Hemolytic Disease of the Fetus and Newborn (HDFN)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
HDFN
AKA Erythroblastosis Fetalis
Fetal or newborn RBCS destroyed by maternal IgG
Maternal Antibodies:
Cross placenta
Sensitize fetal RBCs
Shorten RBC survival
HDFN etiology: when and how does fetomaternal hemorrhage occur?
may occur when fetal cells escape into the maternal circulation
Delivery
Amniocentesis
Abortion
Cordocentesis
Ectopic pregnancy
Abdominal trauma
HDFN Etiology: How does Antibody Production and RBC Destruction occur?
Fetal RBC antigens (mother lacks) stimulate maternal antibody production → antibodies bind to fetal antigens → RBC destruction
HDFN causes BEFORE birth
Indirect bilirubin conjugated by the maternal liver
As RBC destruction continues, fetal
erythropoiesis increases
Erythroblasts release →
erythroblastosis fetalis
Edema occurs (hydrops fetalis)
Cardiac failure may result
HDFN etiology: after birth
Newborn cannot conjugate bilirubin
jaundice and possible kernicterus
Three important factors of HDFN
RBC antibody must be IgG
Only IgG crosses the placenta
Fetus possess an antigen that mother lacks
Gene inherited from the father
Antigen present at birth
Main Types of HDFN
Rh (D antigen)
ABO
Other Antibodies
Rh HDFN
Most severe
D-negative womensensitized during the first pregnancy with a D-positive baby
Subsequent pregnancies are affected
Positive DAT
Jaundice and/or anemia may occur
Exchange transfusion may be necessary
Treatment: Rh immune globulin (RhIG)
ABO HDFN
Most common type of HDFN (1 in 150 births)
Mom = group O; baby = group A or B
First pregnancy may be affected
Mild symptoms possibly due to
A or B substances in tissue = neutralize antibodies
Fetal/infant RBCs = poorly developed
Fetal/infant RBC sites = reduced
Some jaundice may occur
Phototherapy treatment
Other Types of HDFN
Any IgG can cause HDFN
Common causes: Anti-c and anti-K antibodies
Less Common: Kell Abs, Kidd Abs, Duffy, S, and U antigens
Agglutination with paternal cells and maternal serum = a low-frequency antigen
Prenatal Testing Purposes
Identifies D-negative women that have RhIG
Identifies women with antibodies capable of causing HDFN
Prenatal Testing Identify Women at Risk of HDFN
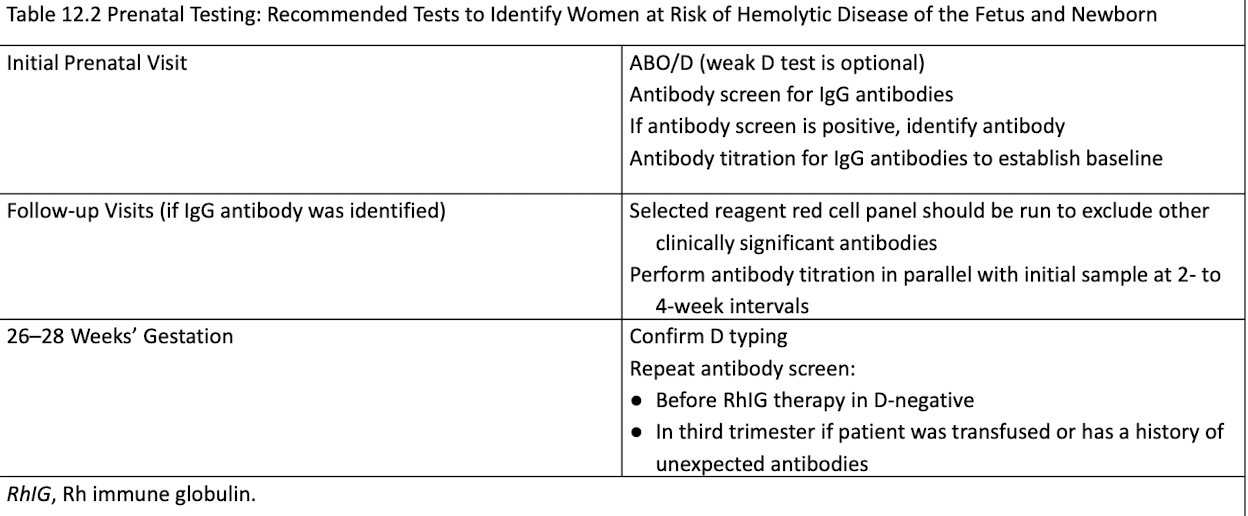
Antibody Titration
Determines if procedures are needed
Baseline titer in 1st trimester, repeated every 4-6 weeks (sample frozen)
Significant rise: 2+ dilutions from baseline
Critical levels: 16 or 32 for anti-D and other Rh Abs
Ultrasound
detects fetal anemia
Increased cardiac output and low blood viscosity
Severity of anemia determined by peak systolic velocity in the middle cerebral artery
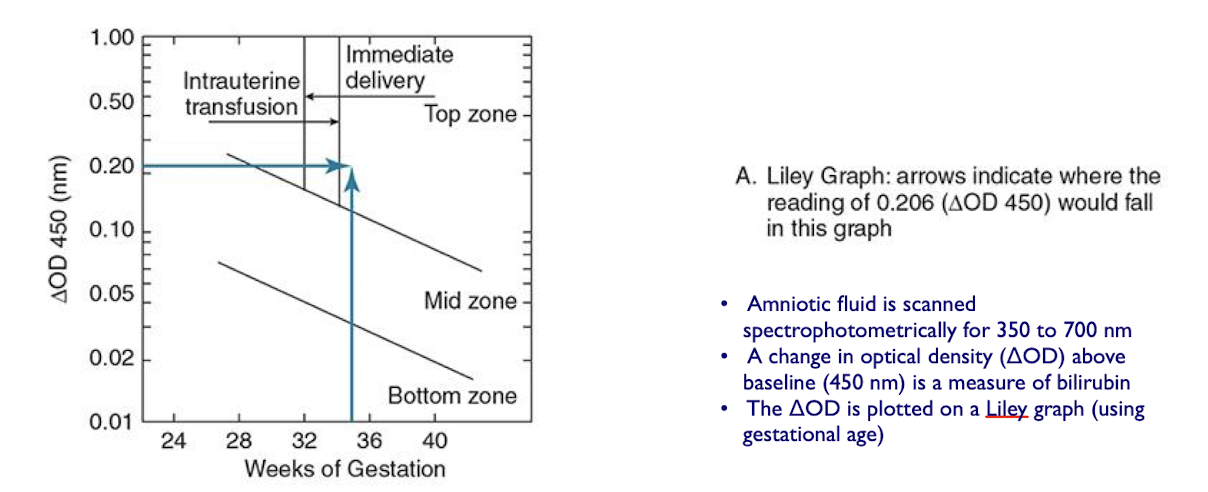
Amniocentesis
ΔOD is plotted on a Liley graph (using gestational age)
Upper zone (zone 3): severe HDFN
Middle zone (zone 2): moderate disease
Lower zone (zone 1): mild disease
Amniocentesis Result Alternatives
Pregnancy continues to term
Intrauterine transfusion is performed
Early labor is induced
Fetal lung maturity must be determined ([L:S] ratio should be > 2:1)
Cordocentesis
Fetal blood sample is taken for:
Hemoglobin and hematocrit testing
Bilirubin testing
RBC genotyping
Mortality rate low (1-2%)
can be used for intravascular transfusions when severe HDFN
Fetal Genotyping
Fetal DNA typed via maternal plasma in 2nd trimester.
Predicts fetal genotype to avoid invasive procedures if antigen is absent.
Postpartum Testing
D testing for infants of D-negative mothers (including weak D).
Possible false results:
False negative: blocked D-antigen sites (perform elution to show anti-D Ab).
False positive: weak D test on antibody-coated RBCs (Rh control positive at AHG phase).
Testing at Delivery (Postpartum Testing)
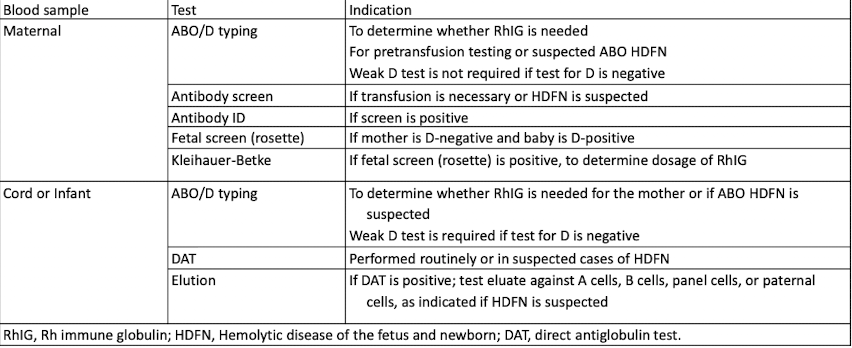
ABO testing (Postpartum Testing)
Only forward grouping performed
ABO antibodies not yet produced
Cord blood is washed to remove Wharton’s jelly (umbilical cord protection)
DAT (Postpartum Testing)
Elution is necessary if DAT is positive and mother’s antibody is unknown or sample unavailable.
Negative eluate: suspect low-frequency antigen.
Positive eluate (A/B cells, negative screen): indicates ABO HDFN.
Intrauterine Transfusions
Interpret ABO/Rh and DAT results carefully
cord blood may show group O, D-negative phenotype due to transfused blood
DAT results may be falsely negative or weakly positive.
Prevention of HDFN
RhIG prevents alloimmunization in D-negative mothers
Prevents formation of anti-D antibody
Antepartum administration: 300 μg at 28 weeks
Postpartum administration
Postpartum administration includes ? for HDFN prevention
Non-immunized women receive one full dose within 72 hours of delivery
More than one dose if fetomaternal hemorrhage >30 mL
Screening for Fetomaternal Hemorrhage
Screen RhIG candidates for fetomaternal hemorrhage.
Perform rosette test on postpartum maternal specimen.
Incubate maternal RBCs with anti-D antibody.
Add D-positive indicator cells.
Rosette observation
Rosette Test and Observation
≤1 rosette/3 low-power fields: 1 RhIG dose.
>1 rosette/3 low-power fields: Quantify bleed needed.
Quantifying Fetomaternal Hemorrhage
Flow cytometry or Kleihauer-Betke test quantifies fetomaternal hemorrhage for additional RhIG doses.
Kleihauer-Betke test:
Fetal hemoglobin resists acid (retains dye)
adult hemoglobin does not (ghost-like).
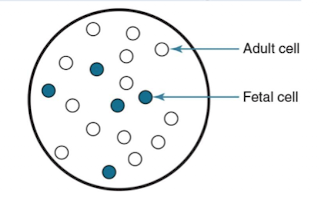
Kleihauer-Betke Calculation
Intrauterine Transfusion
Corrects anemia and prevents heart failure
Blood for intrauterine transfusion
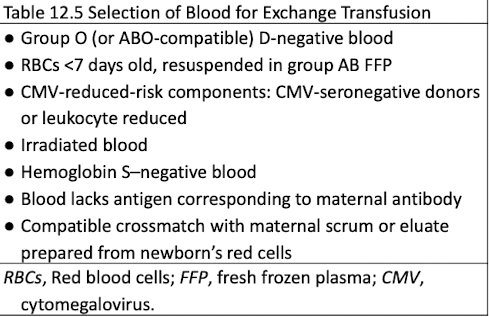
Group O, D-negative RBCs
RBCs collected within 7 days (fresh)
Irradiated to prevent graft-versus-host disease
Negative for cytomegalovirus and/or leukocyte reduced
Negative for hemoglobin S
Phototherapy
Initial treatment for hyperbilirubinemia
Mild cases of HDFN (ex: ABO HDFN )
Uses fluorescent blue light (420 to 475 nm)
Light converts bilirubin to isomers excreted in the bile
If patient is unresponsive → exchange transfusion
Exchange Transfusion
Replacement of 1 to 2 whole blood volumes
Exchange Transfusion
Corrects anemia
Removes newborn’s RBCs and replaces with antigen-negative cells
Reduces bilirubin (preventing kernicterus)
Reduces maternal antibodies
Blood Selection for Exchange Transfusion
ABO and D typing for the infant
Antibody screening with maternal or infant serum/plasma
Use antigen-negative units if antibody present