English Rhetoric Test
1/39
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Rhetoric
the faculty of finding all the available means of persuasion in a particular case
Who is Aristotle?
the father of rhetoric
Exigence
problem, incident, or situation causing the writer to write the piece
How is the rhetorical triangle labeled?
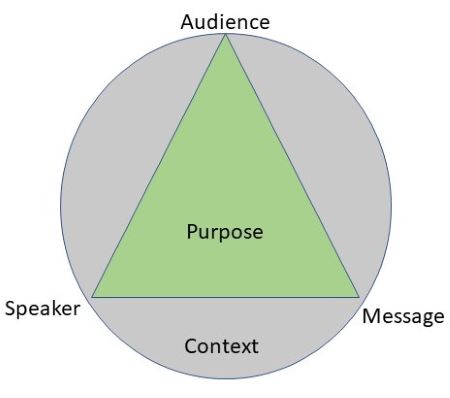
What are the four purposes in writing?
Persuasive, Informative, Expressive, Literary
What should you consider in a rhetorical situation?
Your audience
What kinds of responses might your audience have?
Immediate response, or intermediate response
What do speakers use to find their attitude toward a subject?
Thoughts and personal experiences
Subject/message
The writer/speaker evaluates what they already and needs to know, investigates perspectives, and determines kinds of evidence or proofs that seem most useful
Audience
Speculating about the reader’s expectations, knowledge, and disposition with regard to the subject writers explore
Speaker
Writers use who they are, what they know and feel, and what they’ve seen and done to find their attitudes toward a subject and their understanding of a reader
Voice or persona
The character the speaker creates as they write
Logos
An appeal to reason or logic; a statistic or fact
Logos strategies
Analogy, cause/effect, comparison, cites statistics facts hard evidence, cites authority, established precedent
Ethos
An appeal to ethics or ones character; a credible expert on the topic
Pathos
An appeal to emotions; a happy, funny, or sad approach
Pathos strategies
Sensory description, adjectives and adverbs that label something as good or bad, objects of emotion
Context
The situation in which writing and reading occurs
Purpose
The reason for writing or speaking (to inform, persuade, entertain)
Circular reasoning
When a speaker begins their debate with the point they’re trying to prove (I like chocolate because its my fav and chocolate is my fav cuz I like it)
Cherry picking
when a speaker only chooses the evidence that backs up their argument, while ignoring the other side (participants in workout program get really positive results cause only ppl with positive results responded)
Ad Hominem
Against the man!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! A claim is rejected on the basis of some irrelevant fact about the author of the argument (Sophie: we should review these data sets to make sure we did them right. Mckenna: ofc you suggest that since you’re a bit slow when it comes to math)
Straw man
When a person simply ignores a person’s actual position and uses a distorted exaggerated version (Ava: I think we should hire something to redesign our website. Briana: you’re saying we should throw our money away instead of building up our company products?)
Appeal to Common Practice
Most people doing something is used as evidence to support something (Sophia: the majority of people believe advertisers should spend more money on billboards, so billboards are objectively the best form of advertisement)
begging the question
X is true. the evidence for this claim is that x is true.(god must exist because the Bible says so because the Bible was written by god)
slippery slope
A person asserts that some event will inevitably follow from another (mckenna: we have to stop the tuition increase! before you know it they’ll be charging $40k a semester!)
false dilemma
reducing a complex issue down to one of two choices-either/or argument. (Briana: either 1+1=4 or 1+1=12. 1+1+4 is not true so 1+1=12.)
Red herring
an irrelevent topic is presented in order to divert attention from og issue (reporter: reports of a massive leak! executive: well we invested billions in clean energy)
Post Hoc Ergo propter hoc
when it is concluded that one event causes another simply because the proposed cause occurred before the proposed effect (Carly is scratched by a cat while visiting her friend and was diagnosed with autism two days later, the scratch must have caused it)
hasty generalization
when a person draws a conclusion about a population based on a population that isn’t large enough (Ariana grande is a stuck up arrogant celebrity! they all must be that way…)
appeal to authority
when the person in question is not a legitimate authority on the subject (cigarettes filter smoke! as your dentist I recommend these)
Diction
A speaker’s choice of words
Sophisticated
Highly educated or refined
formal
strangers, notables, pros
informal,
friends and colleagues
colloquial
family and close friends
slang
close friends
nominalization
the process that changes a verb into its noun form
showy vocab
be concise and don’t try to show off the words you know
Syntax
the arrangement of words into phrases, clauses, and sentences, this includes word order, length and sentence structures, schemes