TMS : Chapter 1 -Karteikarten | Quizlet
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What is TMS ?
Set of processes that enable the company to capitalize on talent, by ensuring a match between position and profile, so as to align the company with its external PESTELE environment, and in particular with its customers, to finally make the company durably profitable.
What are the two types of TMS ?
Tight TMS and Loose TMS
Key components of tight TMS ?
• Unity of command
• Horizontal division of tasks (Taylor)
• Impersonality of relations (Weber)
• Formalization or procedures (Weber)
• Bureaucratic, centralized
• Commission errors
Key components of loose TMS ?
• Participative organization (Argyris)
• Self-managed & multi disciplinary teams
• Emotions interactions at work
• Informal autonomous arrangements
• Adhocratic and decentralized
• Omission errors
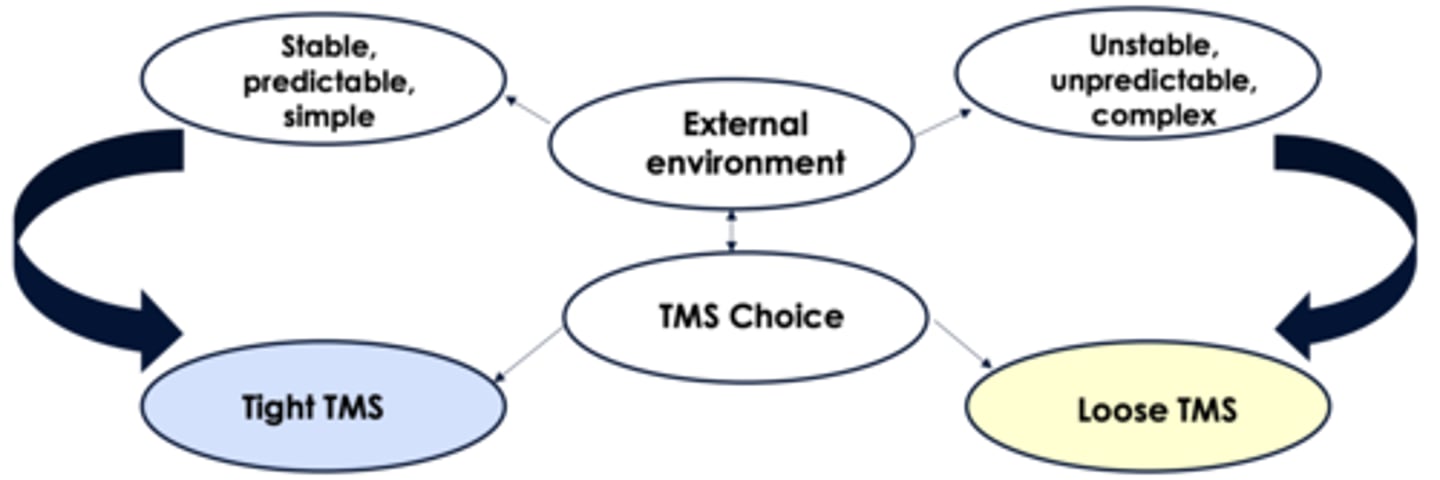
What is the PESTLE environment ? Types of environnements ?
Environnemental influences : Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Ecological, Legal, Ethical
- Simple, predictable : Tight TMS (match special profiles with spe positions)
- Complex, unpredictable : Loose TMS (generalist profiles for diversified positions)
What are the 3 models of tight TMS ?
- Fayol's
- Taylor's
- Weber
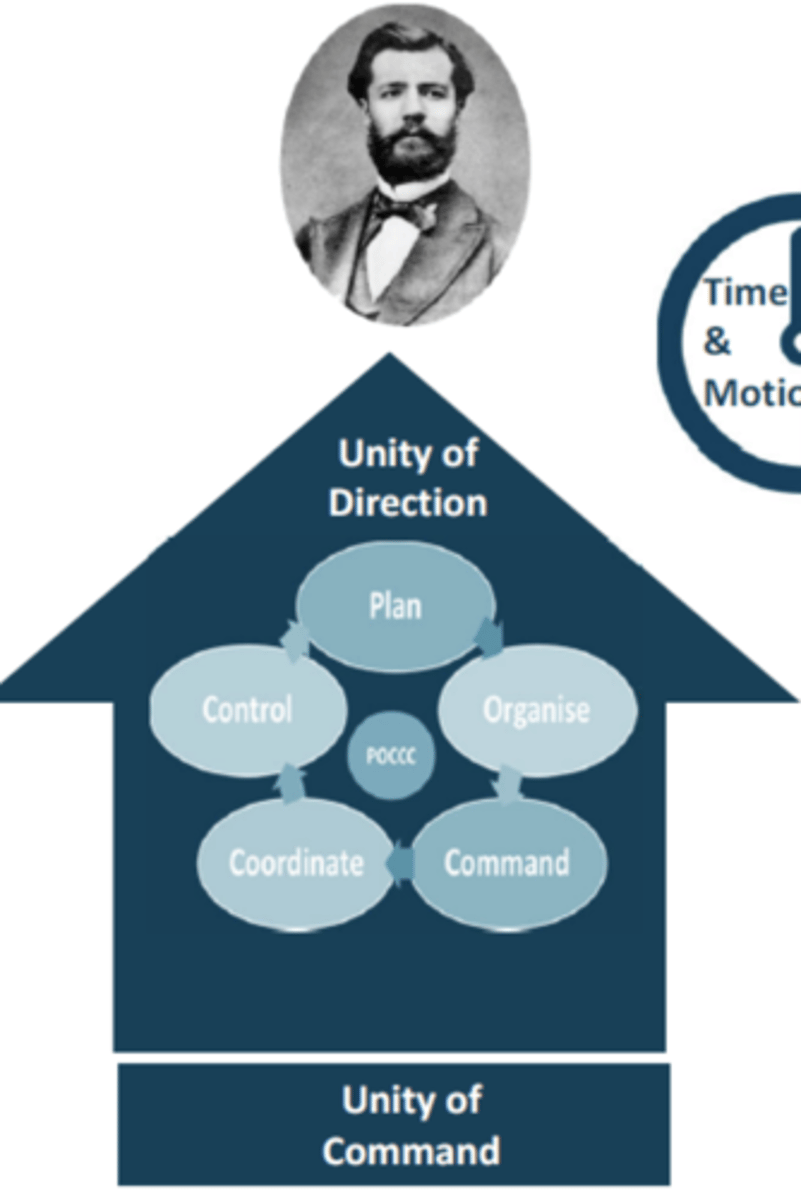
Henri Fayol's model ?
Clear reporting structure :
- POCCC : plan, organise, command, coordinate, control
- Unity of direction : every individual serves strat to be achieved toward clientele
- Unity of command : each operating individual has 1 supervisor to report to
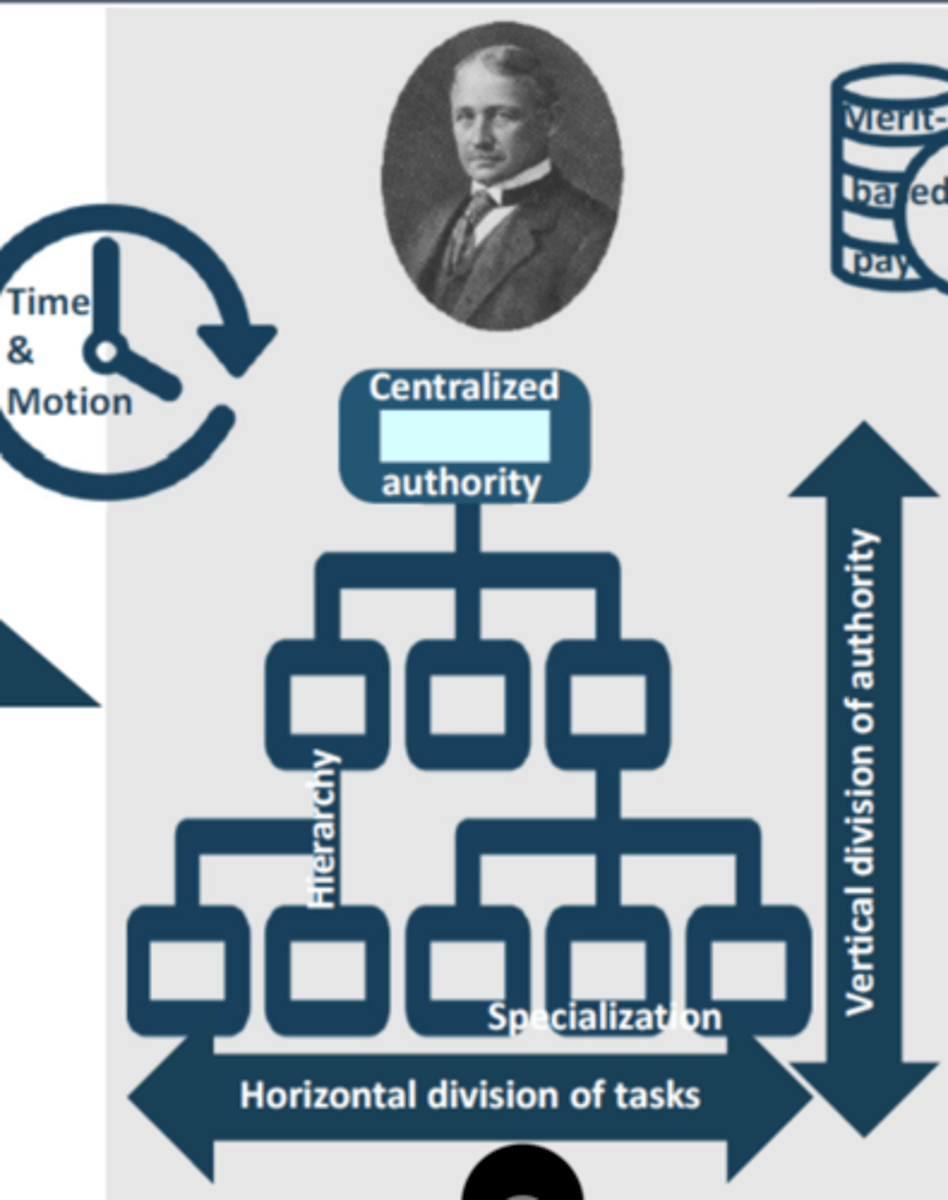
Frederick Taylor's model ? Authority ? Hierarchy ? Divisions ?
Time, motion & efficiency :
• Centralized authority, i.e., authority to make key strategic decisions is legitimately restricted to top management.
• Hierarchy, i.e., a single individual/group/unit has the most authority for strategic decisions, each subsequent level has a lesser authority.
• Vertical division of authority, i.e., attribution of differential levels of command in the chain of command.
• Horizontal division of tasks, i.e., breaking down work into smaller tasks at same hierarchical level along a production line / process.
• Specialization, i.e., involves focusing on a specific task, activity, process, or limited scope of tasks to gain greater efficiency.
• Standardization of positions, i.e., establishment of uniformity in positions with predefined & limited range of allowable actions.
• Time & motion study, i.e., measurement of optimum time & gestures necessary for each task/operation/procedure/process.
Max Weber' model ?
Formal, impersonal, merit
• Formalization, i.e., putting policies, rules, procedures & decisions into written documentation to guide individuals' behavior.
• Impersonality of relations, i.e., individuals at work coordinate in a formal non‐intimate way that focuses on the work to be done.
• Equitable remuneration, i.e., fixed pay based on qualification & merit/productivity/performance‐related variable pay

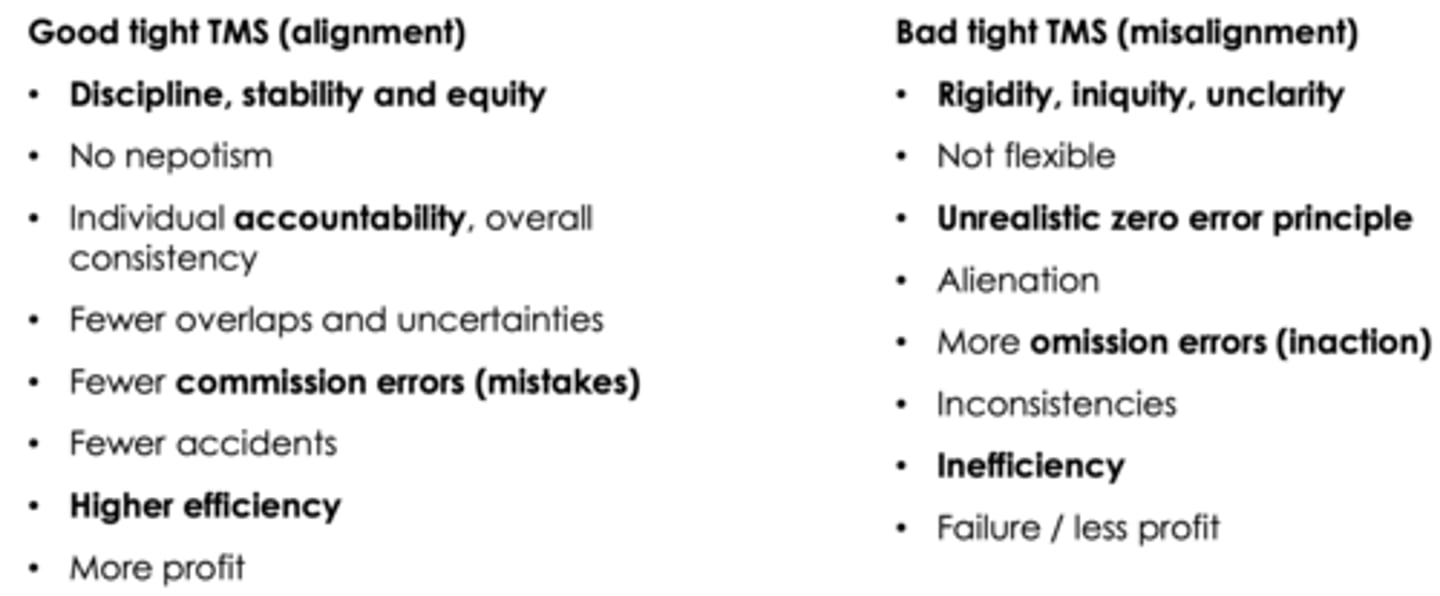
Good vs Bad tight TMS ? What is the goal ?
- Exploitation, maximum profit trough efficiency
Example of loose TMS models ?
- McGregor
- Agyris
- Mayo
McGregor 's model ? How are people ? Reason to work ? Motivator ? Integration ? Design ?
X, Y Theory

Argyris's model ? How is the worker ? Participation ? Management of team ? Arrangements ?
Responsible adults and self directed teams
• Mature worker, i.e., having generic competencies, risk‐oriented & entrepreneurial attitude, looking for interpersonal social growth and involvement in strategic decision‐making.
• Participative egalitarian organization, i.e., "one person, one vote", even regarding top strategic decisions.
• Self‐Managed Multidisciplinary Team, i.e., teams of heterogeneous people, with shared autonomous decision‐making, responsibility and leadership over own work.
• Informal autonomous arrangements, i.e., accommodating yourself & others on a personal & affective basis, oral agreement.
• Cross‐functional tasks, i.e., covering diverse disciplines.
Elton Mayo's model ? Emotions in workplace ? Organisation ? Recognition ? Support ?
Social and relationship needs at work
• Emotional interactions at work, i.e., expression of personal and intimate emotions, friendship and mix of private & professional encouraged in the workplace.
• Adhocratic organizing, i.e., informal intuitive form of self-organizing that changes easily with each situation, thus temporary.
• Personalized recognition, i.e., consideration expressed in a personal, emotional, affective way, mixing private & professional.
• Perceived socio‐personal support, i.e., feelings about others valuing us and the work that we do, in a personal way
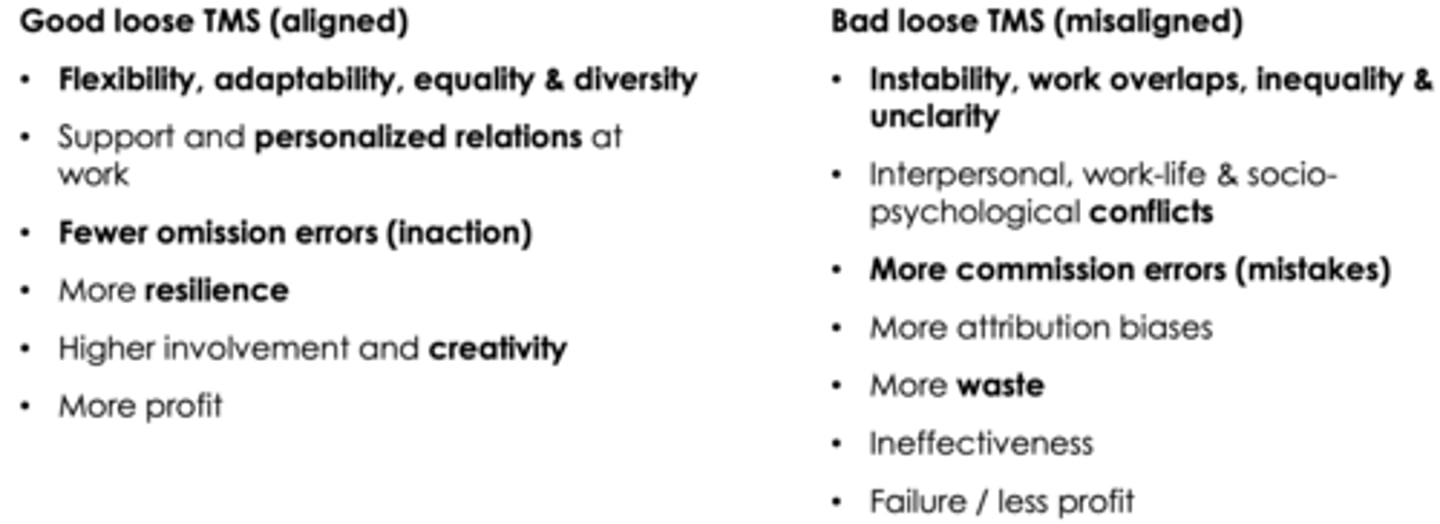
Good vs bad loose TMS ? What is the goal ?
Exploration, maximum profit trough innovation
What happens when methods/tools within TMS are implemented in a good way ?
Additive effect
Good TMS = High performance work system
--> Multiplier effect, expands staff and workplace effectiveness and efficiency
What is the balanced scoreboard ?
Focuses on the most critical measures : Financial, client, business, Innovations/learning
Difference with firms aligned and the misaligned TMS ?
- Less safety incidents
- Lower defects in quality
- Higher customer satisfaction
- Higher productivity
- Higher profitability