Rheumatology 1: Rheumatoid Arthritis and SLE
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
polyarthritis, >, IV, DRB, 1, 4, smoking
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Background
-Chronic, systemic disease characterized by inflammatory ____________, involving small and large joints, some other organ systems, and some constitutional features
-Epidemiology
Females _ males
Onset between 30-50 y/o
-Pathogenesis
Type __ reaction (T cell mediated)
-Genetics
Most associated with HLA ___ _ and _
-Environmental Trigger
Mostly unknown
__________ highly linked trigger to RA
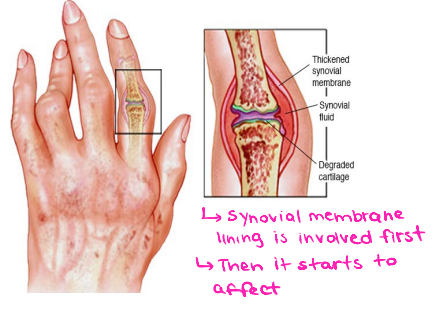
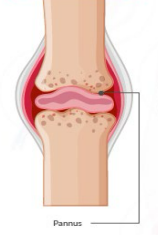
Pannus
A thickened, inflamed layer of synovial tissue that grows over and destroys articular cartilage and bone within a joint
synovitis, ankylosis, bony
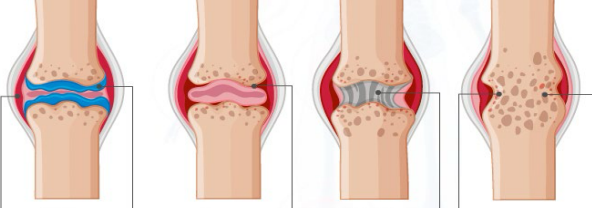
Stages of Rheumatoid Arthritis
____________ → synovial membrane inflamed and thickened, bones and cartilage gradually erode
Pannus formation → excessive cartilage loss, exposed and pitted bones
Fibrous ___________ → joint invaded by fibrous connective tissue
____ ankylosis → bones fused
symmetrical, gradual, MCP, PIP, DIP, pain, >, boggy
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Signs and Symptoms
-____________, polyarticular disease with ______ onset. Classically affects the ___, ___, MTP joints, and wrists (usually spares the ___ joints)
-Joint ____
-Joint stiffness → morning stiffness _ 30-60 minutes, improves with activity
-"_______” joint swelling (synovitis) → much more inflamed than in osteoarthritis
MCP, PIP, ulnar, swan neck, lateral, subluxation, extension, ulnar, ankles, 1, 2
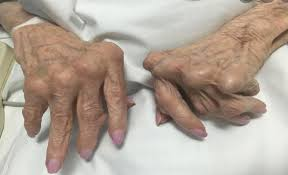
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Joints Affected
-Fingers
___ and ___ joints most common
MCP subluxation, ______ deviation, ____ ____ and Boutonniere deformities, and decreased grip
-Feet
MTP joints most common
_____ drift of toes, plantar ___________ of metatarsal heads
-Wrists
Loss of __________, volar subluxation, and _____ drift
-Elbows
-_______
-Knees
-C_ and C_ can also be affected, leading to life threatening subluxation
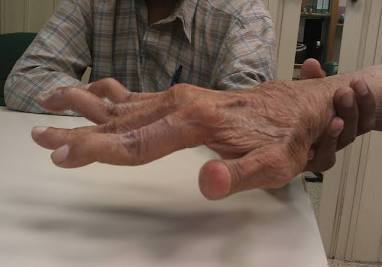
Swan Neck
What deformity is this?
-Associated with RA, characterized by the hyperextension of the PIP joint and flexion of the DIP joint
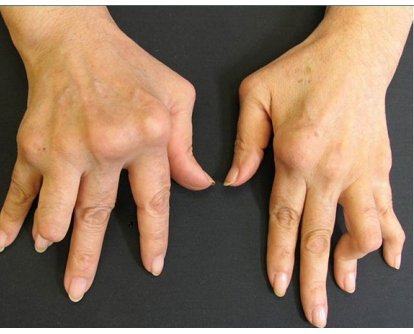
Boutonniere deformity
What deformity is this?
-Associated with RA, characterized by a flexed PIP joint and extended DIP joint, creating a “button hole” appearance
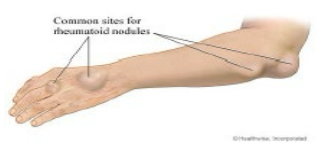
myalgia, fever, nodules, scleritis, splenomegaly
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Systemic Symptoms
-_________, fatigue, low grade _____, and weight loss
-Rheumatoid subcutaneous _______, lung disease, episcleritis/________, vasculitis, and Felty Syndrome
-Felty Syndrome = RA, ___________, and neutropenia
Anti-CCP
What lab test is the most sensitive/specific for RA?
elevated, RF, anemia, inflammatory
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Diagnosis
-ESR and CRP → __________
Assess disease activity/severity, monitor therapeutic response
-__ and anti-CCP
More sensitive/specific for RA
About 20% are seronegative
-ANA → often positive
-CBC w/ diff
_______ and thrombocytopenia (chronic inflammation)
-Synovial fluid analysis
____________ → 10,000 WBC, mostly PMNs
6/10
In order to be diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, a patient must meet _/__ of the diagnostic criteria
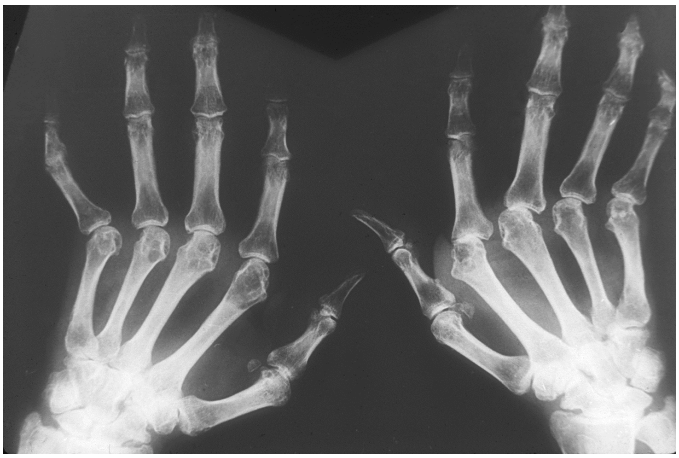
osteopenia, narrowing, erosions, subluxation
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Imaging (X-Ray)
-Could show periarticular ___________ (bone loss), joint space ___________, bone ________, and joint deformities (like ___________)
smoking, DMARD, non-biologic, methotrexate, biologic, JAK
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Treatment
-Treatment
_______ cessation
Control synovitis and prevent joint injury/damage
Refer to rheumatology
Start on ______ ASAP
-Medications
NSAID or glucocorticoids → ASA, COX-1 and 2, prednisone. Use these as a bridge therapy until DMARD starts working
___-_______ DMARD is the gold standard → ___________ is the most common. Could also use leflunomide, hydroxychloroquine, and sulfasalazine
_______ DMARD → TNF blocker (etanercept/infliximab) or IL-6 receptor antagonists (tocilizumab)
Target synthetic DMARD → ___ inhibitor (tofacitinib)
hepatic, Hep B, C, PPD, immunizations, contraceptives
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Health Maintenance
-Get baseline CBC, _______ function, and BMP
-Screen for ___ _ and _
-___ before starting biologic
-Continue with routine ______________
-Varicella zoster vaccine before starting biologic or tofacitinib in those > 50
-_____________ in child bearing ages
autoantibodies, dermatologic, failure, black, >, hormonal, UV light
Systemic Lupus Erythematous: Background
-Chronic, multisystem, inflammatory disease with various _____________
-Ranges from mild _________ and joint symptoms to life threatening internal organ ________ and cytopenias
-Periods of active disease and remission
-Epidemiology
Highest among Asian, _____, and Hispanic patients
F _ M (8:1)
Peak age at diagnosis is 20-40
-Etiology
Mostly unknown
Genetic
_________ (contraceptives, pregnancy)
Immune (Type III reaction or abnormalities in complement)
Environmental (infection, __ _____, smoking)
autoantibodies, DNA, histones, immune complex, glomerular, renal, GI
SLE: Pathogenesis
-Variety of _____________ against → nucleic acids, erythrocytes, coagulation proteins, phospholipids, lymphocytes, platelets, etc.
Most characteristic are ___, ________, and ribonucleoproteins
-_______ ________ formation and deposition into tissues
Damage and inflammation of __________ basement membrane, _____ tubular basement membrane (lupus nephritis), brain, heart, spleen, lung, __ tract, skin, and peritoneum
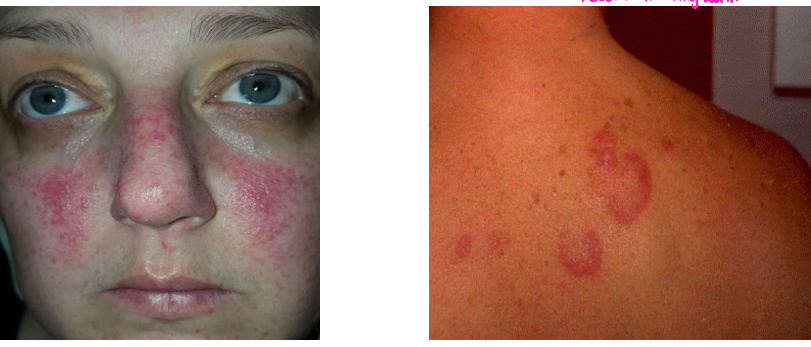
fever, non-erosive, Malar, rash, photosensitivity, ulcers
SLE: Clinical Manifestations
-Constitutional → _____, fatigue, weight loss
-MSK → ___-_______ arthritis, arthralgias, myositis
-Dermatologic → _____ (butterfly) ____, discoid lesions, _____________, oral/nasal ______ (painless), alopecia, urticaria
proteinuria, anemia, pericarditis, pleuritis, psychosis
SLE: Clinical Manifestations, cont.
-Renal → cellular casts, glomerulonephritis, _________, membranous nephropathy, nephrotic syndrome
-Hematologic → hemolytic ______, leukopenia, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia
-Cardiovascular → ___________, vasculitis
-Pulmonary → ________, interstitial lung disease, PE, pulmonary hemorrhage
-Neurologic → __________, seizures, cerebritis, neuropathy
nephritis, scarring, destruction, deposition, biopsy, seizures, hemoptysis, failure, damage
SLE: Critical Clinical Manifestations
-Lupus _________
Spectrum of glomerulopathies, ranging from focal _________ to diffuse ___________ with inflammation and immune complex ___________
Renal biopsy can be helpful with diagnosis, but use UA for screening
-Lupus Cerebritis
Include psychosis, _________, coma and other more subtle cognitive and psych manifestations
-Pulmonary Hemorrhage
Can cause significant ____________ and respiratory ________
-Vasculitis of Major Organs
Organ ______ and failure
Antiphospholipid, thromboses, abortions
SLE: Antiphospholipid Antibodies
-Detected in about 40% of SLE patients
-Can lead to ______________ syndrome
Recurrent arterial/venous _____________, thrombocytopenia, and spontaneous __________
flares, abortions, premature, complications
SLE and Pregnancy
-Severe disease ______ → be sure to educate your patients
-High rates of spontaneous ___________
-High rates of ________ births
-Pregnancy ______________ d/t organ damage from SLE and/or medications for SLE
Procainamide, Hydralazine, reversible
Drug-Induced Lupus
-Most common drugs implicated are __________ and ___________
-Milder form of SLE → rarely any CNS or renal involvement
-Can have + SLE labs
-___________ with discontinuing the drug
Anti-dsDNA, Anti-Sm
What lab tests are the most specific and pathognomonic for SLE?
ANA
What lab test is the screening lab of choice in SLE?
clinical, renal, hematuria, ANA, antiphospholipid, urine
SLE: Diagnosis
-________ diagnosis → ask and assess for clinical manifestations
-Routine Labs
CBC w/ diff, showing leukopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia
BUN/creatinine to look for _____ dysfunction
UA/microscopic urine to monitor for __________, proteinuria, and cellular casts
-More Specific Labs
___ → sensitive but not specific, screening lab of choice
Anti-dsDNA and anti-Sm antibodies → specific but not as sensitive
-Other Common Labs
____________ antibodies
C3 and C4 complement levels
ESR/CRP
_____ protein to creatinine ratio
4, rash, pericarditis, anemia, proteinuria, anti-dsDNA, psychosis
SLE: Classification Criteria (must meet _ of the following)
-____ → malar, discoid, oral ulcers, photosensitivity (each count as 1)
-Arthritis
-Serositis → ____________, pleuritis, peritonitis
-Hematologic → hemolytic ______, leukopenia, leukocytosis, thrombocytopenia
-Renal disease → glomerulonephritis, __________
-Anti-nuclear antibody (ANA)
-Immunologic disorders → ____-_____, anti-Sm, false positive syphilis tests
-Neurologic → seizures or __________ without another cause
inflammation, suppressing, rheumatologist, sun, HTN
SLE: Treatment Goals and Non-Pharmacologic Interventions
-Treatment
Aimed at reducing ____________, ___________ immune system, and monitoring for serious manifestations
Refer to _____________
-Non-Pharmacologic
___ protection
Smoking cessation
Immunizations
Good control of comorbid conditions like ___ and DM
hydroxychloroquine, steroid, prednisone, high, immunosuppressive
SLE: Pharmacological Treatment
-Mild Lupus → anti-malarial w/ or w/o NSAIDs and/or short term low dose steroids
Anti-malarials = ______________ or chloroquine
Low dose _______ = < 7.5 mg prednisone/day
-Moderate Lupus (significant sx but non-organ threatening)
Hydroxychloroquine + short term __________ daily
Often require steroid sparing immunosuppressive agents like azathioprine or methotrexate
-Sever Lupus (life or organ threatening)
Initial intensive = ____ dose steroids alone or in combo with other ______________ agents
High dose steroid = IV “pulses” or oral methylprednisolone
Other immunosuppressive agents = mycophenolate, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, Rituximab
Followed by less intensive and less toxic maintenance therapy