Salivary Gland Neoplasm
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is the most common location for major salivary gland neoplasms?
Parotid gland (60-80%)
What is the most common location for minor salivary gland neoplasms?
Palate (50%)
What are some other locations of minor salivary gland neoplasms?
Tongue and retromolar pad area
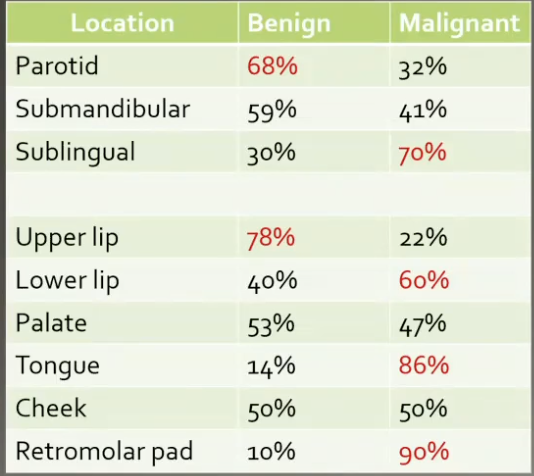
Tumors in which locations are usually malignant?
Retromolar pad and sublingual gland
What is the most common salivary gland tumor overall (benign + malignant)?
Pleomorphic adenoma
What is the most common site for intraoral pleomorphic adenoma?
Palate
What is the most common malignant salivary gland tumor?
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC)
What is the most common malignant tumor in major salivary glands?
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma (MEC)
What is the most common malignant tumor in minor salivary glands?
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
Concerning locations for salivary neoplasm
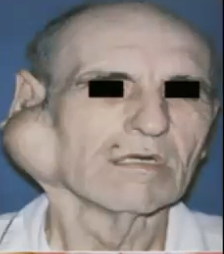
What is another name for Pleomorphic Adenoma?
Benign mixed tumor
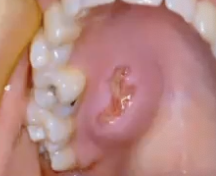
In what age group might you see pleomorphic adenoma?
Middle age
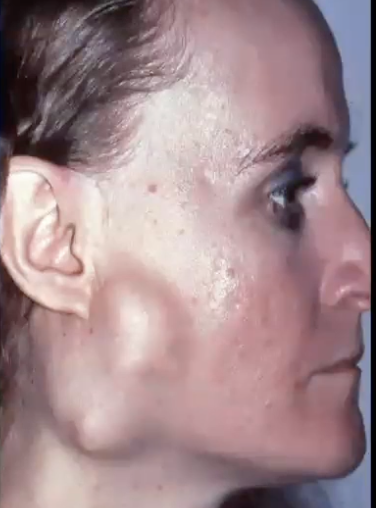
Where might you find pleomorphic adenoma?
Major gland: Superficial lobe of parotid gland
Minor gland: Palate is most common
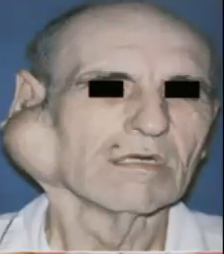
What are some clinical features of pleomorphic adenoma?
Appears as a painless, slowly growing, firm mass
Lesion can grow to grotesque proportions if untreated
Tumor is encapsulated
How would you treat pleomorphic adenoma?
Surgical excision- best prognosis of all tumors
**5% can have malignant transformation: carcinoma ex-pleomorphic adenoma
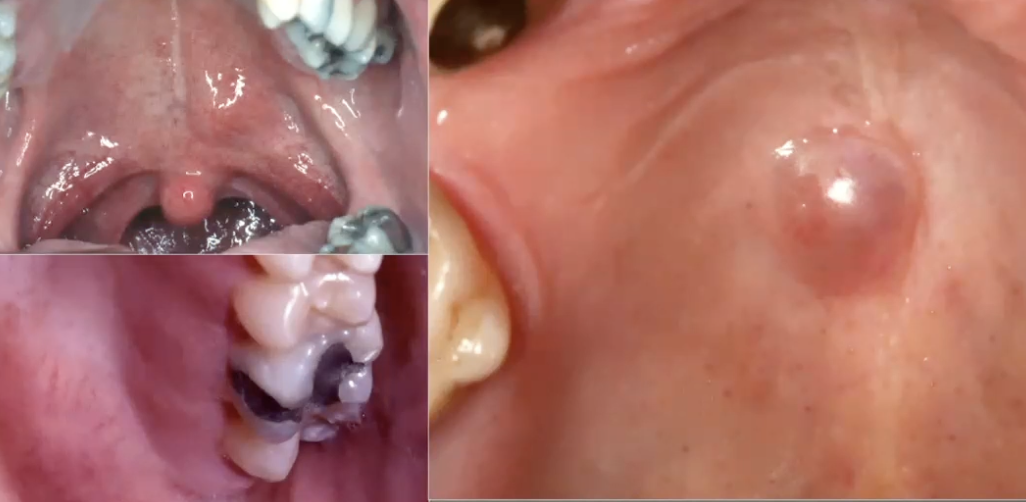
What is this?
Pleomorphic adenoma in the palate
What is another name for Warthin Tumor?
Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum
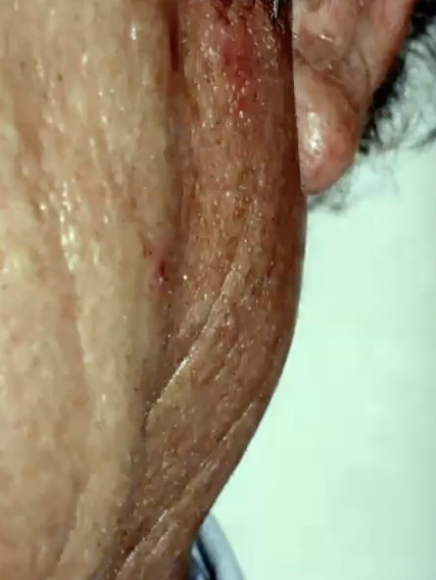
What gland does Warthin Tumor affect the most?
Exclusively in parotid gland (tail)
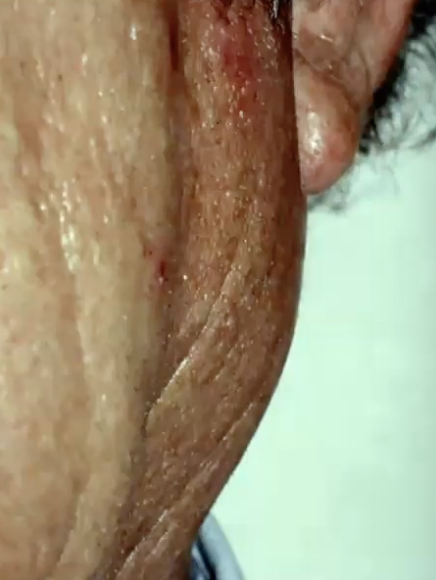
What age group does Warthin Tumor affect?
6th-7th decade (mean age: 55-60 years)
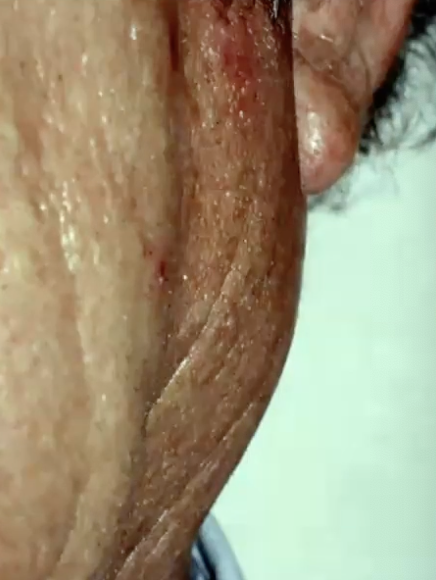
What is the 2nd most common benign tumor of salivary gland?
Warthin Tumor
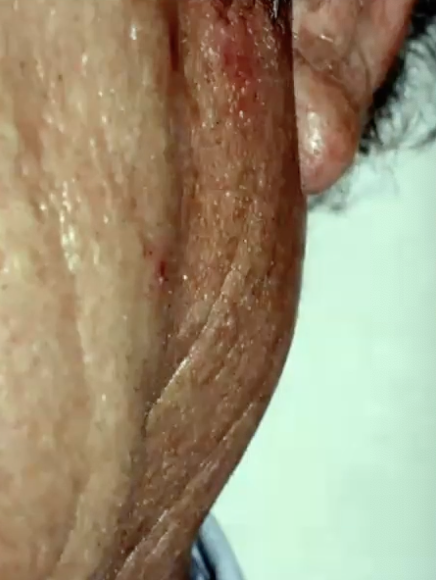
Warthin Tumor is strongly associated with what?
Cigarette smoking; 8-fold greater risk in people who smoke
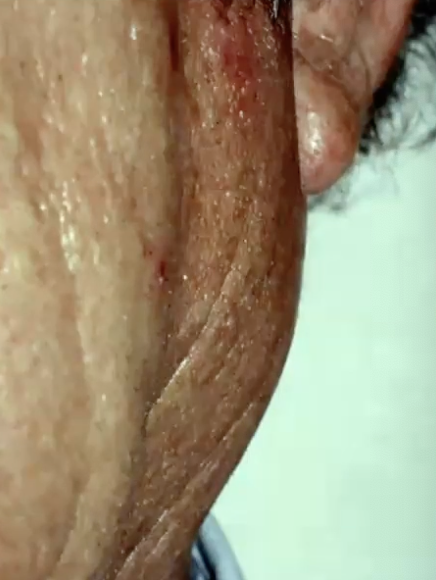
What demographic does Warthin Tumor mostly affect?
More often in males, though recent studies suggest more equal gender radio (increased # of women smokers?)
Warthin Tumor can be
Unilateral or bilateral
What is the treatment for Warthin Tumor?
Surgery
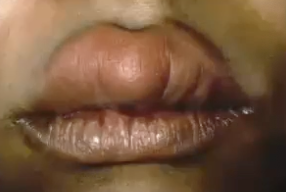
What is another name for Canalicular Adenoma?
Monomorphic Adenoma
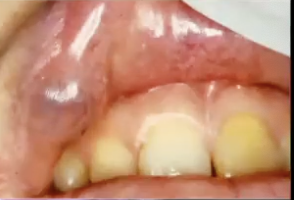
Where might you find Canalicular Adenoma?
Almost exclusively in the minor salivary glands; striking predilection for the upper lip (75%) —> it is a slow growing, painless submucosal mass
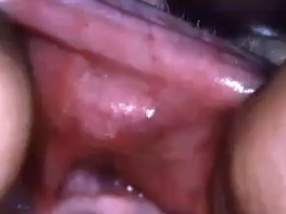
What age group does Canalicular Adenoma affect?
> 60 years
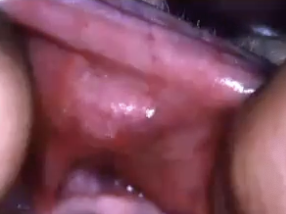
What is the treatment for Canalicular Adenoma?
Surgical excision
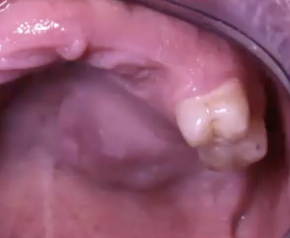
Where might you find mucoepidermoid carcinoma?
Major: Parotid gland
Minor: Palate or retromolar pad area
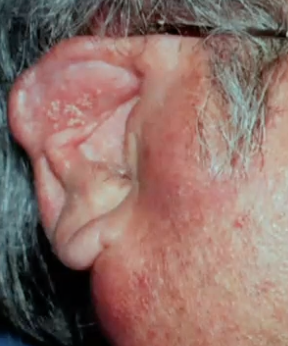
What are some clinical features of mucoepidermoid carcinoma?
Appears as an asymptomatic swelling
Intraosseous tumors can develop in the jaws
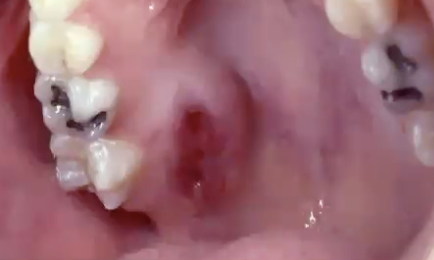
What is the treatment for mucoepidermoid carcinoma?
Depends on the grade
Low-grade: wide surgical excision (95% survival)
High-grade: wide surgical excision + radiation (40% survival)
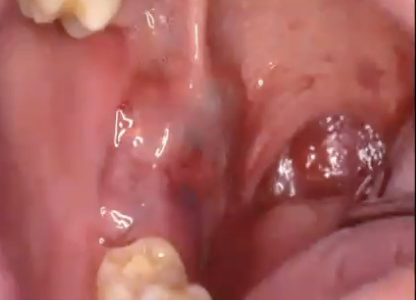
What is this?
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
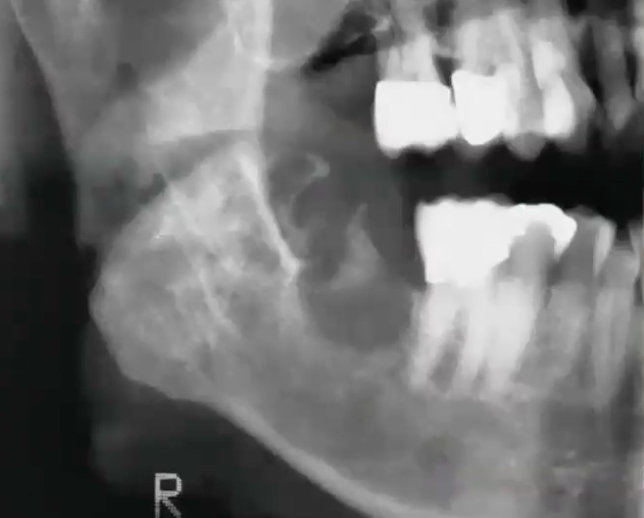
This is only salivary gland tumor that can occur in the bone
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma (intraosseous- looks non-specific)
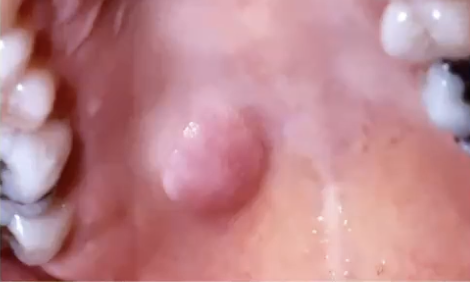
What is the 2nd most common minor salivary gland malignancy?
Polymorphous adenocarcinoma
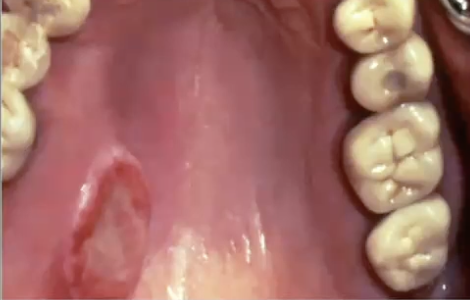
In which demographic would you see polymorphous adenocarcinoma?
2:1 female predilection
6th -8th decade (mean 56 years old), but wide age range
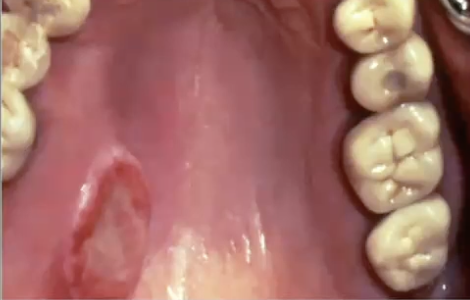
Where might you find polymorphous adenocarcinoma?
Almost exclusively in minor salivary glands
Posterior hard/soft palate (62%)
Buccal mucosa 15%
Upper lip 10%
How would you treat polymorphous adenocarcinoma?
Wide surgical excision
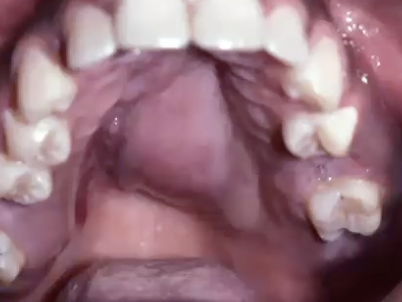
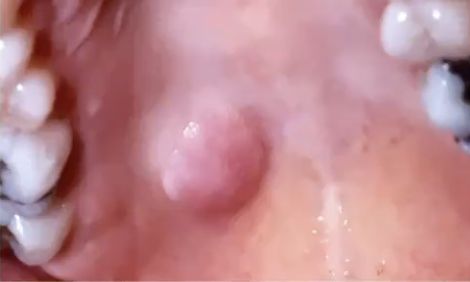
What is the most common malignancy of the submandibular gland?
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
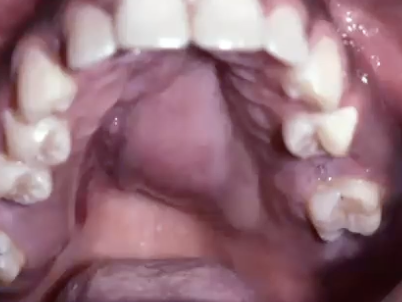
Where might you find Adenoid cystic carcinoma?
Can occur in any salivary gland but 40%-45% are in minor glands
50% palate
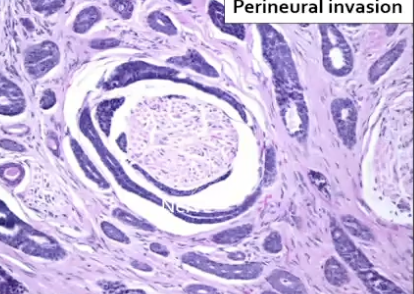
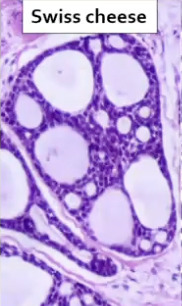
What are some histological features of Adenoid cystic carcinoma?
Swiss cheese
Perineural invasion
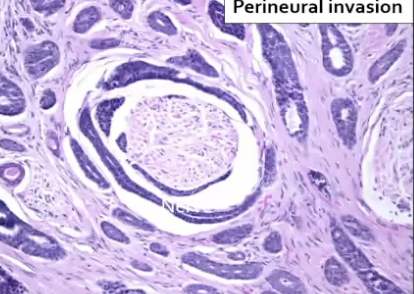
What is a unique characteristic of Adenoid cystic carcinoma?
Causes severe pain because it wraps around the nerve (perineural invasion). Due to this, it can recur and prognosis is not great
How would you treat Adenoid cystic carcinoma?
Surgery and radiation
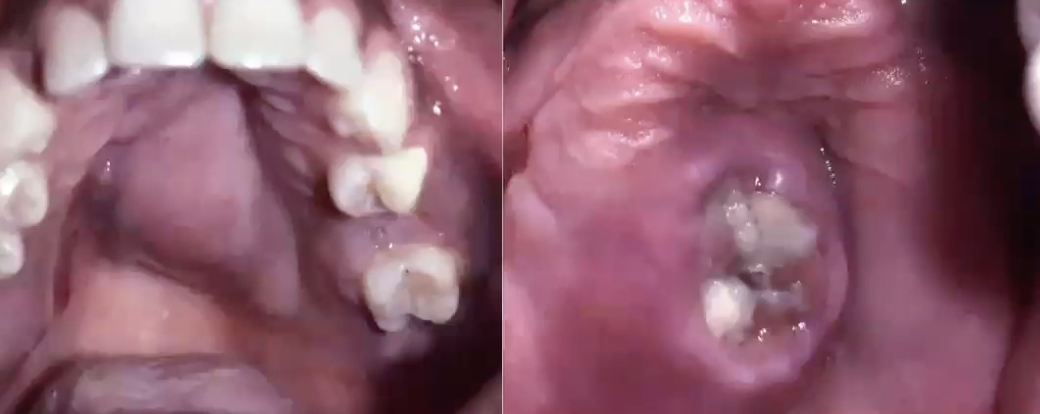
What is this?
Adenoid cystic carcinoma with bone invasion
Which minor salivary gland location is most commonly affected by neoplasms?
Palate
Which of the following is most common site for salivary gland neoplasms?
Parotid gland
Which salivary gland tumor is the most common overall (benign + malignant)?
Pleomorphic adenoma
Which salivary gland tumor has a strong associated with cigarette smoking?
Warthin tumor
Which tumor is almost exclusively found in the upper lip of older adults?
Canalicular adenoma

CBCT showed bone destruction. What is the diagnosis?
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
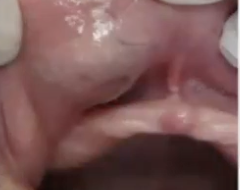
What is the diagnosis?
Canalicular adenoma
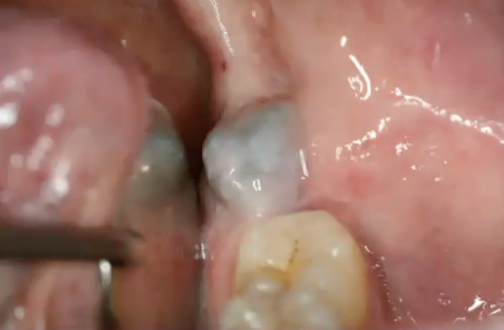
What is the diagnosis?
Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
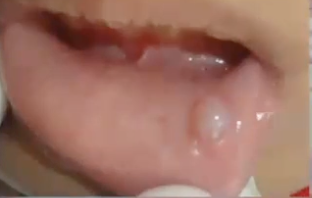
What is the diagnosis?
Mucocele
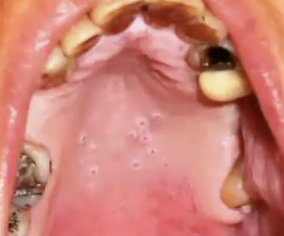
What is the diagnosis?
Nicotine stomatitis
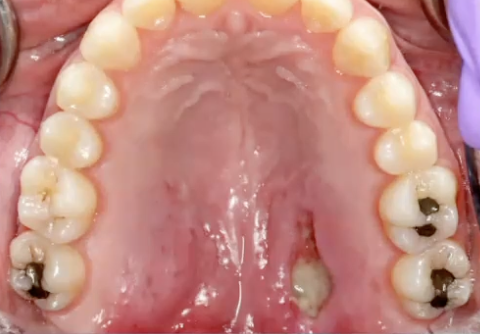
What is the diagnosis?
Necrotizing sialometaplasia
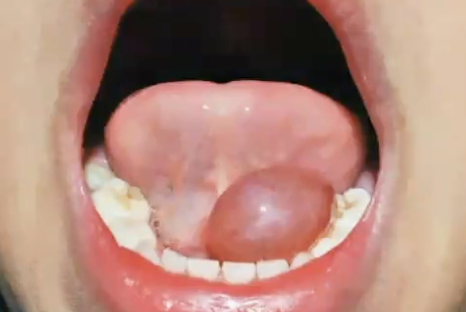
What is the diagnosis?
Ranula
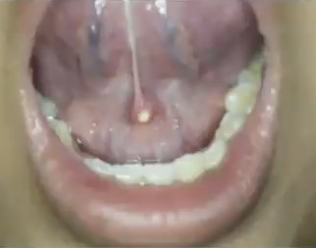
What is the diagnosis?
Sialolithiasis
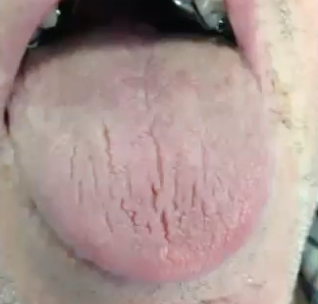
What is the diagnosis
Sjogren syndrome
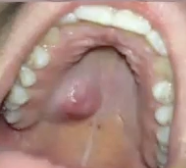
Slowly growing lesion. Been present for over 10 years. What is the diagnosis?
Pleomorphic adenoma