BIO 2120 2nd Test Top Hat Questions
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Carbohydrates are relatively reactive and are associated with a number of biological reactions. This is most likely due to which of these factors?
They contain a number of carbonyl and hydroxyl groups.
Which process of cellular respiration does not occur within a mitochondrion in a eukaryotic cell?
Glycolysis
During glycolysis, when each molecule of glucose is catabolized to two molecules of pyruvate, most of the potential energy contained in glucose is ________.
retained in the two pyruvates
Glycolysis is active when cellular energy levels are ________; the regulatory enzyme, phosphofructokinase, is ________ by high levels of ATP.
low; inhibited
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is released during which of the following stages of cellular respiration?
Oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and the citric acid cycle
The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to ________.
act as an acceptor for electrons and hydrogen, forming water
Energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ into which location in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondrial intermembrane space
Over Break, you gained 7 pounds - even though you hardly ate anything and drank lots of fluids! You resolve to exercise more to lose weight. Your hours on the treadmill pay off, and you lose 5 pounds. The mass that you lost during exercise included sugars, lipids, and proteins. Where did those atoms go?
Much of the mass that you lost was exhaled as carbon dioxide and water
Where is most of the water in oxidative respiration reaction produced?
In the electron transport chain
Nucleic acids are polymers made up of which of the following monomers?
Nucleotides
Which of the following descriptions best fits the class of molecules known as nucleotides?
A nitrogenous base, a phosphate group, and a sugar
Consider the DNA nucleotide sequence ATCTTACATCGA. What does this sequence best represent?
The primary structure of DNA
What is the difference between a ribonucleotide and a deoxyribonucleotide?
Ribonucleotides have a hydroxyl group on the 2 carbon of their sugar.
Nucleic acids have definite polarity, or directionality. How are these ends described?
One end has an unlinked 3' hydroxyl; the other end has an unlinked 5' phosphate.

The sequence of one strand of DNA is shown below. Which of the following is the reading sequence of its complementary strand?
5′ TAAACCGG 3′
If E.coli cells are grown in a medium containing radioactive 32P-labeled phosphate, which of these molecules will be labeled?
Nucleic acids
In the Hershey and Chase Experiment, which radioisotope was found inside the E. coli cells after bacteriophage infection.
32P was inside, concluding that DNA is the genetic material.
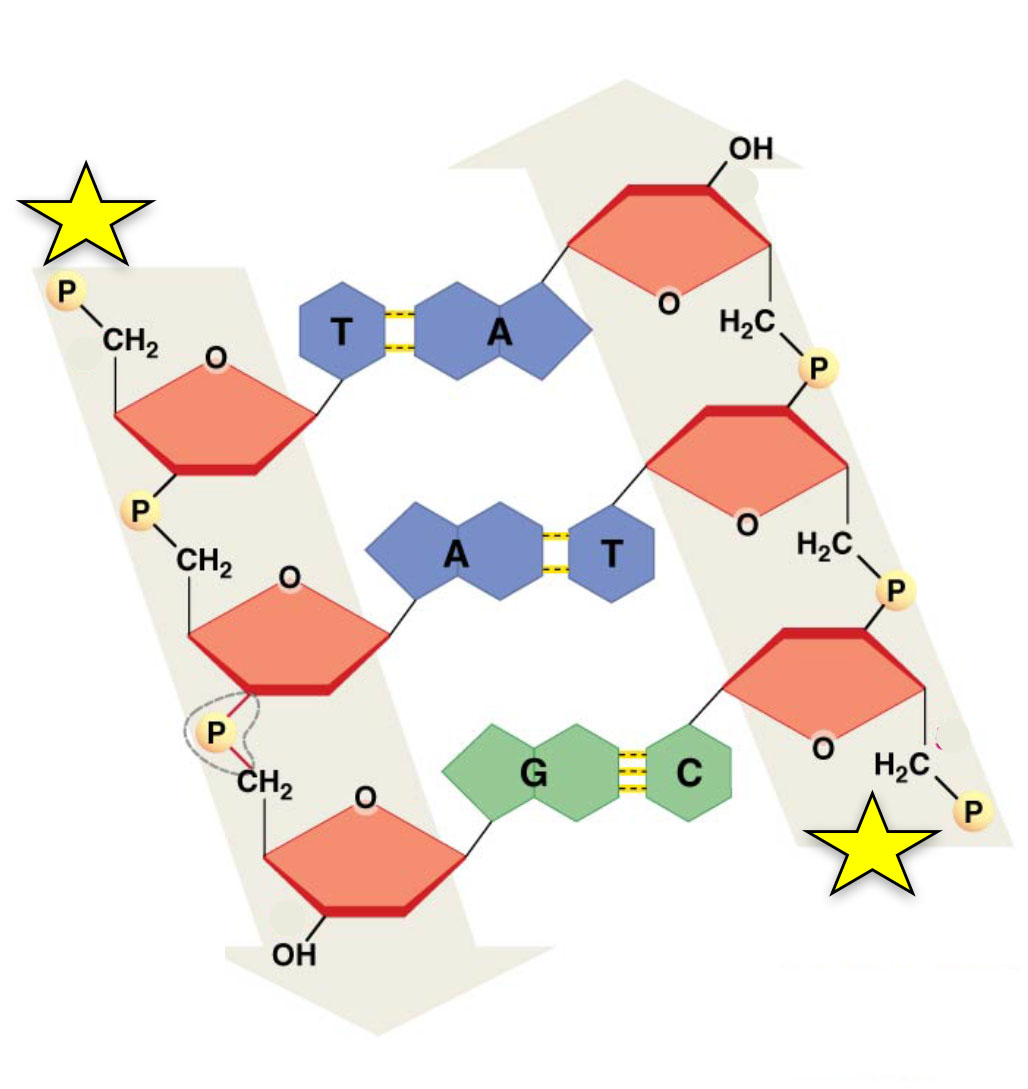
What name/label is given to the ends of the strands at the position of the stars?
5' ends
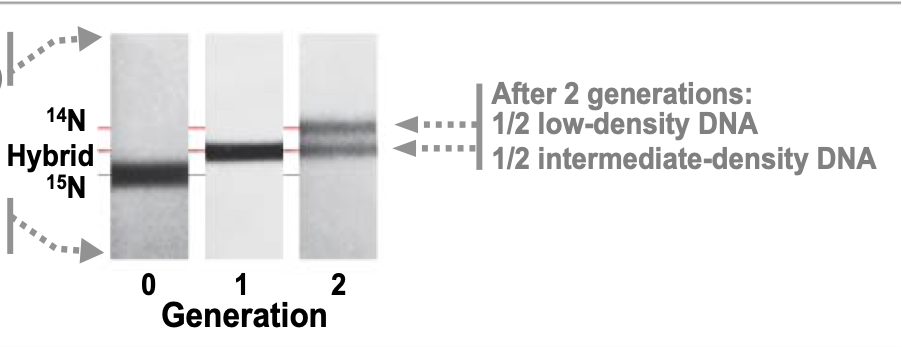
In Meselson Stahl Experiment, E. coli cells grown on 15N medium are transferred to 14N medium and allowed to grow for two more generations (two rounds of DNA replication). DNA extracted from these cells is centrifuged. What density distribution of DNA would you expect in this experiment?
One low-density and one intermediate-density band
In the polymerization of DNA, a phosphodiester bond is formed between a phosphate group of the nucleotide being added and ________ of the last nucleotide in the polymer.
the 3' OH
Semiconservative replication involves a template. What is the template?
One strand of the DNA molecule
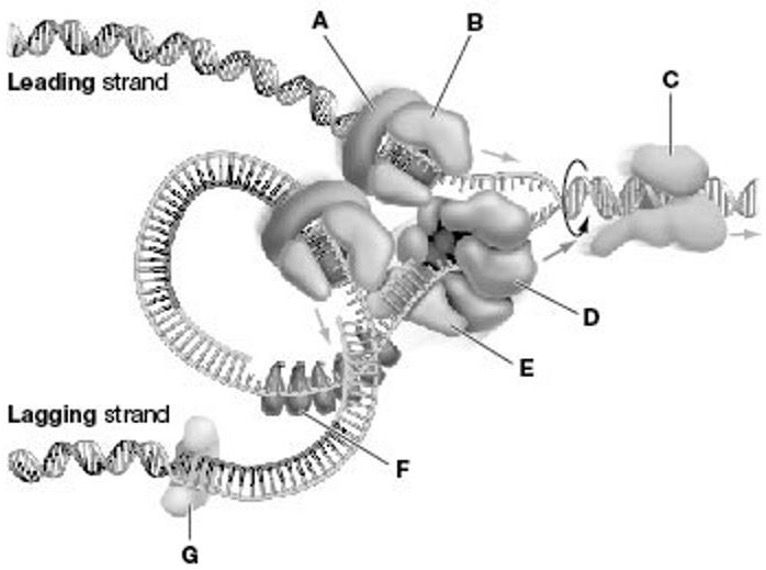
In the figure, which structure causes the two strands of DNA to separate?
D
The leading and the lagging strands differ in that ________.
the leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the opposite direction
Which of the following would you expect of a eukaryote lacking telomerase?
A reduction in chromosome length in gametes
Beadle and Tatum discovered that metabolic pathways are studied most effectively using which of the following techniques?
Using single gene mutations resulting in nonfunctional enzymes specific to a metabolic pathway
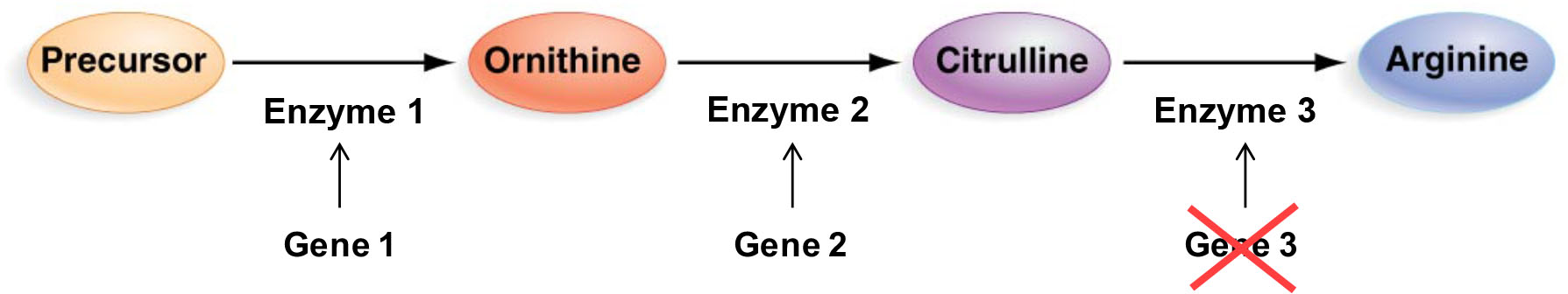
What growth phenotype would you predict for a mutation in Gene 3?
Cells will grow on medium with Arginine
The statement "DNA → RNA → Proteins" ________.
is known as the central dogma
Codons are part of the molecular structure of ________.
mRNA
What does it mean when we say the genetic code is redundant?
More than one codon can specify the addition of the same amino acid
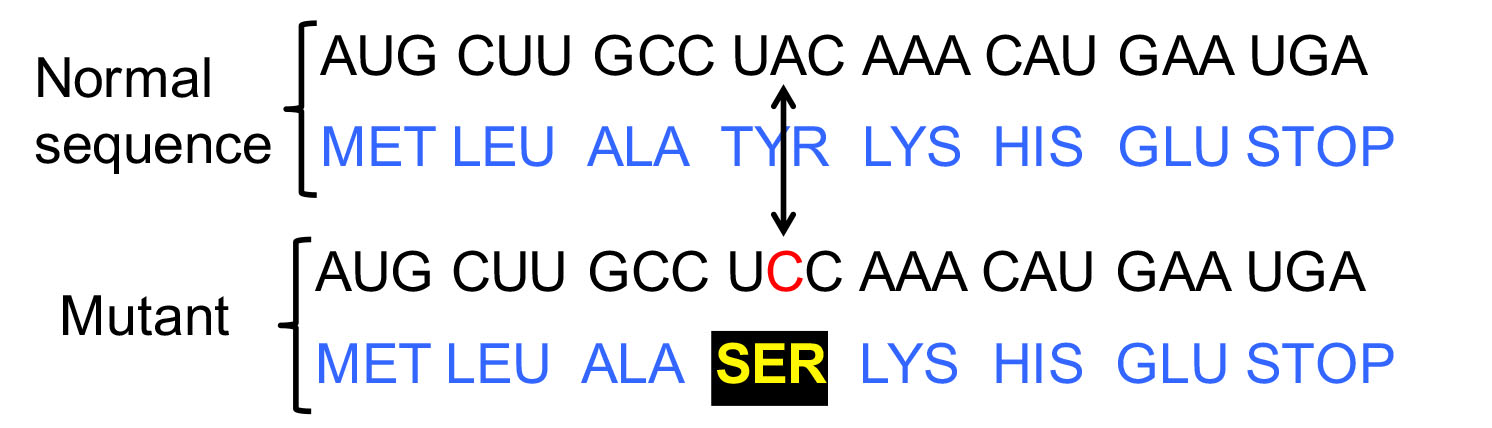
What type of mutation does this represent?
Missense
The hydrolysis of ATP gives rise to ADP and iP and the reaction has a DG of -7.3 kcal/mol. We infer from this that the reaction is .........
exergonic and proceeds spontaneously
Which has more free energy?
NADH
The molecule that functions as the reducing agent (electron donor) in an oxidation-reduction reaction would have what characteristic?
loses electrons and loses potential energy
The active site of an enzyme is the region that ________.
is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme
In RNA transcription, Sigma ……
is a regulatory subunit of prokaryotic RNA polymerase
makes the initial contact with the promoter during the initiation of transcription
binds to the -35 and -10 boxes in bacterial promoters
David Pribnow studied the base sequences of promoters in bacteria and bacterial viruses. He found two conserved regions in these promoters (the −10 box and the −35 box). These two regions of the promoter ________.
bind the sigma subunit that is associated with RNA polymerase.
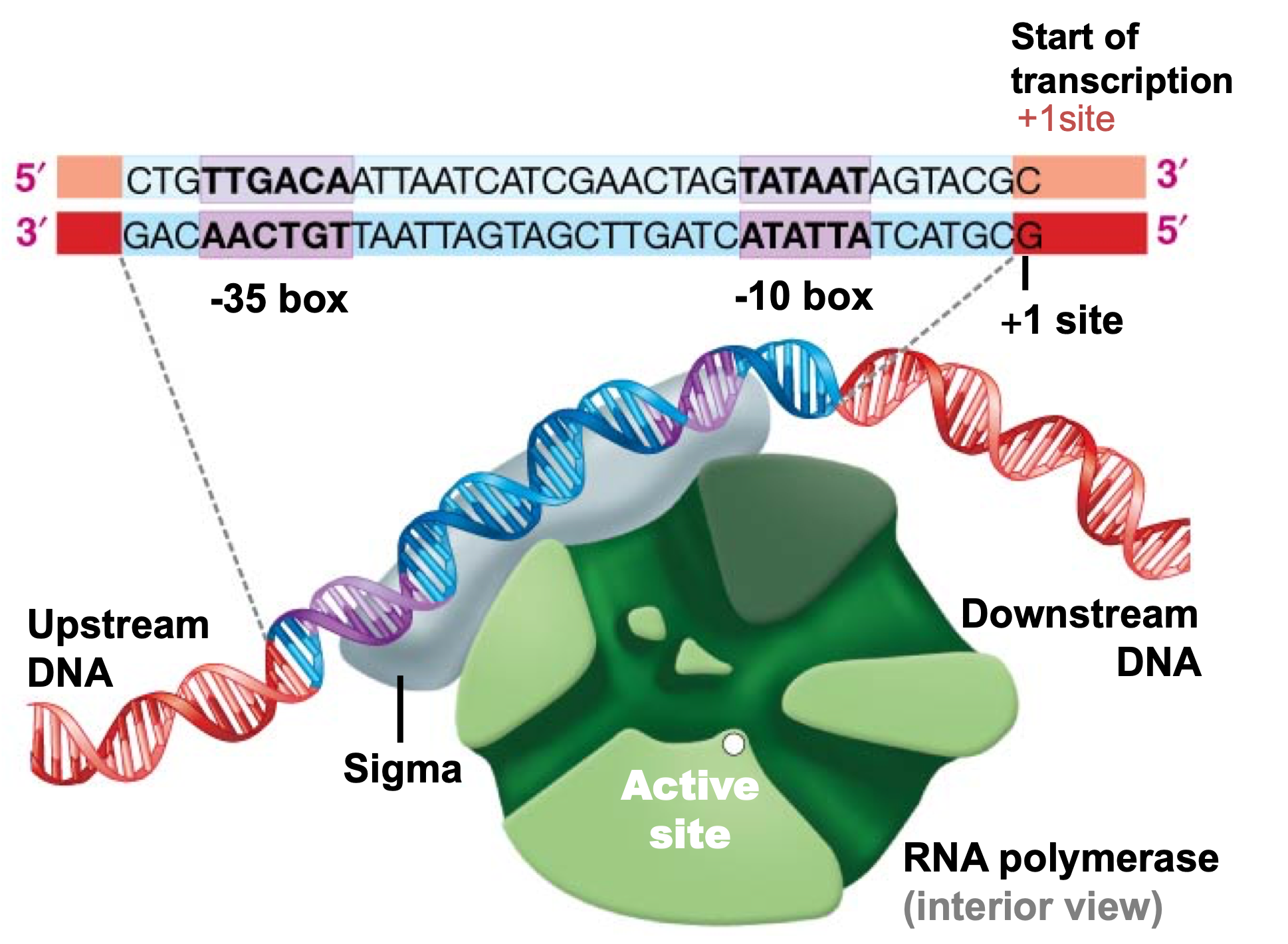
The promoter is the site to which RNA polymerase will bind. Identify the length of the promoter sequence where the RNA polymerase may bind.
TTG............AAT
If the sequence of DNA is
5’-CATGAATAGGGT-3’ (coding strand/non-template strand)
3’-GTACTTATCCCA-5’ (template strand)
then the mRNA sequence after transcription is:
5’-CAUGAAUAGGGU-3’
In making proteins, which of the following occurs in prokaryotes but not in eukaryotes?
Concurrent transcription and translation.
In the figure, what is the function of the anticodon (AGU ) on the loop of the tRNA?
It base pairs with a codon of mRNA
There are as many different aminoacyl tRNA synthetases as there are different tRNAs.
False
There are 61 mRNA codons that specify an amino acid, but only 40 tRNAs. This is best explained by the fact that ________.
the rules for base pairing between the third base of a codon and tRNA are flexible.