Intro to Kinesiology & Biomechanics
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PPT 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Kinesiology
study of human movement
biomechanics
physics (mechanics) of motion produced by biological systems
integrates biological characteristics with mechanics
examines forces acting upon, within, and produced by a body
Mechanics
efforts of forces and energy on the motion of bodies
statics vs dynamics
Statics
study of systems in a state of equilibrium
at rest or in constant state of motion
Dynamics
study of systems in a state of changing motion
Kinetics
study of forces that inhibit, cause, facilitate, or modify motion of a body/system
changing someway to aid motion
Kinematics
study of the spatial and temporal characteristics of motion without considering what’s causing the motion
space and time
Ergonomics (occupational biomechanics)
Interactions of humans and machines
attempt to improve human-machine system
manipulating the work environment to enhance safety
changing the task to make it compatible with the user’s characteristics
enhancing the organization of tasks to better accommodate needs of the use
Pedagogy
teaching and coaching used to enhance performance
adapted physical education
process of teaching movement activities to persons with disabilities
Motor Control, Development, & Learning
What are the 3 aspects that motor (movement) behavior is studied?
Motor Control
How nervous system controls coordinated skill performance
“muscle memory”
coordination
depends on open-loop (reflexive) OR close-loop
Motor Development
how motor control changes over time
voluntary motion begins when the nervous and muscular systems are ready
starting at birth, body’s in state of dynamic state of change
Motor Learning
How humans learn motor skills
trial-and-error
focuses primarily on neurological aspects of attaining and retaining motor skills (muscle memory)
Gentile Model (of motor learning)
Initial Stage
generating a movement pattern to achieve some degree of success
Fixation and Diversification
adapt movement to specific demands of situation
consistency
perform with economy of movement
Motor Learning Stages (3)
Cognitive
movements are slow, inefficient, controlled consciously
trial and error & requires lots of focus
Associative
movements are more fluid, reliable, efficient
some parts controlled autonomously - in between phases
Autonomous
movements highly accurate, efficient, consistent. Flow state, most/all control is autonomous
System
any structure/organization of related structure whose state of motion is of analytical interest
Anthropometry
describes the shape of the system
varying body shape & limb proportions affect motion
measurements: height, weight, volume, proportion, shape
BMI (bone density & muscle can alter index)
Somatotype
Waist-to-hip ratio; Crural Index (tibia to femur ratio); torso to leg
Somatotype (3 types)
used to characterize body types broadly:
Endomorph= short & Stour
hold fat in belly, hard to drop fat in belly
Mesomorph= muscular and lean
hold fat in waist
Ectomorph= long and lengthy
hard to gain muscle- need lots of calories & protein
3 Cardinal Planes
planes that divide body perfectly in half:
frontal (coronal), sagittal, transverse
plane, axis
MOVEMENTS OCCUR IN A _______ AND AROUND AN ________!!!
Motions in Multiple Planes
circumduction
pronation/supination of the ankle
Degrees of Freedom
number of independent ways a system can move (aka # of planes and axis it can move around)
6 possible degrees of freedom
2 movements (opposite of one another)= 1 DOF
constraints= cannot move along any axis
center of mass
point that represents the average location of a system’s mass. as we move, center of gravity moves with us
all 3 carinal planes meet in the middle, passing through this point
gravitational pull is concentrated here
line of gravity
imaginary vertical line that passes through center of gravity
gravity’s force is always down
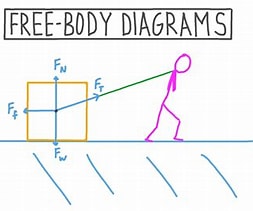
free-body diagram
simplified representation of the system free of the movement environment
discrete skill
movement with a definite beginning and end-point
ex: baseball pitch
continuous skill
cycles of motion performed repeatedly with no well-defined beginning/end points
same motion; ex: cycling
Serial skills
movements that appear to be continuous but are really a combination of discrete motions
ex: triple jump (sprint, leap, then jump and land)
Repeated discrete skill
at the end of the stroke the body is not in position to begin the next stroke
“recovery phase” is necessary
ex: rowing
Closed Skill
skill performed under standar environment conditions
ex: basketball free throw in gym
open skill
skill that must be altered because of changing dynamics of activity, environment, or object of interest
ex: during a basketball game, no two passes are identical
Translation (linear movement)
motion along one axis in which all points of the system move at the same time, in same direction
rectilinear translation= path of system is straight line
curvicular translation= path of system is angled
rotation motion
occurs when the system is restricted to move around a fixed axis- therefore in a circular path
aka angular motion
ex: skip-it
General motion
combination of linear and angular motion
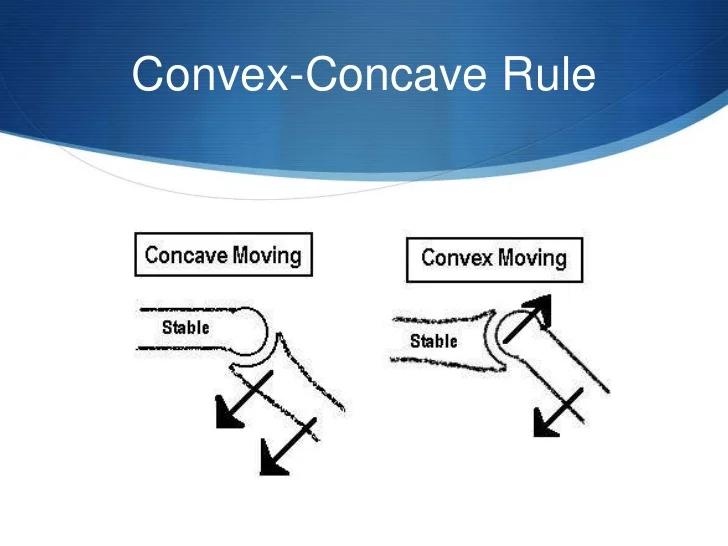
concave, convex
If ________ surface is fixed, _______ convex rolls and glides in opposite directions.
concave-convex rule
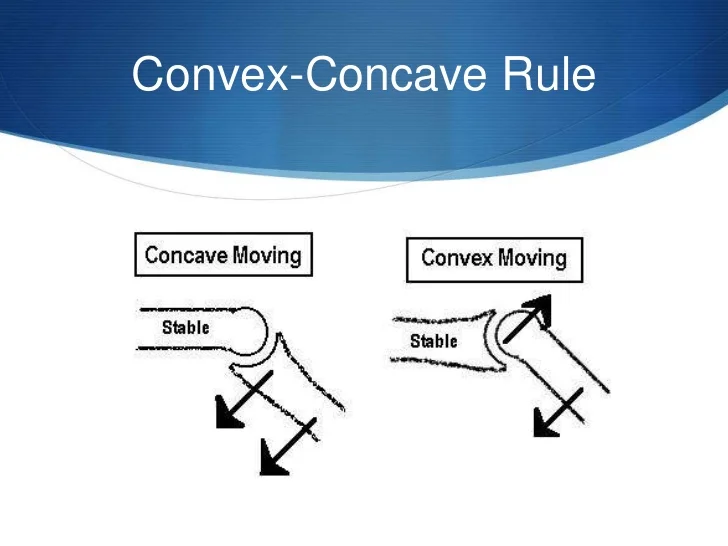
convex, concave
When _______ surface (femur) is fixed, _______ surface (tibia) rolls and glides in same direction.
concave-convex rule
Simple kinetic chain
What kind of kinetic Chain?
each segment participates in no more than 2 linkages
ex: knee (femur & tibia)
Complex Kinetic Chain
What kind of kinetic Chain?
a segment linked to 2 or more linkages
ex: sacrum (articulates with L5 vertebrae and 2 hip joints)
motion at one link affects force transfer and motion at other links
optimal performance requires efficient sequencing and timing of links (coordination)
Open Kinetic Chain
What kind of kinetic Chain?
the most distal segment is free to move
ex: leg extension because can move and adjust feet
Closed Kinetic Chain
What kind of kinetic Chain?
most distal segment is stationary
less mobility, cannot focus on specific muscle/group
Functional Kinetic Chain
What kind of kinetic Chain?
complex chain; some links are open and others are closed kinetic chain
ex: running
Compensatory Motion
adaptions at normal kinetic chain links resulting from abnormal motion at another link
ensures certain tasks are performed
Disadvantages: requires more energy & changes in force patters (pain)