3.1) Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Anton Van Leeuwenhoek
a Dutch scientist known for his works with microscopy and considered one of the pillars of microbiology.
Robert Hooke
English scientist who first observed cells and also coined the term due to the appearance of what he saw as being those of a honeycomb shape.
Light microscope
Most common type of microscope
Cell theory
Through microscopes this concept was born. It is the idea that living organisms are composed of basic, structural units called cells.
All living organisms are composed of one or many cells.
Cells are the basic unit of structure and organization in organisms.
Cells must come from pre-existing cells.
Give the 3 main ideas of cell theory
DNA is passed between cells during cell division.
All cells of organisms have the same basic chemical composition.
Energy flow occurs within cells.
Advancements in technology also added 3 more concepts with regared to the cell theory, these are:
Prokaryotic
Eukaryotic
What are the 2 types of cell?
Plasma membrane
Cytosol
Chromosomes
Ribosome
What components do all cells share in common?
Plasma membrane
serves as an outer covering that protects the insides of a cell from its surrounding environment.
It is usually composed of phospholipids arranged in a bilayer;
Cytosol
fluid region in the cell where other cell components are found
Chromosomes
structures that contain genetic material in the form of DNA
Ribosomes
Particles that synthesize proteins
Cytoplasm
This refers to the inside of both cell types but in eukaryotic cells, this refers to the region between the nucleus and the plasma membrane.
Permeable
This term is used to describe a material that allows all substances (both large and small molecules) to pass through it freely.
Plasma Membrane
A semi-permeable layer that separates the insides of a cell from the external environment
the location of chemical exchanges for many life functions.
Cytoplasm
The fluid internal environment of the cell where all internal components of the cell (called “organelles”) are suspended.
Nucleus
Stores the genetic material of the cell.
Nucleoid
In prokaryotes, this genetic material is located in a region called the _______?
Nuclear Membrane
Encloses the nucleus and protects the genetic material.
Nucleoplasm
The environment within the nucleus.
Nucleolus
An area in the nucleoplasm where the genetic material is highly concentrated.
“Highly concentrated genetic material" means there's a lot of DNA in a specific area, often packed tightly for organization, storage, or efficiency in processes like cell division or gene expression.
Nuclear Pore
Gateway of materials into or out of the nucleus
Mitochondrion
Produces energy for the organism, having the moniker “powerhouse of the cell" due to this function.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Sites for lipid and protein synthesis.
Rough ER
Contains ribosomes
site for protein synthesis
In addition, it also functions as the cell’s membrane-making machine.
Smooth ER
Contains cell types used in metabolic processes, especially lipid synthesis, as well as storage of calcium ions.
Golgi Apparatus
Site for modifying, sorting, and storing of compounds synthesized by the ER.
Lysosome
Contains digestive enzymes that help break down food or damaged organelles.
Peroxisome
Helps break down fatty acids to be used as cellular fuel.
Ribosome
Sites of protein synthesis.
Can be found attached to the rough ER or free in the cytosol.
Vacuoles
Storage of food and other chemicals.
Centriole
Organelle for cell division.
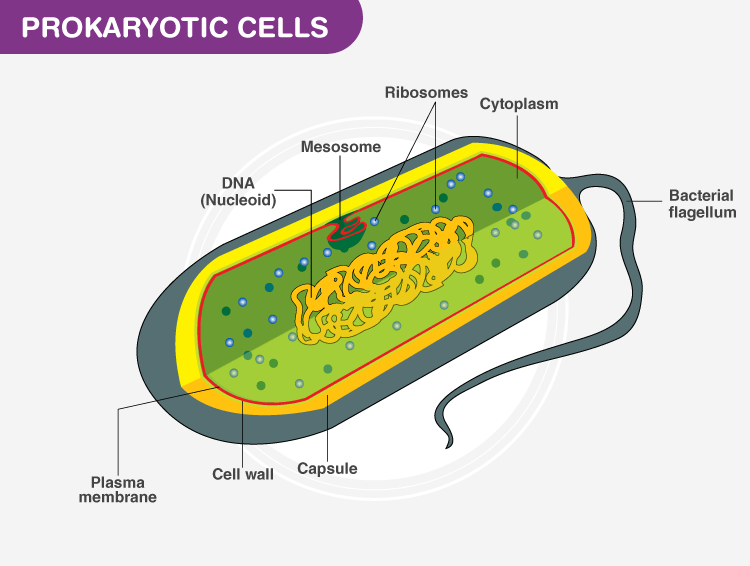
Prokaryotes
refers to organisms with cells that are simple, often single (unicellular), and lack a nucleus, or any other membrane-bound organelle.
Its DNA is found in the central part of the cell: a darkened region called the nucleoid.
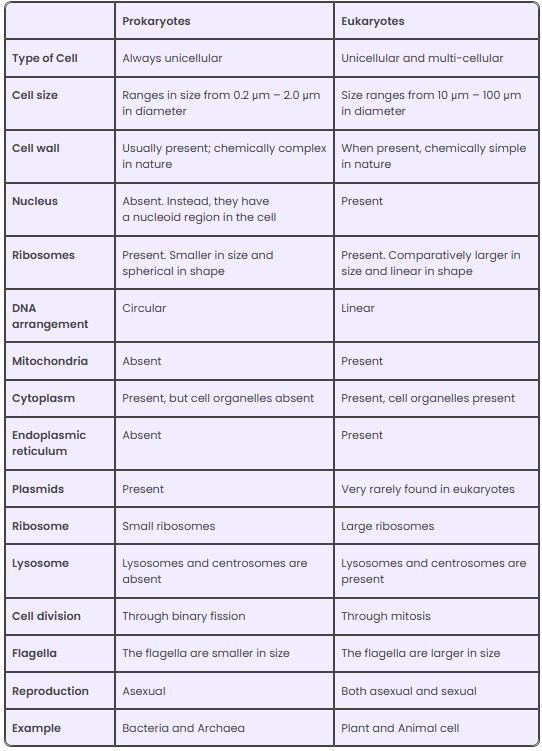
How different are prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
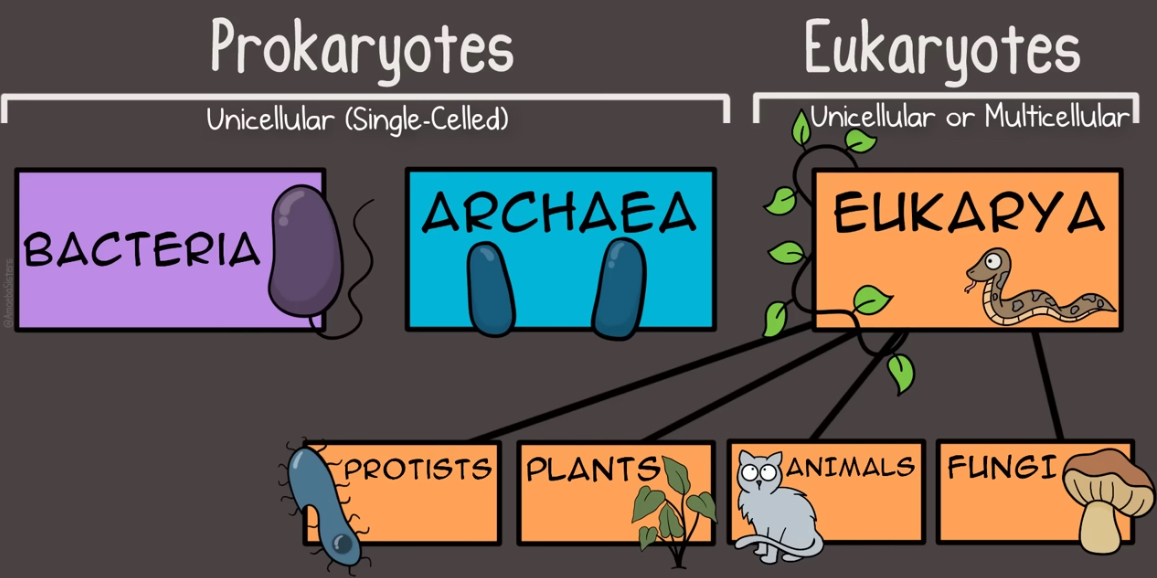
Bacteria
Archaea
What are the two distinct groups of prokaryotes?
Peptidoglycan
What do we call the cell wall of bacteria?
it is composed of sugar and amino acids
Have many polysaccharide capsule
This cell wall acts as an extra layer of protection, helping maintain cell shape, and preventing dehydration
Bacteria
Identify which type of prokaryote:
✅ Description:
Most common and widespread prokaryotes.
Found in soil, water, air, and inside living organisms.
Can be harmful (pathogenic) or beneficial (e.g., gut bacteria).
Bacteria
Identify which type of prokaryote:
🔧 Structure / Parts:
Cell wall made of peptidoglycan
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm with ribosomes
Nucleoid (region containing circular DNA)
May have:
Capsule (for protection, attchment to surface)
Flagella (for locomotion)
Pili (for attachment, exhange genetic material)
Plasmids (extra DNA)
Bacteria
Identify which type of prokaryote:
🧪 Examples:
Escherichia coli (E. coli) – lives in human intestines
Streptococcus pneumoniae – causes pneumonia
Lactobacillus – used in yogurt production
Conjugation
the transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells by direct cell-to-cell contact or by a bridge-like connection between two cells. This takes place through a pilus. It is a parasexual mode of reproduction in bacteria.
Archaea
Identify which type of prokaryote:
✅ Description:
Look similar to bacteria but are genetically and chemically different.
Often live in extreme environments (heat, salt, acid).
Considered ancient life forms.
🔧 Structure / Parts:
No peptidoglycan in cell walls (unlike bacteria)
Plasma membrane has unique lipids
Cytoplasm, ribosomes, and nucleoid like bacteria
May also have:
Flagella
Pili
Plasmids
Archaea
Identify which type of prokaryote:
🧪 Examples:
Halobacterium – lives in salty environments
Thermophiles – live in hot springs or hydrothermal vents
Methanogens – produce methane gas; found in swamps or animal guts