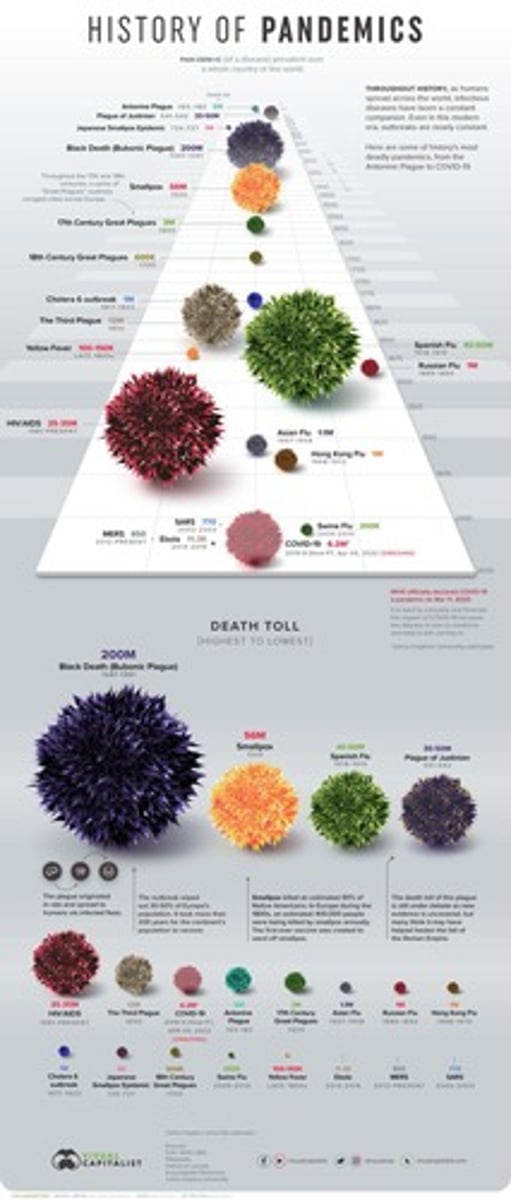
Chapter 16: Understanding Epidemiology and Disease Transmission
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Epidemiology
Study of disease frequency and spread factors.
Etiologic agent
Cause of a disease identified by epidemiologists.
Morbidity rate
Percentage of cases in a population.
Mortality rate
Measure of deaths in a population.
Prevalence rate
Number of infected individuals at a time.
Incidence rate
New cases per population per time period.
Sporadic diseases
Occasionally seen diseases in populations.
Endemic diseases
Diseases constantly present in a population.
Epidemic diseases
Unexpected increase in disease cases over time.
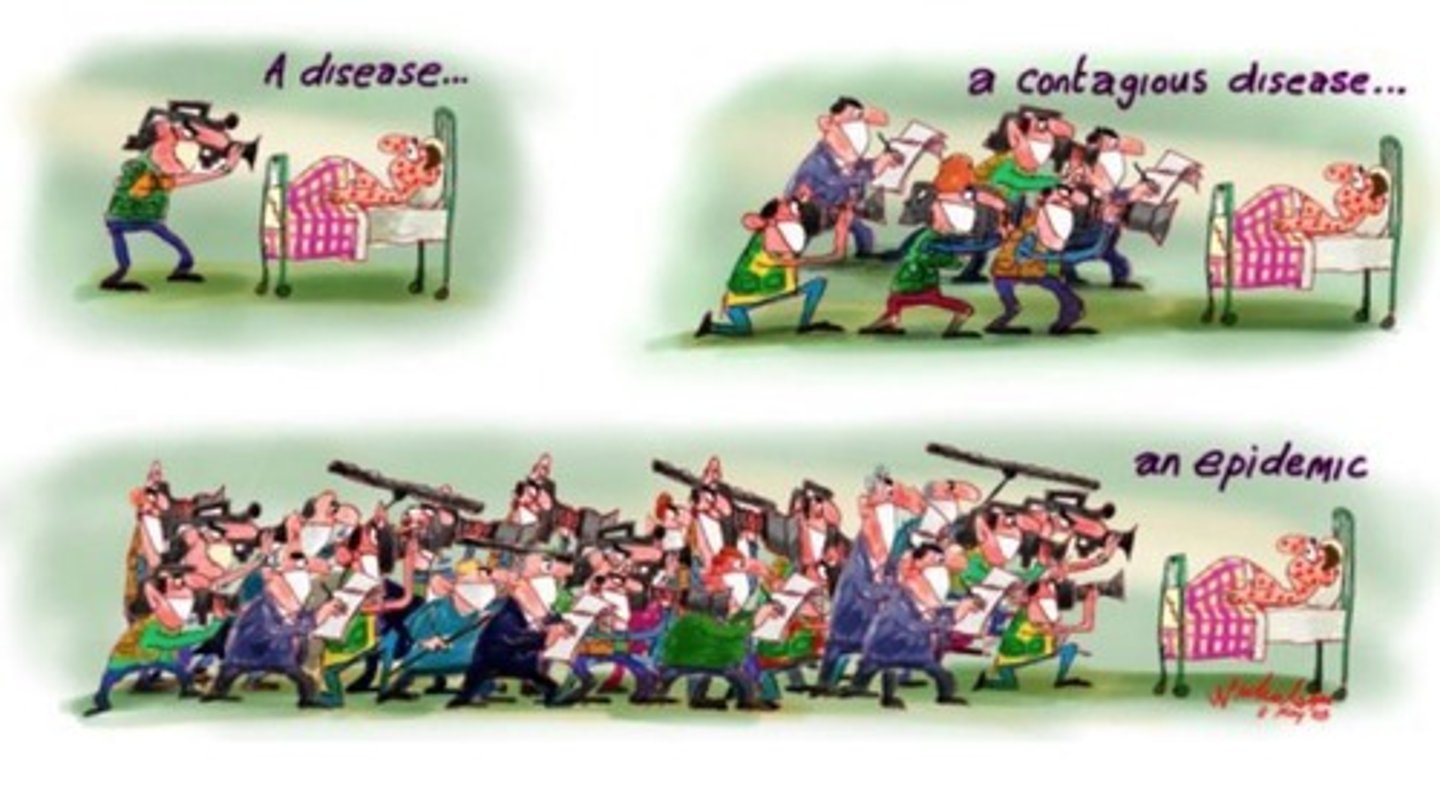

Pandemic diseases
Epidemic diseases spread worldwide.
Common source outbreak
Single source infects multiple individuals.
Point source outbreak
Infection from a source for a short time.
Continuous common source
Infection occurs over an extended time.
Intermittent common source
Infections stop and start periodically.
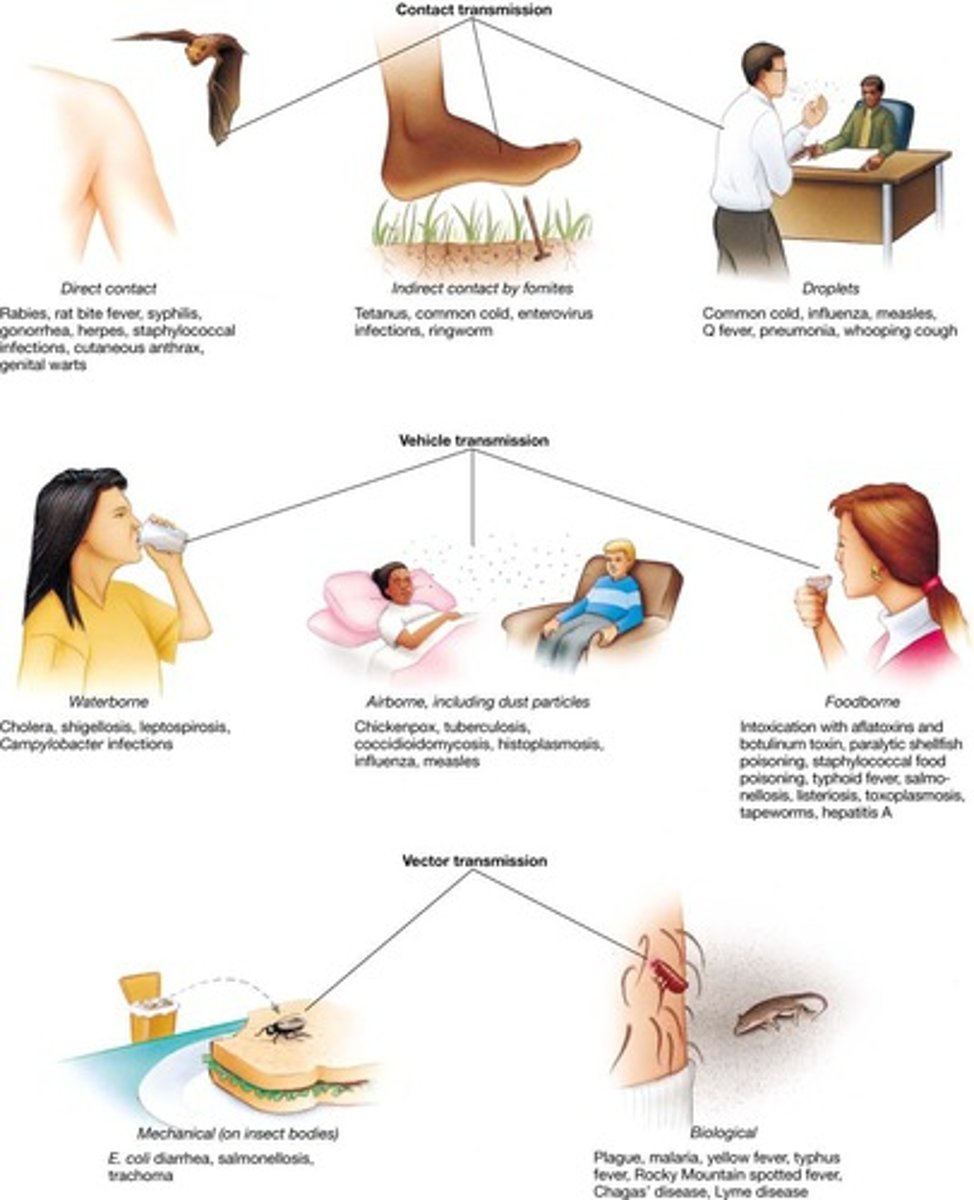
Propagated spread
Infection spread through person-to-person contact.
Observational studies
Data collected from participants without manipulation.
Descriptive epidemiology
Describes characteristics of disease in populations.
Analytical epidemiology
Analyzes relationships between risk factors and disease.
Retrospective studies
Looks back at data from past events.
Prospective studies
Follows participants into the future.
Case Control studies
Compares individuals with and without a disease.
Cross sectional studies
Analyzes data from a population at one time.
Experimental studies
Investigates causal relationships through manipulation.
Zoonotic diseases
Diseases transmitted between animals and humans.
R0 (Basic reproduction number)
Indicates contagiousness of an infectious disease.
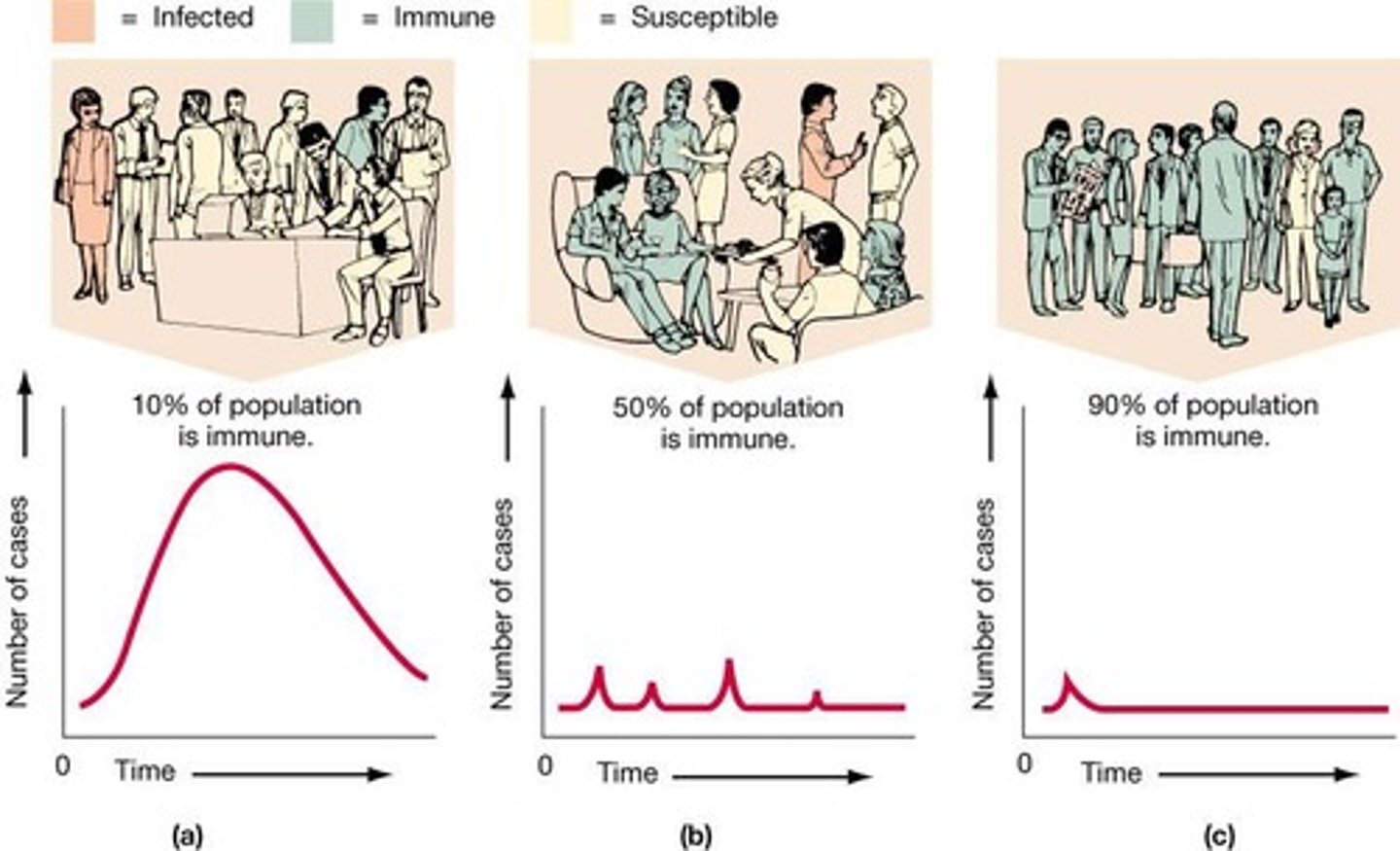
Herd immunity
Resistance to disease in a population.
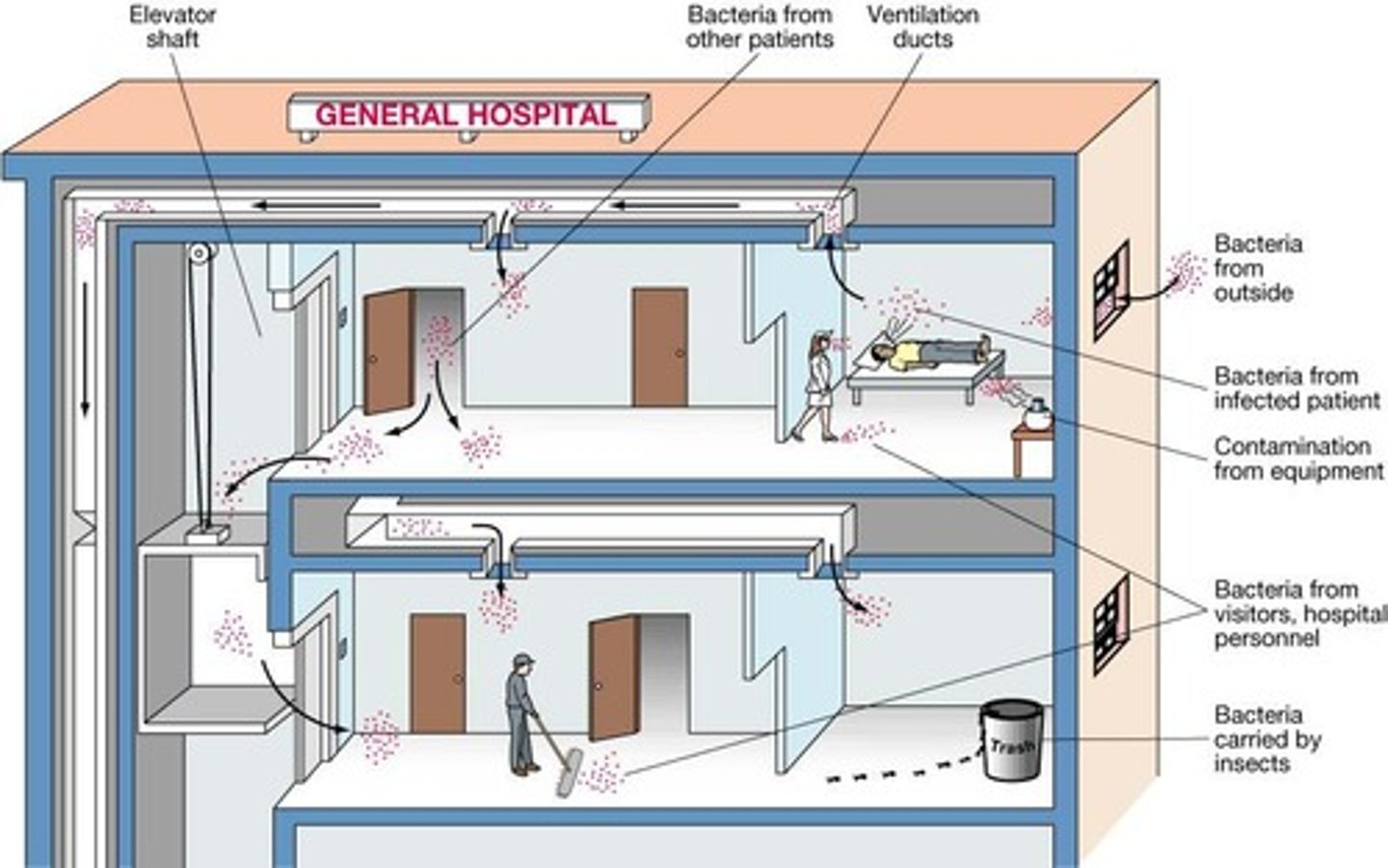
Nosocomial infections
Infections acquired in healthcare settings.
Universal precautions
Infection control practices in healthcare settings.

Notifiable diseases
Infectious diseases that must be reported.
Quarantine
Isolation of healthy individuals exposed to disease.
Isolation
Separation of sick individuals from healthy ones.
Disease eradication challenges
Factors hindering complete elimination of diseases.