Wave and light
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
7 Quantities that defines a wave
Amplitude, wavelength, frequency, period, wave speed, crest, trough
Amplitude
Height of the wave; measures energy
Wavelength
Distance between two crests or compressions
Frequency
Number of waves passing a point per second
Period (T)
Time for one full wave to pass a point.
Wave speed (v)
How fast the wave travels
Crest
Highest point of a transverse wave
Trough
Lowest point of a transverse wave
Amplitude (Symbol, unit and unit symbol)
A, meters, m
Wavelength (Symbol, unit and unit symbol)
Lambda, meters, m
Frequency (Symbol, unit and unit symbol)
f, hertz, Hz
Period (Symbol, unit and unit symbol)
T, seconds, s
transverse wave and example
Particles move up and down at right angles to the direction of the wave. Light waves, water waves.
longitudinal wave and example
Particles move back and forth parallel to the direction of the wave. Sound waves.
What type of wave is light?
Transverse, it travels as electric and magnetic fields; does not need a medium.
What type of wave is sound?
Longitudinal caused by vibrations; needs a medium to travel.
What is a mechanical wave?
A wave that transfers energy through vibrations of particles, it requires a medium to move.
Why can’t sound travel in space?
There’s no particles for vibrations to pass through.
In which state do waves travel fastest?
Solids because particles are closely packed, so vibrations transfer energy more quickly.
What does convergent mean?
Rays or waves come together
In which state do waves travel slowest?
gases as particles are far apart
What does divergent mean?
Rays or waves spread apart
What is the focal point?
The point where light rays meet after reflection or refraction.
How does light travel?
Light always travels in a straight line through a uniform medium
What is the law of reflection?
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
Incident ray = incoming light
Reflected ray = outgoing light
Normal line = 90 degrees to the surface
How do you measure angles of incidence and reflection?
Draw a normal line at 90 degrees to the mirror. Measure angle of incidence between the incident ray and normal. Measure angle of reflection between the reflected ray and normal.
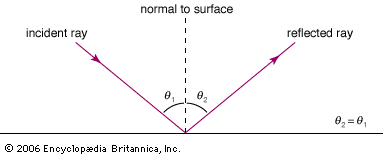
What happens when light hits a flat mirror?
Light reflects evenly, the image appears upright, same size and laterally inverted
What happens when light passes through a prism?
Light refracts and splits into colours, known as dispersion
Convex Mirror
It curves outward and makes light rays diverge, producing a smaller, upright, and virtual image
Concave Mirror
It curves inwards and makes light rays converge to a focal point, forming images that can be larger or smaller depending on distance
Convex Lens
It is thinner in the middle and makes light rays diverge, forming a smaller, upright image such as lenses for short-sighted eyes.