Physiology Laboratory Quiz #1 - Key Terms and Definitions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what does blood contain?
ECF (extracellular fluid)
protein molecules (ex: antibodies)
blood hormones
RBC, WBC, and platelets
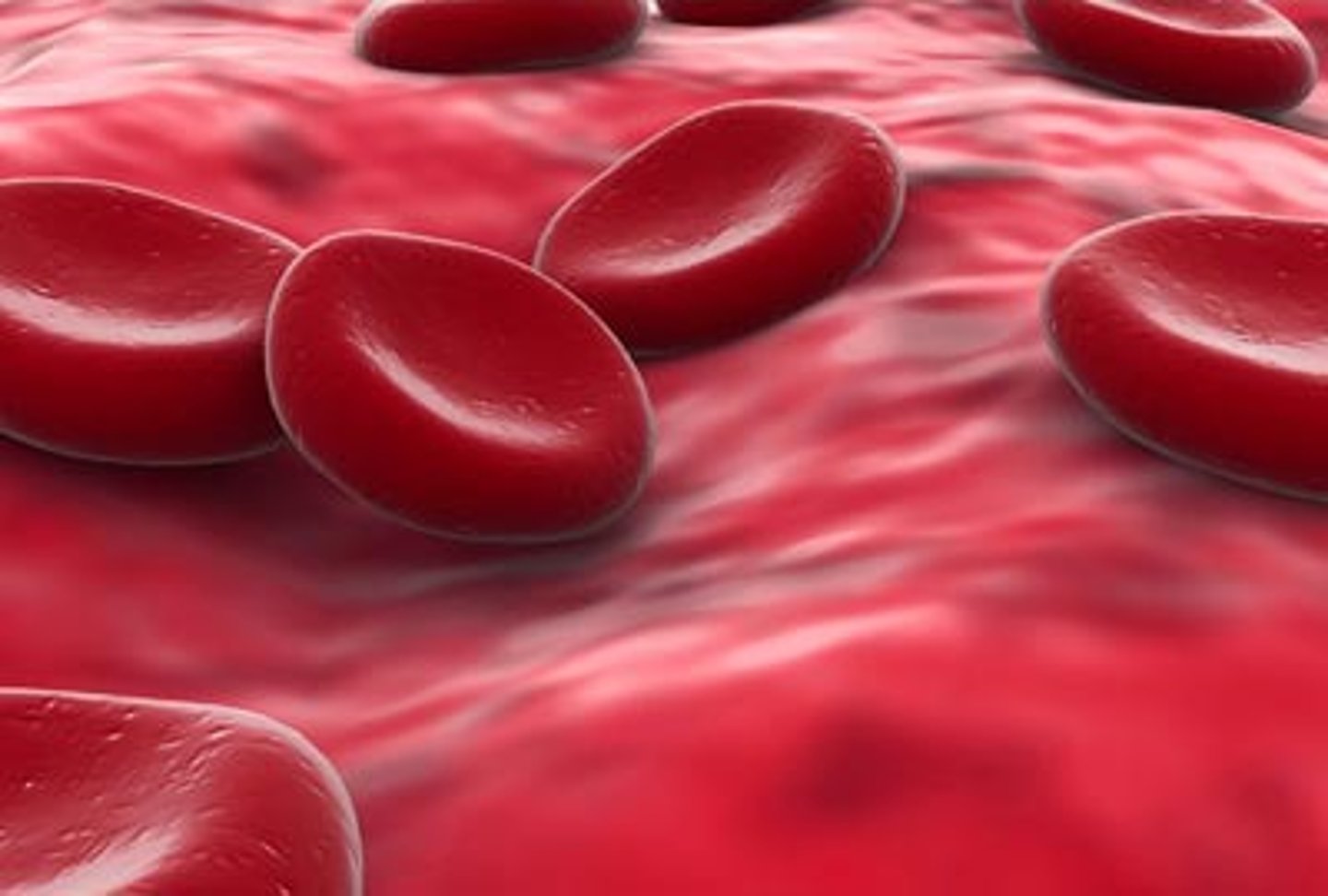
erythrocyte
red blood cell
where are erythrocytes produced?
red bone marrow
why do erythrocytes have a short life span?
lack a nucleus and mitochondria
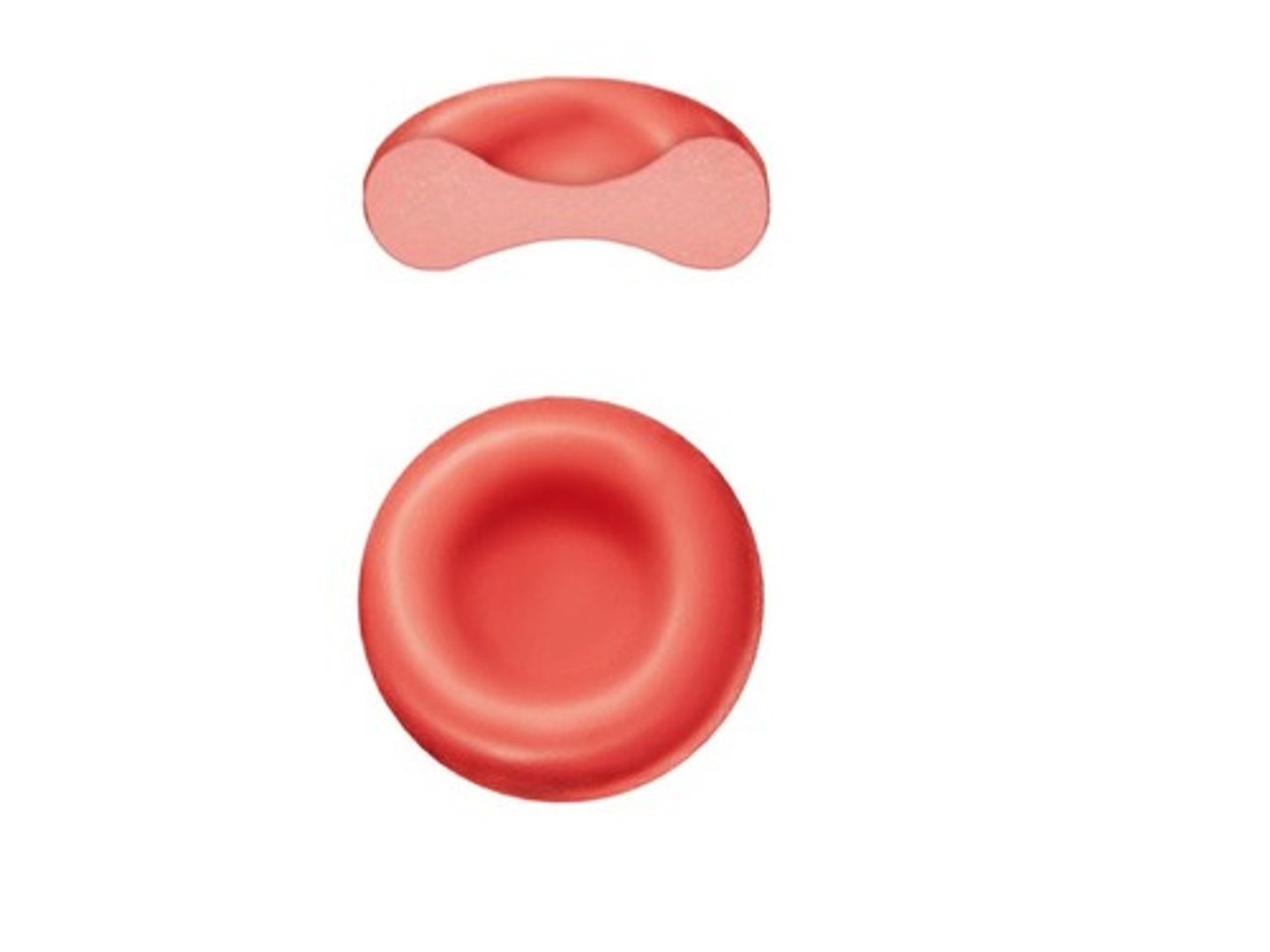
what is the fancy term for the shape of erythrocytes?
biconcave
spectrophotometer
an instrument that reads the density of blood samples, finding the glucose and hemoglobin ranges in blood
normal glucose range
70-99 mg/dL blood
pre-diabetic glucose range
100-125 mg/dL blood
diabetic glucose range
126+ mg/dL blood
normal hemoglobin range
12 to 18 g/dL
what is a hematocrit?
separates blood sample into different components
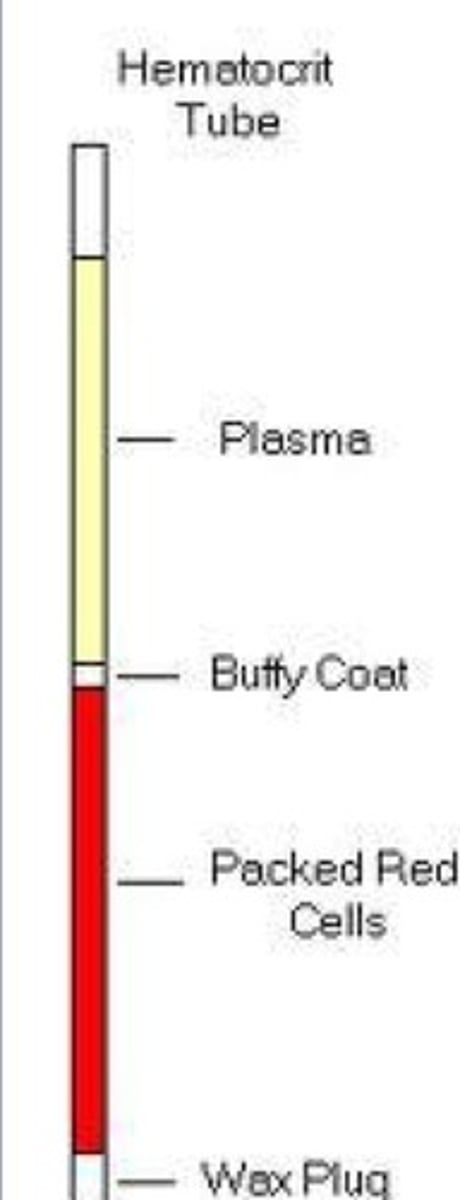
hematocrit equation

hematocrit average range
38% - 48%
hemacytometer slide
a specialized microscope slide that contains a grid pattern
average RBC count
4.5 million - 6 million RBCs/uL blood
-osis
too much
-penia
too little
erythrocytosis
elevated RBC count
erythrocytopenia
deficiency of RBCs
erythropoiesis
production of red blood cells
what causes erythrocytosis?
bone marrow disorders, low O2, blood doping
blood doping
artificially raising RBC count; increases rates of cellular respiration and creation of ATP
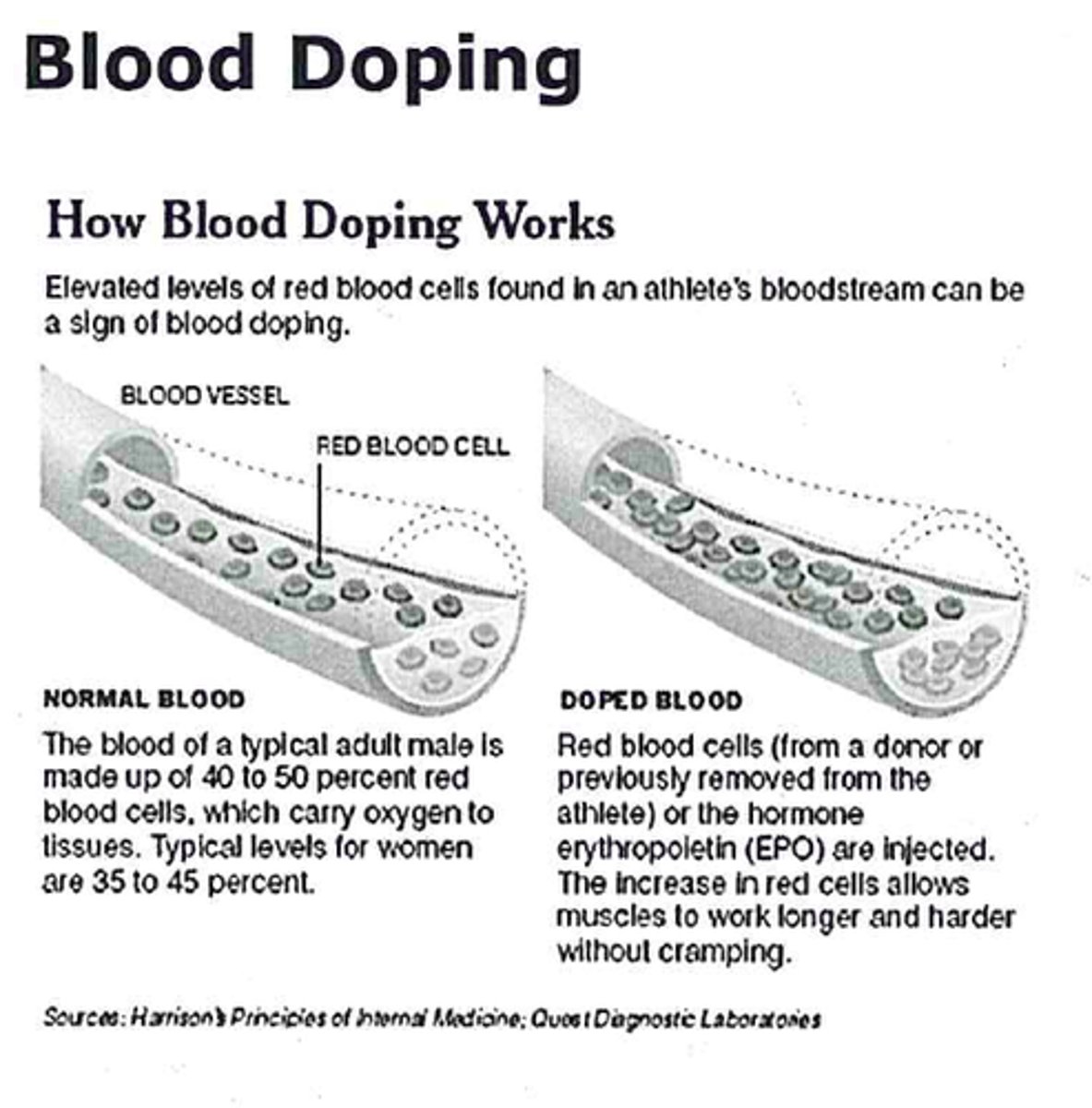
why is blood doping dangerous?
leads to blood viscosity and forces heart to work harder, which can cause a heart attack
what should blood doping be used for?
chemo, kidney failure
what causes erythrocytopenia?
anemia