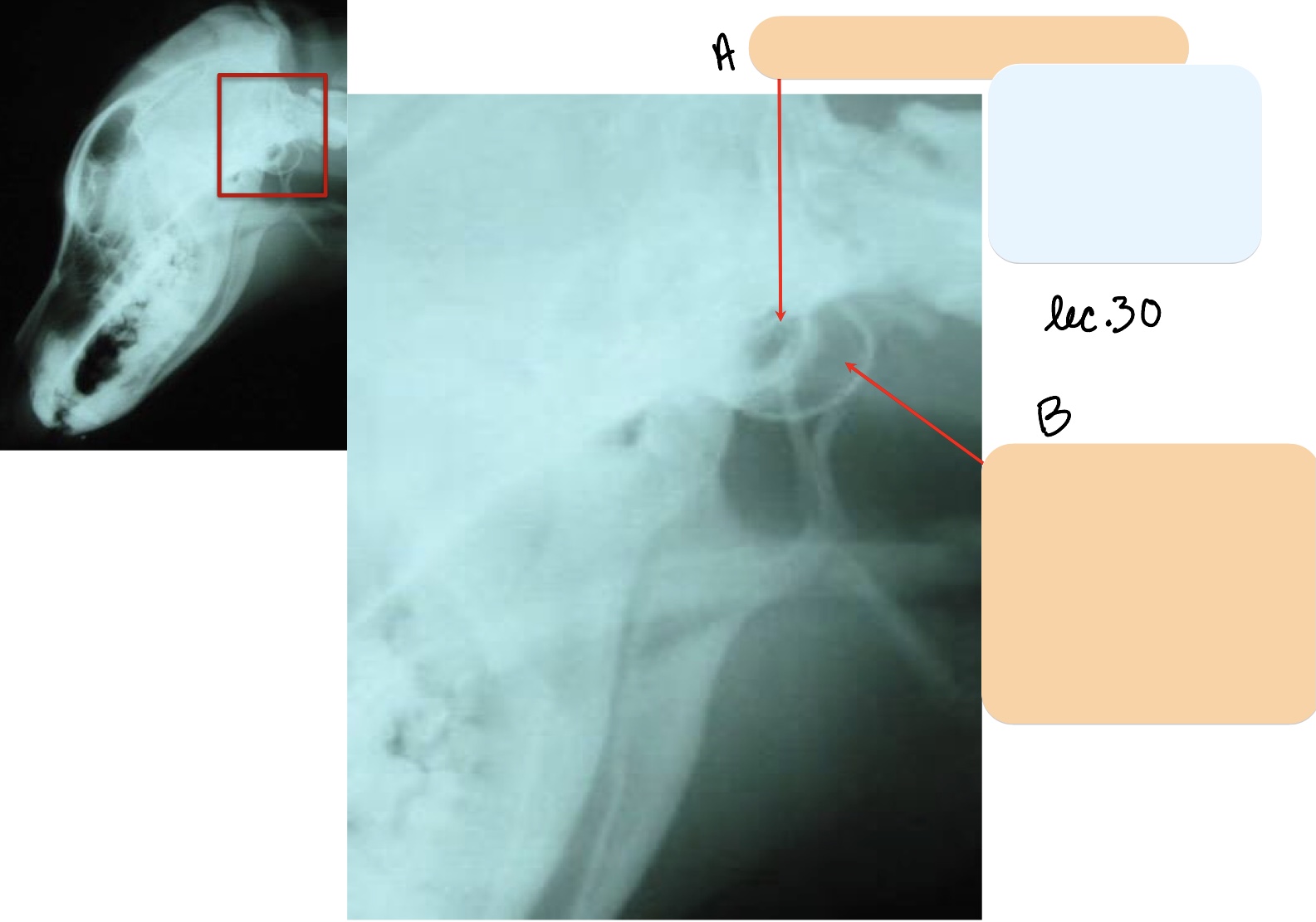
Name the structure(s) indicated by a and b.
external acoustic meatus
tympanic bulla
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
sphenoid bone
presphenoid
basisphenoid
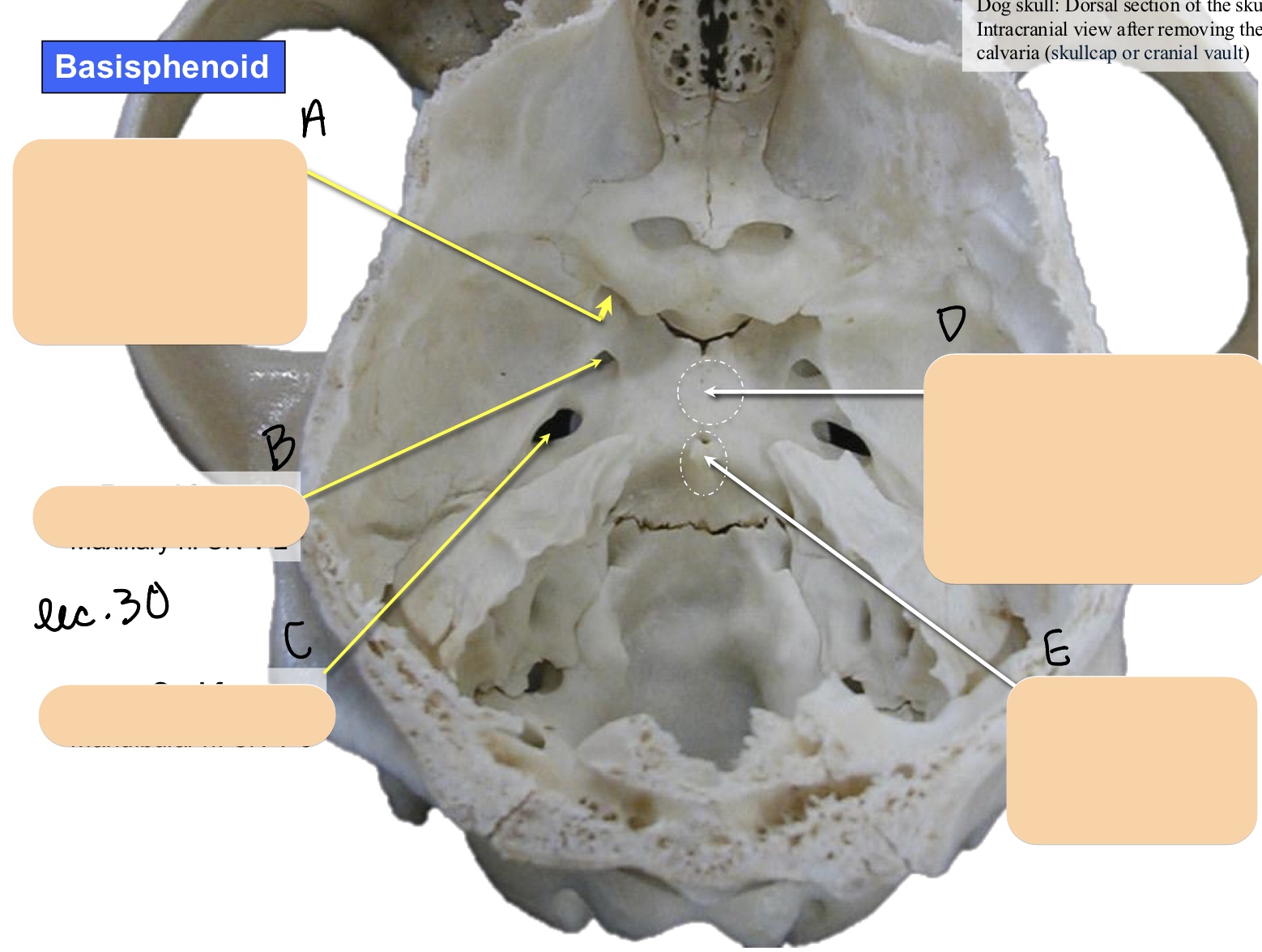
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
orbital fissure
round foramen
oval foramen
Name the structure(s) indicated by d and e.
hypophyseal fossa
dorsum sellae
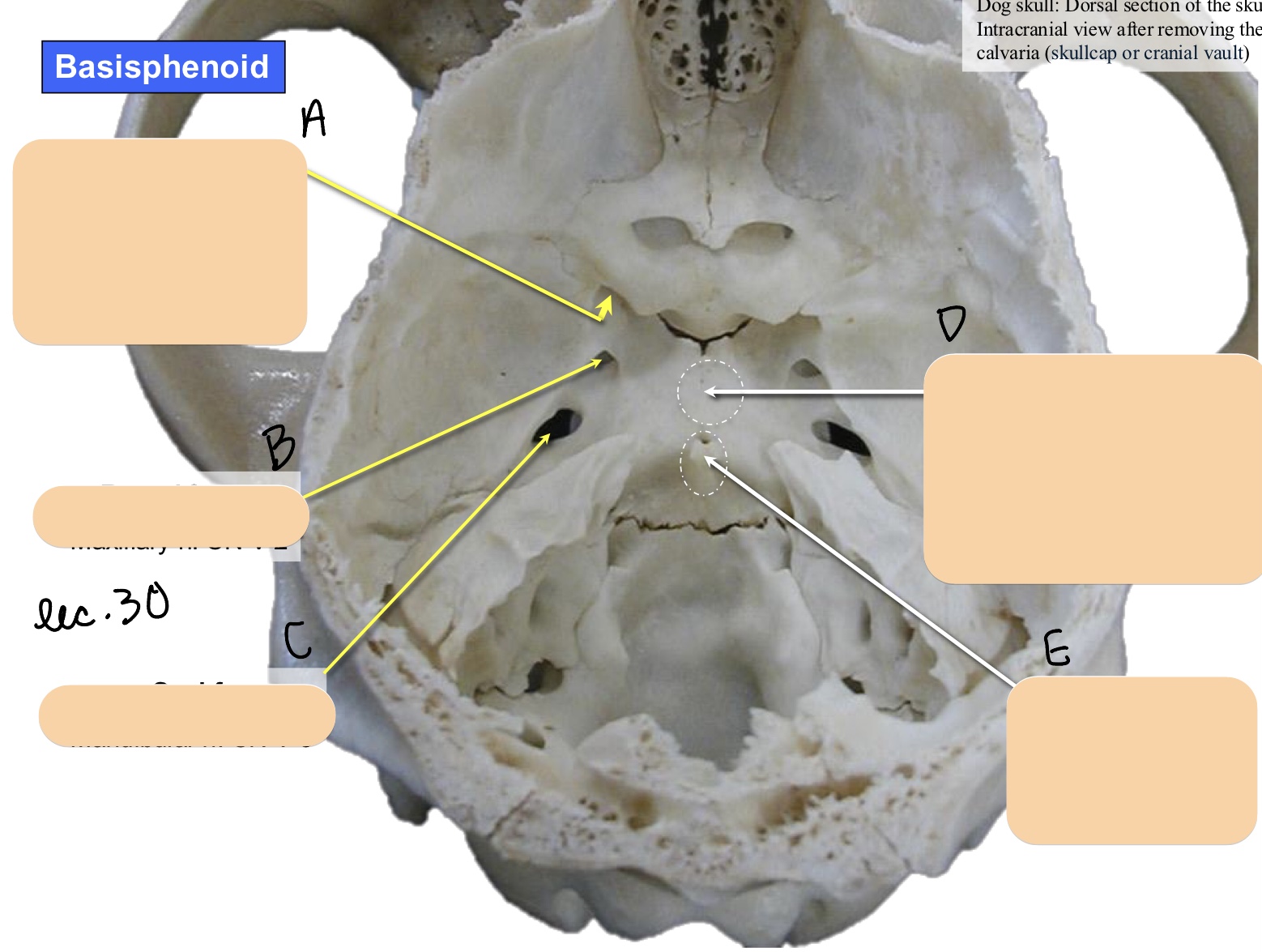
Name the structure(s) indicated by a and b.
dorsum sellae
hypophyseal fossa
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b and c.
orbital fissure
mandibular fossa
oval foramen
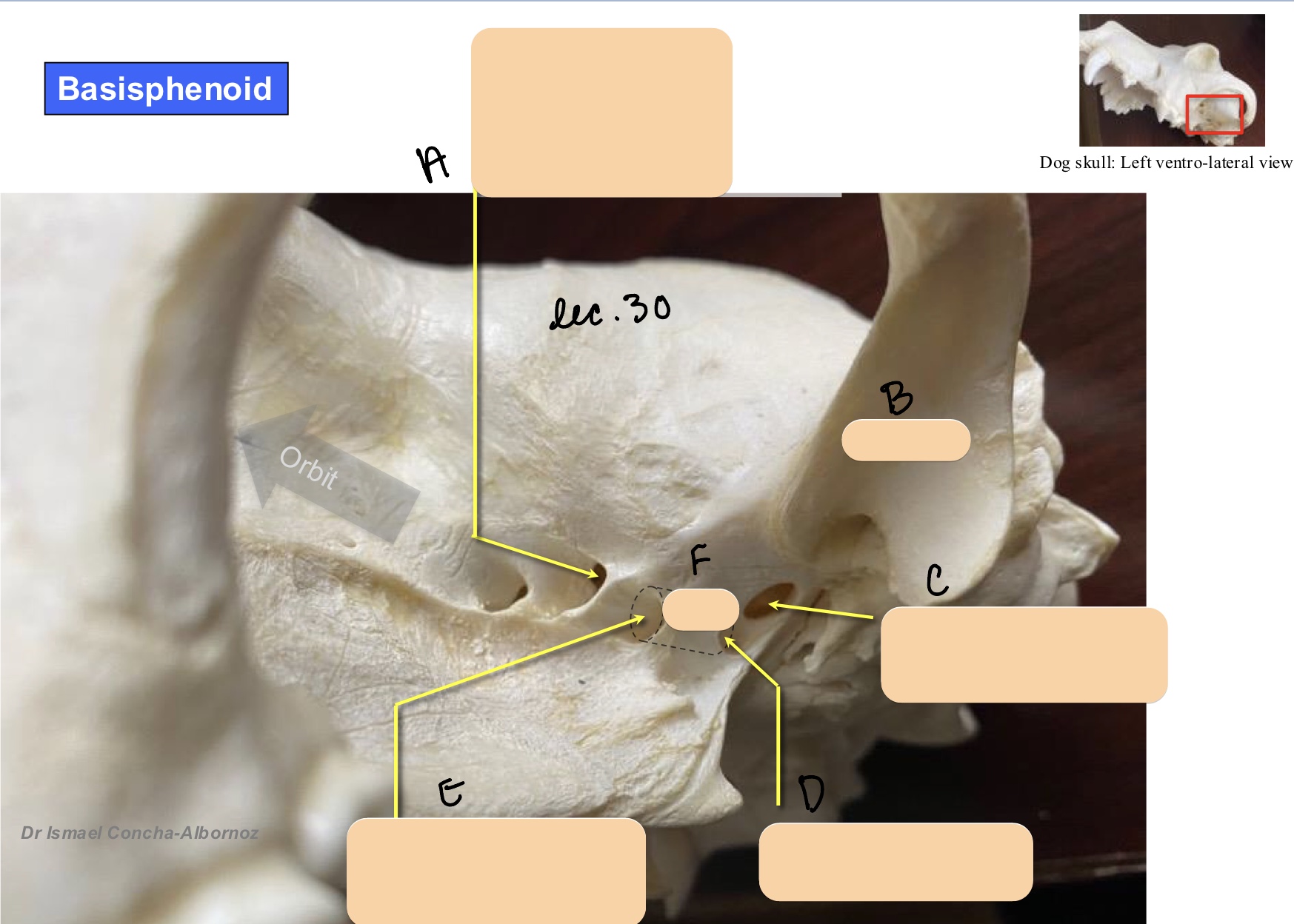
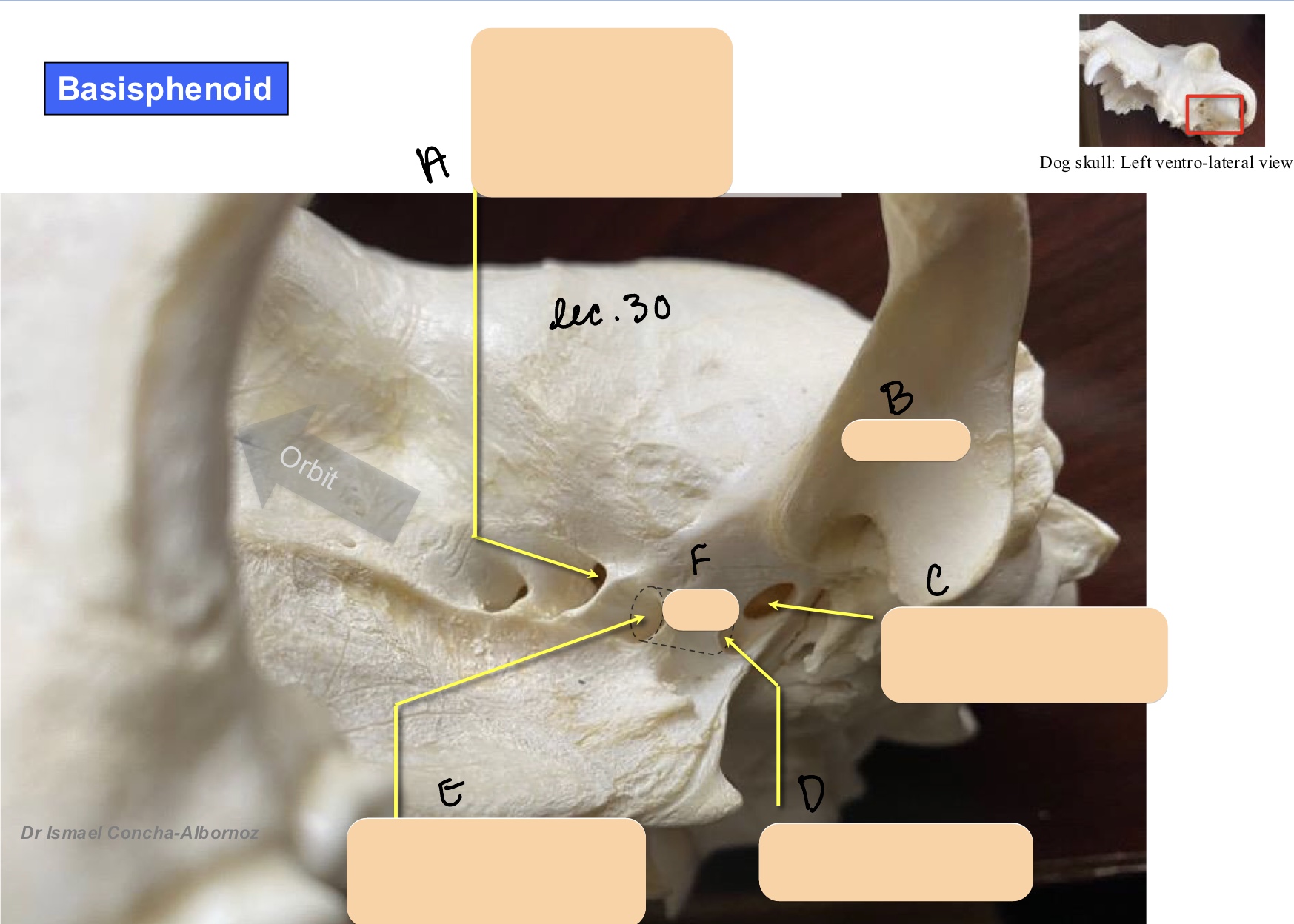
Name the structure(s) indicated by d, e, and f.
caudal alar foramen
rostral alar foramen
alar canal
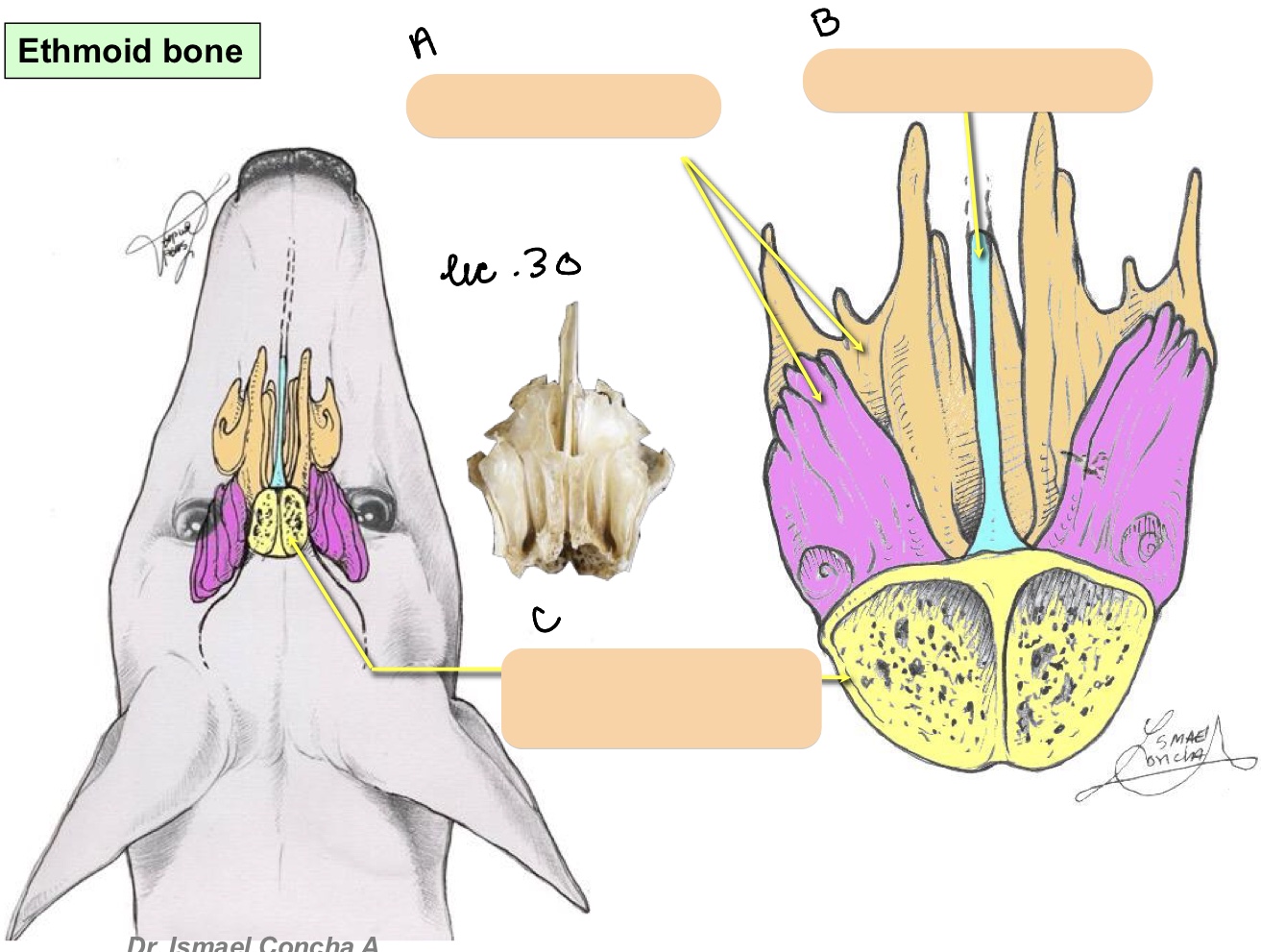
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
ethmoidal labyrinth (ethmoturbinates bones)
perpendicular plate
cribriform plate
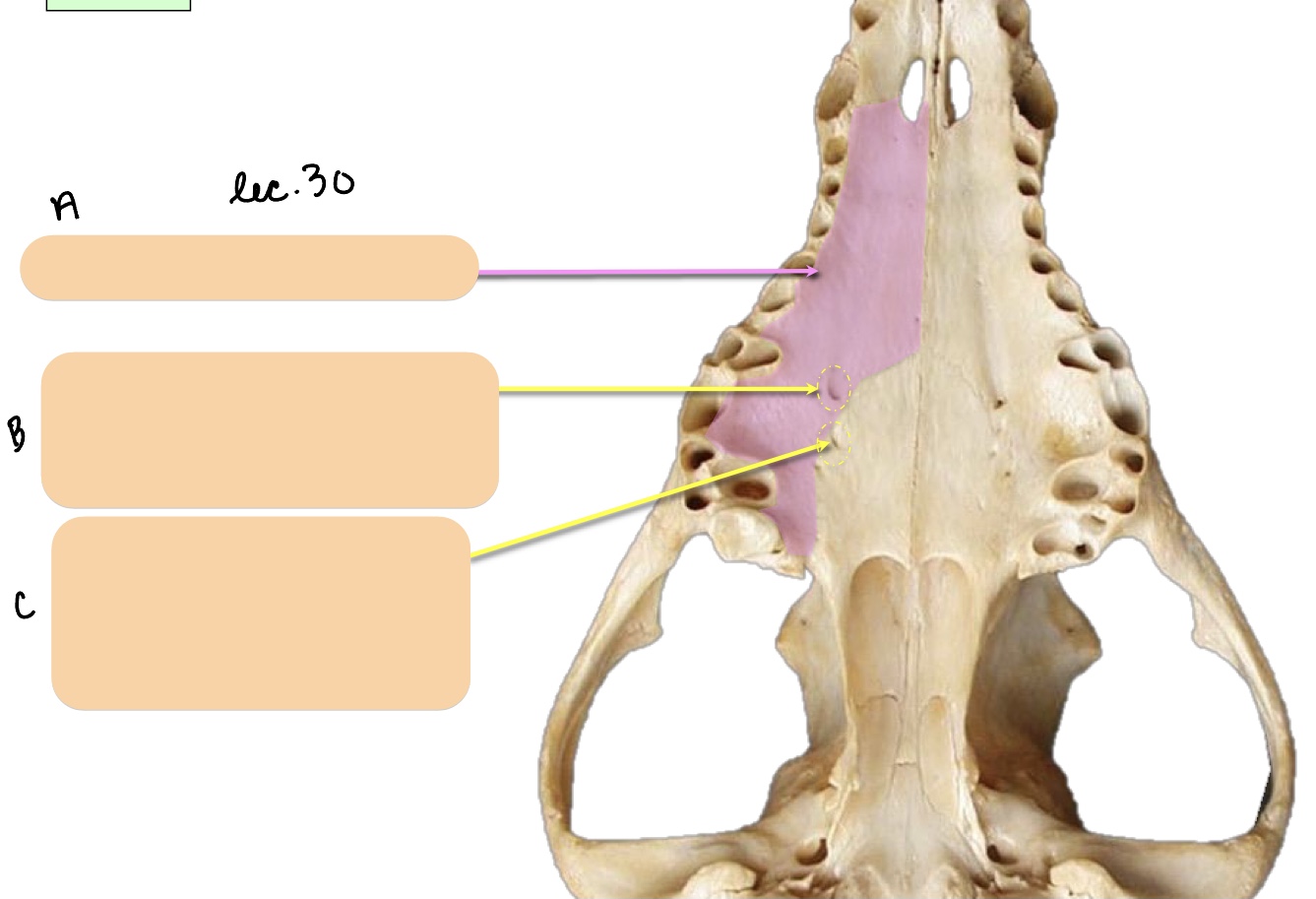
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
palatine process of maxilla
major palatine foramen
minor palatine foramen
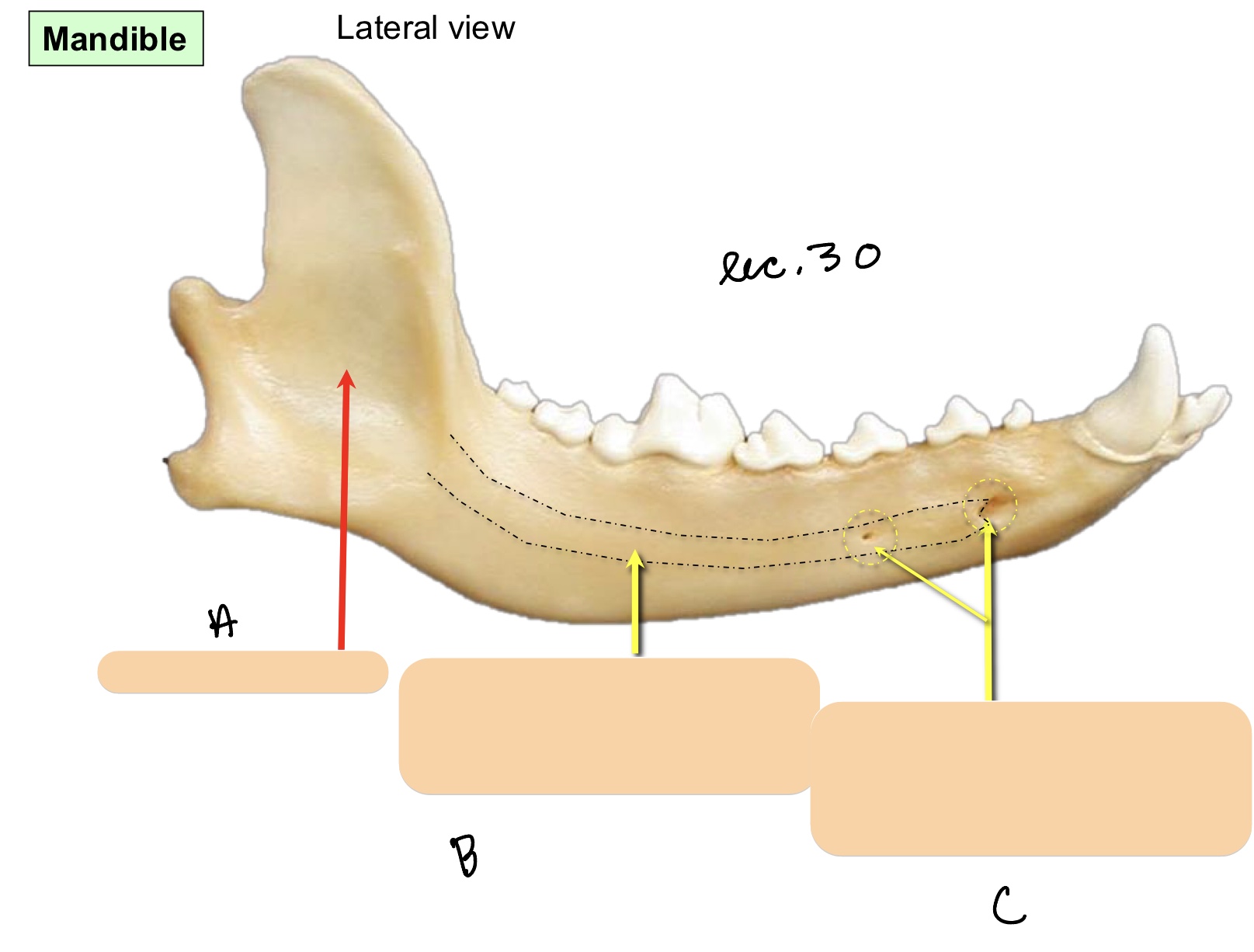
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
messeteric fossa
mandibular foramen
mental foramina
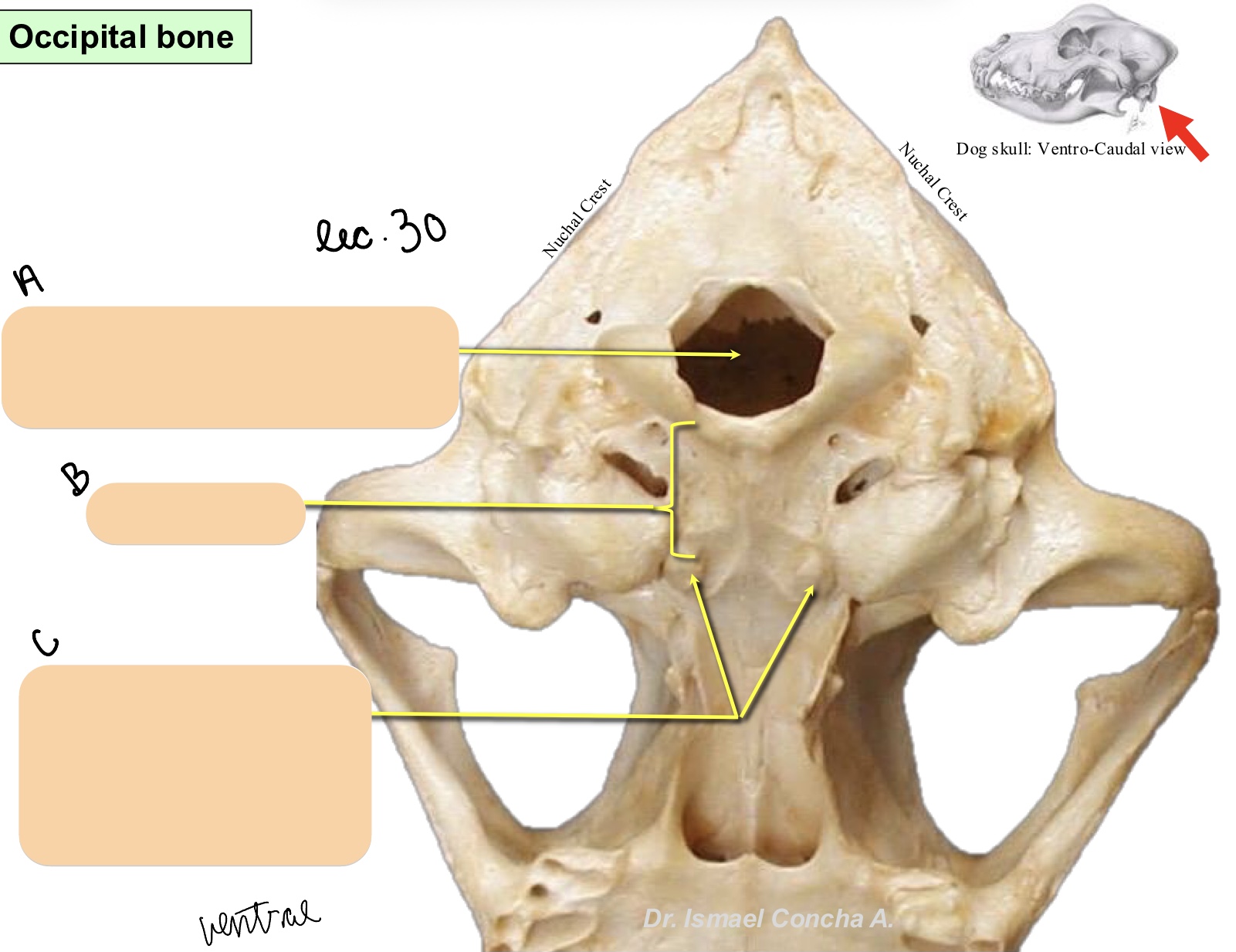
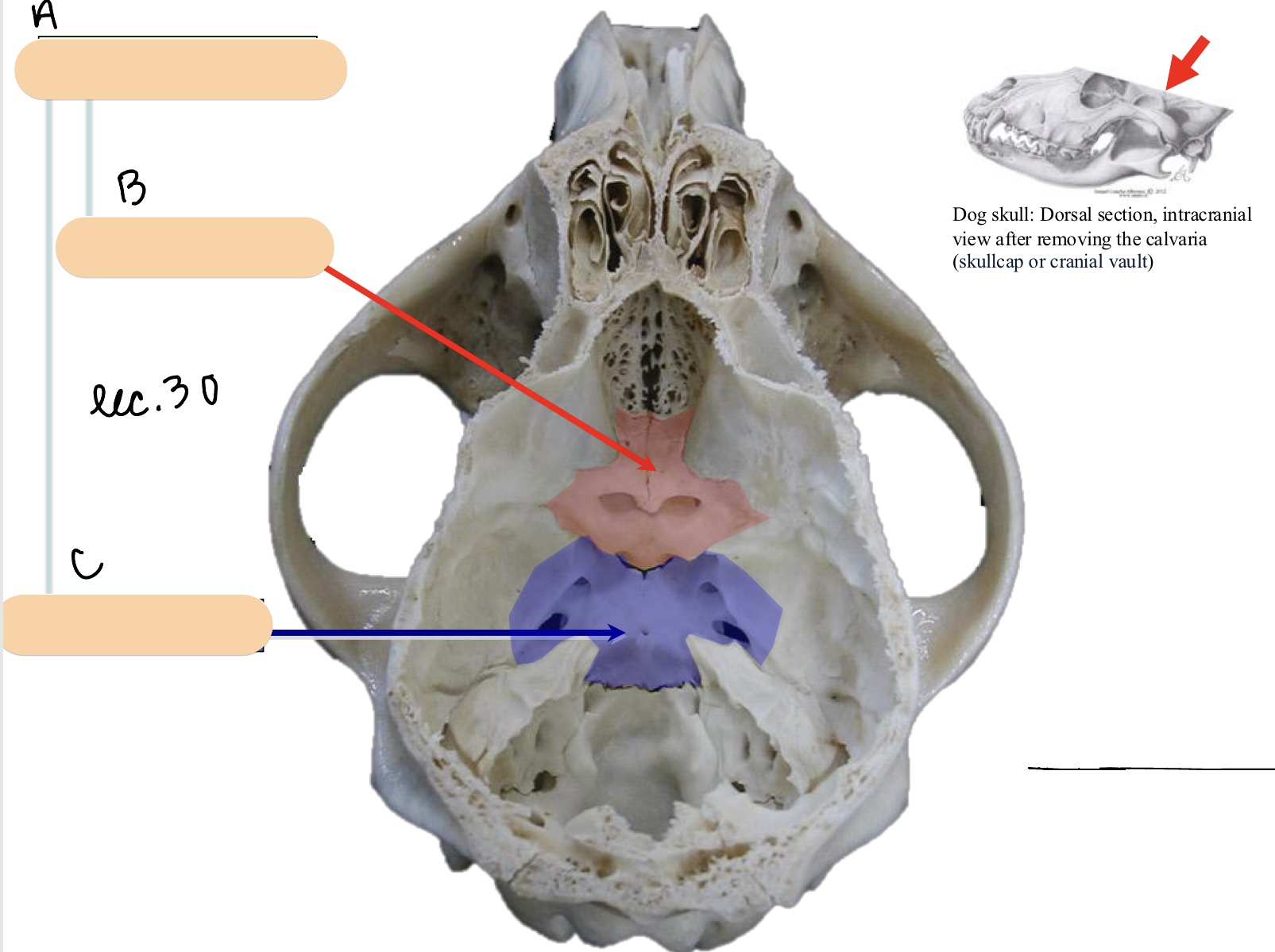
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
foramen magnum
basilar part of occipital bone
muscular tubercles
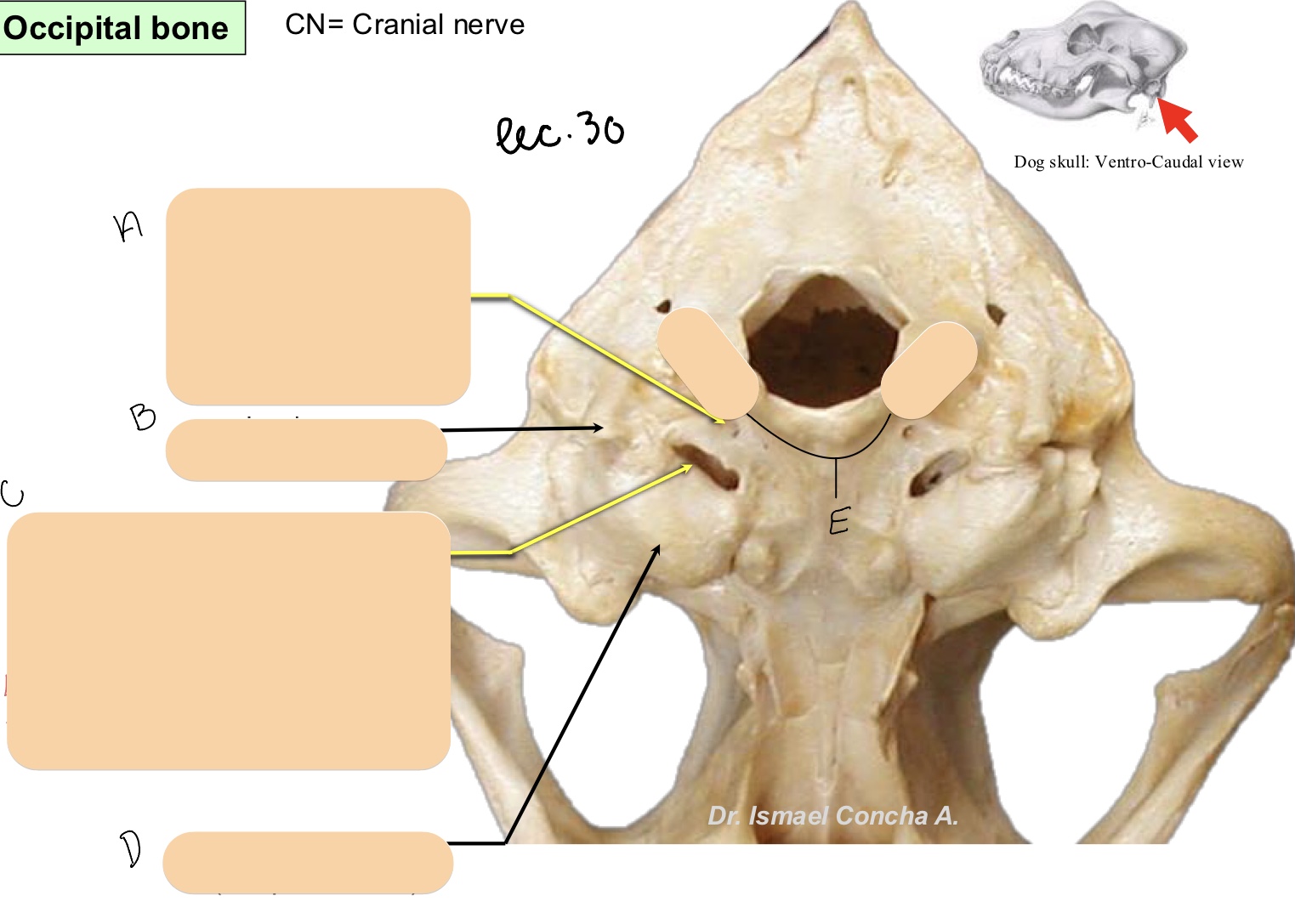
Name the structure(s) indicated by a, b, and c.
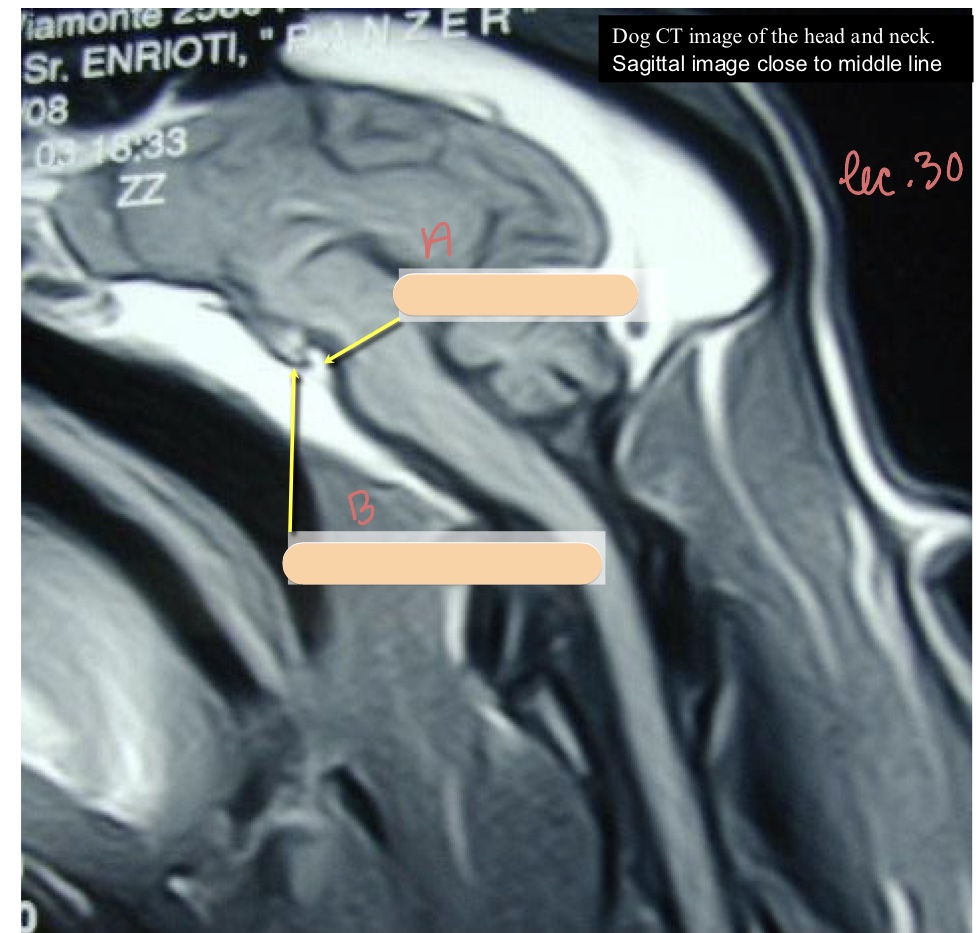
hypoglossal canal
jugular process
tympana-occipital fissure