L15 Hox Genes and EvoDevo (Imported from Quizlet)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Most of the genes are all the same in all animals (True or False)
True
Much of what makes us different (morphologically) is caused by what?
Changes in expression of a common set of genes
What can be applied to any organism and what does it provide?
CRISPR, it provides genetic modelling
Genes control what?
Morphology
Bryoza is also known as ...?
Ectoprocta
How do we determine if proteins are similar?
Protein blast alignment
How does protein blast alignment work?
Input the amino acid sequence of the proposed protein
The blast program searches huge databases for other proteins which have similar sequences
This shows an alignment of an uncharacterised protein (query) to a protein called zen (subject)
Similarity between protein sequence suggests what?
That the protein evolved from the same common ancestor and that the proteins have similar molecular functions
There are ___ vertebrate FGFs that fall into _ clusters based upon protein sequence alignment
22, 4
What has a single representative in each of the 4 groups?
Ciona (Ci)
What does this single representative suggest?
That the common ancestor of the sea squirt and vertebrates had 4 FGFs
How do so many FGFs arise?
Gene duplication: changes in ploidy (entire genome duplication) and local duplications (smaller areas duplicate)
New copes of genes that arise in the genome are called ...?
Paralogues
All these different FGFs are _________, share the same ancestor through duplication events
Paralogues
After duplication, it is likely that the duplicate gene are at first what?
Redundant
What is neofunctionalization?
1 normal gene and 1 with a new function
Whole regions being duplicated is an error during ...?
Mitosis
The extra copy can change in what ways?
Pattern of expression, structural in the protein (both small changes caused by point mutations and big changes caused by domain swapping)
Changes in ________ are thought to be the most common driving force in the morphological evolution of animals
Expression
Why are changes in expression patterns of genes thought to play a major role in morphological evolution?
Because enhancers can change easily (they are promiscuous)
What is meant by crossing over?
Exchange the ends of their chromosomes, could bring an enhancer close to the gene
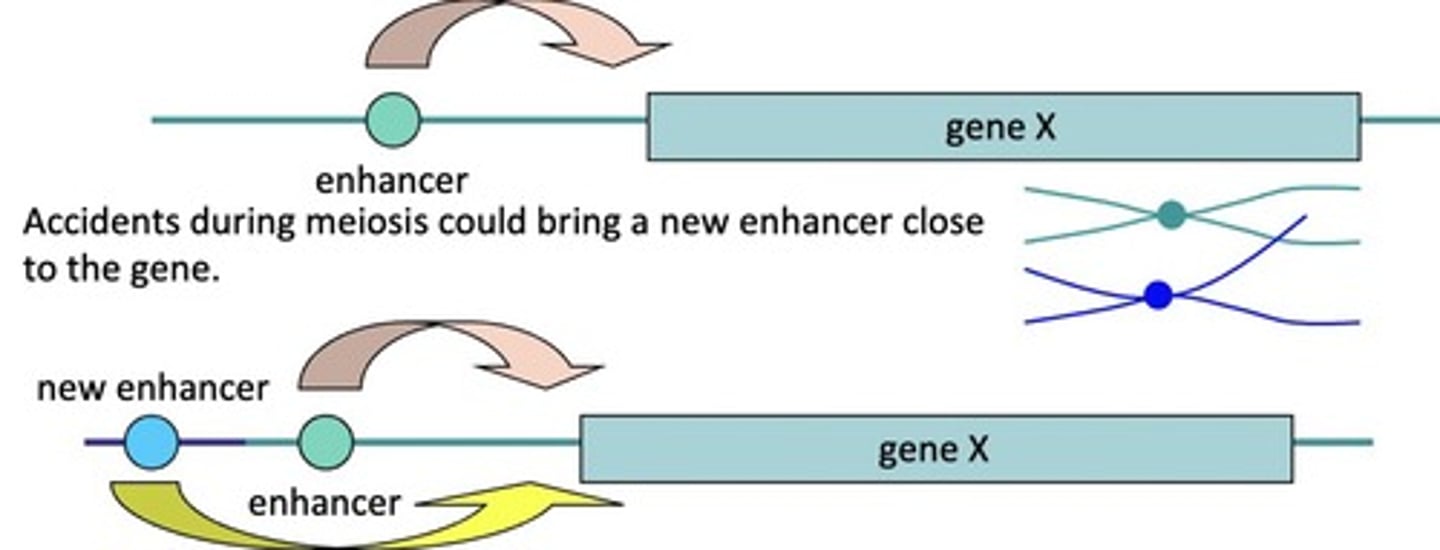
It should be relatively easy to add or delete sites by ...?
Rearrangements, insertions, deletions or base pair substitution
Changes that effect protein structure (changing amino acids) would have to be more precise so as not do what?
Introduce a stop, change the reading frame, interfere with the protein's folding or disrupt RNA splicing
Mutations in proteins are more likely to be __________
Damaged
What is the cervical?
Neck vertebrae
What is the thoracic?
Chest vertebrae
What do hox genes specify?
Segment identity
Transcription factors that are found in clusters in the genome, all have similarity suggesting what?
That they originated from the same gene
What does changing hox gene expression result in?
Changes in segmental identity
Humans also have hox genes (True or False)
True
Changes in segmental identity is seen in _______, especially in the ________
Humans, somites
Changes in expression of regulatory genes can correlate to what?
Morphological changes
Expression of the gene C6 starts more _______ in chick
Posteriorly
What does the position of the expression of C6 in chick correlate with?
A longer neck (more cervical vertebrae) and less chest (fewer thoracic vertebrae) than in mice
Limbs form at the junction between the _____ and ________ vertebrae
Cervical, thoracic
Pythons lack what?
Limbs
Pythons have no ___________ and severely reduced _________
Forelimb, hindlimbs
All vertebrae anterior to the hindlimb have _____ and a mixed ________/________ morphology (except for the atlas)
Ribs, cervical/thoracic
Shift in hox gene expression may explain what in snake evolution?
Loss of limbs
Expansion of HoxC6 and HoxC8 could confer many of the _____________ ________ (shift towards thoracic) seen during the evolution of snakes
Morphological changes
There is also a lot of evidence that changes in hox gene expression had roles in the evolution of _______ and ______
Insects, limbs
By experimentally changing expression of a single gene we can create ________ organs
Ectopic
Organs are very complex structures, so genes that are capable of such big tasks are called ...?
Master regulatory genes
What do master regulatory genes regulate?
Whole gene networks
This adaptability that takes place during development is sometimes referred to as ...?
Evolutionary robustness
Crustaceans have legs on their __________ but insects don't
Abdomen
Why do crustaceans have legs on their abdomen but insects don't?
Because of changes in the protein sequence
What evolution may explain why insects don't have legs on their abdomen?
Ubx
In fly embryo, the ____ _________ _______ specifies leg precursor cells
Dlx transcription factor
In fly embryos, Ubx is expressed in the ________ where it ________ Dlx expression
Abdomen, represses
Crustacean Ubx does not act as what?
A repressor of Dlx
Ubx is __________ in the abdomen of crustacean embryos, but it doesn't _____ ____ Dlx expression
Expressed, turn off
It is thought that the Ubx gene became able to ________ ____ in an ancestor of drosophila
Repress Dlx