Revenue, profit and objectives
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What is the formula for TR?
Quantity x price
What is the formula for AR?.
TR/Q, AR = P
What is the formula for marginal revenue?
The change in total revenue as a result of selling one more unit,
Change in TR/Change in Q
What is meant by price taker?
This is when the firm is too small to influence market price, it must face a lot of competition in the market.
What is meant by price maker?
The firm has a large market share and can therefore influence the market price- it could be a monopoly.
Graph of price taker
The AR curve is horizontal because the price received for the good is constant, demand is also perfectly elastic due to their being perfect substitutes.
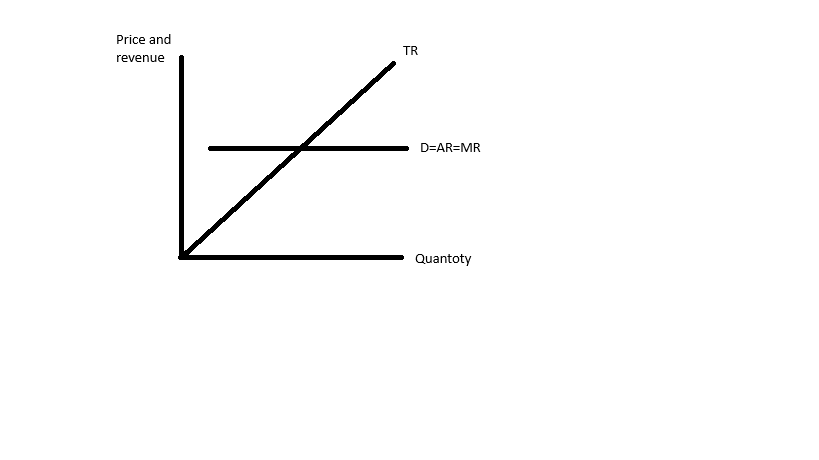
Graph of price maker
Firms must lower price to increase revenue shown by the downward sloping D curve.
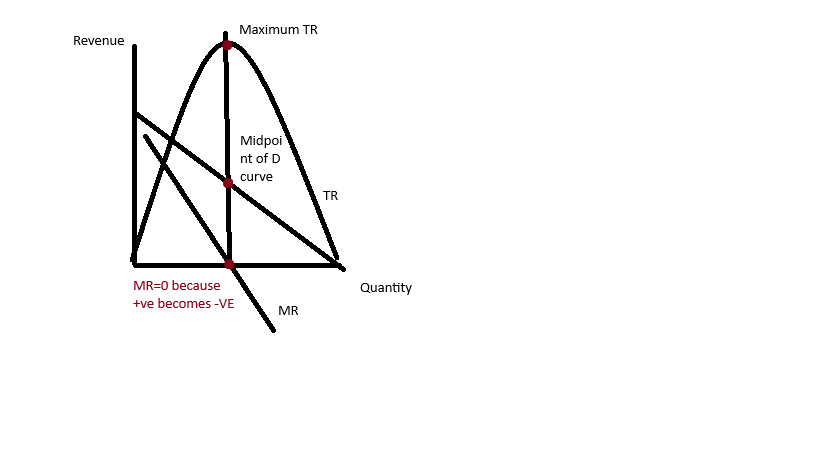
What is the formula for profit?
TR-TC
What are the two types of profit?
Normal
Supernormal
What is normal profit?
The minimum amount of profit required by the entrepreneur to keep them in the industry, sometimes seen as the wage.
What is supernormal profit?
Any profit earned over and above normal profit.
When does supernormal profit occur?
When TR is higher than TC.
What is an objective/aim?
A statement of intent, a target that the firm wants to achieve.
What objective do economists assume all firms have?
Profit maximisation
What is profit maximisation?
The profit made when there is the greatest possible positive difference between TR and TC.
What is the profit maximisation rule?
Profit is maximised at the level of output where MC=MR and MC are rising.
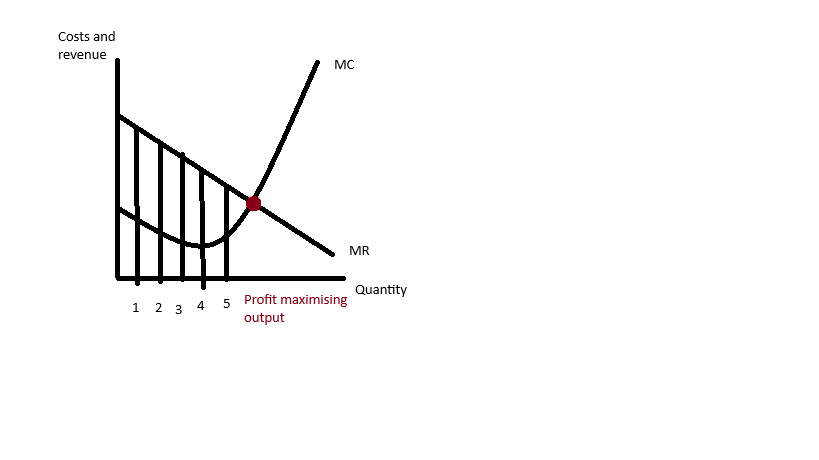
Costs and revenue graph for price maker
If the firm produces at maximum profit output the total profits is equal to the area between the MR and MC curves, every unit after this a marginal loss is made.
What are the advantages of profit maximisation?
enables firms to reward workers with greater wages and bonuses, may motivate the workforce which will reduce costs in the long run
enables firms to reward their shareholders with higher dividends, prevents take-over
retained profit can act as a buffer during potential economic crises
What are the disadvantages of profit maximisation?
In practice it is difficult to know the exact marginal revenue and cost
firms may have other objectives
profit satisficing, occurs when there is a separation of ownership and control and managers do enough to keep owners happy
Objective: Growth/Expansion
Increasing the capacity of the firm, growth brings economies of scale which allows firms to charge lower prices.
What two ways can market share be measured by?
Sales volume or sales value
What is sales value?
The value of sales is known as revenue, market share by sales revenue is the firm’s sales revenue as a proportion of total market sales revenue.
What is the formula for sales value?
Firm’s total revenue/Total market sales revenue x 100
What is sales volume?
The volume of sales is the number of units of output that are sold, market share by sales volume is the firm’s total output as a proportion of total market output.
What is the formula for sales volume?
Firm’s total output/Total market output x 100
Objective: Profit satisficing
This occurs due to:
owners of small firms, being a larger firm involves more workers, more time, more decisions etc.
Lack of information, difficult to identify where the profit maximizing position is
Other aims, may look into maximizing long run profit
Objective: Survival
Early stages of training, risky to be successful in a new business
trading becomes difficult, during a recession or falling demand
Threat of take-over
Objective: Sales revenue maximisation
This was identified by William Baumol in the 50’s, this will be favoured by those whose salaries are linked to sales or price taker firms.
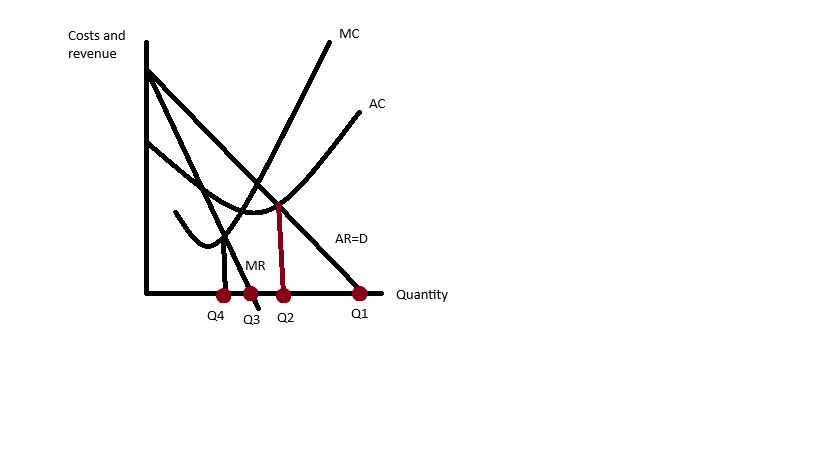
Graph for sales vs profit maximisation
Q1, sales volume maximisation (the most aa firm can sell), will occur when P is 0 but 0 revenue.
Q2, sales volume maximisation with a profit constraint, normal profit occurs where AC=AR
Q3, sales revenue maximisation, mid point of D curve and where MR=0
Q4, profit maximisation, using the profit maximisation rule
Objective: Image and social responsibility
Firms have become concerned over their ‘corporate image’ as it can affect sales, firms that have environmental credentials may achieve greater sales
Objective: Improving service/providing a public service
Some firms may be run on a ‘not for profit’ basis and aim to provide the best possible service to taxpayers at the lowest cost.
Objective: Managerial objectives
Their must be some divorce of ownership form control, happens when there are a large number of owners e.g. PLC, can include:
maximise personal salary
maximise departmental budget
improve their status