Research || 1st Semester || Midterms
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Research
any systematic investigation of any social or natural phenomena where results and conclusions are aimed at contributing to generalizable knowledge
Inductive Research
starts with empirical observations and then works to form a theory
Deductive Research
research that reduces the general to the specific.
Basic Research
pure science that aims to increase the scientific knowledge base
Applied Research
scientific study that aims to solve practical problems
Exploratory Research
seeks to test the feasibility of undertaking a more extensive study regarding a particular phenomenon
Descriptive Research
seeks to make careful observations and detailed documenta
Explanatory Research
seeks to explain observed phenomena.
Research Design
blueprint for the collection, processing measurement, and analysis of data
Research Method
techniques and tools for gathering data or evidence
Research Methodology
bridges the specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information about a topic
IMRAD Format
introduction, method, results, discussion
Data
any information that has been observed and collected to validate research finding
Primary Sources
Provide raw and first-hand information
a. Observation
b. Interview
c. Questionnaire
Non-participating Observation
Observing behavior without interacting with the participants
Participant Observation
Means the observer takes part in the situation being studied while carrying out the research
Hawthorne Effect
Individuals modify or improve an aspect of their behavior in response to their awareness of being
Focus Group Discussions
group discussions intended to identify the beliefs and opinions of a selected group of people on a specific topic
In-depth Interview
one-on-one discussions
Structured Interview
questions are planned and created in advance
Semi-Structured Interview
asks only a few predetermined questions while the rest of the questions are not planned in advance.
Unstructured Interview
no fixed set of questions and no systematic scoring procedure
Questionnaire
- list of questions or items used to gather data from respondents
- specific tool or instrument for collecting the data.
Secondary Sources
- records that explain or interpret primary sources
Population
large collection of individualss
Sample Size
subset of the population
Slovin's Formula
determine the sample size of the population
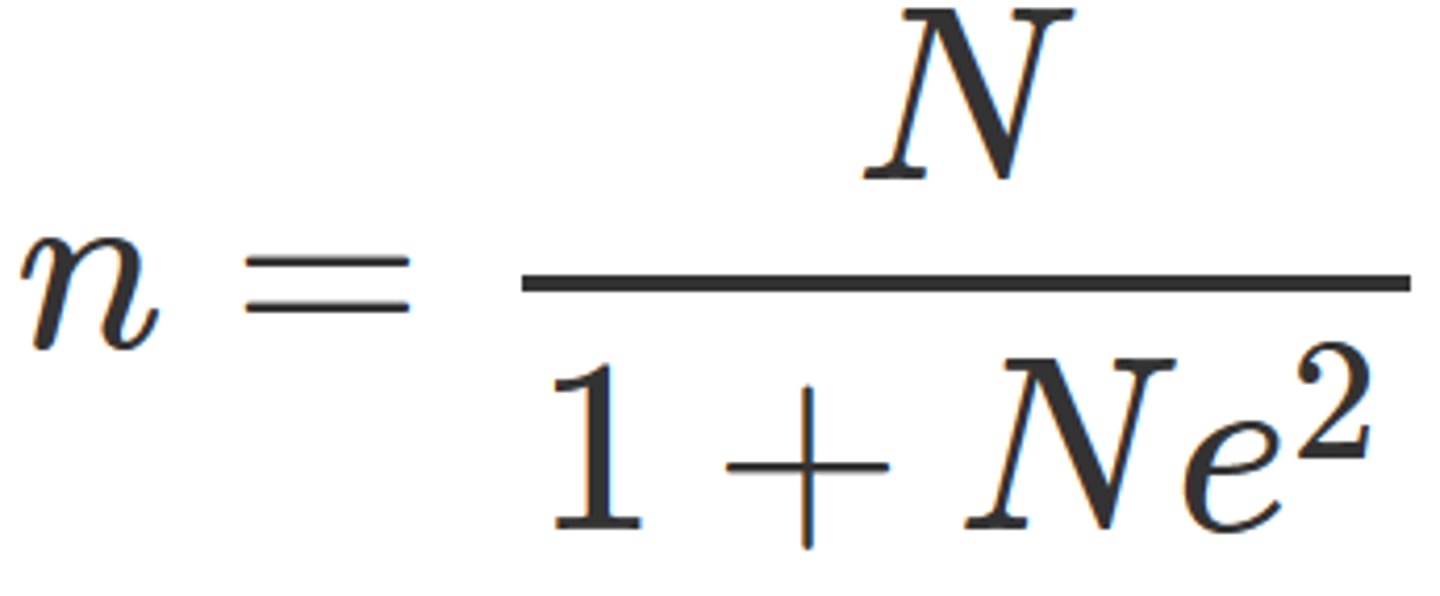
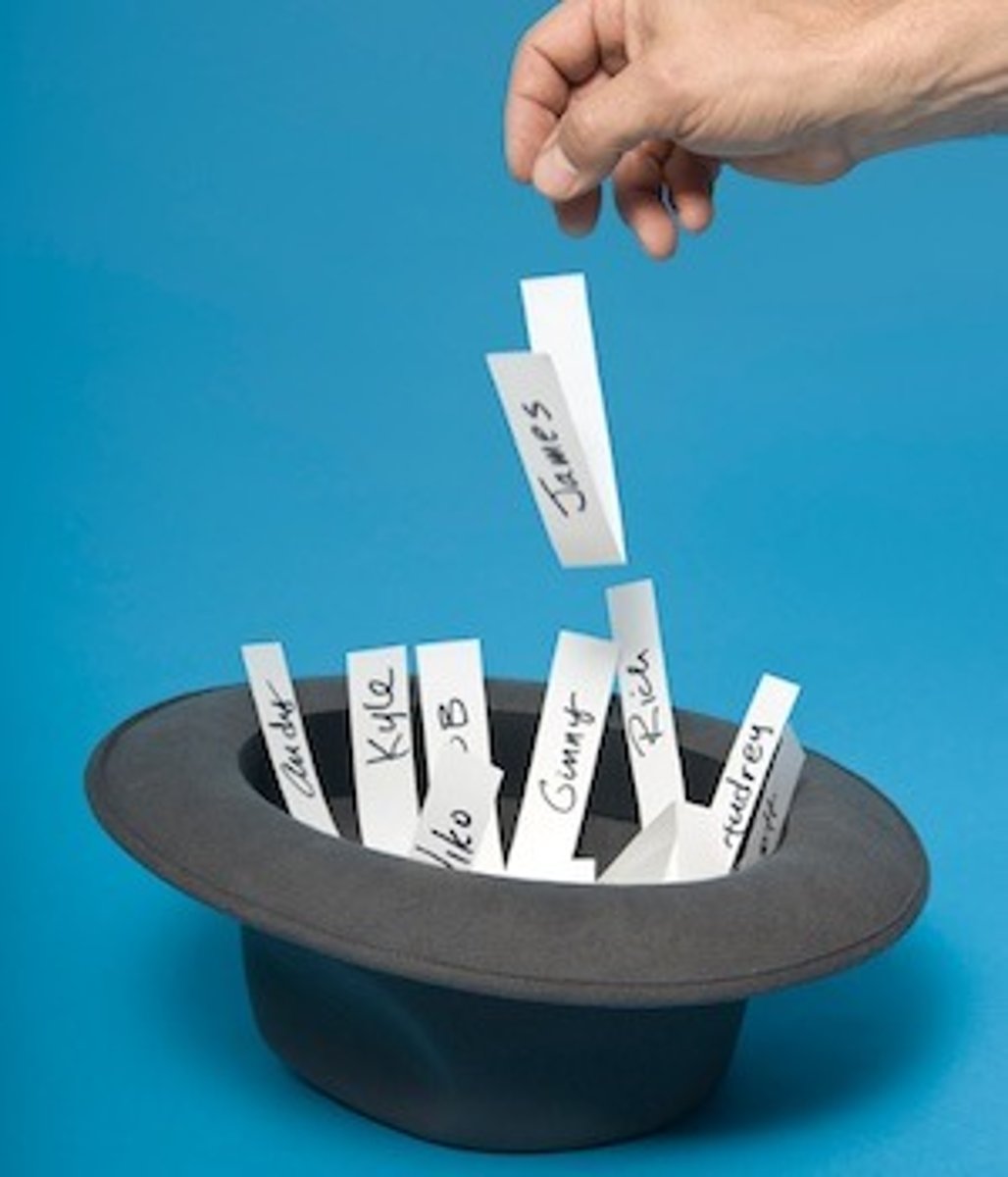
Simple Random Sampling
every sampling unit has a known and equal chance of being selected
ex. fishbowl

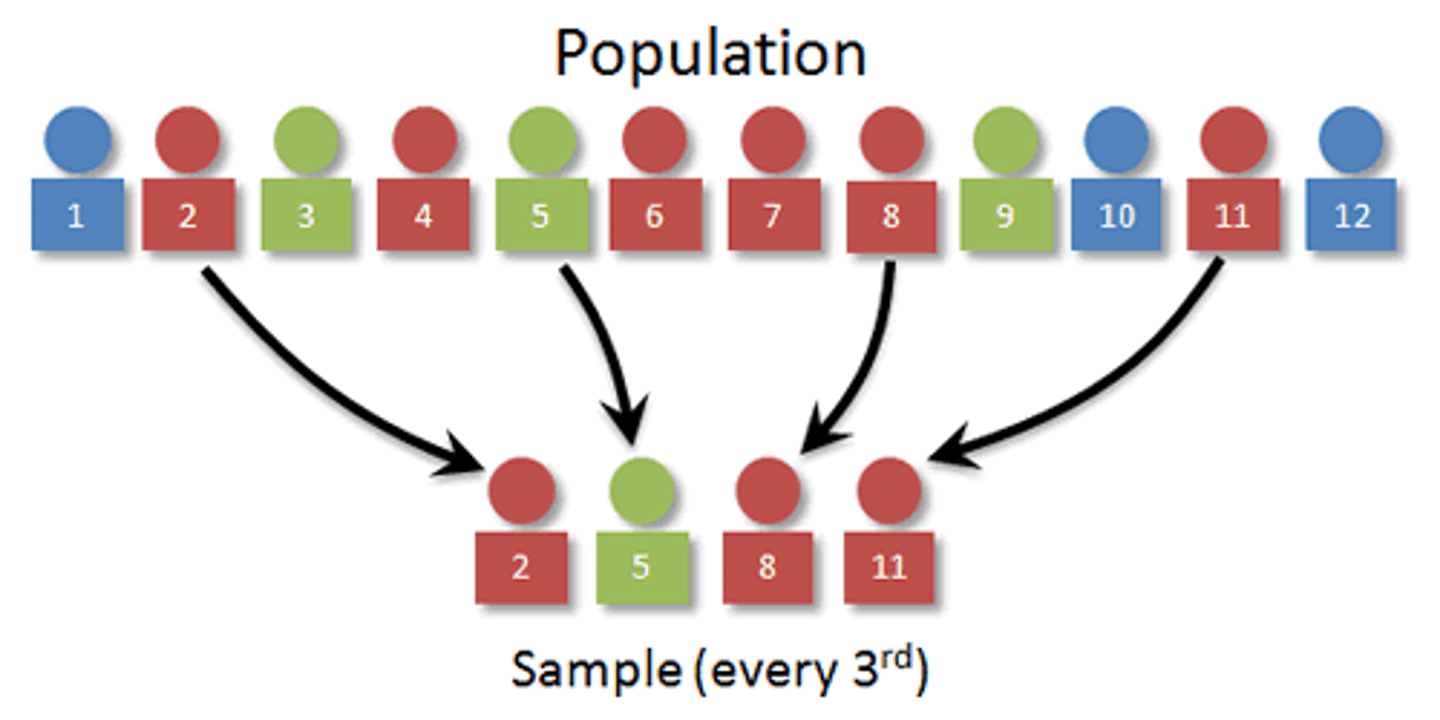
Systematic Random Sampling
selects every nth person from the population
ex. 3, 6, 9, 12, 15...
Stratified Random Sampling
separation of the target population into different groups, called strata, and the selection of samples from each stratum

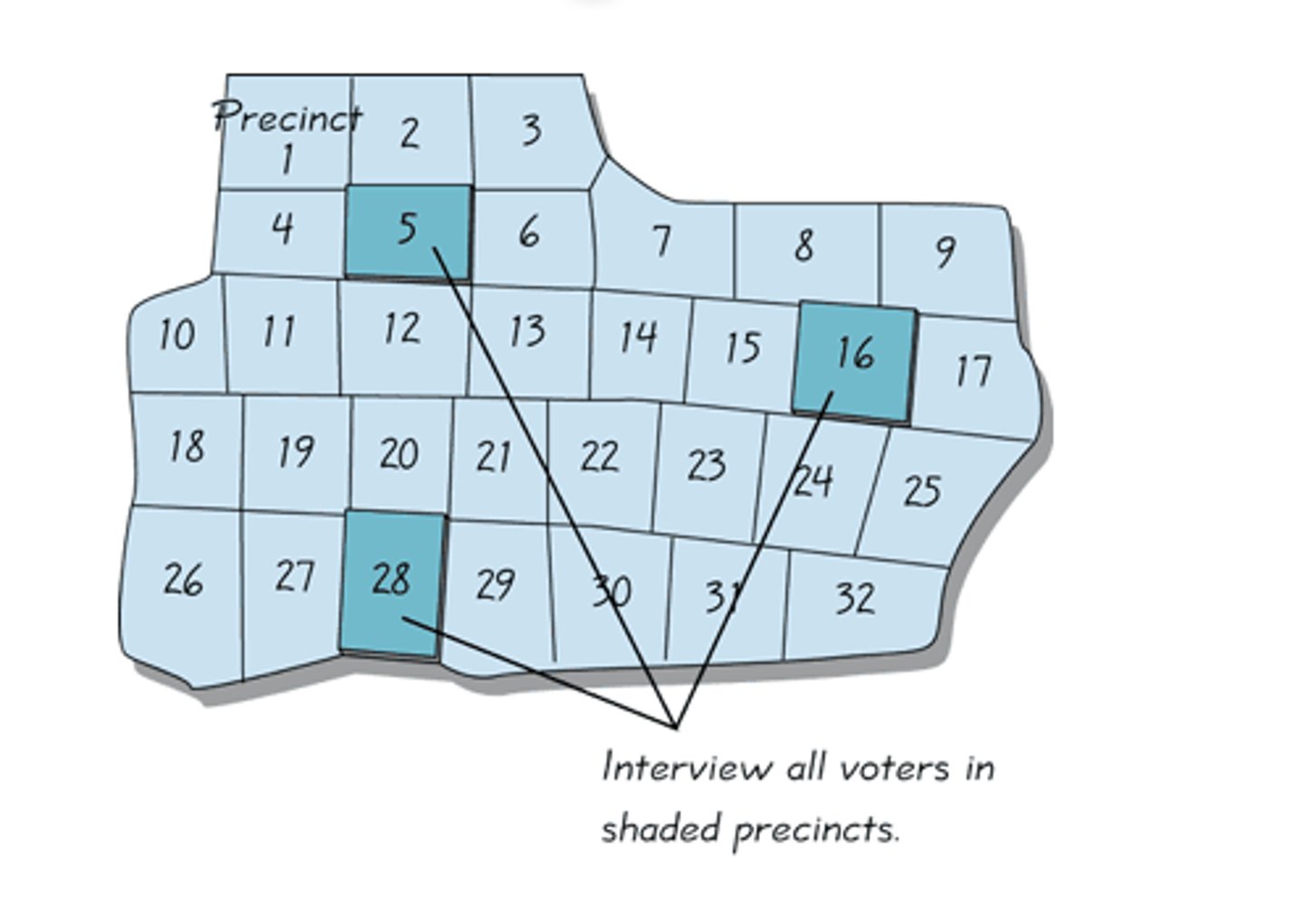
Cluster Random Sampling
involves random selection of groups of individuals
Convenience Sampling
choosing individuals who are easiest to reach
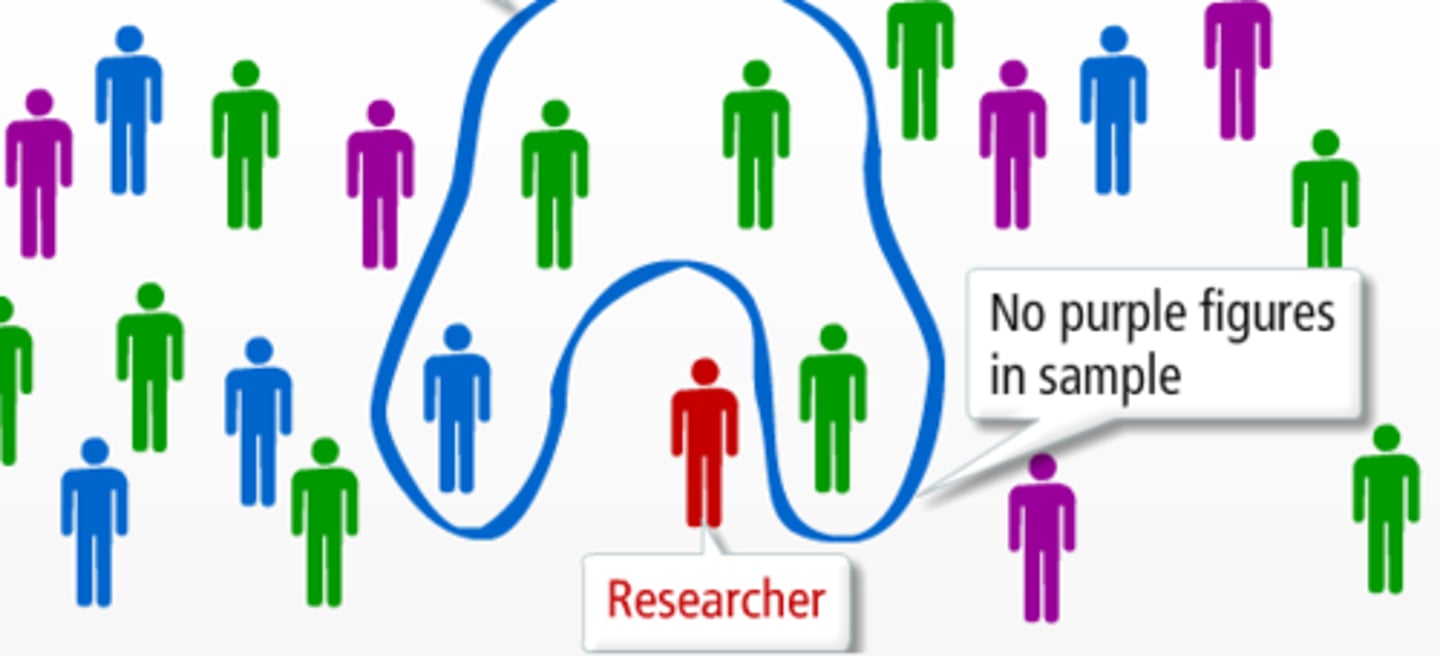
Purposive Sampling
a biased sampling technique in which only certain kinds of people are included in a sample
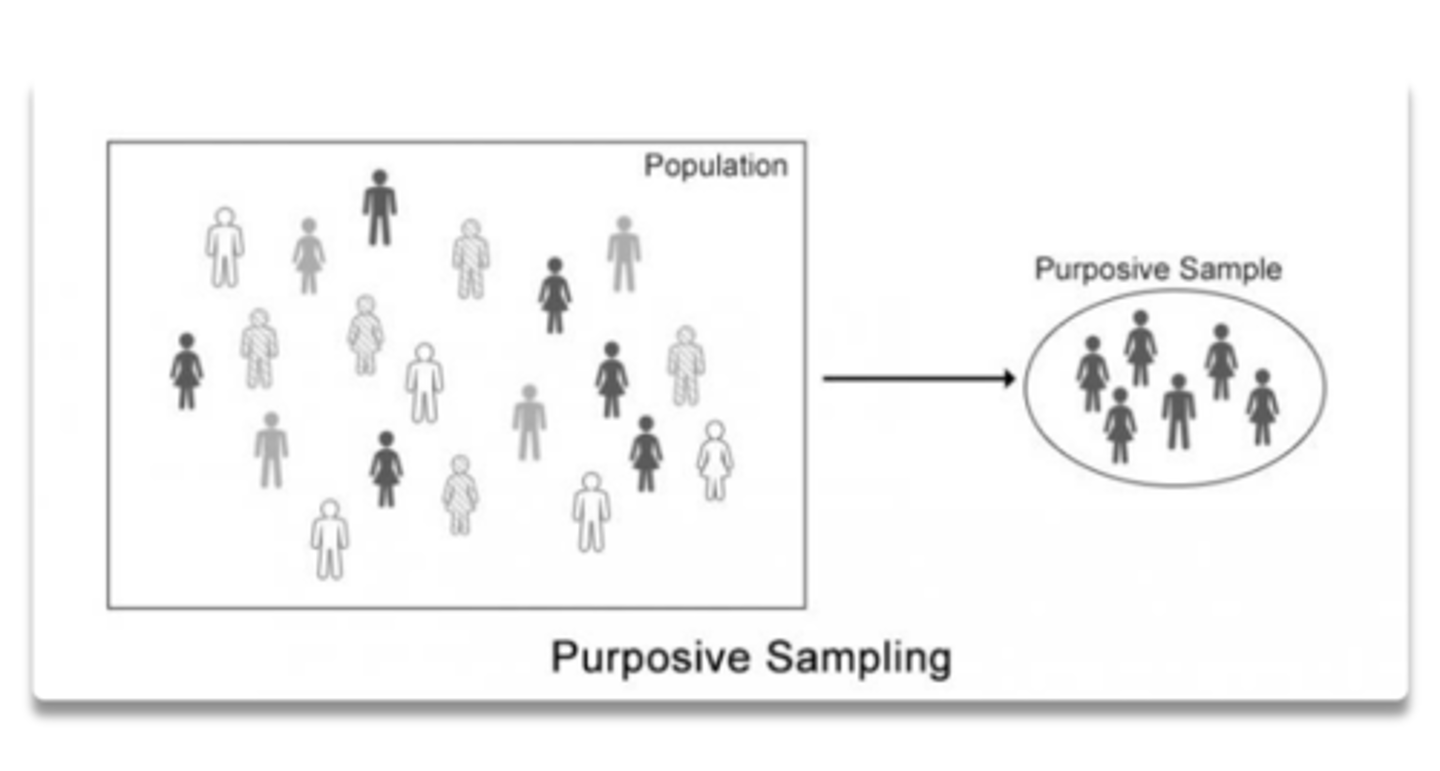
Snowball Sampling
participants are asked to recommend a few acquaintances for the study

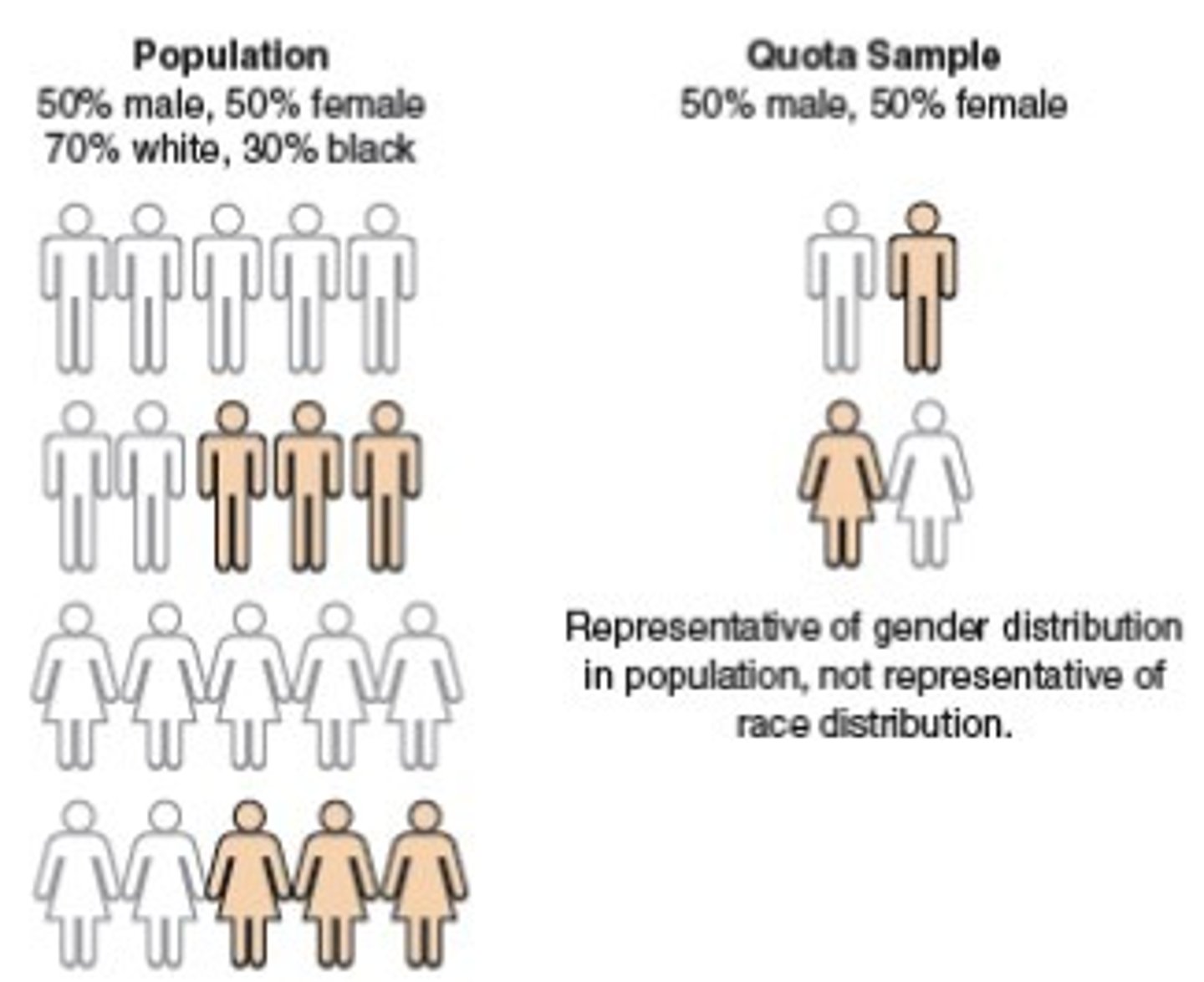
Quota Sampling
An interviewer or researcher selects a sample that reflects the characteristics of the whole population
Qualitative Sampling Technique
- purposive sampling
- in-depth interview
Quantitative Sampling Technique
- probability sampling
- survey questionnaire
Experimental Sampling Technique
- observation
- quantitative
- variables
Systematic
methodical
Empirical
based on observation or experiment
Logical
set of knowledge
Cyclical
starts with the problem and ends with the problem
Replicable
repeatable