Section 2.5 The Structure of the Atom
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
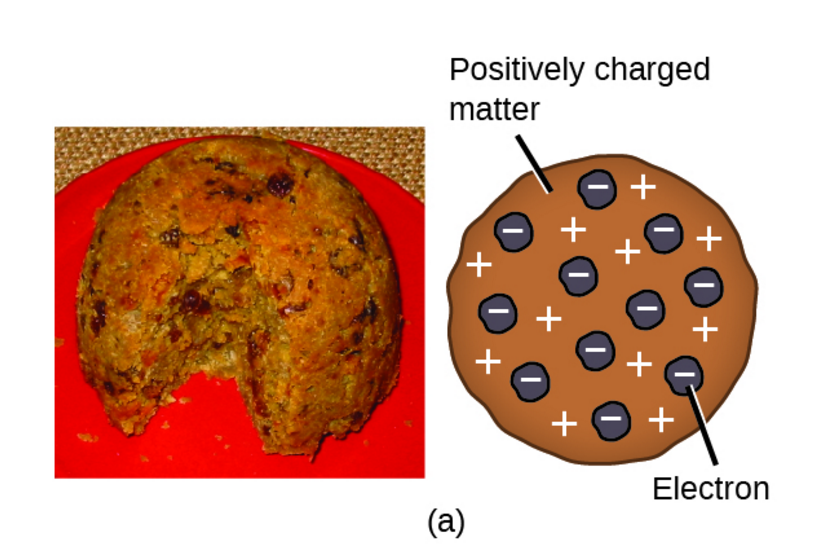
The Plum Pudding Model
(see image) J.J. Thomson proposed that the negatively charged electrons were small particles held within a positively charged sphere. The Plum Pudding model, suggested by Thomson. It’s like a blueberry muffin; the blueberries are the electrons, and the muffin is the positively charged sphere.
Radioactivity
the emission of small energetic particles from the core of certain unstable atoms. (discovered by Henri Becquel and Marieu Curie). This allowed researchers to experimentally probe the structure of an atom.
At the time, scientists had identified 3 different types of radioactivity
Alpha particles, Beta particles and Gamma Rays (see image)
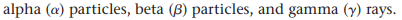
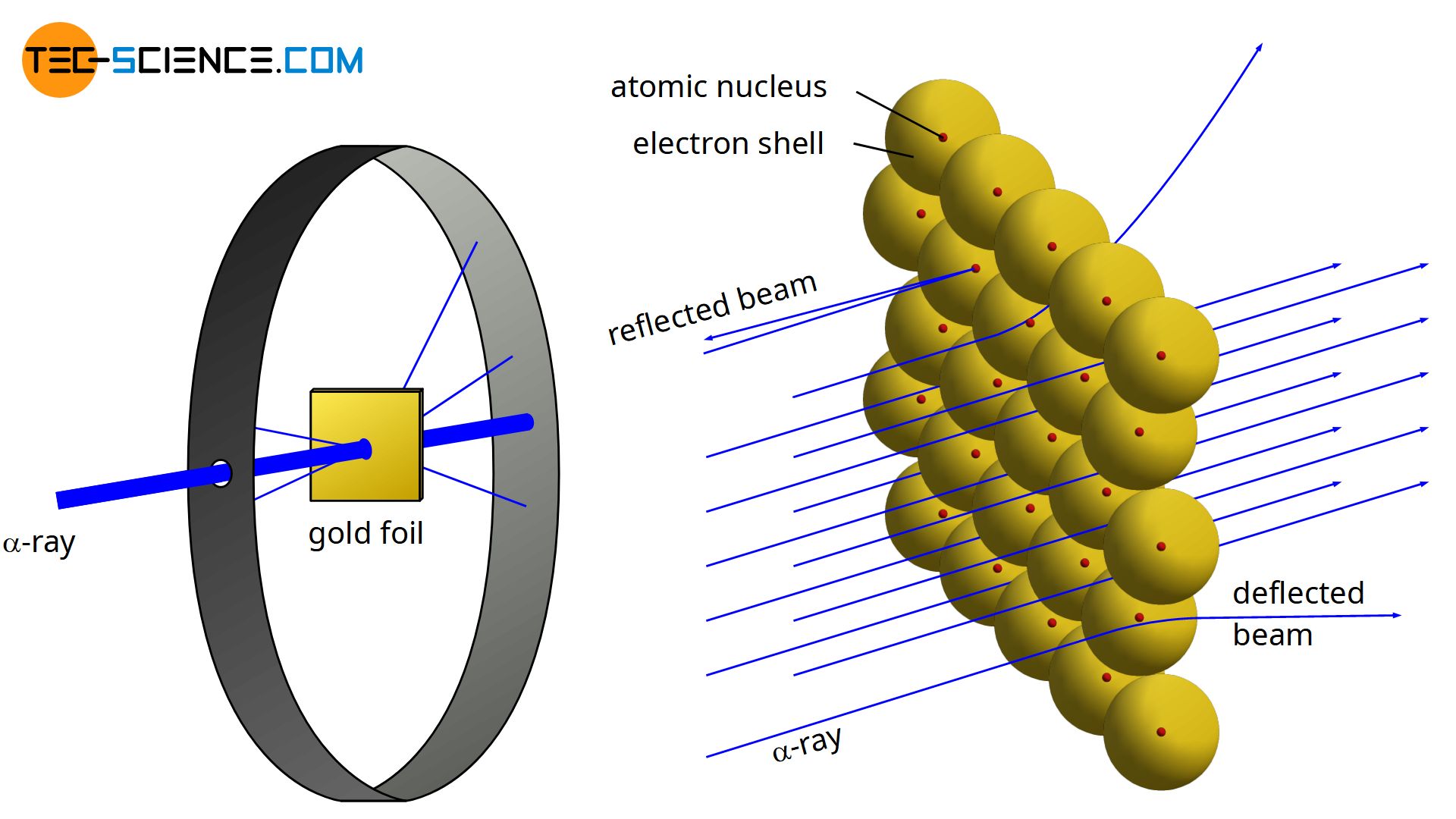
Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment
(see image) Rutherford’s gold foil experiment was done to find out what atoms are like on the inside.
What he did:
He fired tiny, positively charged particles (called alpha particles) at a very thin sheet of gold.
The gold foil was so thin it was only a few atoms thick.
What he expected (based on the plum pudding model):
He thought the particles would pass straight through, because atoms were believed to be solid all the way through.
What actually happened:
Most particles went straight through the gold.
Some were slightly deflected (bent)
A very few bounced straight back.
What this showed:
Atoms are mostly empty space (that’s why most particles passed through).
The positive charge and most of the mass are packed into a tiny, dense center called the nucleus.
Electrons are outside this nucleus.
Conclusion: Rutherford discovered that atoms are mostly empty space with a small, heavy, positively charged center.
Nuclear Theory
Proposed by Rutherford
Most of the atom’s mass and all of its positive charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus.
Most of the volume of the atom is empty space, throughout which tiny, negatively charged electrons are dispersed.
There are many negatively charged electrons outside the nucleus as there are positively charged particles (protons) within the nucleus, so the atom is electrically neutral.
Neutrons
neutral particles within the nucleus. The mass of a neutron is similar to that of a proton, but a neutron has no electrical charge.
An atom is like a…
cloud. Mostly empty space.
If matter really is mostly empty space, then why does it appear so solid?
Matter appears solid because the variation in its density is on such a small scale that our eyes cannot see it. EX: Matter looks solid because any tiny spaces or differences in how tightly packed it is are so small that our eyes can’t notice them. Even though there are tiny gaps between atoms or molecules, they’re way too small for us to see, so the material seems completely solid.