VTA 130 Endoparasite List and Review
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
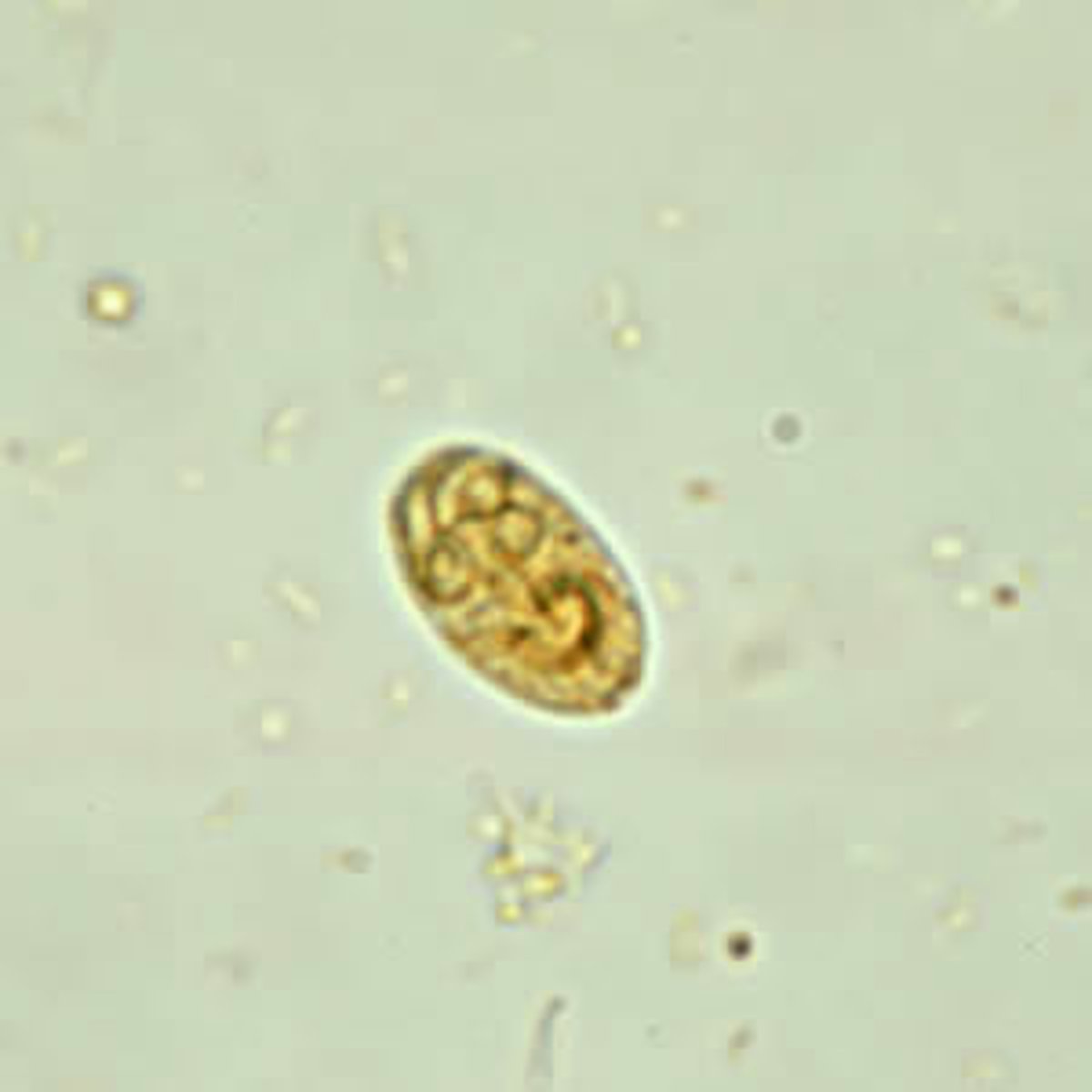
Giardia lamblia
cyst
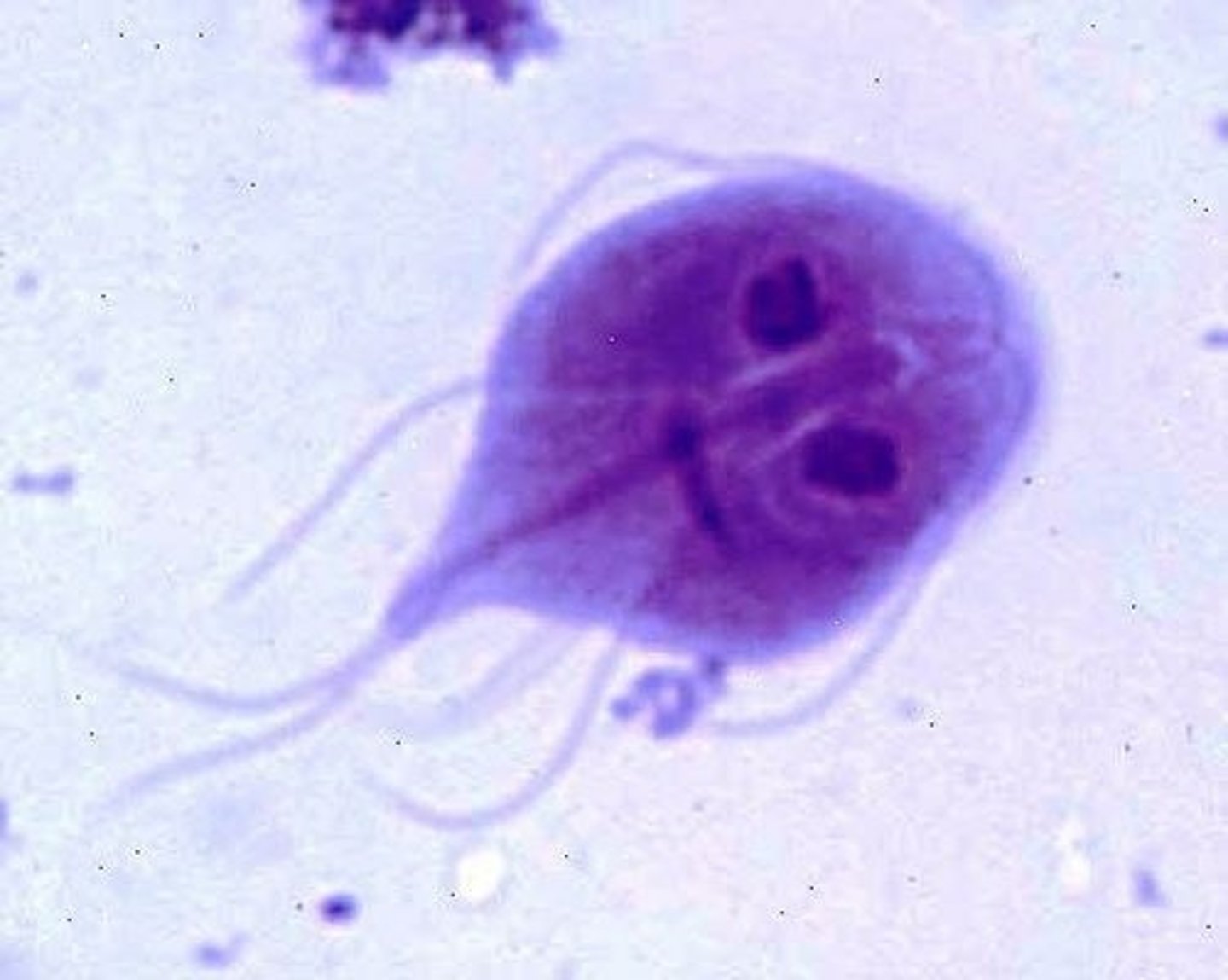
Giardia lamblia
trophozoite
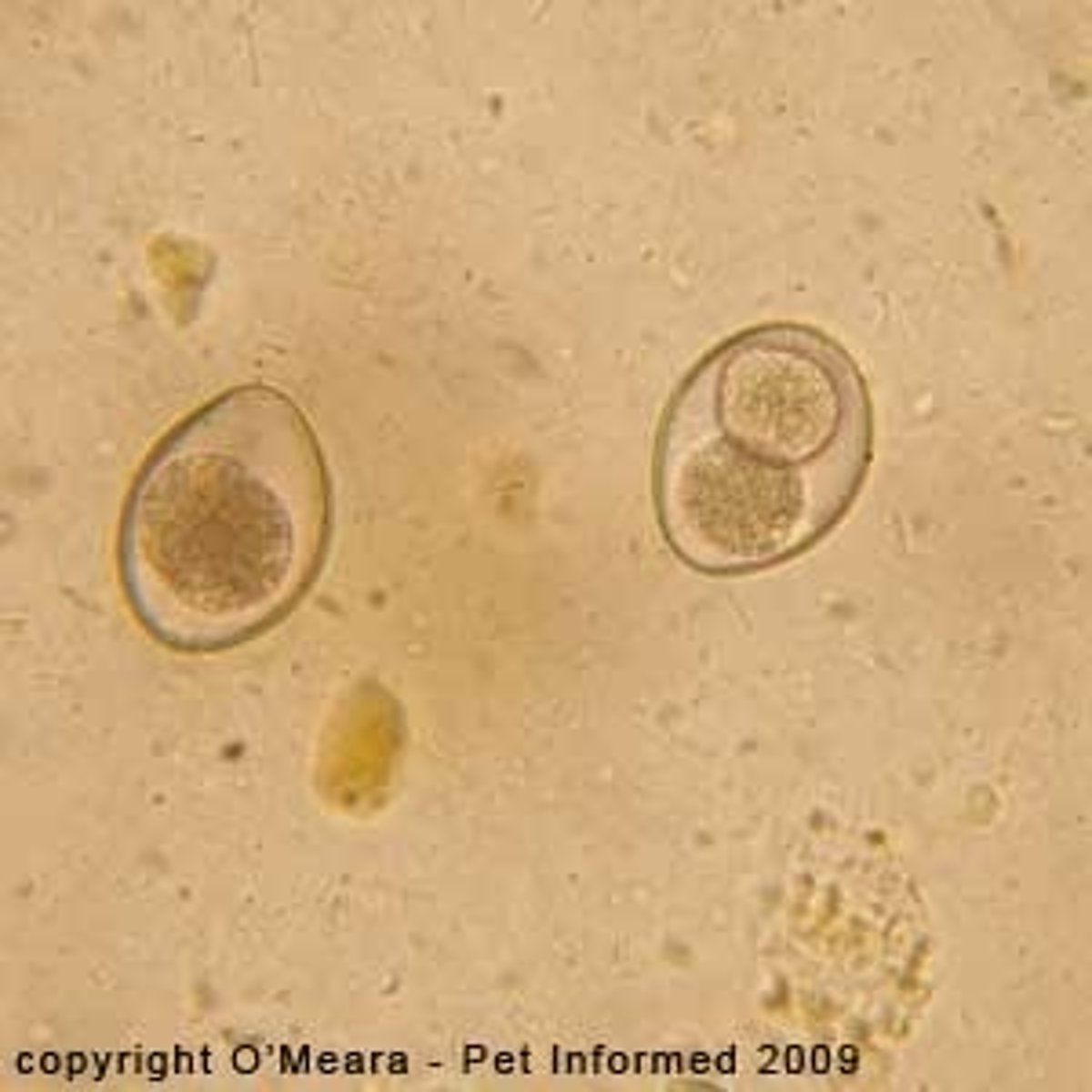
Isospora spp. (coccidia)
Cyst
Dipylidium caninum (tapeworm)
egg
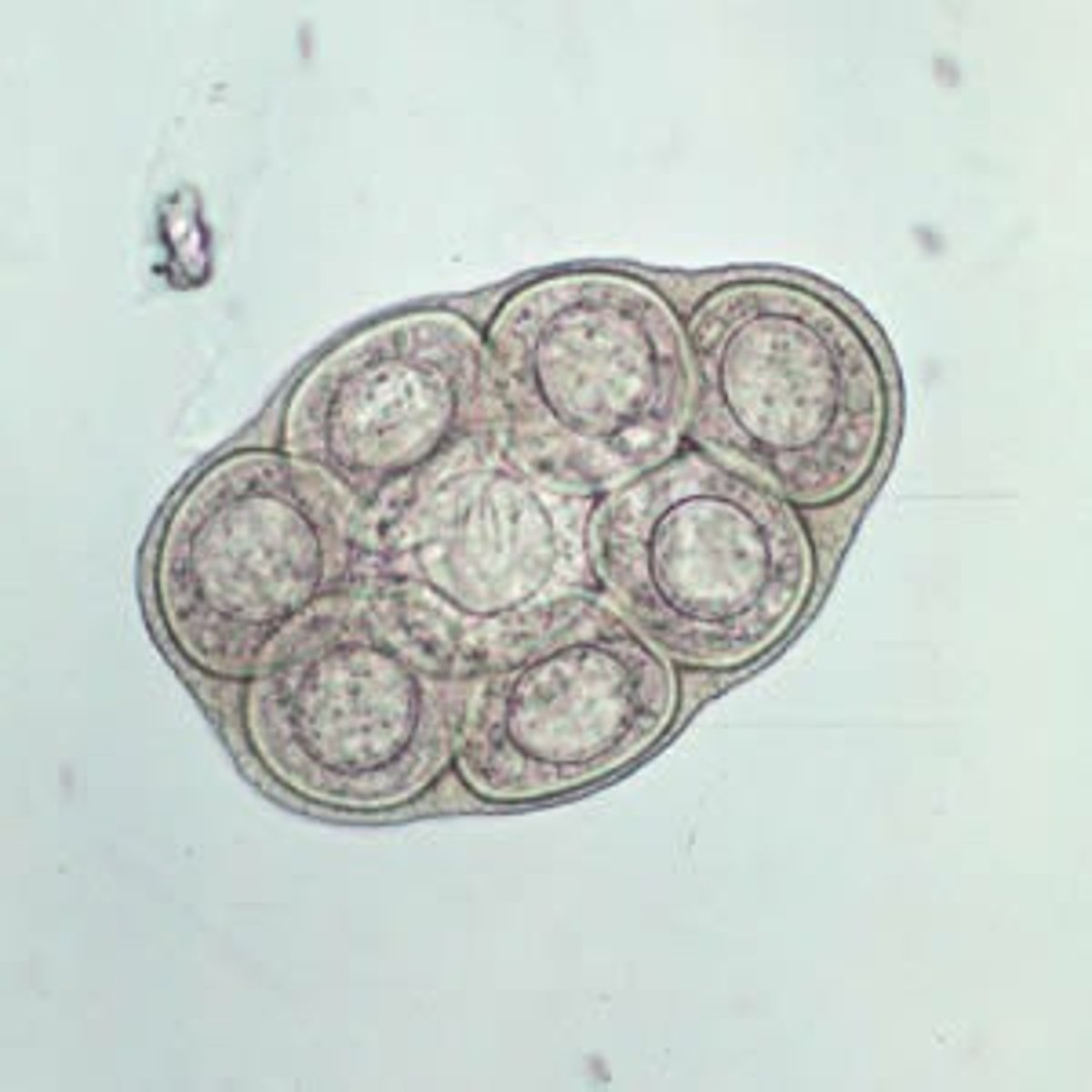
Taenia spp. (tapeworm)
egg

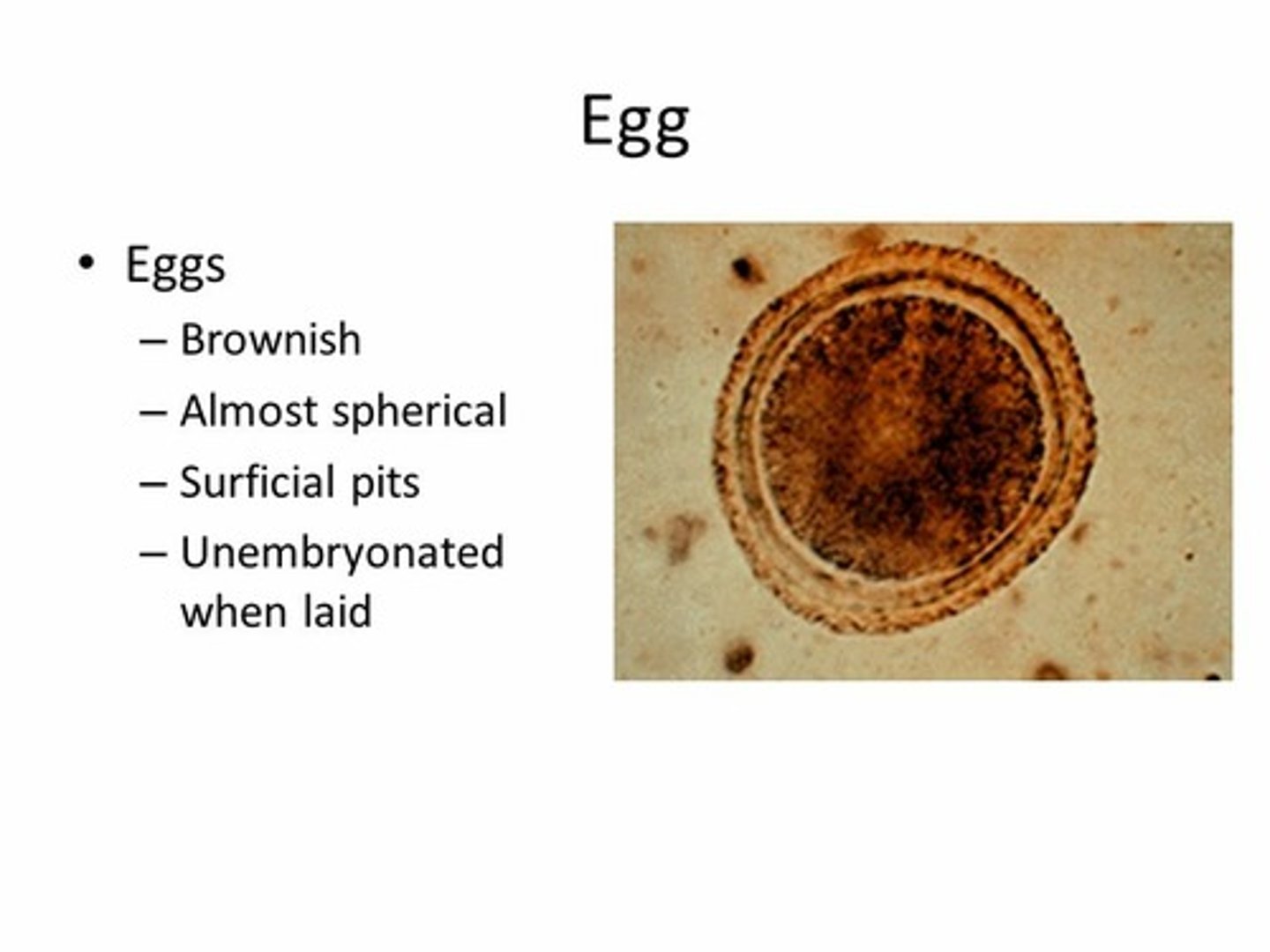
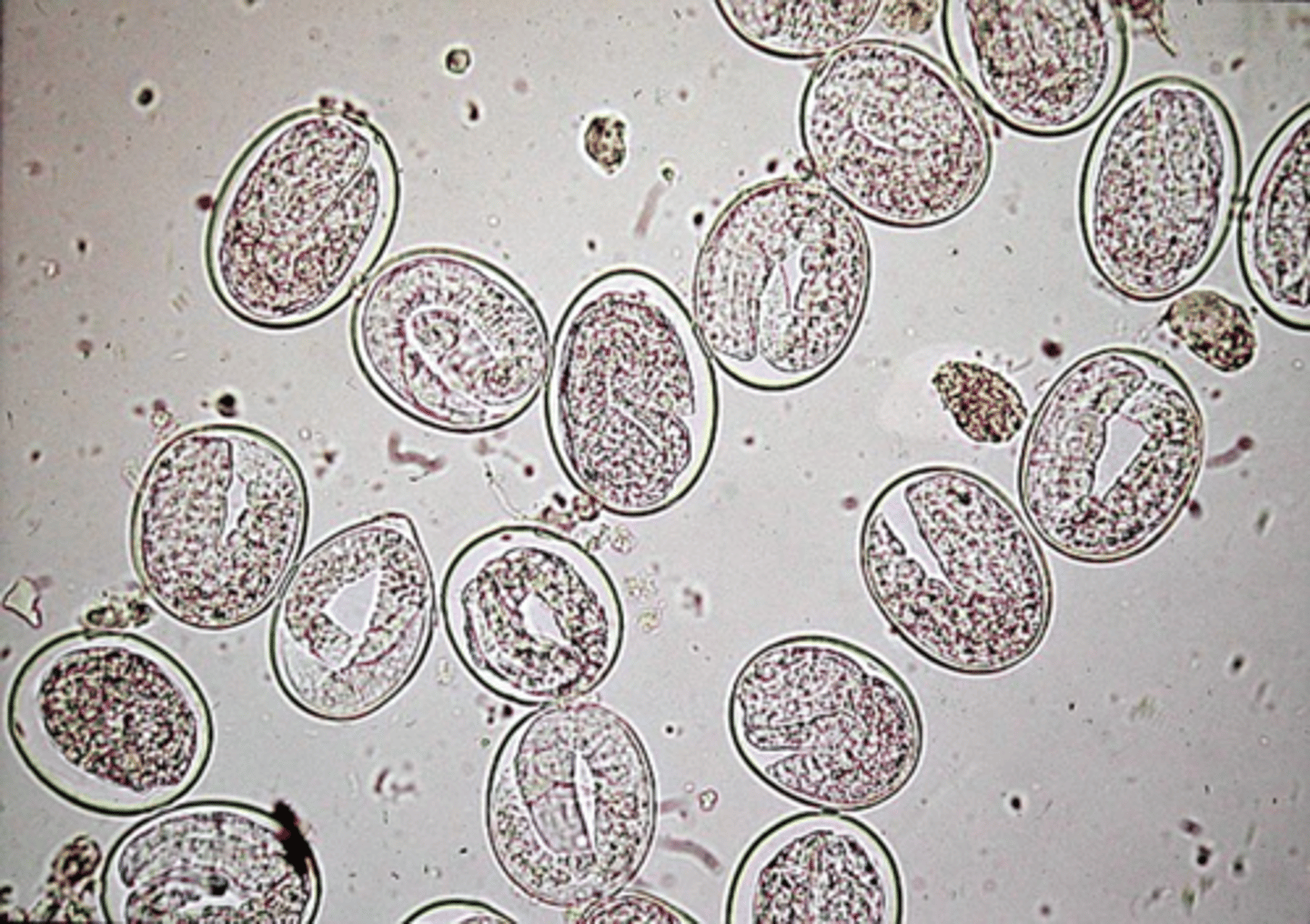
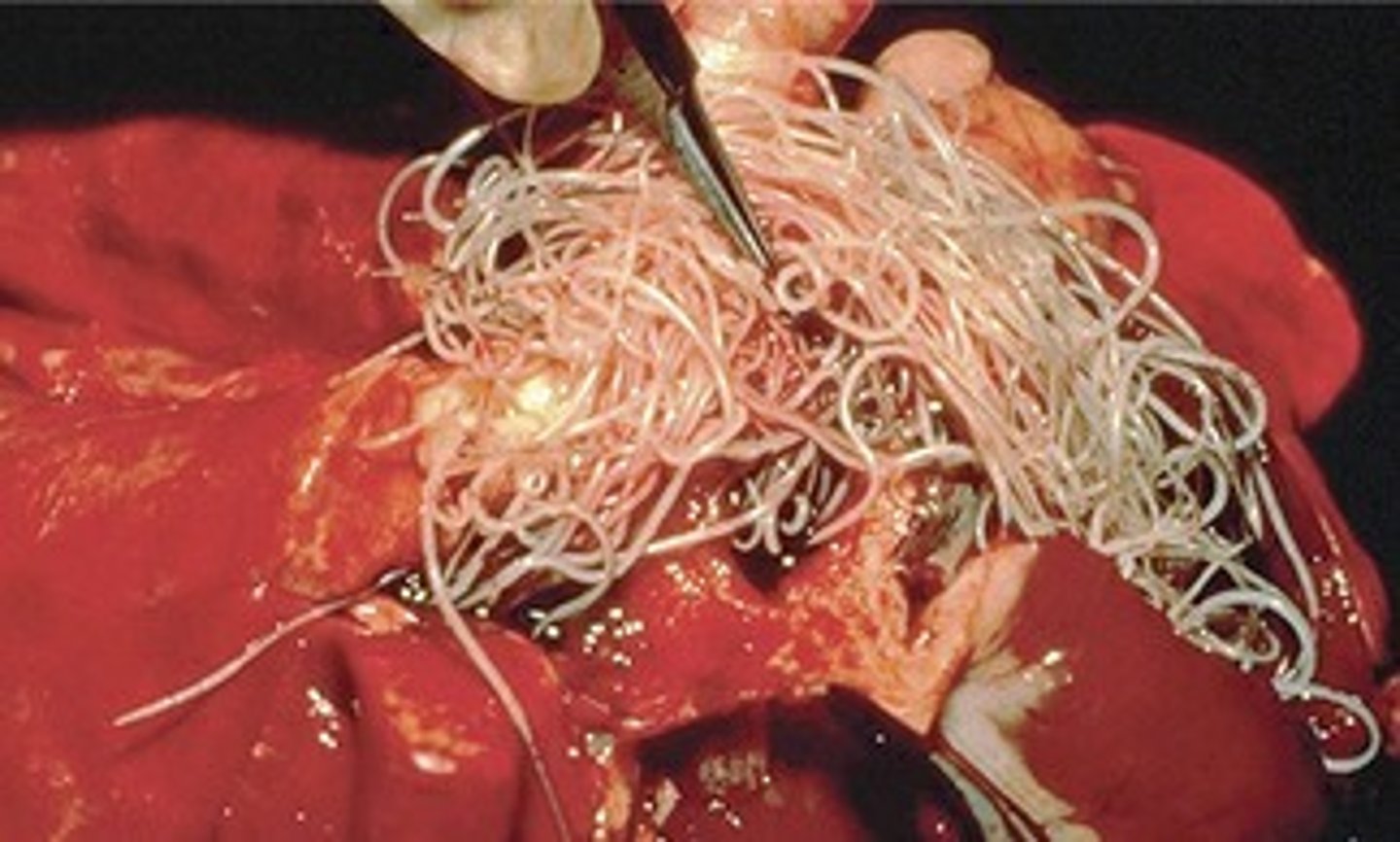
Toxocara spp. (ascarids- roundworms)
egg
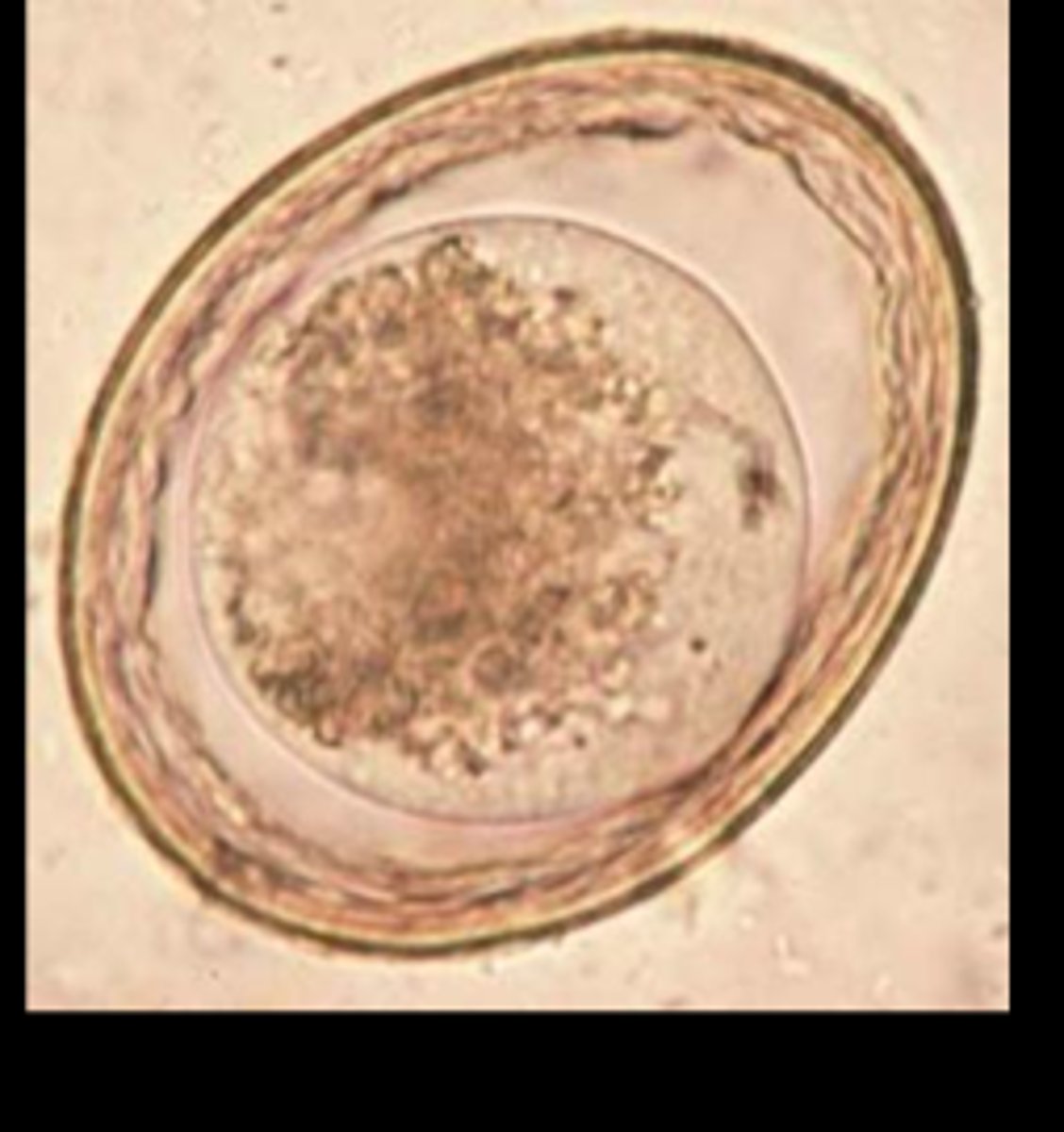
Toxascaris leonina (ascarids-roundworms)
egg
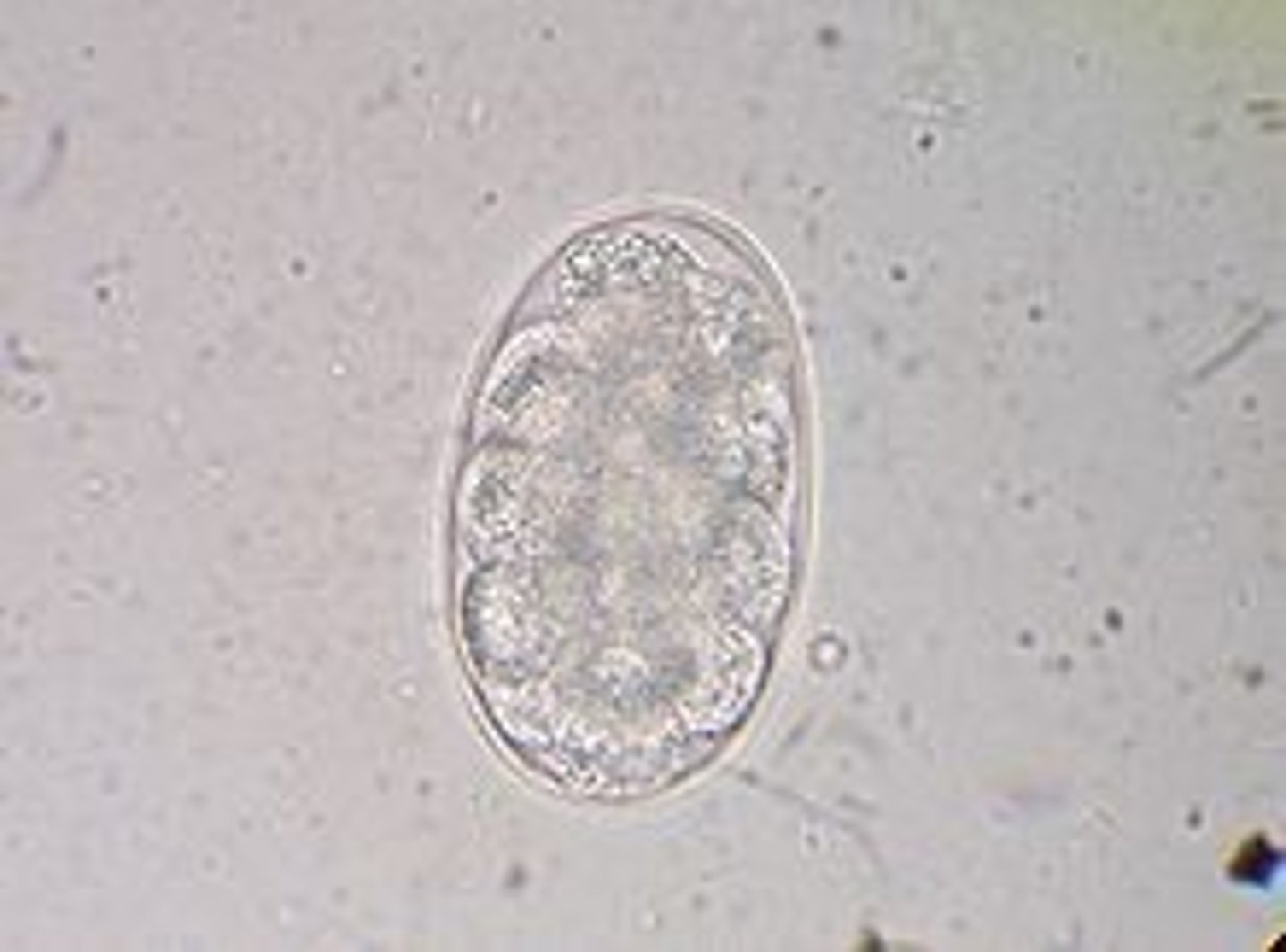
Ancylostoma caninum (hookworm)
egg
Strongyloides spp. (pinworm)
egg
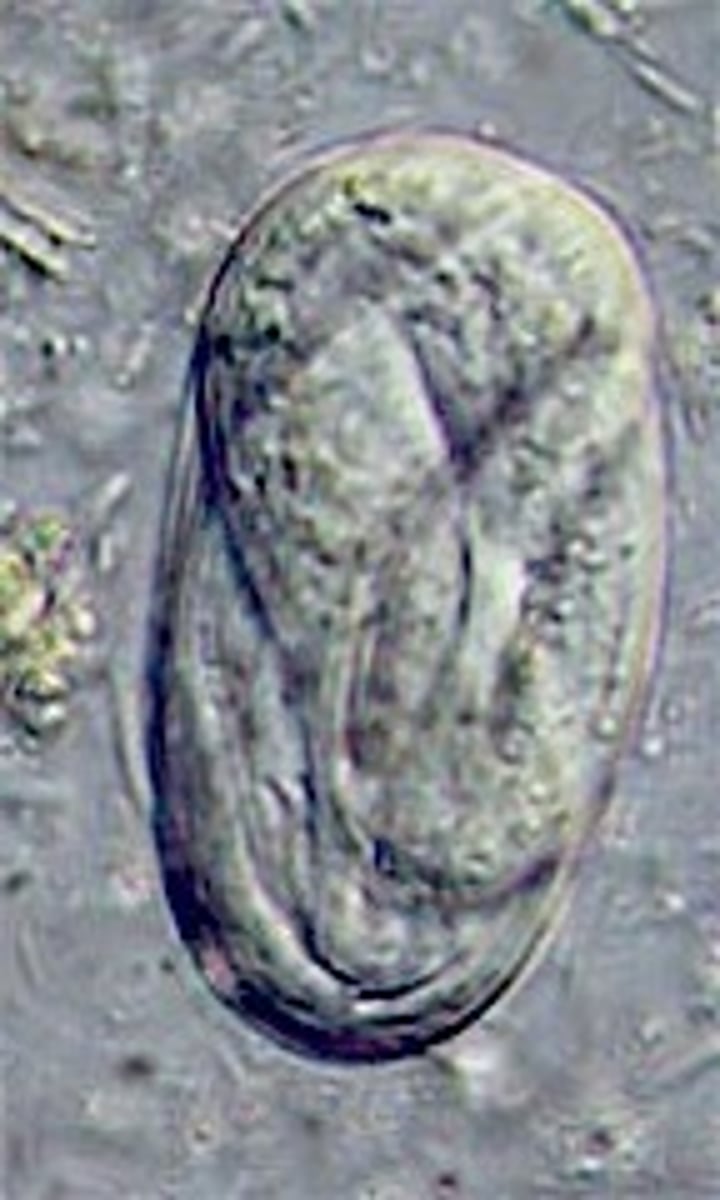
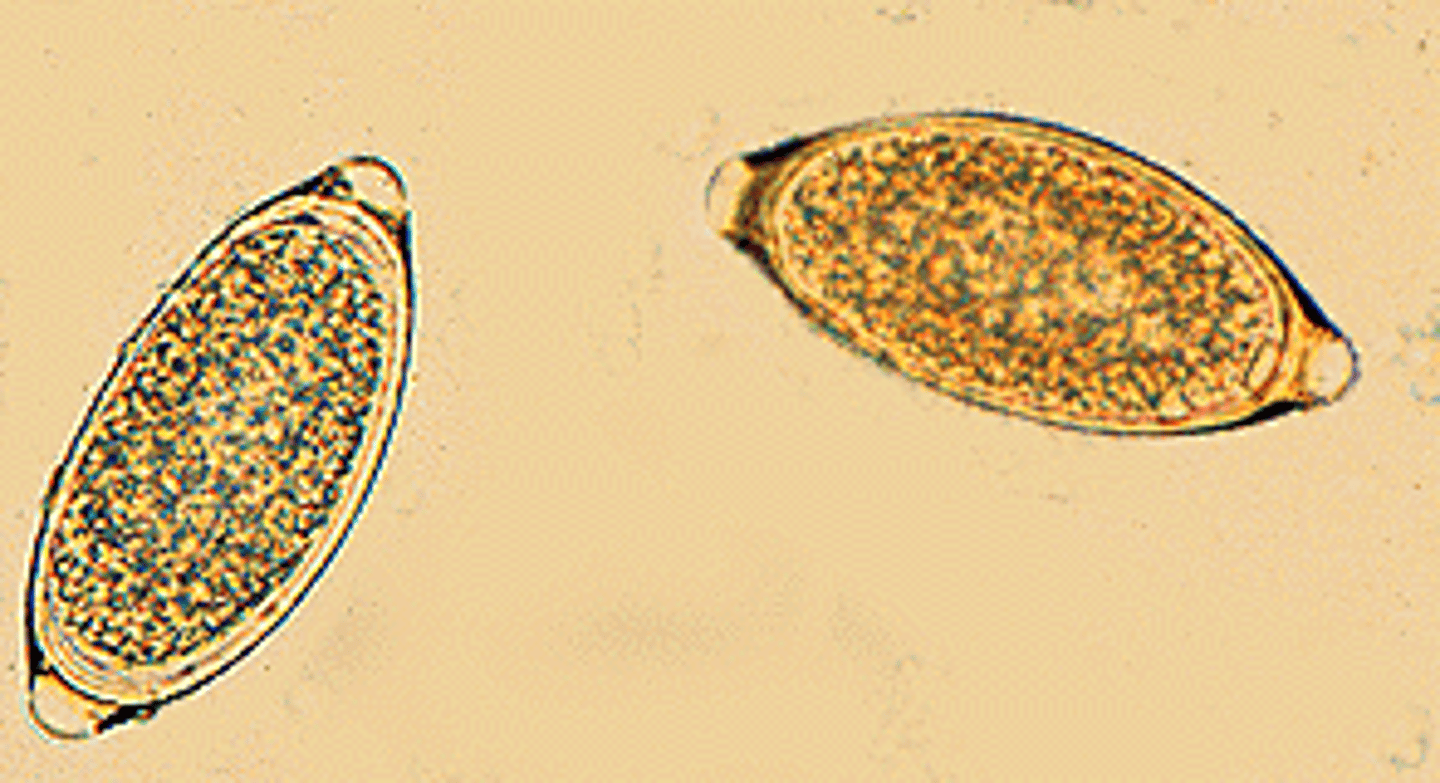
Trichuris vulpis (whipworm)
egg
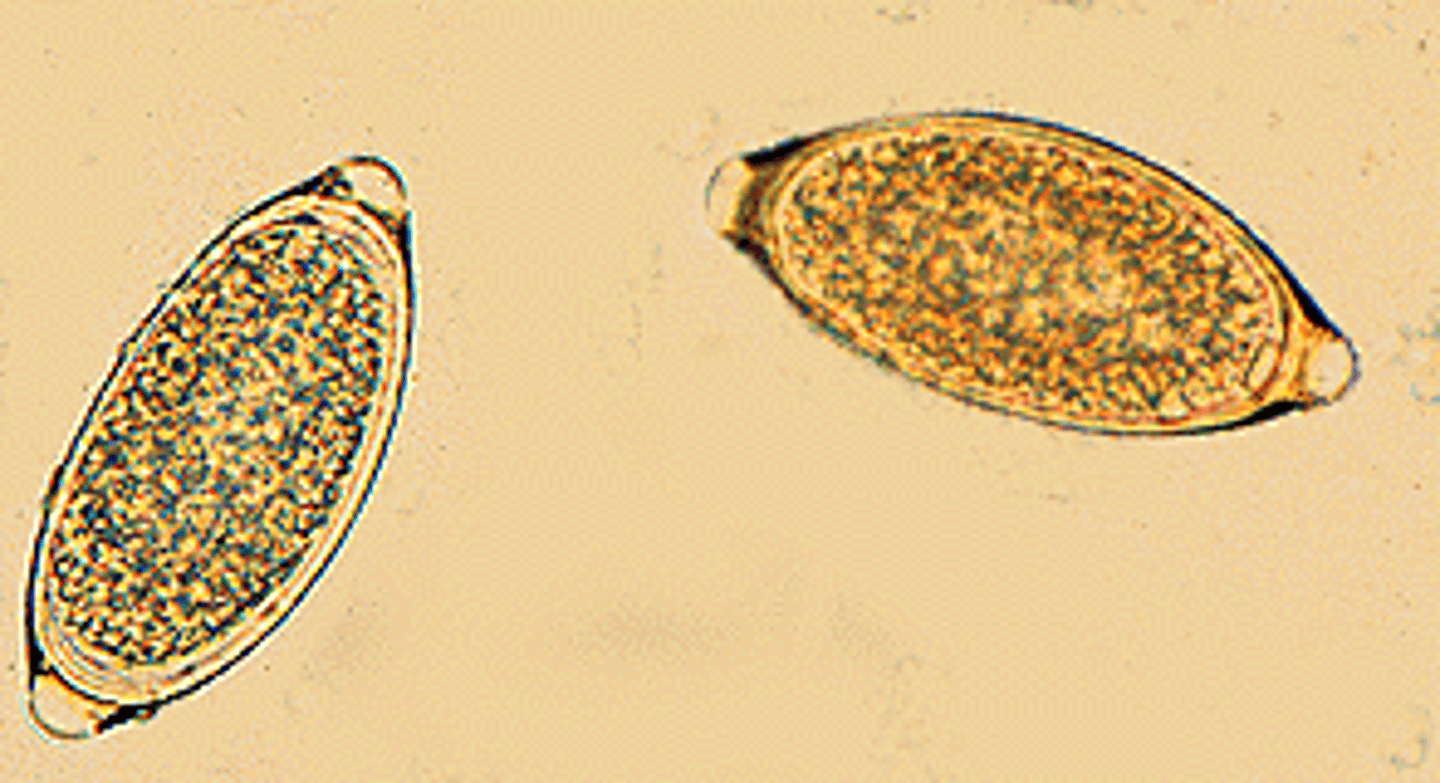
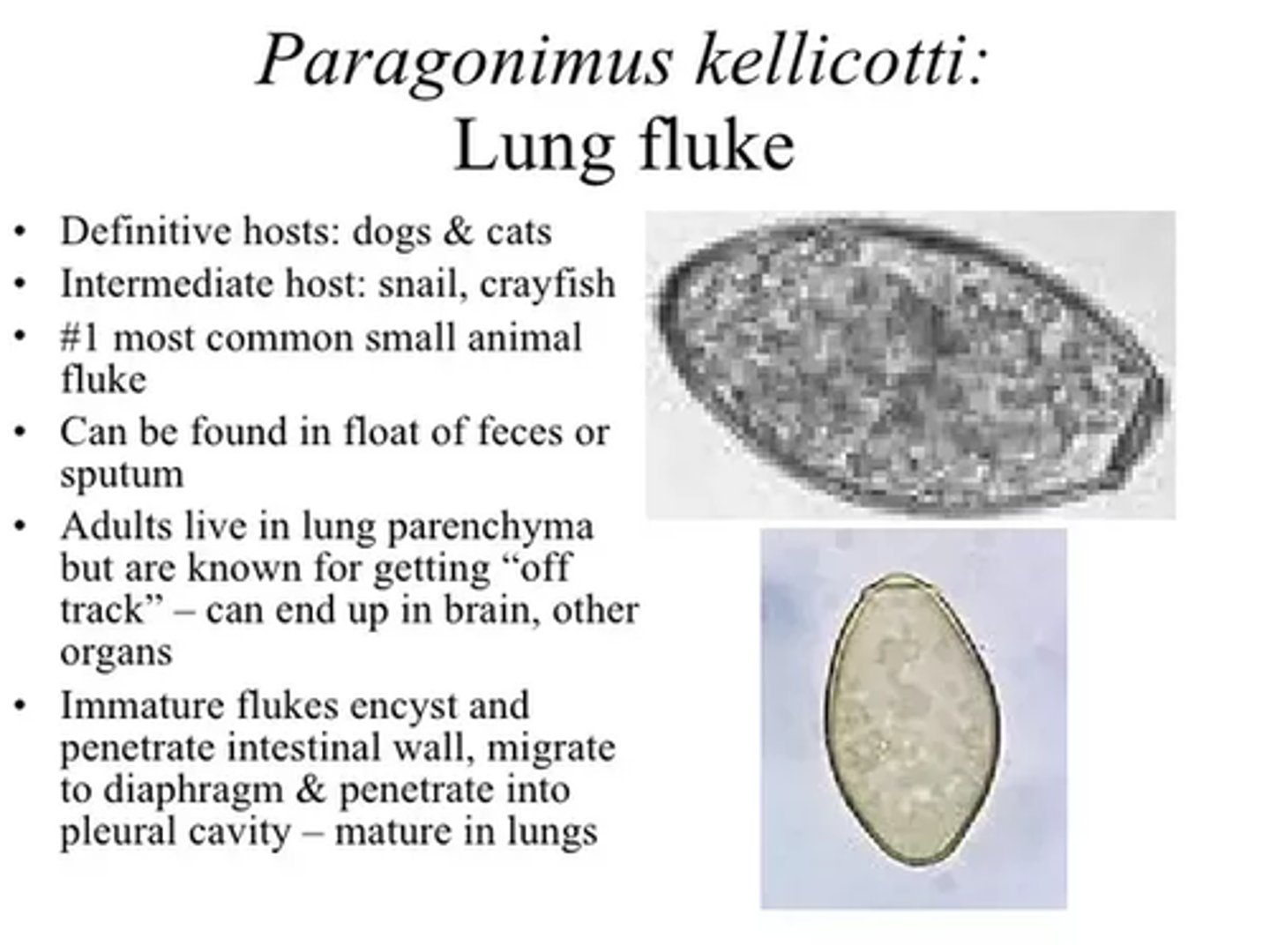
Paragonimus kellicotti (trematode)
egg
Endoparasites and the 4 common types
Parasites that live within the body of their host. Nematodes, Cestodes, Trematodes, Protozoa.
What are Nematodes
they are a phylum of pseudocoelomate worms that are round in shape. over 1 million species, 16K are parasitic. The 5 most common type of nematodes are: ascarids, hookworms, pinworms (threadworms), whipworms, and heartworms.
Ascarids (roundworms)
They are the largest of the roundowrms. There are several common types: Toxocara canis (dogs, humans), Toxocara cati (cats, humans), and Toxocaris leonina (dogs, cats, rodents, humans).
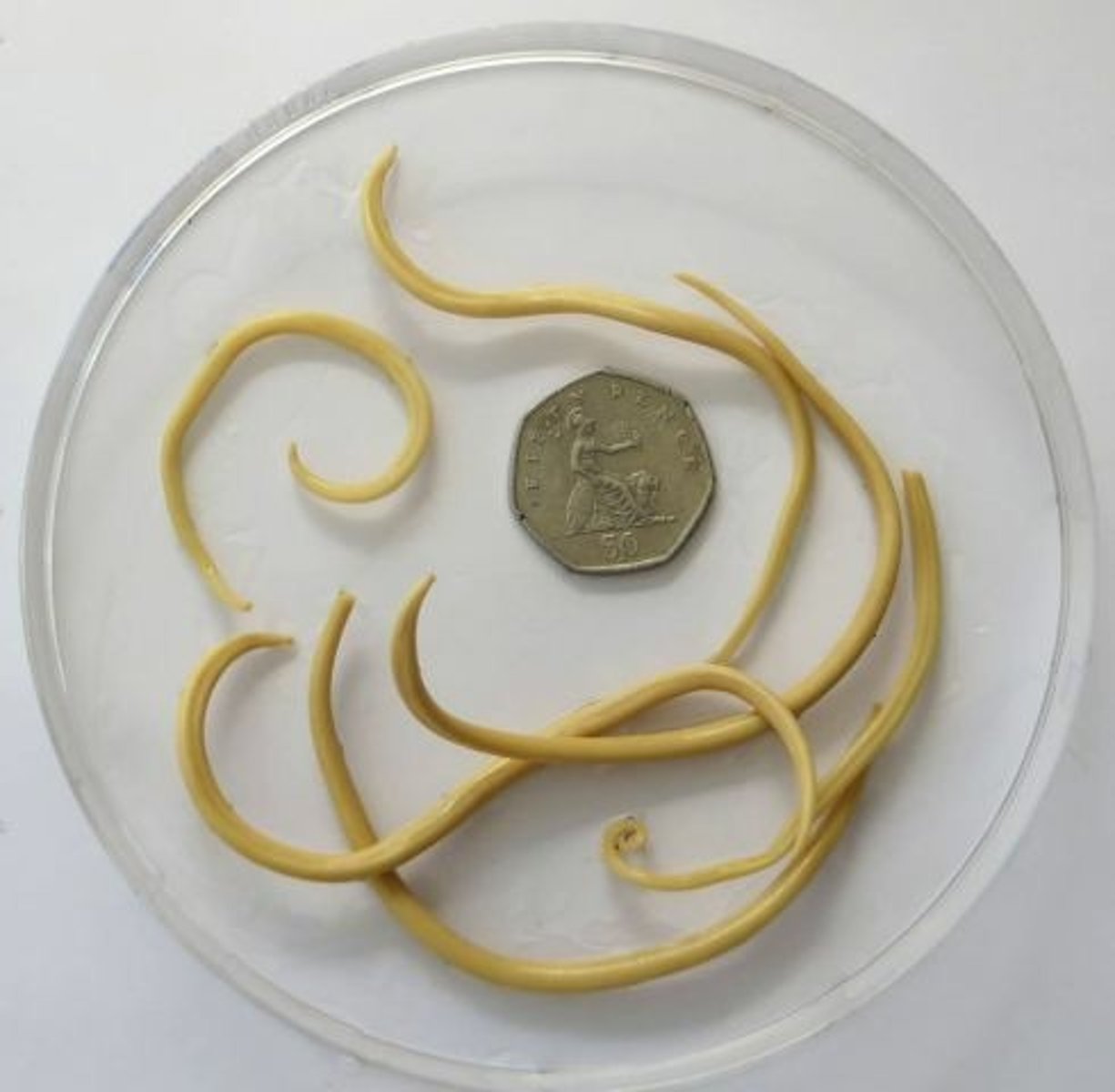
How are ascarids transmitted?
eggs are shed in the feces and milk of an infected host. It can be contracted by ingesting feces, milk, or meat of an infected animal. the eggs are ingested and by the host and will hatch in the small intestines. the larvae will penetrate the mucosa of the small intestine, migrate through the liver, to the heart, and then to the lungs. They will develop further in the lungs to be coughed up and re-swollowed to continue the life cycle.
Symptoms and damage the ascarids can cause
the worms will absorb nutrients from the host, it will interfere with digestion and damage the lining of the GI. Symptoms include diarrhea, vomiting, loss of appetite, malnourishment/thinning, dull coat, and even intestinal blockage. Ascarids may cause neonates to have a very distended abdommen. (pot belly) The neonates can be infected by the miilk from an infected mother. They can also cross the placenta and live inside the fetuses lungs. Almost all neonates are born with roundworms.
How are ascarids diagnosed?
By visualization of eggs in the fecal analysis (float and/or smear) or visible worms in the stool.
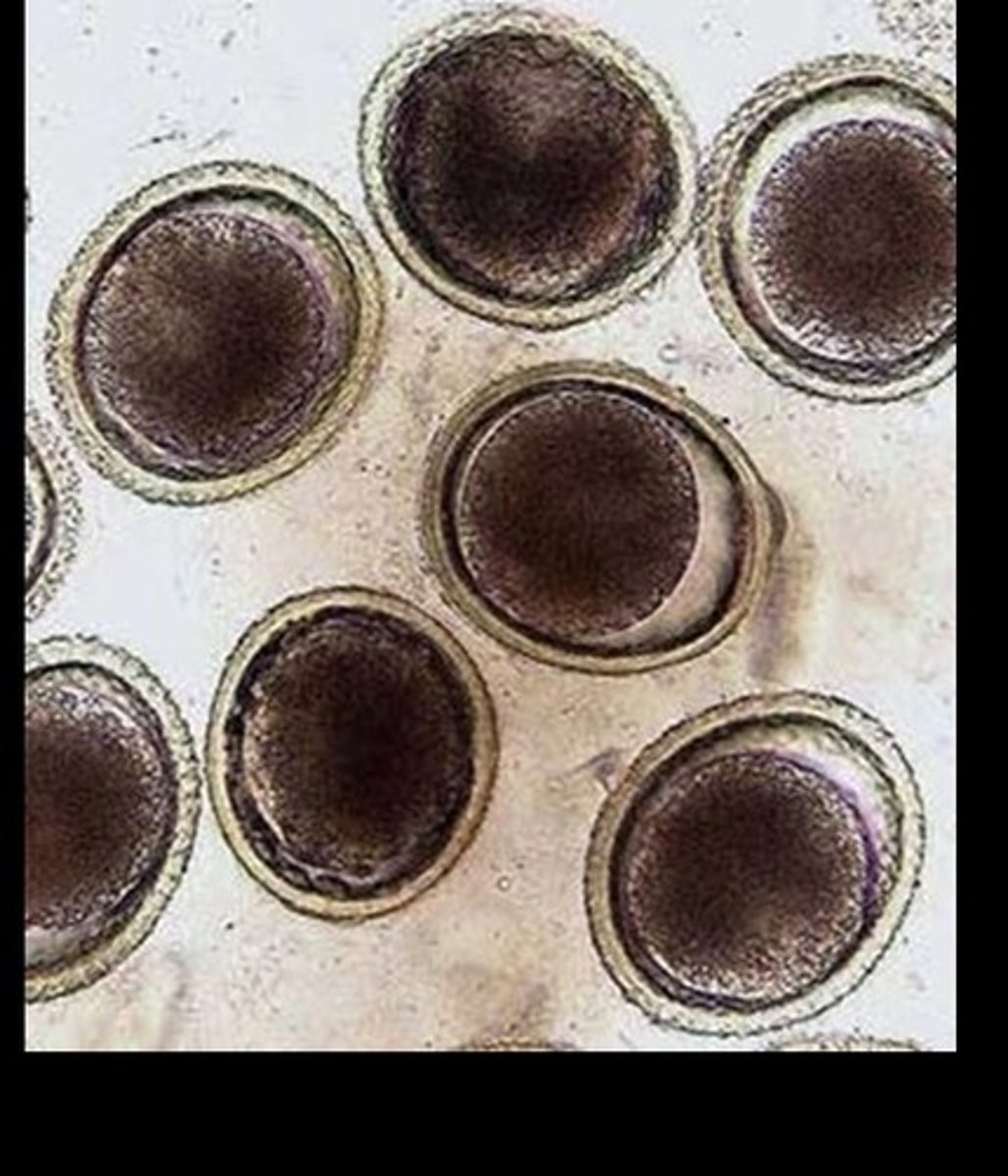
What is a Hookworm and what are the common species
They are small parasitic roundworms that suck blood from the hosts intestinal walls. Ancylostoma caninum (dogs and humans), Anacylostoma braziliense (cats, humans) , Unicaria stenocephala (dogs, cats, humans) , and Ancylostoma tubaeforme (cats).
How are hookworms transmitted and what do they do?
they penetrate the skin, then enter the venous circulation, going to the lungs. They migrate to and develop/ in the lungs wo be caughed up and swallowed. Symptoms include: diarrhea, coughing / pneumonia, hemorrhage / anemia, creeping eruptions of severe pruritus as a result of the cutaneous larva movement.
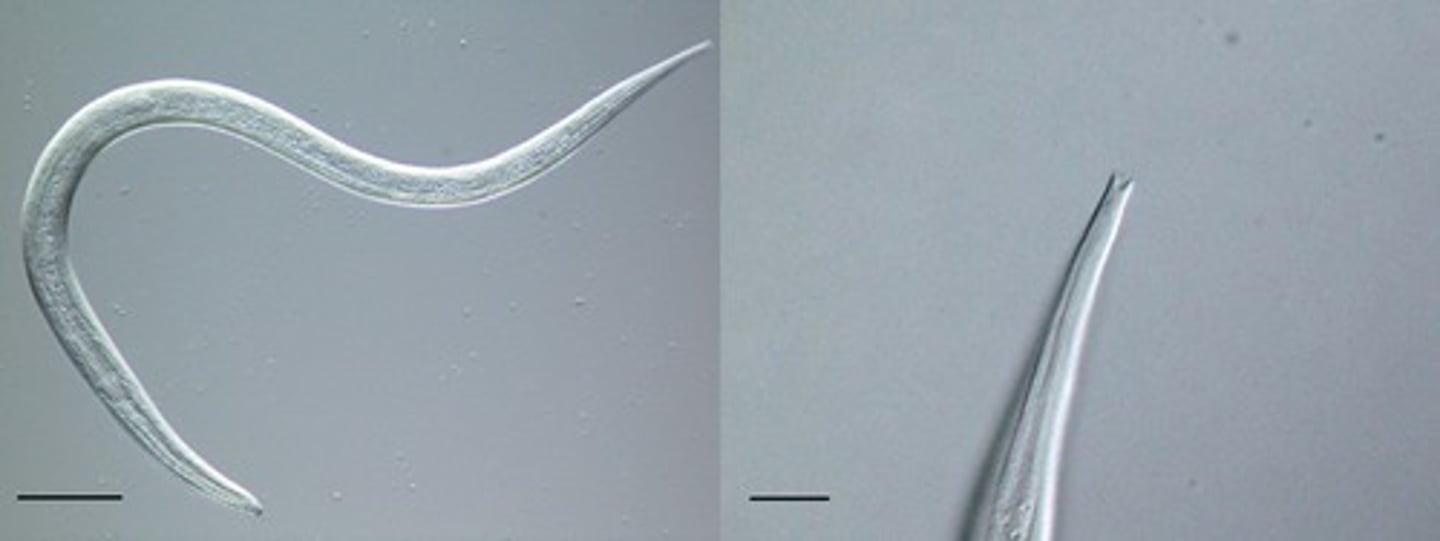
How are hooks worms diagnosed?
By visualization of eggs in a fecal analysis (floating and/or smear)
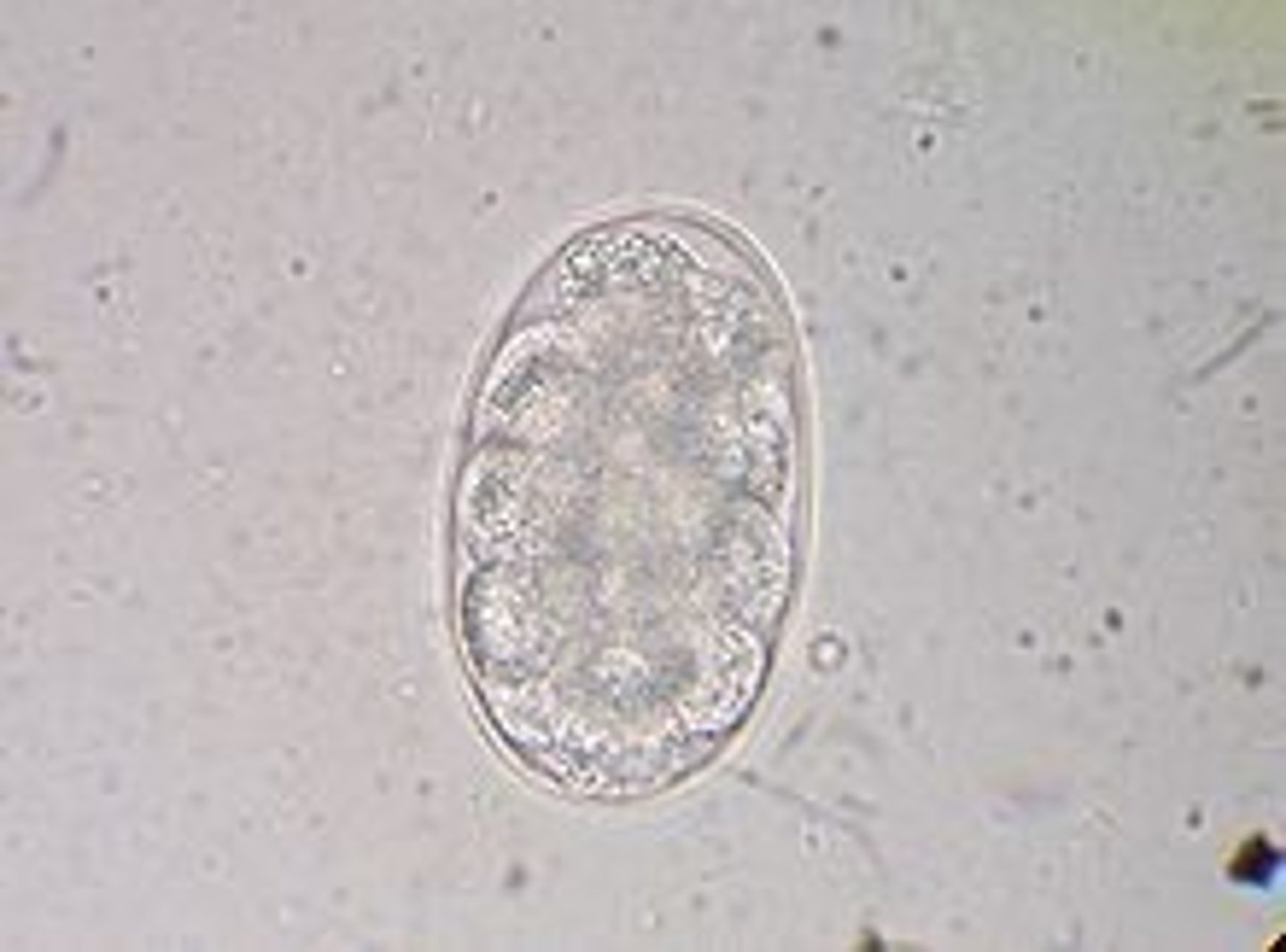
What are Whipworms?
they are parasitic worms with a thick tail and a whip-like body that infects the large intestine of the host. Trichuris Vulpis is a common type of whipworm that infects K-9s. Dogs, humans, pigs, rodents, and cats (rare) can get whipworm.
What do whipworms do and how are they diagnosed?
the eggs are ingested and the larvae are released into the intestines. they will penetrate and implant themselves into the mucosa of the small intestines where they develop for 2 weeks. they will travel through the large intestine where they attach, feed, and reproduce. they are diagnosed by the visualization of eggs in a fecal analysis (float and/or smear)
What is a Pinworm (threadworm)?
a small parasitic nematode that is similar to the hookworm. The strongyles species are often reffered to as strongyles. There are 3 types: strongyloides canis (dogs), strongyloides stercoralis (dogs, cats, humans), strongyloides westri (horses)
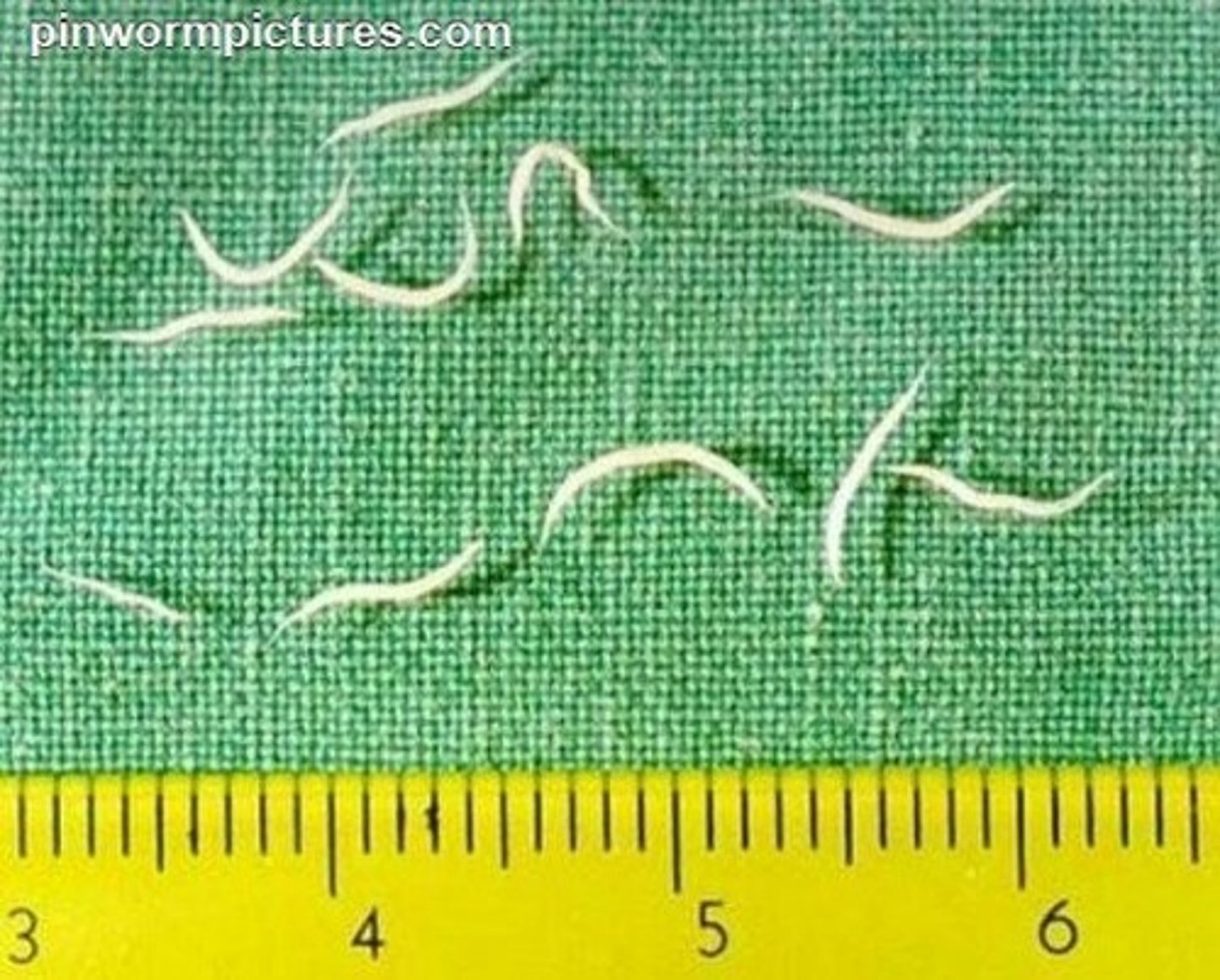
How are pinworms transmitted, what do they do, and how are they diagnosed?
eggs and larvae are shed inn the feces of infected hosts. contracted via skin penetration or larvae or eggs. they will migrate to the lungs to be coughed up and swollowed to continue the life cycle. they are diagnosed by the visualization of eggs in a fecal analysis (floating and/ or smear)
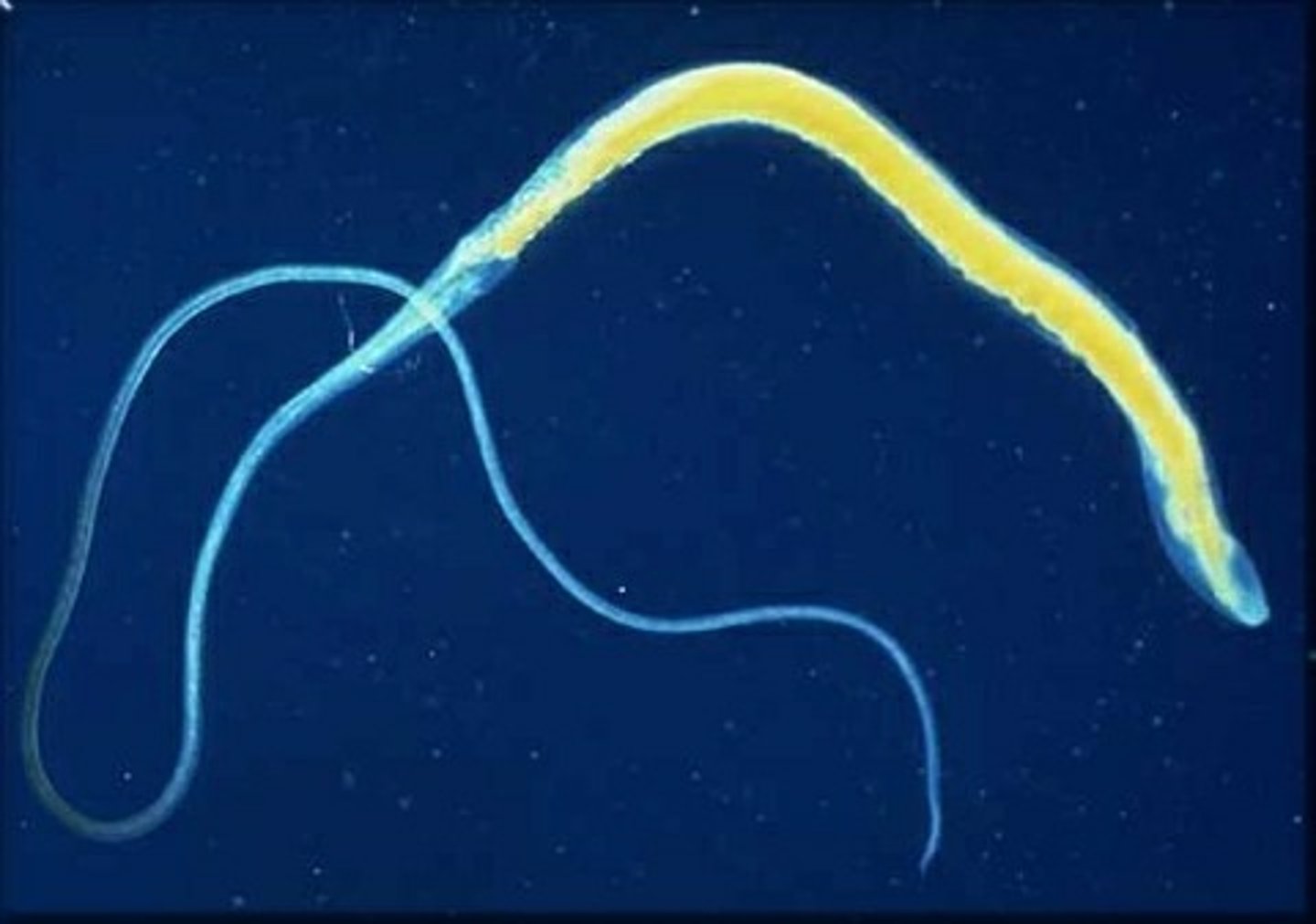
Disofilaraia Immitis (HEARTWORMS)
a parasitic nematode that resides in the circulatory system. mosquito is the vector for heartworm. Dogs and cats (rare) can get heartworms. It is transmitted via mosquito. the juvinile form (microflaria) is carried by infected mosquitos. once transmitted the microflaria will grow and develop into adult worms and reside in the heart and lung arteries.
Symptoms, diagnosing, and treatment for heartworms
symptoms can include coughing, exercise intolerance, and heart failure. it is diagnosed by checking for microfilariae in the blood smear. it is most easily detected by blood analysis checking for the heartworm antibody. (heartworm snap test) heart worms can take up to 6 months once infected to come out in tests. this is controlled by mosquito preventative medication and mosquito control. actual infestations are treated with microfilaricide and adulticide.
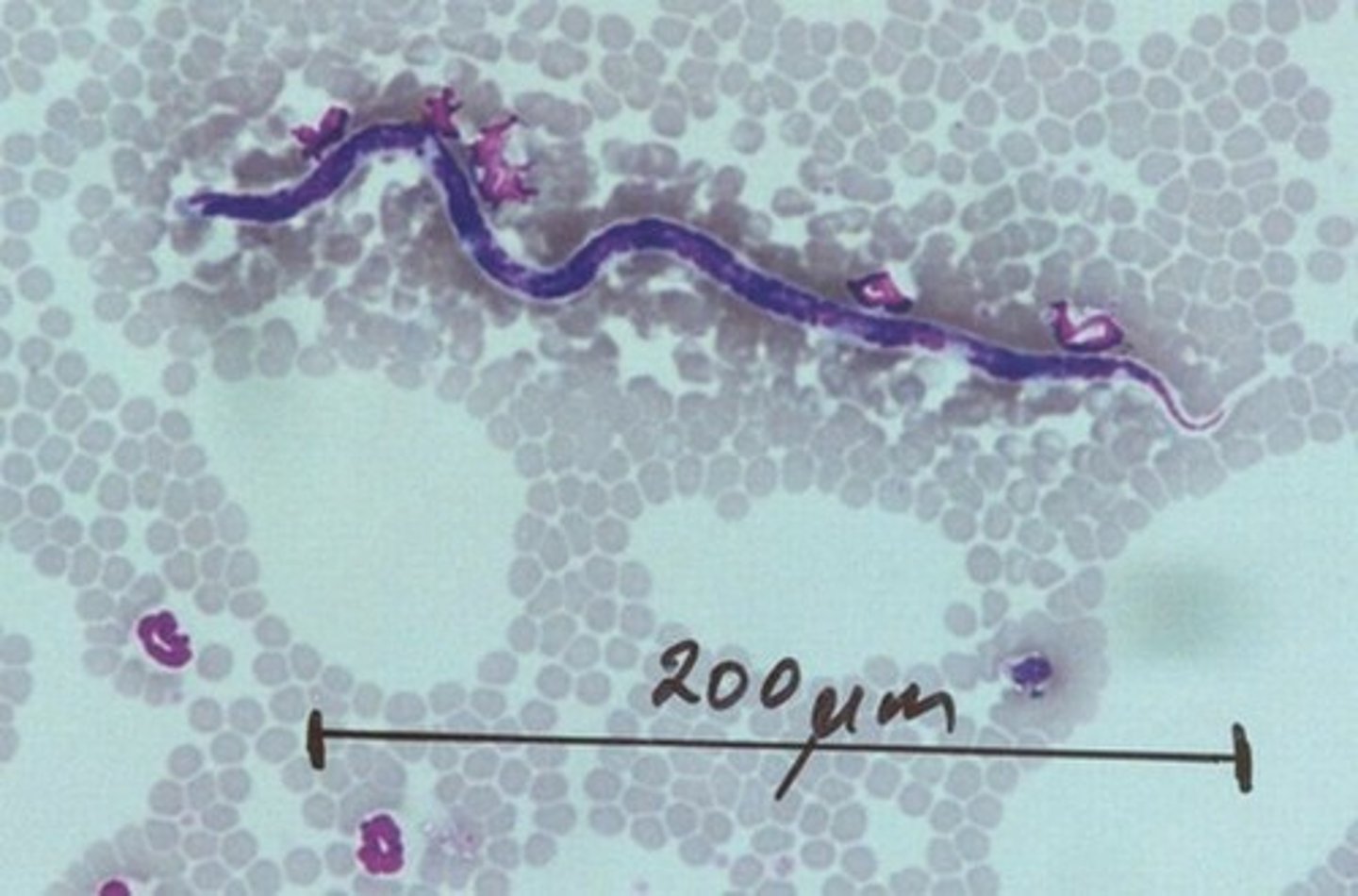
What are Cestodes (tapeworms)
they are segmented flat worms that are only found in the intestines of their host. (TAPEWORM SEGMENTS ARE CALLED PROGLOTTIDS) each proglottid contains both male and female sex organs and can reproduce on their own. each once contains thousands of egg packets that can hatch up to 30 new tapeworms.
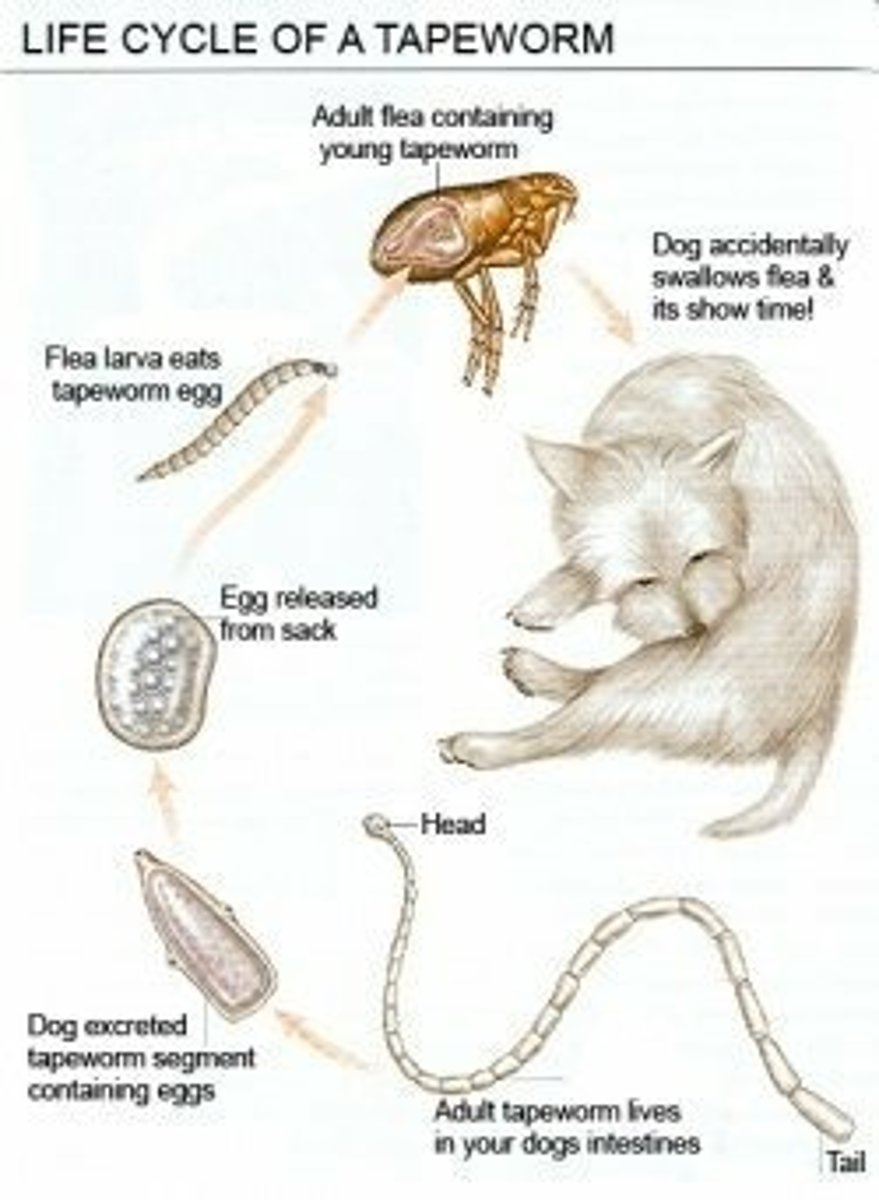
What are the common types of tapeworms, how are they transmitted?
2 common types (dipylidium caninum, and several members of the taenia genus) dogs, cats, and humans can get them. they are transmitted when a proglottids break off from the original worm and are shed in the feces. once they come into contact with dry air, the proglottids will release their egg packets. Dipylidium caninum tapeworms are contracted by ingesting infected fleas. the flea is the intermedite host. Taenia tapeworms are contracted by ingesting infected animals, like rodents.
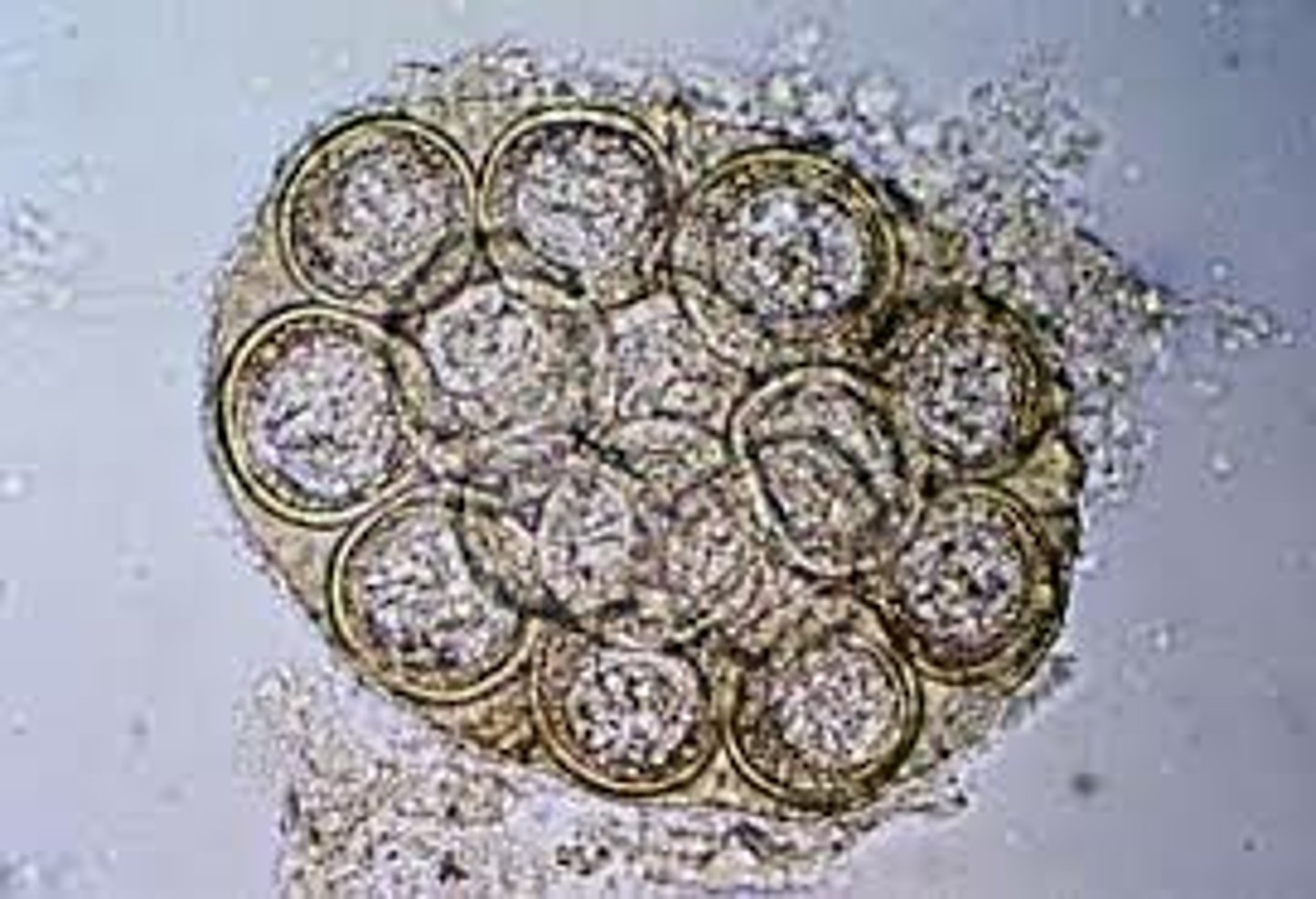
What are Trematodes (flukes)
unsegmented flat worms with leaf-shapped bodies. they invade either the blood, or the tissue. most are found in the intestinal tract, liver, and lungs. commonly found in cattle and sheep (some species can infect humans)
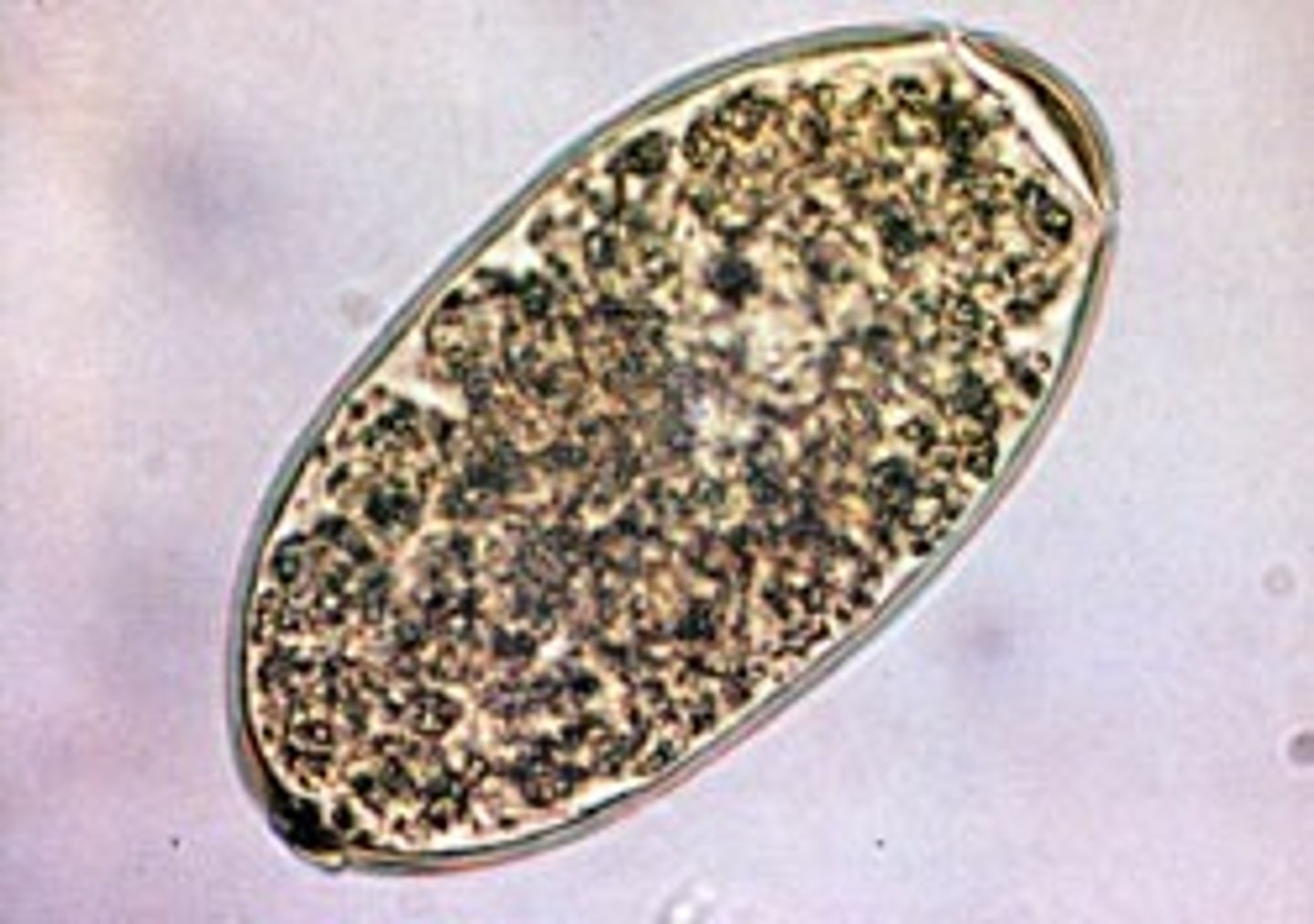
What are protozoa
unicellular (one cell) organisms. can reside in the blood, tissues, or GI tract. common types are Giardia and several subclass Coccidia.
Giargia Lambia
water-borne protozoa that infects the small intestines. it has 2 life stages: cyst (egg) and trophozoite (motile feeding form. (THE CYST FORM IS INGESTED AND DEVELOPS INTO THE TROPHOZOITE IN THE SMALL INTESTINE) This is commonly found in cats, dogs, humans, and beavers (beaver fever) It is also found most common in young dogs or cats in a shelter setting.
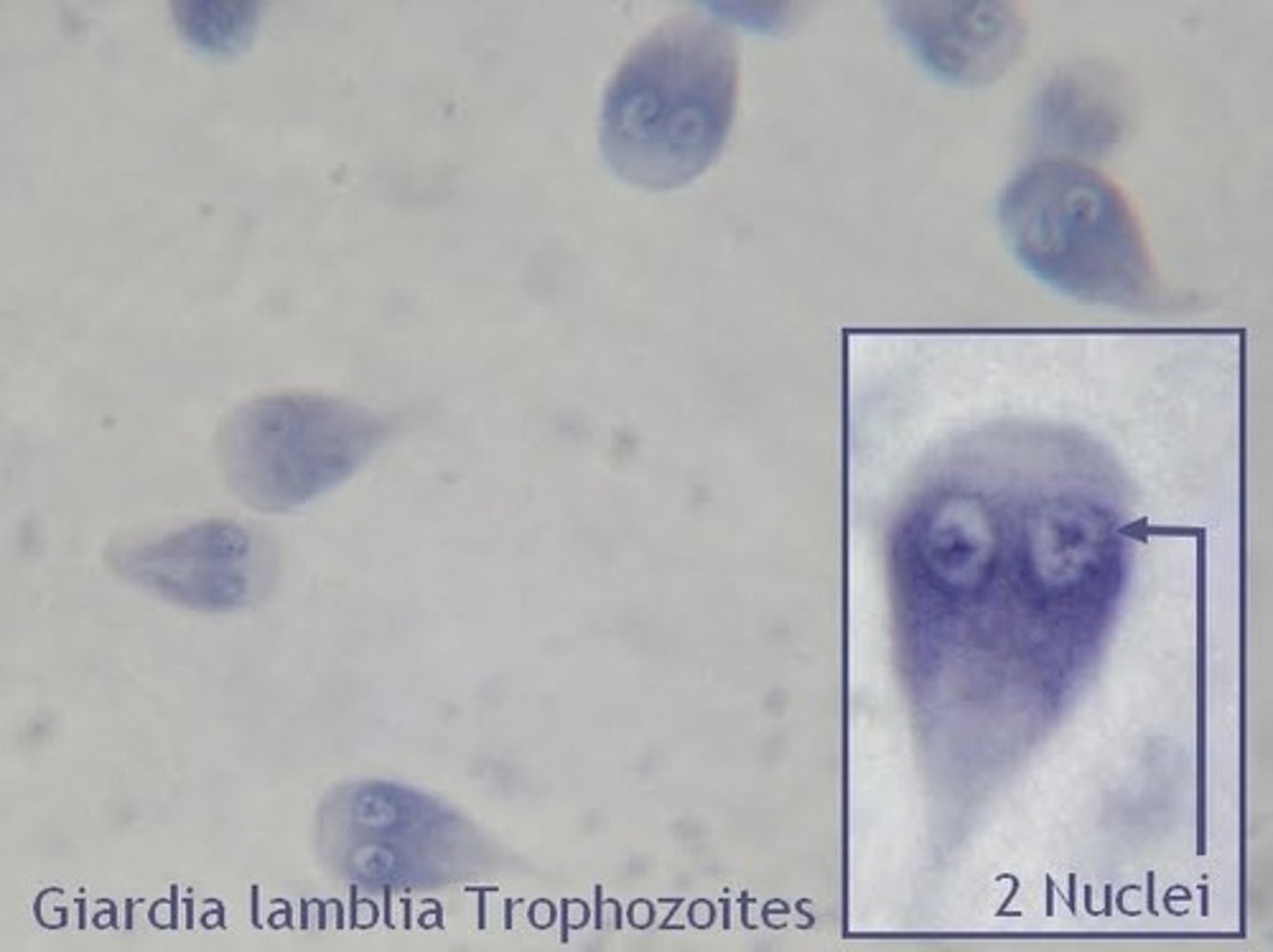
How is Giardia Lamblia transmitted, diagnosed, and what does it do?
the cysts are shed in the feces. Giardia is contracted through ingestion of contaaminated water or feces. Giardia can often be asymptomatic, but it can cause vomiting, foul-smelling diarrhea, and loss of appetite. It is diagnosed via direct smear or SNAP test. the prepatent period for a cyst is 5 days. Giardia is one of the smallest intestinal parasites and should be seen using a 40x objective lense. Throphozoites are ususally only seen whhen the patient is experiencing runny stool because they do not have traction to stay within the GI system.
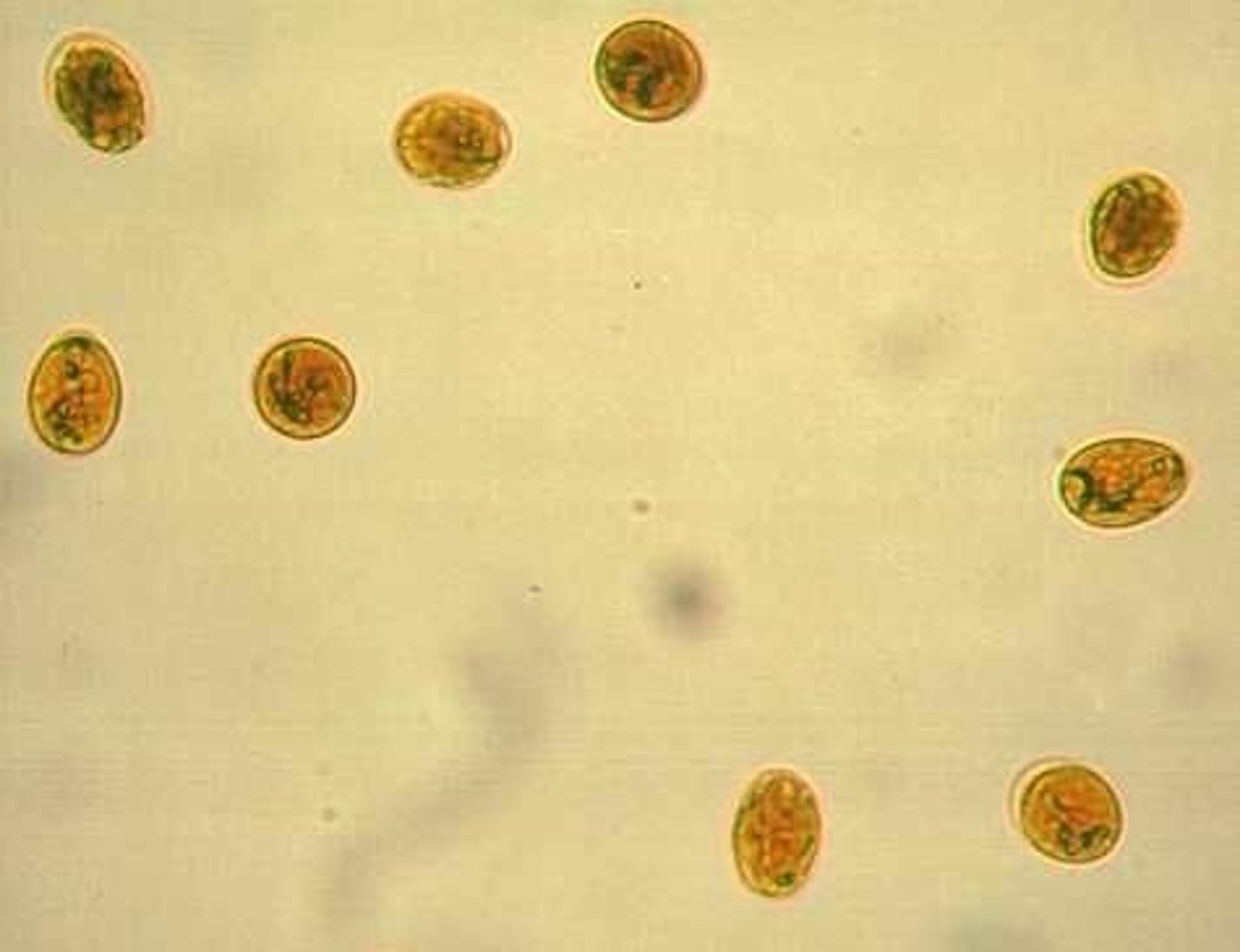
What is a Coccidia
a class of sporulating protozoa that releases oocysts into the enviroment from the hosts body. (the oocysts are very hardy and can survive a long period of time in water)
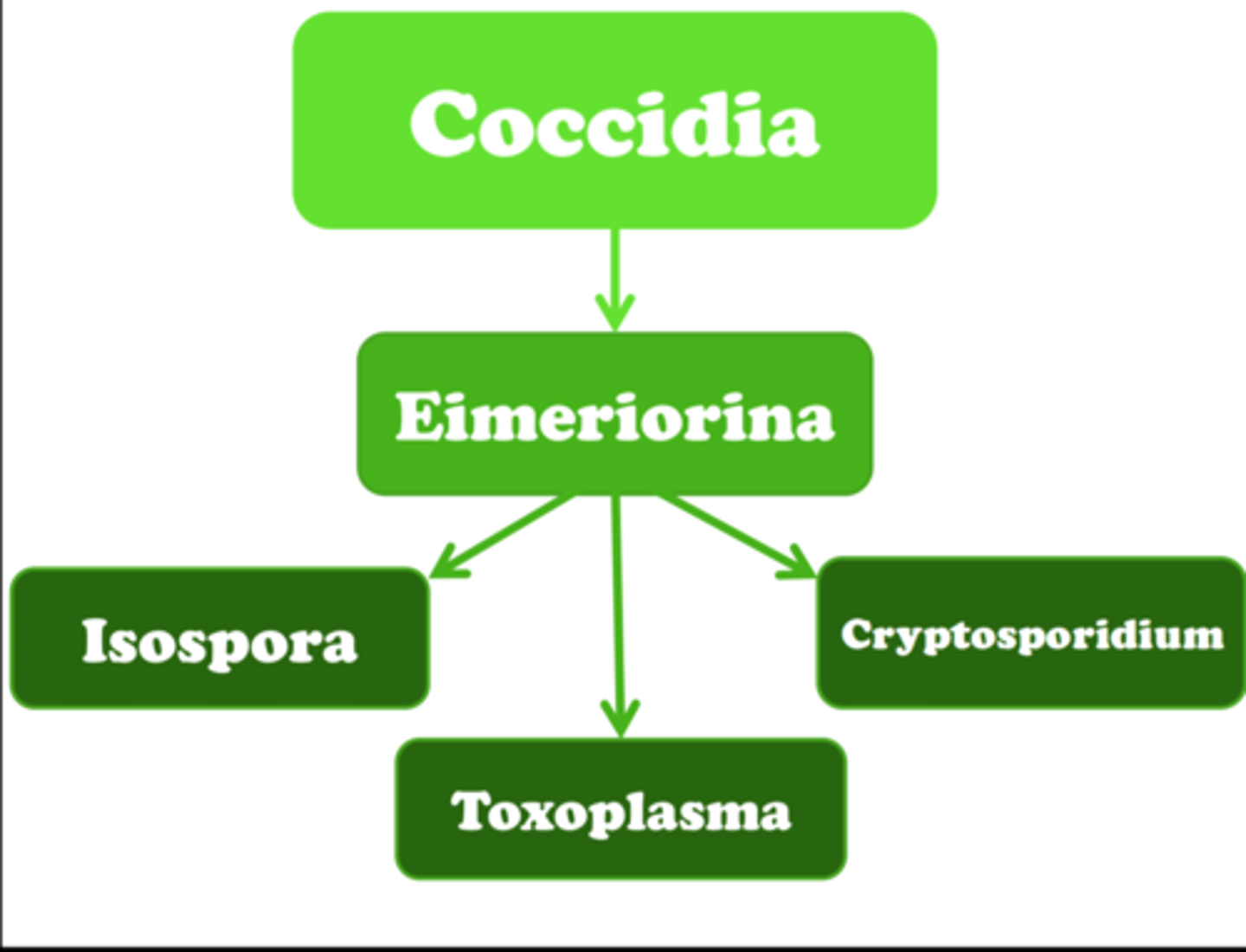
Coccidia --> Eimeriorina
eimeriorina is a suborder of the subclass coccidia. the most common coccidian parasites are members of eimeiorina: Isopora spp. Toxoplasma gondii. Cryptosporidium spp.
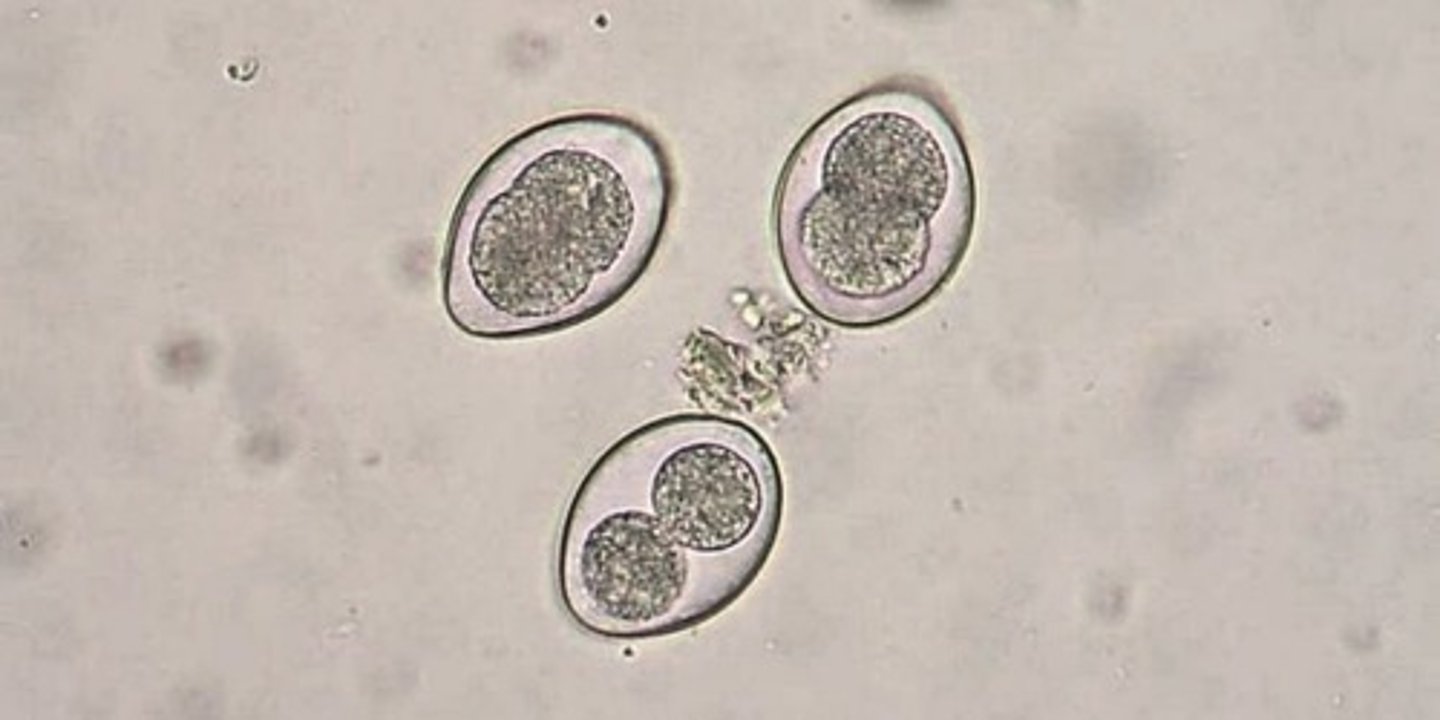
What is Isospora?
a coccidia species, most common type. 2 major types of isopora are Isospora Canis (dogs) and Isospora Felis (cats). It causes watery diarrhea, several infections can lead to blood in the stool. It is diagnosed by the visualization of oocytes on fecal smear/floatation.
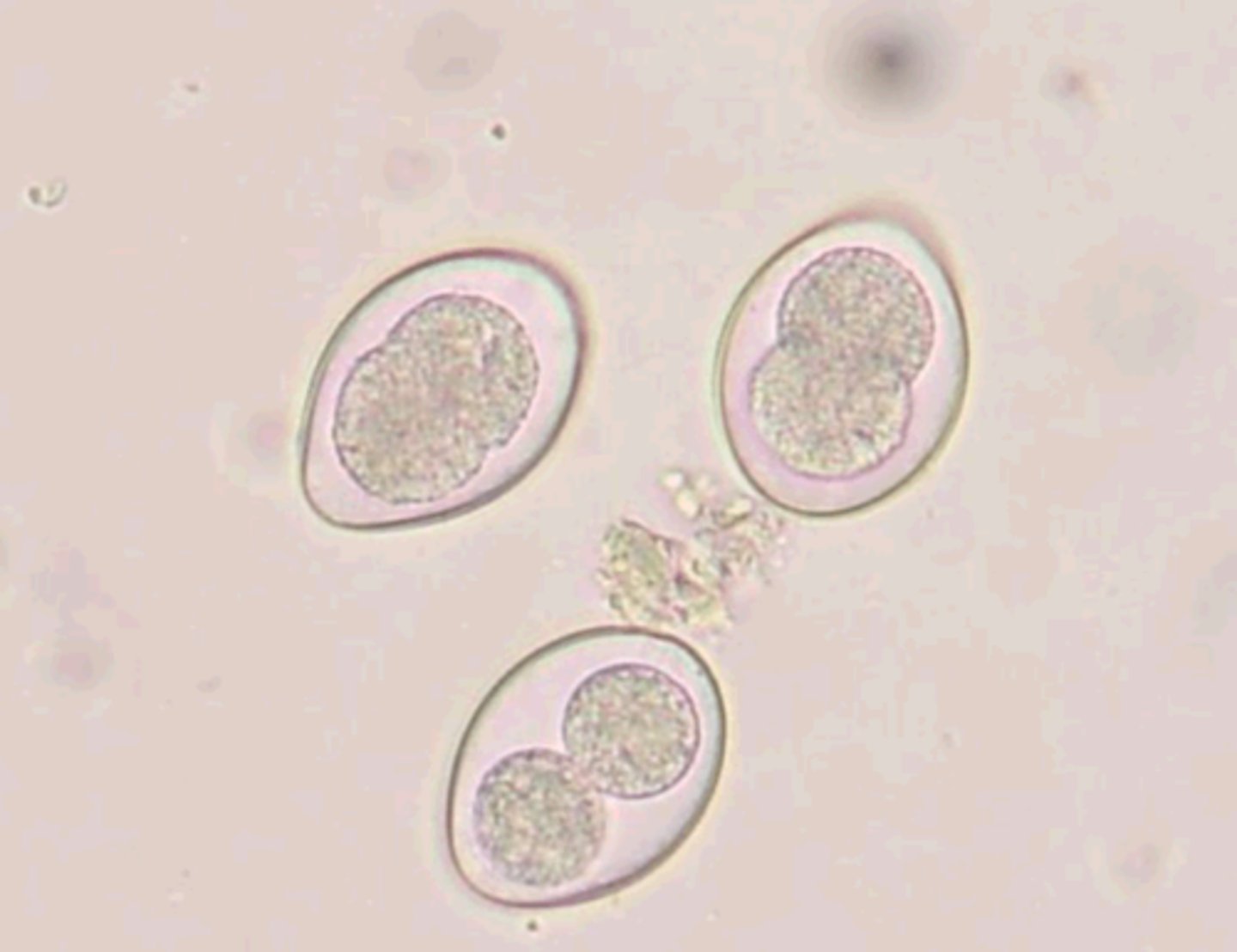
What is Toxoplasma Gondii
is a subclass of Coccidia. it is a prasitic protozoa that infects the GI tract of the obligate host and the tissues of the intermediate hosts body. cats are the definitive host for the unsporulated stages, rodents and birds are the ideal inntermediate host. Most mammals including humans are incidental or dead-end hosts. cats are uneffected by the parasite. in other hosts they migrate to tissues in the body causing an infection. the infection in a pregnant human can cause harm to a fetus.
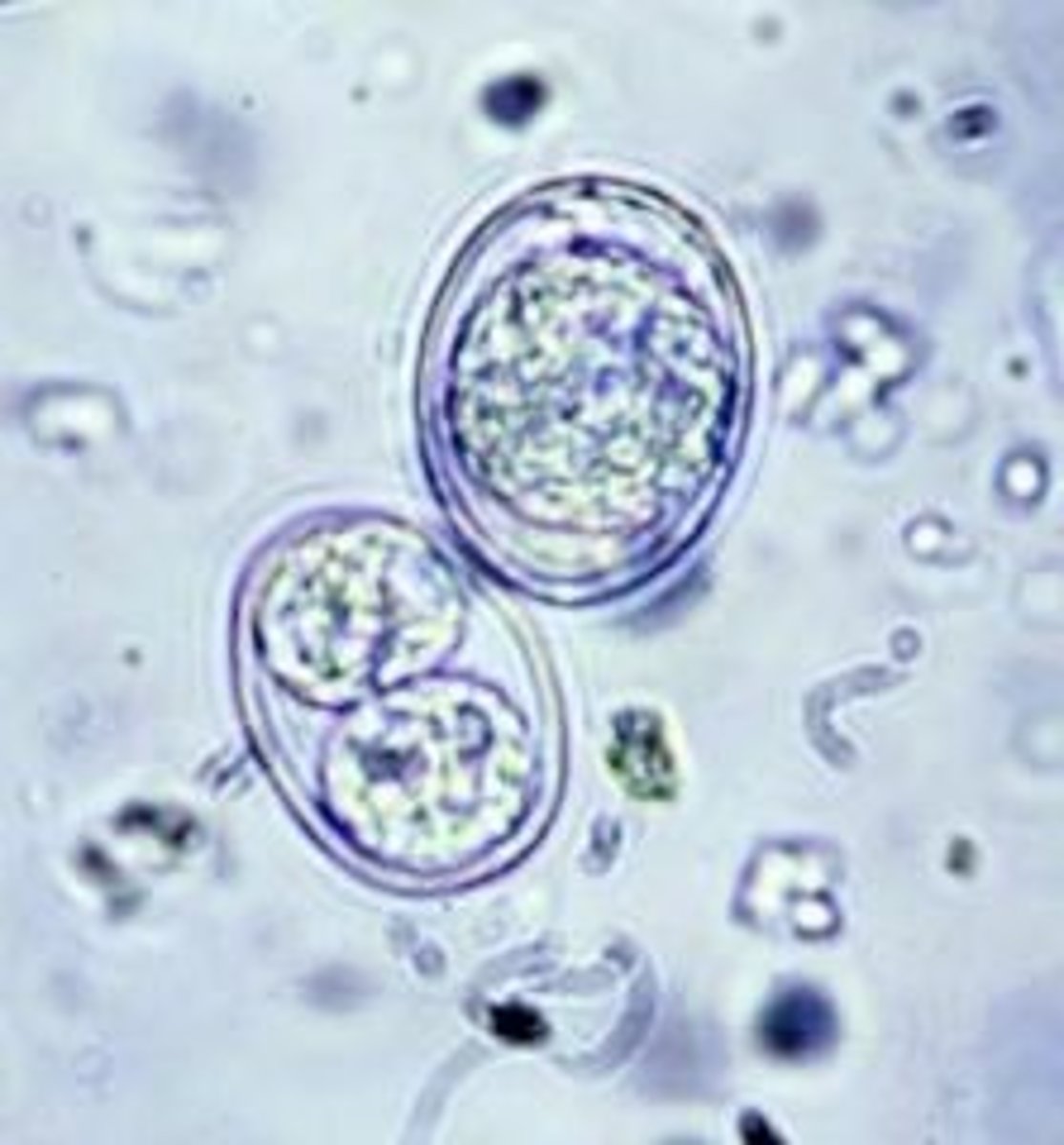
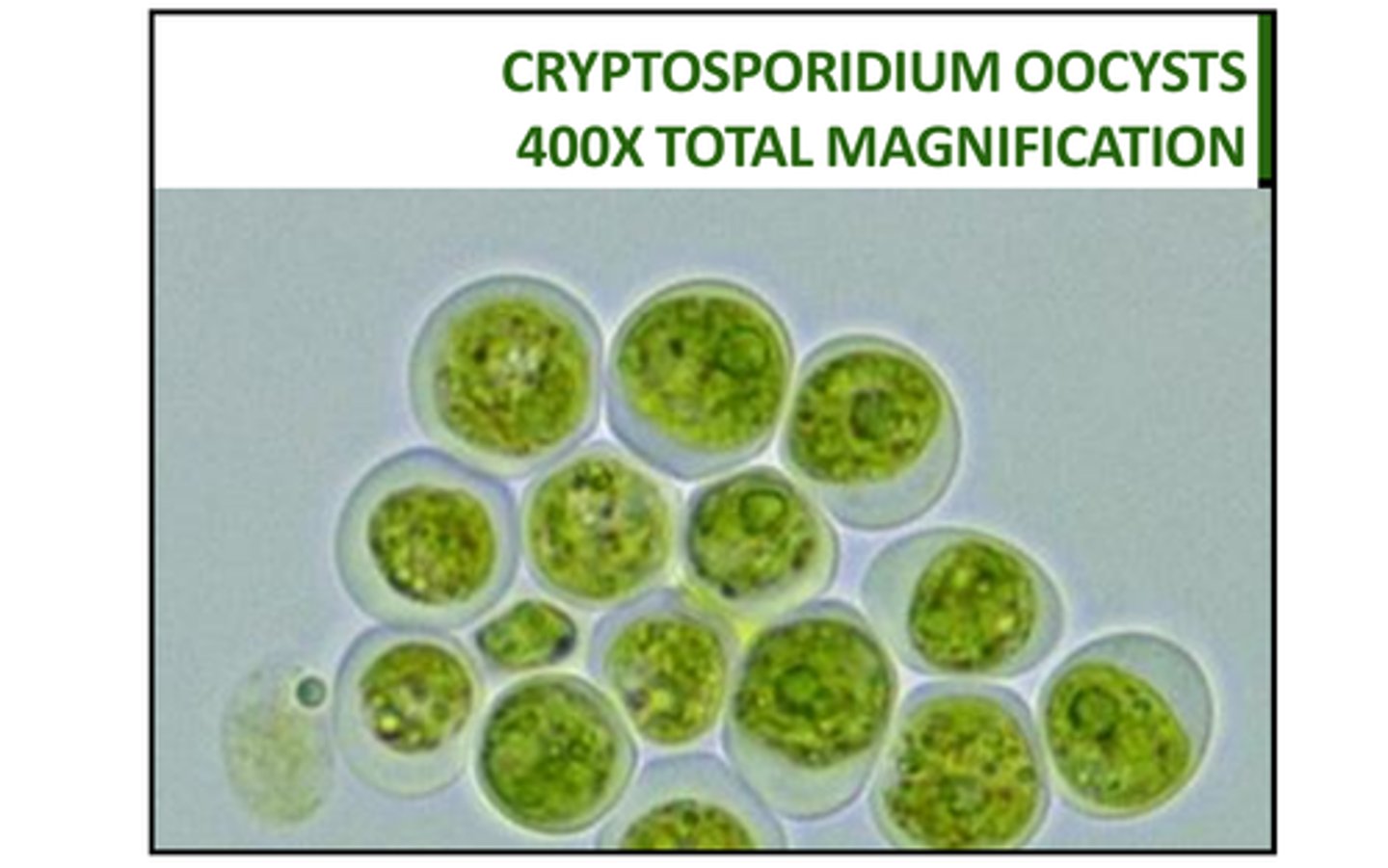
What is Cryptosporidium
primarily a water-borne protozoa, very hardy, resistant to chlorine. common in young ruminants, humans, dogs, cats, cattle, sheep, goats. is becoming an issue in reptiles (1 cause of death in calves in the 90s). Oocytes are shed in the feces of the animals, it is commonly contracted by ingesting the contaminated water or feces. it can cause acute diarrhea so death is common by this from dehydration. most cattle devlop a resistance to this bacteria after 1 month of age. it is diagnosed by the visualization of the oocysts in a fecal sample after a 5-7 day prepatent period. commonly left untreated in livestock and self-limiting in humans.