Dermatology 5
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
26/05
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Which gene is most frequently associated with Acral Lentiginous Melanoma? (explain relevance in 1 sentence)
c-KIT gene. Treatment implication: targeted by Imatinib
List the most important drugs in treatment of metastatic melanoma
Tyrosine kinase inhibitors
BRAF/MEK inhibitors
c-KIT inhibitors
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
anti-CTLA4 monoclonal antibodies
anti-PD1 monoclonal antibodies
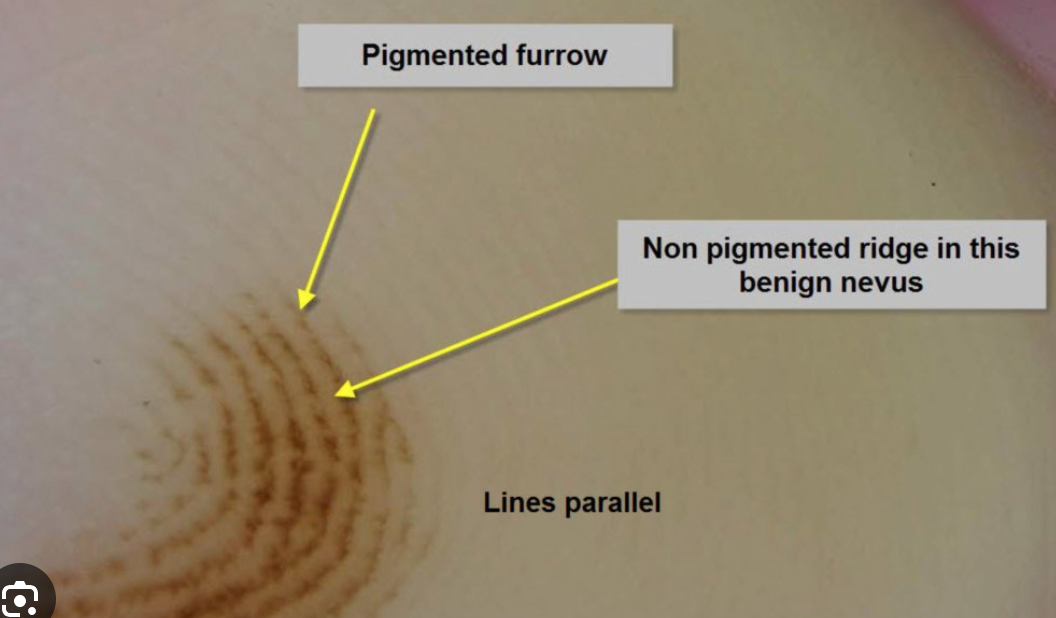
What are the typical dermoscopy features that enable us to distinguish between acral melanoma and acral nevus?
The presence of parallel ridge pattern (pigmentation on the ridges of acral skin) is a hallmark of acral melanoma
Explain the clinical progression to lentigo maligna melanoma
Chronic UV-radiation exposure leads to Lentigo Maligna (precursor/in situ lesion in the horizontal growth phase) presenting as a macula with suspicious features (ABCDE, ugly duckling sign, etc.) generally on the face, scalp and ears. When not excised, it progresses in 90-95% of cases to Lentigo Maligna Melanoma (invasive melanoma in vertical growth phase) typically presenting as a dark nodule over the macula.
Explain when Mohs micrographic surgery is preferred for treatment of basal cell carcinoma
Mohs micrographic surgery is preferred in the treatment of BCC in these cases:
Tumor is located in high-risk or cosmetic sensitive area (e.g. face, nose, eylids, ears)
Recurrent lesion
Aggressive histological subtype (morpheaform, infiltrative)
Poorly defined margins.
It gives the highest cure rate with maximal tissue preservation.
Which are the most common sites of seborrheic dermatitis and why?
The most common sites are:
Sternal area
Scalp
Face (forehead, paranasal/nasolabial region, chin, eyebrows, eyelids, jaw, beard area)
The reason is that in these regions there is a higher quantity of sebaceous glands.
List and define what are the key histopathological features of the dermis and epidermis in psoriasis
DERMIS:
Dilation of blood vessels
Lymphocyte infiltration
EPIDERMIS:
Parakeratosis: thickening of the stratum corneum with presence of nucleated cells
Munro’s microabscesses: abscesses in the stratum corneum of the epidermis due to infiltration of neutrophils from the papillary dermis into the stratum corneum
Pustules of Kogoy: sterile collections of neutrophils in the stratum spinosum
Acanthosis: thickening of the whole epidermis
Hypogranulosis: decreased or absent granular layer in the epidermis
List the endogenous risk factors of melanoma (7)
MC1R gene variations
Germline mitations (CDKN2A, CK4)
Personal or family history
Individual with numerous nevi
Presence of atypical nevi
Congenital melanocytic nevus >20cm
Fair skin phototypes
List the exogenous risk factors of melanoma
Chronic UV radiaiton exposure
Sunburns
Artificial UV sources
Geographical and environmental factors
Iatrogenic immunosuppression (e.g. organ-transplant patients)
List the treatment used in actinic keratosis: those indicated for single lesions and those used for field cancerization.
TREATMENT FOR SINGLE LESIONS:
Cryotherapy
Curettage and cautery
Laser therapy
FOR FIELD CANCERIZATION:
Photodynamic therapy
Topical treatments, including
5-Fluorouracil (creaml formulations, sometimes combined with salicylic acid)
Imiquimod
Diclofenac
Tirbanibulin
Define Kaposi sarcoma and list the types
Kaposi sarcoma is a low-grade angioproliferative tumor mainly associated with HHV-8 infection.
Classic Kaposi sarcoma
Endemic (African) Kaposi sarcoma
Epidemic (AIDS-related) Kaposi sarcoma
Iatrogenic (transplant-related) Kaposi sarcoma
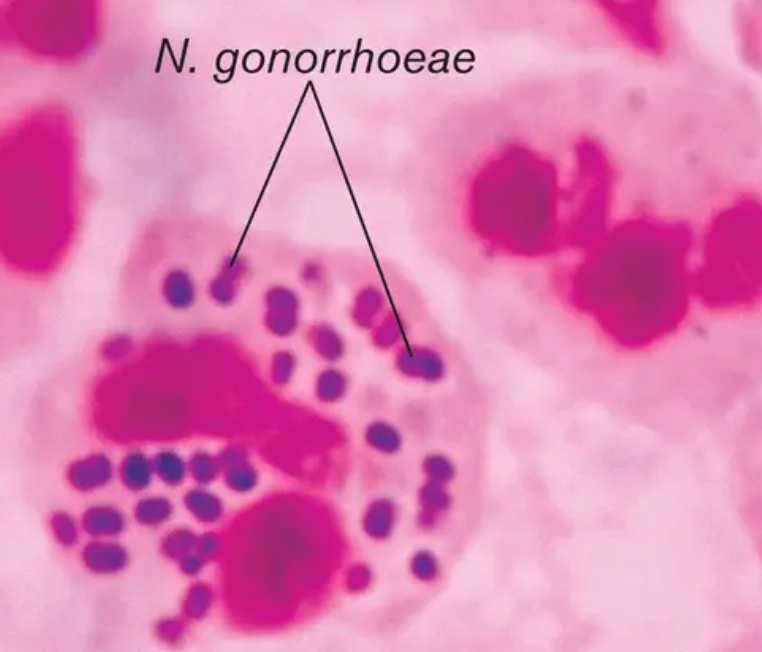
What is the most important and quickest step in the diagnosis of gonorrhea?
Gram stain detects the gram-negative diplococci in urethral discharge.