BIOC 202 CHO metabolism: PDC & Krebs cycle
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
PDC & Krebs cycle
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
what is the goal of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
to turn pyruvate into acetyl-CoA
Draw overall rxn catalyzed by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
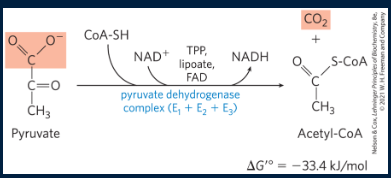
where does the conversion of pyruvate → acetyl-CoA occur?
mitochondrial matrix
what is the net reaction of PDC?
Pyruvate + NAD+ + CoA-SH → Acetyl-CoA + NADH + CO2 + H+
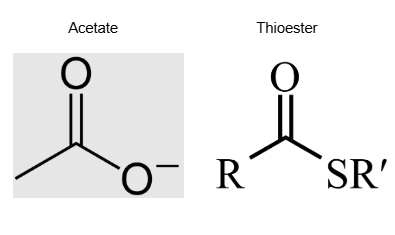
what does the conversion of pyruvate → acetyl-CoA involve? what is the intermediate?
involves decarboxylation/dehydration of pyruvate into an acetate in to form of a thioester (intermediate), followed by the formation of Acetyl-CoA
what enzymes is the PDC composed of?
E1: pyruvate dehydrogenase
E2: dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
E3: dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
what are the 5 cofactors involved in PDC? what are they bound to?
thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) - bound to E1
Lipoaminde - bound to E2
NAD+ - free
FAD - bound to E3
CoA-SH - free
what is CoEnzyme A (CoA, CoASH) composed of?
ADP
pantothenic acid (pantothenate) → Vit B5
Beta-mercaptoethylamine (where the reactive thiol group is)

what is CoA a carrier of?
acyl groups

what sort of bonds does CoA form? acetyl-CoA + H2O → (reversible) ?
high energy thioester bonds
acetyl-CoA + H2O → acetate + CoA-SH (delta G standard = 31 KJ/mol)
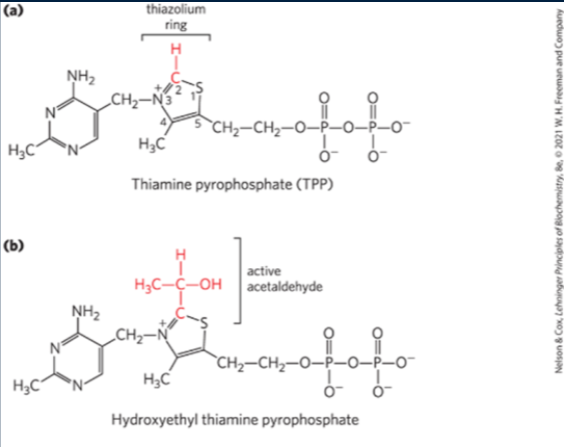
where is thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) derived from? what does it form? what does it carry? what does it promote?
Vitamin B1
reactive carbanion
aldehydes
decarboxylation
how is lipoamide formed?
Lipoic acid can be attached to lysine on E2 to form lipoamide

what does lipoic acid (lipoamide) do in PDC?
oxidizes aldehydes to acyl groups, resulting in the acyl group being bound to a disulfide group
Describe the steps of the PDC mechanism
Pyruvate enters E1 (pyruvate dehydrogenase), binds to TPP and becomes decarboxylated (forming CO2) to form the intermediate hydroxyethyl-TPP
oxidized lipoamide arm enters E1
The hydroxyethyl group is oxidized to an acetyl group and is now bound to the newly reduced lipoamide arm (which we now call a dihydrolipoyl group)
The reduced arm carrying the acetyl unit moves into E2 (dihydrolipoyl transacetylase) and the acetyl group is transferred to CoA, forming acetyl CoA. Acetyl-CoA can leave the enzyme
the reduced dihydrolipoyl lipoamide arm moves into E3 (dihyrolipoyl dehydrogenase) where it’s oxidized by FAD. FAD is reduced to FADH2
NAD+ enters E3 and reoxidizes FADH2 back to FAD. NAD+ is reduced to NADH, which leaves E3. Can then repeat another round of PDC

PDC regulation: high [acetyl-CoA]
allosterically inhibits E2
PDC regulation: high [NADH]
allosterically inhibits E3
where does the main control of PDC occur and how is it done?
occurs at E1, where phosphorylation of a serine by a kinase leads to inhibition of E1, thus the entire complex
(ATP → ADP) (PDC → PDC-P)
what is the name of the kinase that causes phosphorylation of PDC?
PDC associated kinase
what stimulates the kinase that slows down PDC?
acetyl-CoA
NADH
ATP
what inhibits the kinase that causes phosphorylation of PDC? What does this result in?
Pyruvate
NAD+
ADP
results in PDC gradually becoming active again
what enzyme dephosphorylates E1 in PDC? what does this do?
phosphatases
results in more activation (slowly dephosphorylates E1)
PDC-P → PDC
how can dephosphorylation of E1 in PDC be quicker?
cell signaling such as high calcium and insulin, activates the PDC associated phosphatase (PDCAP) which rapidly dephosphorylates E1, leading to rapid increase in PDC activity
what is the Krebs cycle also called?
citric acid cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA)
what is the importance of the Krebs cycle in the cell?
It oxidizes acetyl-CoA into CO2 and in the process, generates high energy e- (in the form of NADH and FADH2) and GTP. These e- are used in oxidative phosphorylation to generate ATP. Additionally, the Krebs cycle is also a source of many biological precursors
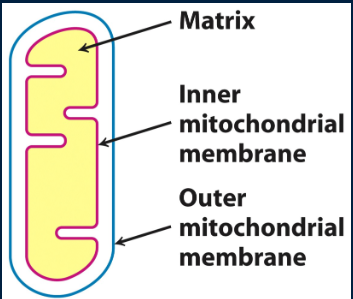
where in the cell does the Krebs cycle occur?
mitochondrial matrix
how many rxns in the Krebs cycle?
8
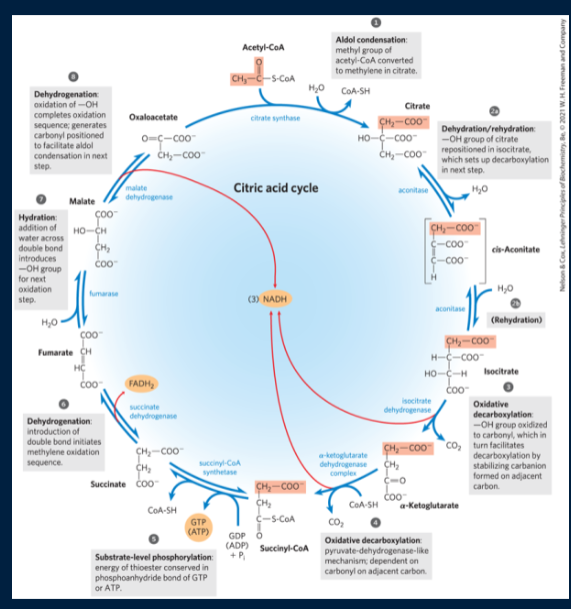
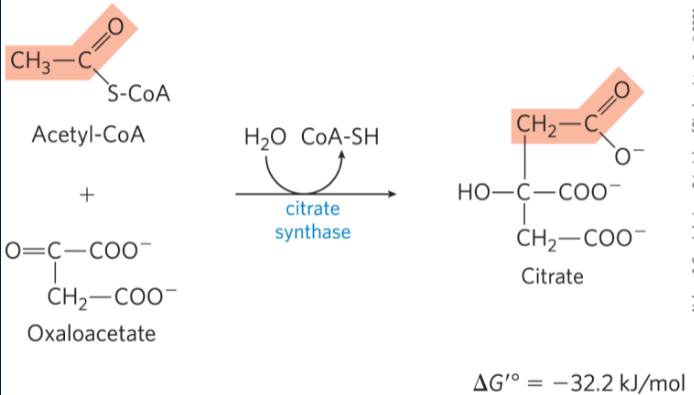
explain and draw rxn 1 of Krebs cycle
Citrate synthase forms citrate by binding oxaloacetate to acetyl-CoA (going from C4 to a C6) (only orange parts came from glucose). Irreversible rxn
what is rxn 2 in the Krebs cycle done thru (what mechanism)?
aldol condensation
hydrolysis of citryl CoA to citrate and CoA-SH. This drives the entire rxn forward
what is a synthase?
an enzyme specializing in catalysis of joining 2 units w/ out direct participation of ATP
what is synthetase?
an enzyme specializing in the catalysis of joining 2 units together with the help of ATP (or NTP)
explain + draw rxn 2 of Krebs cycle
aconitase converts citrate to isocitrate (OH group is moved). Citrate is dehydrated (removal of water) into cis-aconitate. Cis-aconitate is then hydrated (addition of water) into isocitrate

what cofactor helps aconitase in rxn 2 of Krebs cycle? what does it do?
iron-sulfur cluster (4Fe-4S). this cluster moves e- for this rxn?
in rxn 2 of Krebs cycle, where is the OH moved?
onto CH2 that came from oxaloacetate
delta G standard is positive during rxn 2 of Krebs cycle. How is the rxn driven?
driven by the delta G standard of rxns 1 & 3
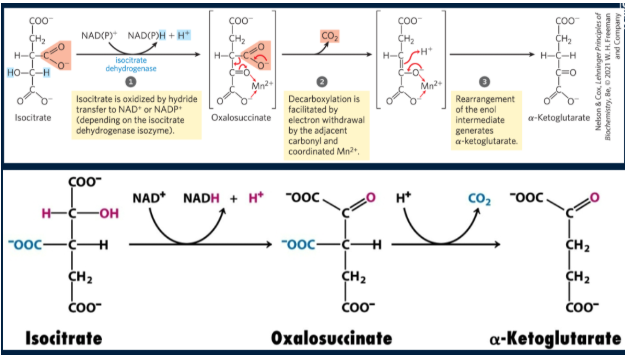
explain + draw rxn 3 of Krebs cycle
isocitrate is oxidized/decarboxylated to alpha-ketoglutarate by isocitrate dehydrogenase. NADH and CO2 are produced. First, isocitrate is oxidized to oxalosuccinate, generating NADH. Next, oxalosuccinate is decarboxylated to alpha-ketoglutarate (alpha-KG) spontaneously. Rxn is irreversible
CO2 lost did not originate from the acetyl-CoA that just entered the cycle
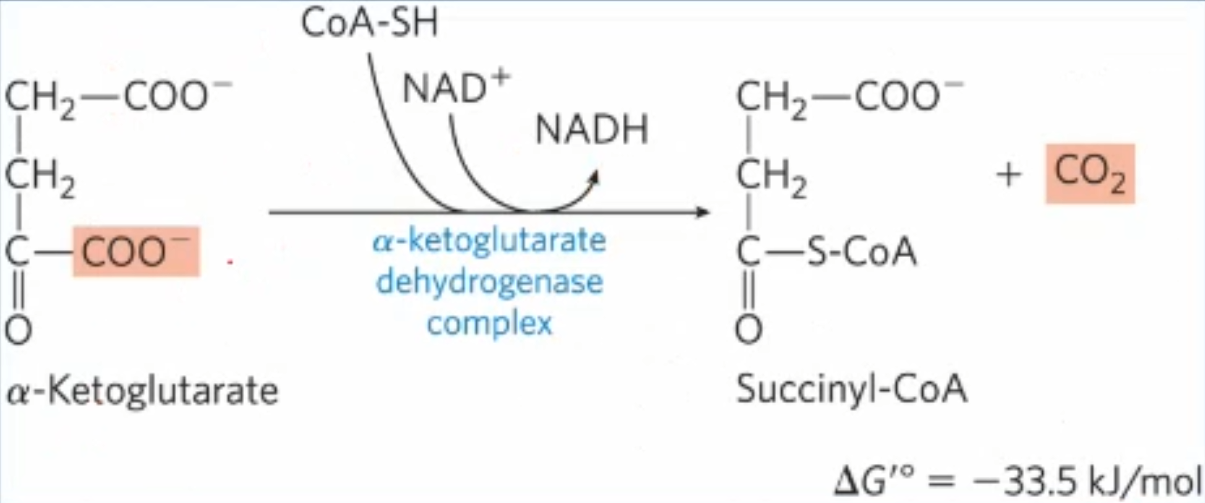
explain + draw rxn 4 of Krebs cycle
alpha-KG dehydrogenase complex (same method as PDC, same 5 cofactors, similar E1 & E2, identical E3)). Alpha-KG is first decarboxylated, then oxidized and lastly bound to CoA by the alpha-KG complex, generating succinyl-CoA, CO2, and NADH. Goes back to 4 carbons. Irreversible rxn
Explain + draw rxn 5 in Krebs cycle
Succinyl CoA synthetase converts succinyl CoA to succinate, generating GTP & CoASH
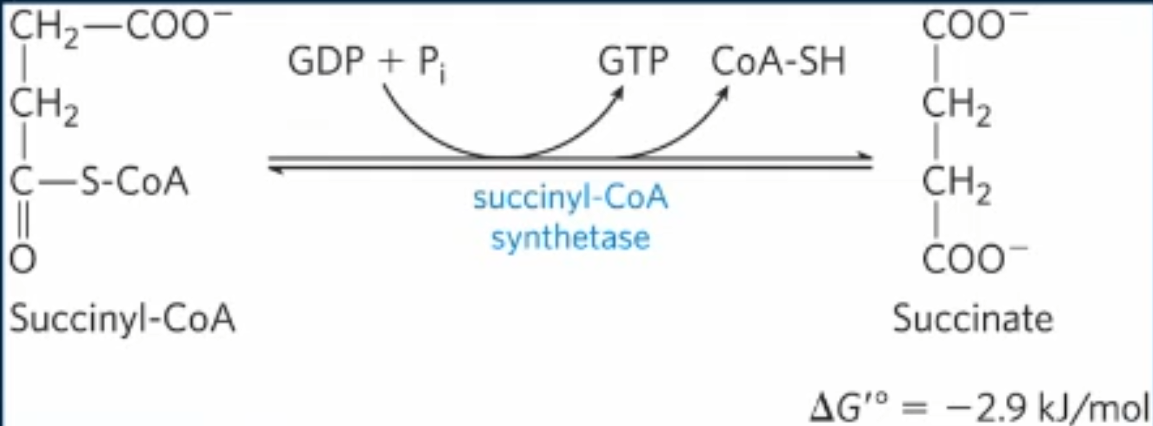
what is rxn 5 of Krebs cycle driven by?
negative delta G in cleavage of thioester bond
GTP + ATP → GDP + ATP
how can GTP be converted to ATP?
by a nucleoside diphosphate kinase
there are ____ of succinyl-CoA synthetase that use ___ to generate ____
there are isoforms of succinyl-CoA synthetase that use ADP to generate ATP
what do steps 6-8 in Krebs cycle end up forming? (regeneration of what?)
succinate → oxaloacetate
explain + draw rxn 6 of Krebs cycle
succinate dehydrogenase oxidizes succinate, generating FADH2 and fumarate. Free energy is not enough to reduce NAD+ but is sufficient for FAD. (make sure to draw fumarate in trans config)

what complex is succinate dehydrogenase a part of?
complex 2
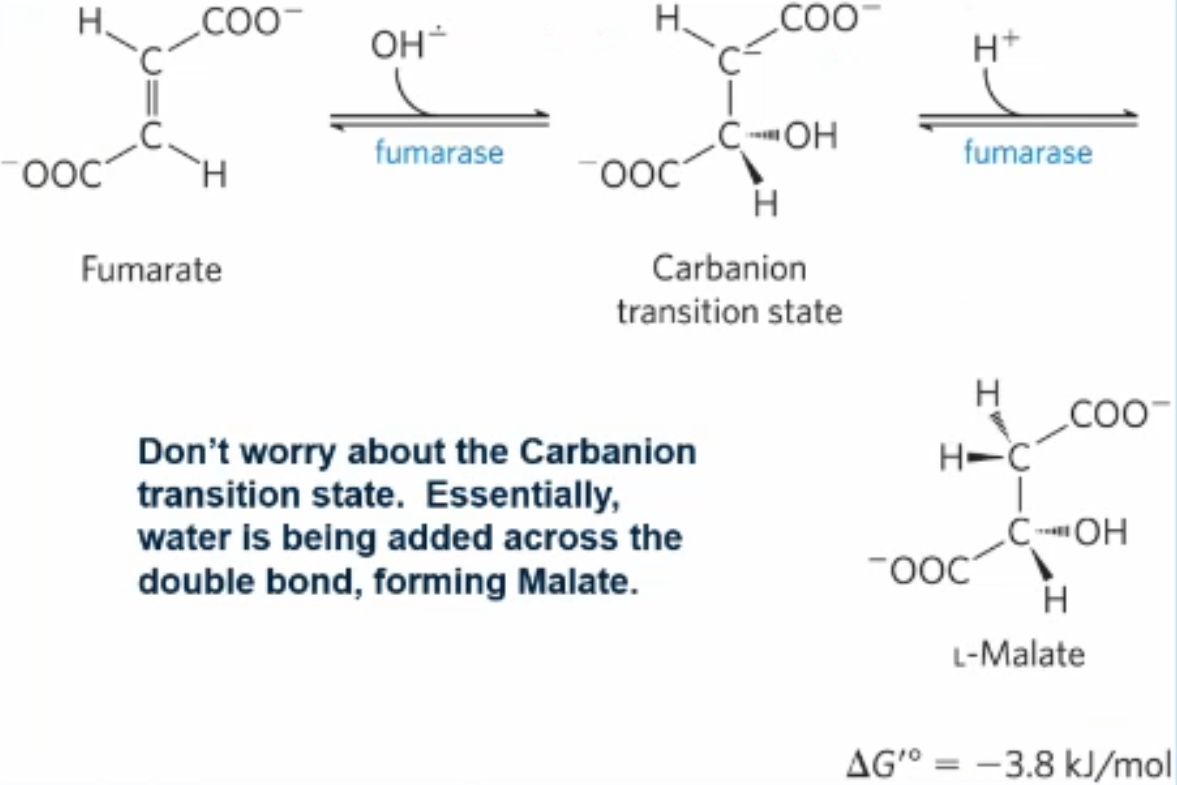
Explain + draw rxn 7 of Krebs cycle
fumarate adds water across the double bond of fumarate, forming L- malate (sterochem is important)
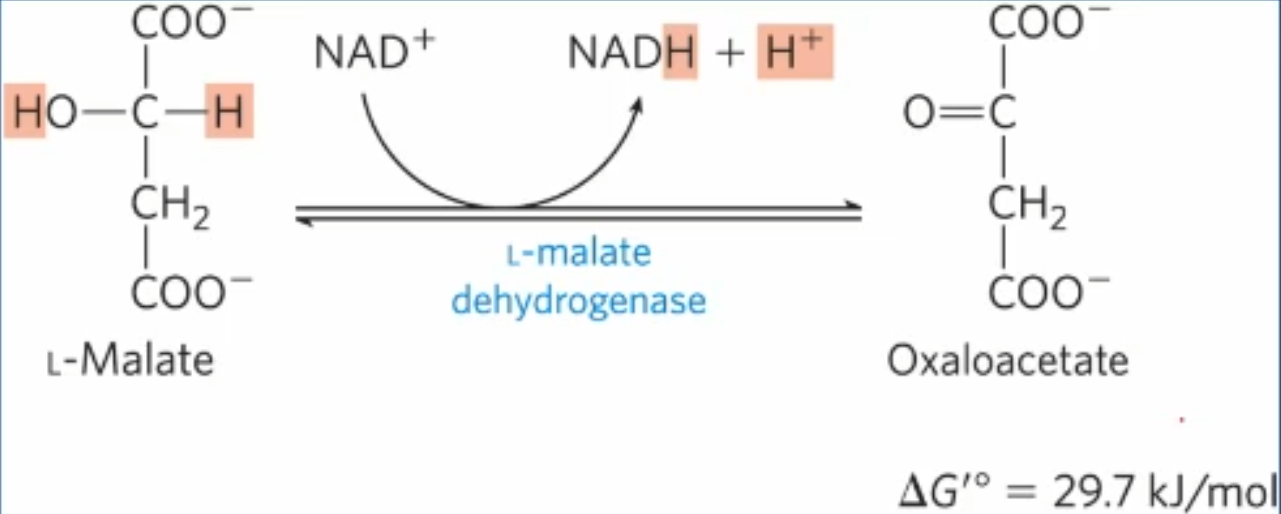
explain + draw rxn 8 of Krebs cycle
malate dehydrogenase oxidizes malate to oxaloacetate generating NADH
what is the net rxn of Krebs cycle?
acetyl-CoA + 3 NAD+ + FAD + GDP + Pi + 2H2O → 2CO2 + CoASH + 3 NADH + 3 H+ + FADH2 + GTP

Krebs cycle regulation: what inhibits isocitrate dehydrogenase?
NADH & ATP
Krebs cycle regulation: what inhibits alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase?
NADH, ATP, Succinyl CoA
Krebs cycle regulation: what inhibits citrate synthase (only in bacteria)
ATP