Unit 6: Geometric and Physical Optics
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/34
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
1
New cards
Electromagnetic waves
Electromagnetic waves are a type of wave that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields that travel through space at the speed of light.They are produced by the acceleration of charged particles and include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.Electromagnetic waves have a wide range of applications, including communication, medical imaging, and energy production.
2
New cards
Electromagnetic Spectrum
It can be categorized by its frequency. The full range of waves is called the electromagnetic spectrum.
3
New cards
Interference
The phenomenon of superimposition of two or more waves having the same frequency emitted by two coherent sources.
4
New cards
Diffraction
It is defined as the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of the geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture.
5
New cards
Single-Slit Experiment
A diffraction pattern will also form on the screen if the barrier contains only one slit.
6
New cards
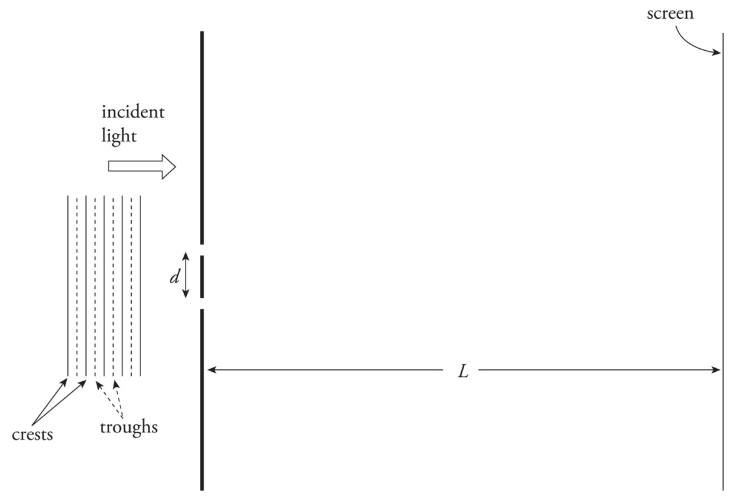
Young’s Double Slit Experiment
The incident light on a barrier that contains two narrow slits, separated by distance d. On the right there is a screen whose distance from barrier L, is much greater than d.
7
New cards
Constructive and Destructive Interference
constructive interference: d sinθ = m λ
destructive interference: d sinθ = (m+1/2) λ
* where, m = 0, 1, 2, 3, etc.
* λ = wavelength of light
* d = distance
destructive interference: d sinθ = (m+1/2) λ
* where, m = 0, 1, 2, 3, etc.
* λ = wavelength of light
* d = distance
8
New cards
Angle of incidence
The angle that the incident beam makes with the normal is called the angle of incidence.
9
New cards
Angle of reflection
The angle that the reflection makes with the normal is called the angle of reflection.
10
New cards
Angle of refraction
The angle that the transmitted beam makes with the normal is called the angle of refraction.
11
New cards
Laws of reflection
The incident, reflection, and transmitted beams of light all lie in the same plane.
The relationship between the incident and reflected ray:
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
The relationship between the incident and reflected ray:
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
12
New cards
Maximum index of refraction
***n = c/v***
* c = speed of light (3\*10^8 m/s)
* v = speed of light in a particular medium
* n = refractive index
* c = speed of light (3\*10^8 m/s)
* v = speed of light in a particular medium
* n = refractive index
13
New cards
Snell’s Law
* n 1 sin θ′1 = n2 sin θ′2 If n2>n1, the beam will bend/refract toward the normal.
* If n2
* If n2
14
New cards
Total internal reflection
Total internal reflection occurs when:
* n1> n2 and θ1> θc, where, θc = sin−1 (n2/n1)
* θc is the critical angle.
* n1 and n2 are the refractive indexes in respective mediums.
* n1> n2 and θ1> θc, where, θc = sin−1 (n2/n1)
* θc is the critical angle.
* n1 and n2 are the refractive indexes in respective mediums.
15
New cards
Mirror
A mirror is an optical device that forms an image by reflecting light.
16
New cards
Plane mirror
* Our image is behind the mirror and stands at an equal distance as we stand before the mirror.
* An image is said to be real if light rays actually focus on the image.
* A real image can be projected onto the screen.
* The images produced by the flat mirror are virtual.
* In a flat mirror, we see an upright image because it's virtual.
* In real images, the image is upside down.
* The image formed by plane mirrors is neither diminished nor enlarged.
* An image is said to be real if light rays actually focus on the image.
* A real image can be projected onto the screen.
* The images produced by the flat mirror are virtual.
* In a flat mirror, we see an upright image because it's virtual.
* In real images, the image is upside down.
* The image formed by plane mirrors is neither diminished nor enlarged.
17
New cards
Spherical mirror
A spherical mirror is a mirror that’s curved in such a way that its surface forms part of a sphere.
18
New cards
Relationship between focal length and center of curvature
***F = R/2*** where,
* F = focal length (the focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light).
* R = radius of curvature (the radius of curvature is the radius of a hollow sphere of which the mirror/spherical mirror is a part).
* F = focal length (the focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light).
* R = radius of curvature (the radius of curvature is the radius of a hollow sphere of which the mirror/spherical mirror is a part).
19
New cards
Concave mirror
A mirror whose reflective side is caved in toward the center of curvature.
20
New cards
Convex mirror
A mirror whose reflective side curving away from the center of curvature.
21
New cards
Mirror equation
***1/so + 1/si =1/ f***
* so = object distance
* si = image distance
* f = focal length
* so = object distance
* si = image distance
* f = focal length
22
New cards
Magnification equation
***M = hi/ho = -si/so***
* M = magnification
* hi = height of the image
* ho = height of the object
* si = image distance
* so = object distance
* M = magnification
* hi = height of the image
* ho = height of the object
* si = image distance
* so = object distance
23
New cards
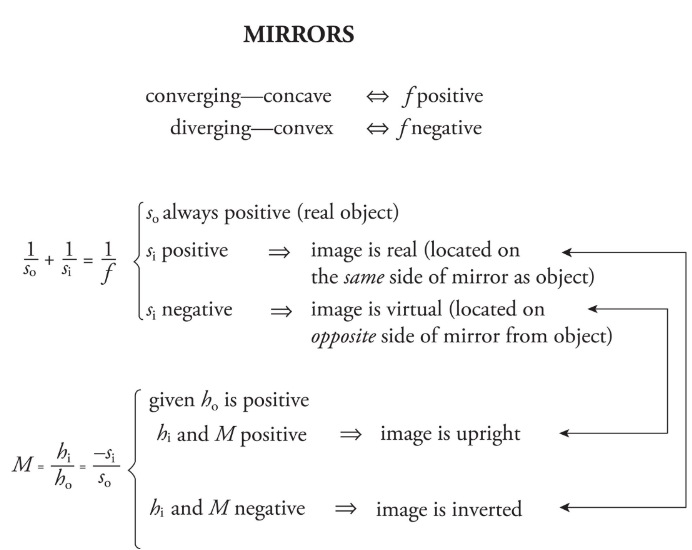
conclusion on mirrors
24
New cards
Converging lens
Bi-convex lens
25
New cards
Diverging lens
Bi-concave lens
26
New cards
Power of Lens
***P = 1/f***
* P = power of the lens
* f = focal length of lens
* P = power of the lens
* f = focal length of lens
27
New cards
light
Light is a form of energy that travels in a straight line when in one medium (material).The speed of light is 3x108m/9c m/s (or 300,000,000 m/s)
28
New cards
Visible Spectrum
The continues of colors that make up with light.
29
New cards
Geometric optics
Using light rays to determine how light behaves when it strikes an object.
30
New cards
light ray
is a line and arrow representing the direction and straight-line path of light.
31
New cards
Real Image
An image which light actually comes from the image
32
New cards
Virtual image
an image which light does not arrive at or actually come from the image location, light only appears to come from the image
33
New cards
Centre of curvature
The centre of the sphere whose surface was used to make an image
34
New cards
Principal axis
This is a line through the centre of curvature which runs through midpoint of mirror.
35
New cards
Focus
Focus is the point at which lights rays parallel to principal axis converge when reflected.