AP Psych U2P2 (2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8)
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Encoding
process of transforming information into a form that can be stored and retrieved by the brain
Mnemonic Devices
memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices
ex: acronyms, rhymes, story mnemonics
Method of Loci
Imagine placing items you need to remember in specific locations in a familiar place. To recall the items, mentally walk through the place to visualize or “see” the items in their locations.
Chunking-Grouping
breaking down information into smaller, manageable chunks (usually to be stored more efficiently in short-term memory)
Hierarchies-Grouping
Concepts/information are organized in levels of importance or inclusivity. This helps organize information and understanding relationships between different concepts and how they fit into a larger framework.
Spacing Effect
the tendency for information to be retained better when rehearsal is distributed over time
Massed Practice
cramming information into a single, long study session
Distributed Practice
spacing out study sessions over a longer period of time
Serial Position Effect
the tendency to remember information presented at the beginning and end of a list better than the information in the middle
serial = cereal: top is crunchy (yum), bottom is soggy (gross), middle is forgettable
Primacy Effect
The tendency to remember information presented at the beginning of a list
think primary! primary school teacher primary colors early in your life and you remember them well
Recency Effect
The tendency to remember information presented at the end of a list (most recently)
Storage
the process of retaining coded information over time
Sensory Memory
the initial stage of a memory that briefly stores sensory information
Short-Term Memory
memory that holds a limited amount of information for a short period of time
Working-Memory
short term memory that actively processes information, holds 7 ± 2 items at once, and acts as a mental work space
Long-Term Memory
memory that stores information for an extended period
Maintenance Rehearsal
repeating information over-and-over to keep information in short-term memory
think of maintaining a garden, you must keep cutting the bushes for it to hold its shape
Elaborative Rehearsal
the process of connecting new information to existing knowledge
when you elaborate on something, you add additional knowledge to the topic at hand
Memory Retention
the ability to store and recall previously learned information or experiences; it involves holding on to information over time
Autobiographical Memory
memory for personal experiences; basically the same as episodic memory
what do you need to know when you’re writing an autobiography?
Retrograde Amnesia
The inability to remember events that occurred before the onset of amnesia
(cant remember OLD memories)
Anterograde Amnesia
The inability to form new memories after the onset of amnesia
(can’t remember NEW memories)
Physical Impairment
Damage to the brain or nervous system can impair memory
Developmental Limitations
children and older adults may have difficulty forming and retrieving memories
Alzheimer’s Disease
progressive brain disorder that causes memory loss and cognitive decline
ex: many people with this problem often struggle to remember names, dates, and recent events
Infantile Amnesia
Inability to remember events from early childhood
(young and dumb)
Retrieval
The process of accessing and bringing into consciousness the information stored in memory when its needed
Recall
ability to retrieve information from memory without any cues
Recognition
ability to identify previously learned information when it is presented
Retrieval Cues
stimuli that help you retrieve a certain memory or piece of information from your long-term memory
Context-Dependent Memory
remembering information better when in the same context or environment where it was learned
Mood-Congruent Memory
the tendency to recall information that is consistent with one’s current mood
State-Dependent Memory
remembering information better when in the same physiological or psychological state as when the information learned
ex: drinking coffee while studying and then drinking coffee before taking a test
Testing Effect
enhanced memory retention through repeated testing or practiced retrieval
Metacognition
awareness and understanding of one’s own thought processes
ex: recognizing when you don’t understand a concept, using effective study strategies
Forgetting Curve
This explains how quickly memory fades over time without reinforcement / OR / A graph depicting the decline of memory retention over time
Ex: forgetting information learned for a test immediately after taking it
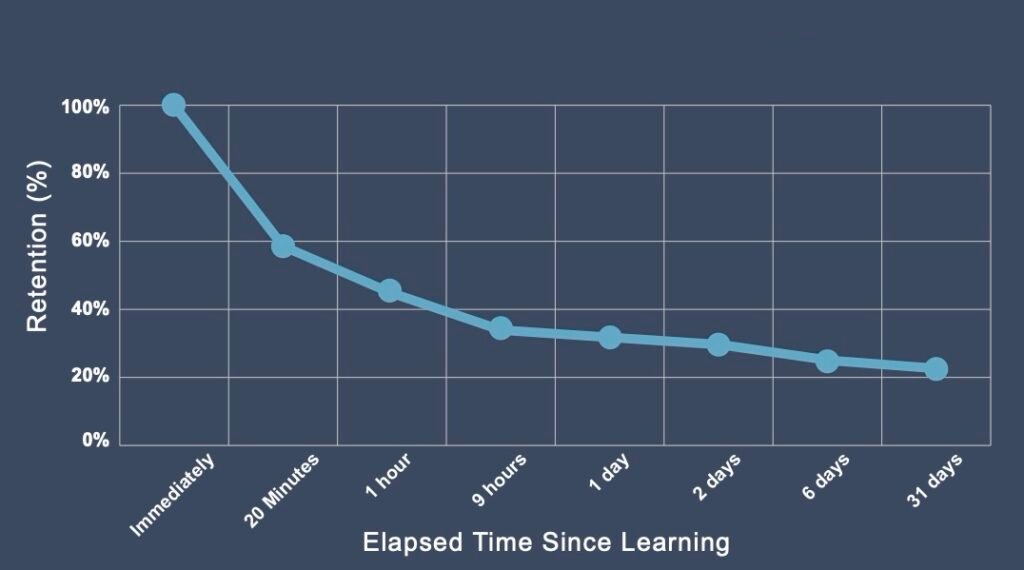
Encoding Failure
It is the inability to effectively store or retrieve information in long-term memory due to a failure in the initial encoding process. It occurs when information is not properly transferred from short to long term memory.
Proactive Interference
tendency of previously learned information to interfere with the learning of new information
example: calling your current gf by your ex’s name (pro move)
Retroactive Interference
tendency of newly learned information to interfere with the retrieval of previously learned information (old memories are messed with bc of new knowledge)
example: forgetting your old street address after moving cities
Tip-of-the-Tongue Phenomenon
temporary inability to retrieve specific information from memory, often accompanied by a feeling of knowing it
Repression (psychodynamic)
unconscious process that involves pushing anxiety-provoking thoughts and memories out of conscious awareness
ex: forgetting a traumatic childhood memory
Misinformation Effect
tendency for false or misleading information presented after an event to alter one’s memory of the event
ex: a witness’s memory of a crime being influenced by leasing questions
Source Amnesia
inability to remember the source of a memory while retaining the memory itself
ex: confusing a dream for a real event
Constructive Memory
process of reconstructing memories, often influenced by person beliefs, biases, and expectations
ex: distorting memories to fit a narrative
Memory Consolidation
process of stabilizing a memory trace after initial acquisition AND process by which short-term memories are transformed into long-term memories during sleep or rest periods (physical process)
exs: during sleep and strengthening though repetition or review
Imagination Inflation
tendency for repeatedly imagining an event to increase the likelihood of falsely believing that the event actually occured
Intelligence
the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
g (general intelligence)
a general mental ability that influences performance on a variety of cognitive tasks
Multiple Intelligence
Coined by Howard Gardner: refers to right relatively independent intelligences (varies from country to country)
linguistic, logical-mathematical, musical, bodily-kinesthetic, spatial, intERpersonal, intRApersonal, naturalistic
Intelligence Quotient (IQ)
score derived from intelligence tests that measures a person’s cognitive abilities relative to others of the same age
(mental age ÷ chronological age) × 100
Mental Age
an individual’s level of mental development relative to others
Chronological Age
the number of years a person has lived
Psychometric Principles
They are guidelines for constructing psychological tests that are reliable, valid, and standard. They ensure that a test measures what it is intended to measure.
Standardization
test that is administered and scored in a consistent manner
ex: SAT and ACT
Validity
a test that measures what it is intended to measure
ex: a driving test that accurately assesses driving skills
Construct Validity
psychological concept or trait that a test is designed to measure
ex: intelligence, personality
Predictive Validity
test’s ability to predict future performance or behavior
ex: SAT predicting college GPA
Reliability
Test that produces consistent results over time or across different administrations
ex: a bathroom scale consistently showing the same weight
Test-Retest Reliability
a measure of reliability that assesses the consistency of test scores over time
Split-Half Reliability
measure of reliability that assesses the consistency of scores on 2 halves of a test
(a good test would have consistent scores on both halves)
Stereotype Threat
The fear that one's behavior will confirm an existing stereotype of a group with which one identifies. This fear can actually lead to decreased performance.
Stereotype Lift
phenomenon where individuals benefit from positive stereotypes about their group
Flynn Effect
observation that IQ scores have been steadily rising over time
Achievement Tests
tests that measure a person’s knowledge or skill in a specific area
Aptitude Test
tests that assess a person’s potential for learning or acquiring new skills
ex: prospective career test that identify suitable occupations
Fixed Mindset
the belief that intelligence and abilities are fixed traits
Growth Mindset
the belief that intelligence and abilities can be developed through effort and practice