unit 12
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
what are observational studies
non experimental
observe describe and analyse individuals or populations without intervention
what are the 2 major catagories of epidemiological studies
experimental
non-experimental
experimental + descriptive
none
experimental + analytical
clinical trials
field trials community trials
non-experimental + descriptive
ecological
cross-sectional
case reports
case series
non-experimental + analytical
Cohort
case-controlled
ecologic study is what (catagotiries)
non-experimental
descriptive
Ecological study
what is the unit of analysis in an ecologic study?
the group or community level - not the individual
Ecological study
what does an ecologic study examine
intergroup variability
(compares rates of disease between different populations or areas)
Ecological study
what is the main purpose of an ecologic study
to generate hypotheses about potential associations
Ecological study
if a finding in an ecologic study shows a correlation what is the necessary next step
the findings must b confirmed in more rigorous studies on individual
Ecological study
an example of how ecologic studies are commonly used
measuring disease rates for different geographic areas and relating them to area characteristics like median income, air pollution.
Ecological study
what is a classic example of an ecologic study at the country level?
examining the relationship between country’s gross domestic product (GDP) and its populations life expectancy
Ecological study
what is ecological fallacy
the error of assuming that association observed at the group/population level is true at an individual level
Ecological study
ecological fallacy
the data is often correct however the correlation is what is wrong
Explain Emile Durkheim's suicide study as an example of ecological fallacy.
A: Group level: Protestant areas had higher suicide rates than Catholic areas (attributed to social cohesion).
Individual level: Catholics living in Protestant areas had a higher suicide rate than Catholics in Catholic areas. The individual risk was linked to social isolation within the broader community, not just religion.
read
done
Ecologic studies
what is aggregation bias (caused by ecological fallacy)
data may show an opposite effect to what is happening at individual level
cross sectional
non-experimental
descriptive
what is a cross-sectional study
snapshot of a population at one point in time
what can a cross sectional study measure
attitudes, behaviours, health conditions (past or present) or risk factors (past or present)
cross sectional study
how are participants selected
from a target population using a simple random sample
cross sectional study
during sampling you can also
oversample particular subgroups/strata (e.g favour a specific age group)
cross sectional study
what is a DESCRIPTIVE cross-sectional study
measures one parameter
(e.g measuring the prevalence of diabetes in adults over 40)
cross sectional study
what is an ANALYTICAL cross sectional study
measuring both outcome and exposure to look for an association
(e.g measuring the prevalence of obesity and the prevalence of diabetes in the same population to see if they are linked)
case-control
non-experimental
analytical
case-control
what is known about the outcome at the time of the case-control
it has already occurred
case-control
what is known about the exposure at the time of the case-control
data on exposure to potential risk factors is collected retrospectively ( usually form questionaries)
case-control
what is the direction of the investigation
from outcome back to exposure
case-control
how does a case control study begin
identifying individuals with the disease (cases) and without the disease (controls ) and looking back to compare past exposure
case-control
what is the primary measure of association
the odds ratio
case-control
why is relative risk not calculated
because the investigator chooses the number of cases and controls (rather than following a whole population from exposure to outcome)
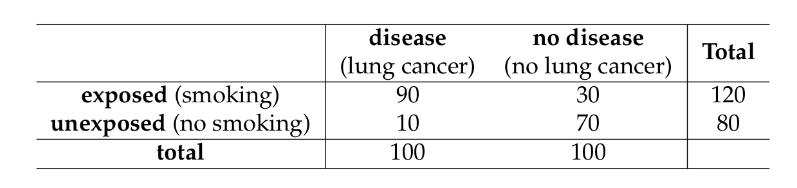
calculate odds ratio
(90/10) / (30/70) = 21
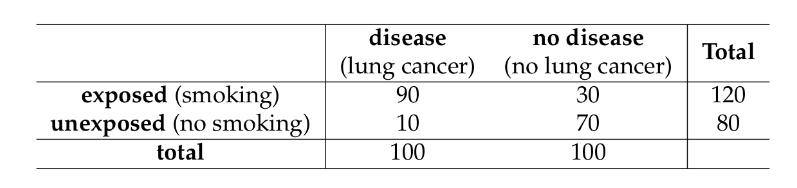
calculate relative risk
(90/120) / (10/80) = 6
(risk exposed / risk unexposed)
case-control
issues
what biases
selection bias
information bias
reverse causality
case-control
how do we reduce selection bias
selecting controls from the same population as cases
(making them as similar as possible expect for the outcome)
case-control
how to reduce information bias
asking both cases and controls about a number of exposures in the same manner
(bc sick people more likely to remember or report an exposure)
case-control
how to reduce reverse causality
need other study designs to confirm findings
case-control
what is matching in case controlled studies
cases are individually matched to control key characteristics
(e.g age, sex)
and a matched pair analysis takes place
case-control
what is a nested cross sectional study
cases and controls are selected from within an existing cohort study.
to examine other possible risk factors
Cohort
non experimental
analytical
cohort study
how does it begin
identifying groups (cohorts) of people based on their exposure status (exposed vs not exposed)
cohort study
what is known about the outcome at the start of the study?
the outcome has not occurred yet
cohort study
what happens after the exposed and unexposed cohorts have been identified
they are followed up
cohort study
what is the direction of the investigation
moves forward in time
from exposure (present) to outcome (future)
cohort study
why is the follow up essential to happen ASAP
so that any differences can be explored
cohort study
what is a bias
measuring bias
cohort study
how to reduce measuring bias
collecting data on exposure and outcomes