Ap Psych unit 3B
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
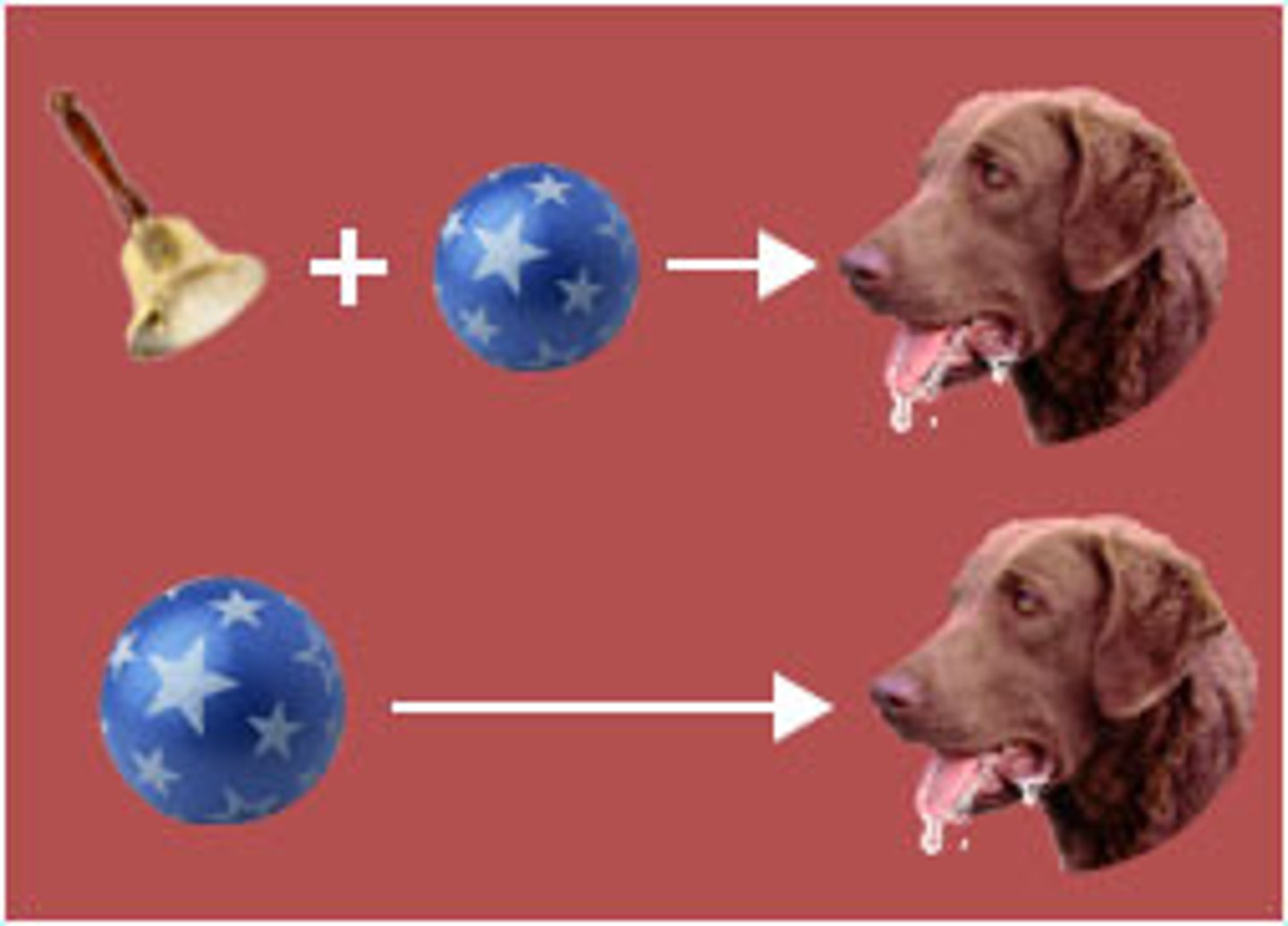
Habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation
associative learning
linking two stimuli, or events, that occur together
adverse conditioning
Associates unpleasant state with unwanted behaviour
biological preparedness
animals are biological predisposed to learning some stimulus

Discrimination
in classical conditioning, the learned ability to distinguish between a conditioned stimulus and stimuli that do not signal an unconditioned stimulus
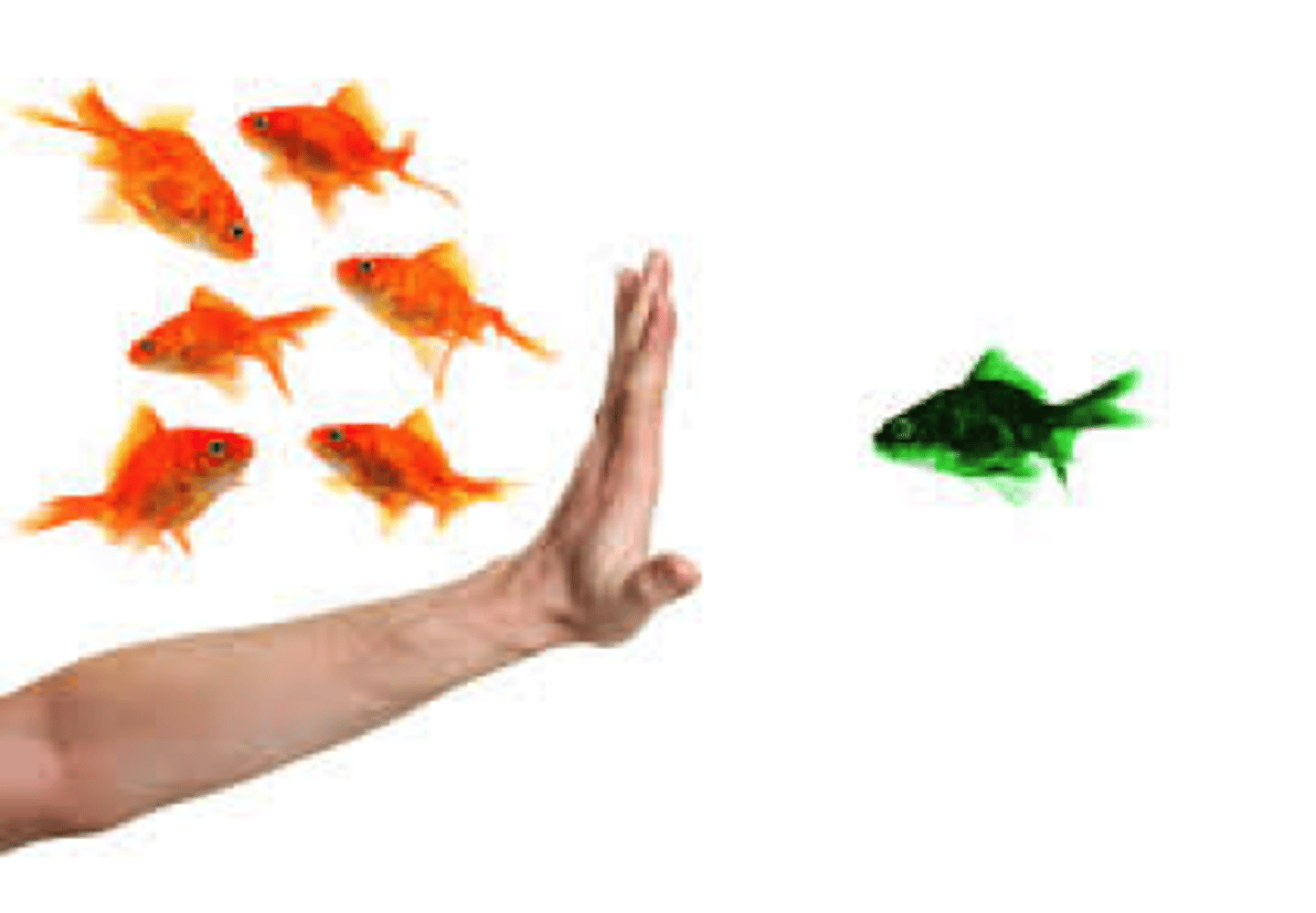
Generalization
the tendency, once a response has been conditioned, for stimuli similar to the conditioned stimulus to elicit similar responses

insight
a sudden realization of a problem's solution

latent learning
learning that occurs but is not apparent until there is an incentive to demonstrate it

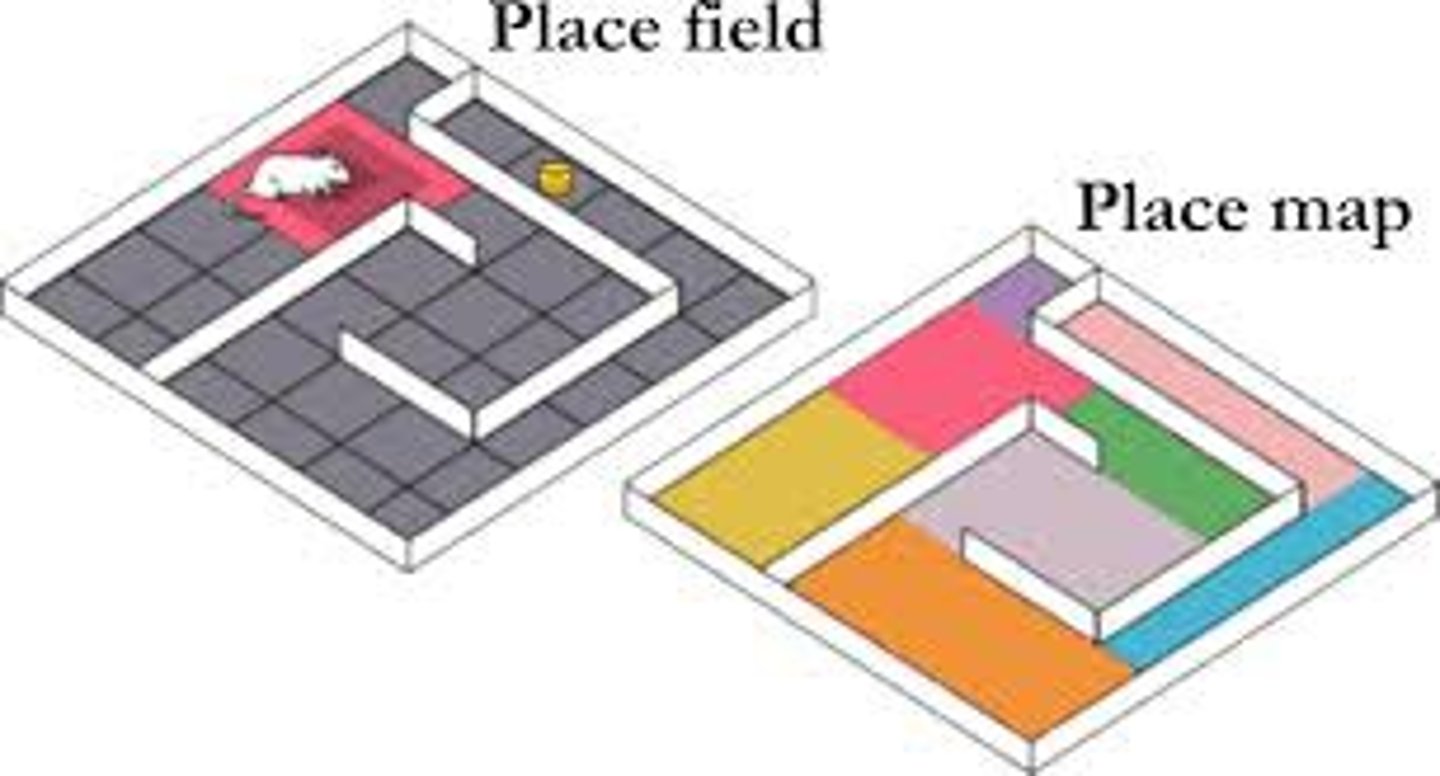
cognitive map
a mental representation of the layout of one's environment
mirror neurons
Frontal lobe neurons that fire when performing certain actions or when observing another doing so. The brain's mirroring of another's action may enable imitation, language learning, and empathy.

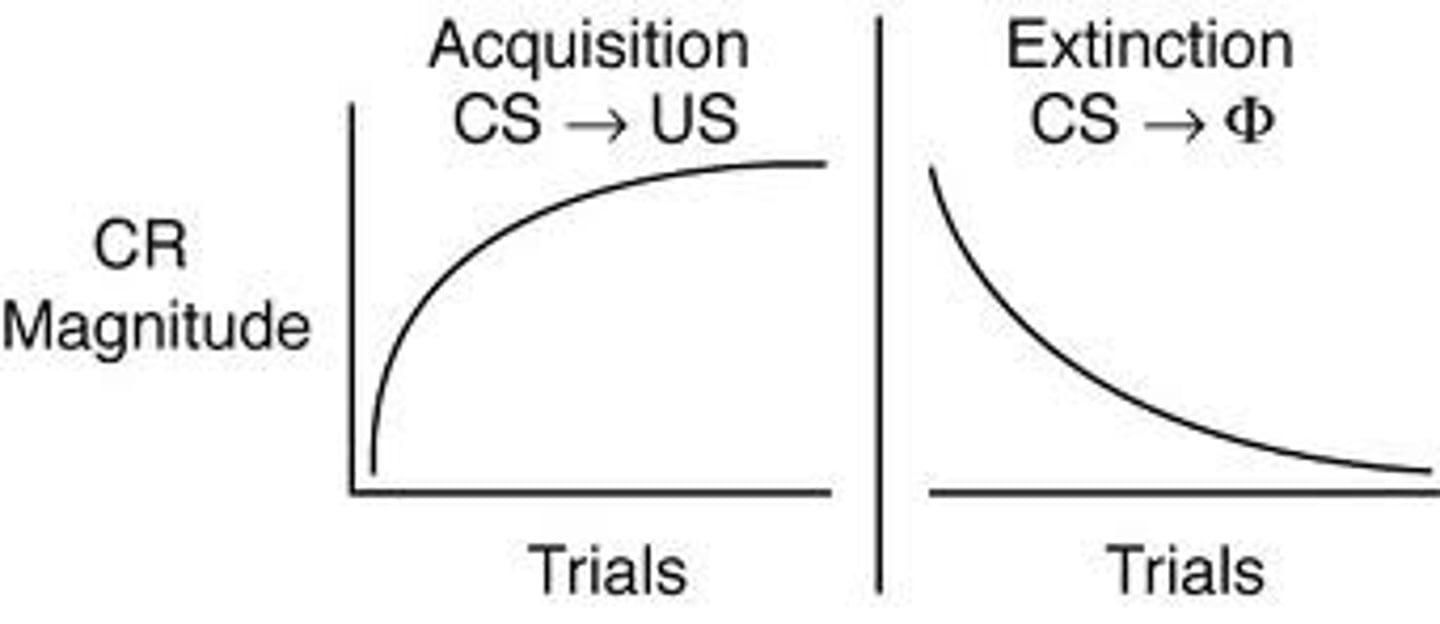
acquisition
learning of an association
one trial learning
when conditioning occurs after a single experience involving relatively intense fear, pain, or sickness

respondent behavior
occurs as an automatic response to some stimulus

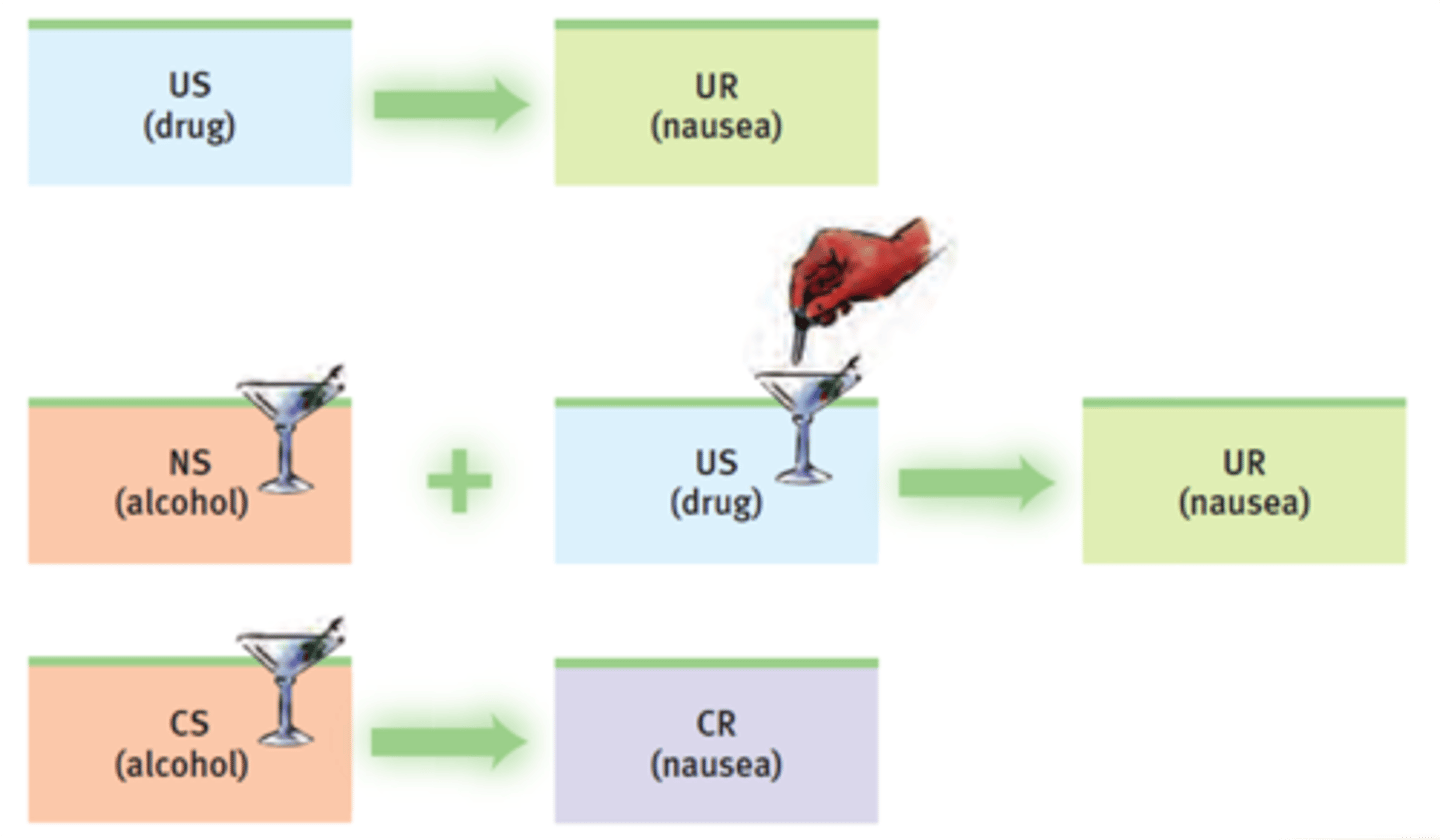
neutral stimulus
a stimulus that elicits no response before conditioning

unconditioned stimulus (UCR)
natural (unlearned) behavior to a given stimulus

unconditioned response
In classical conditioning, the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus (US), such as salivation when food is in the mouth.
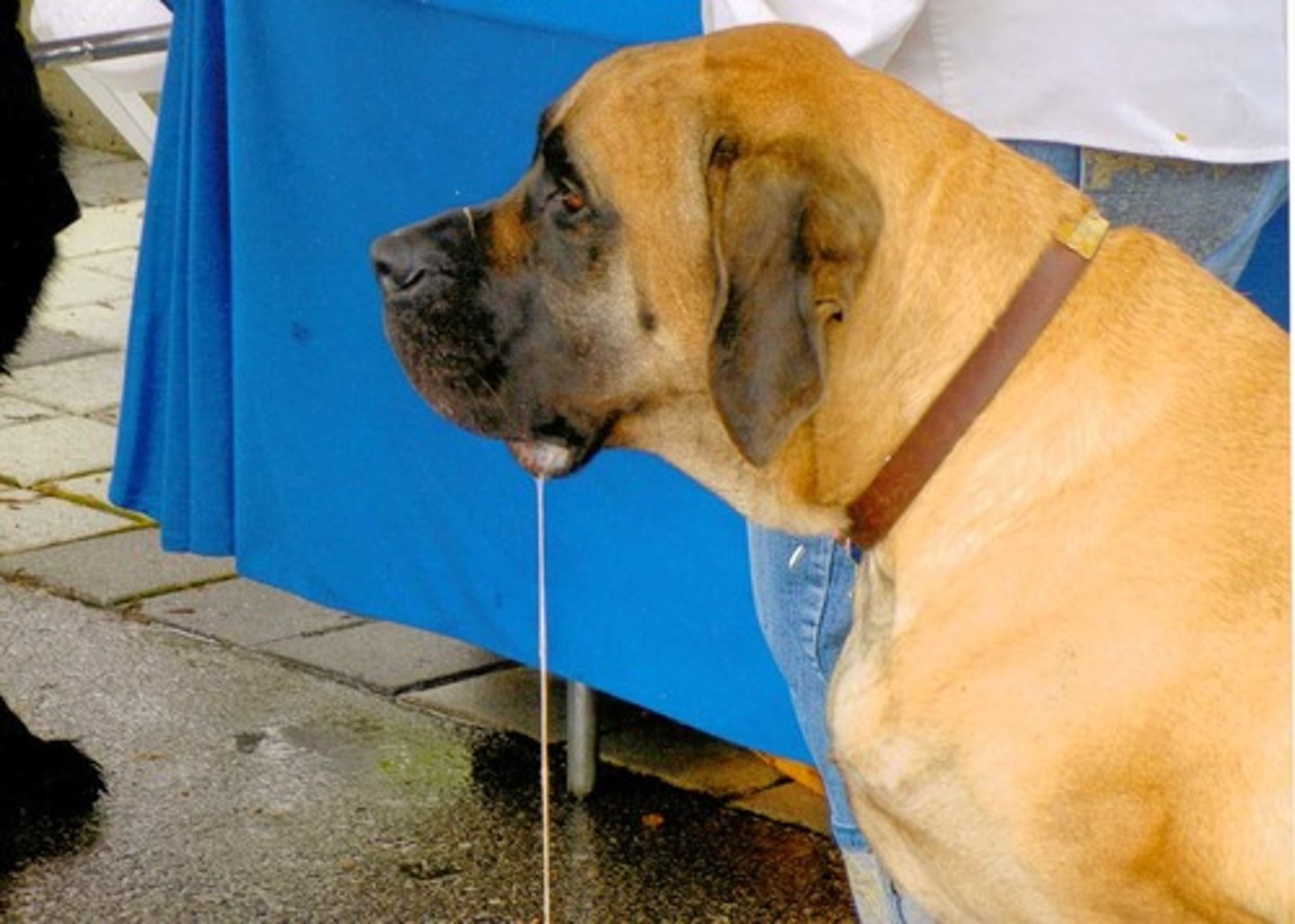

conditioned stimulus
a stimulus that elicits a response only after learning has taken place

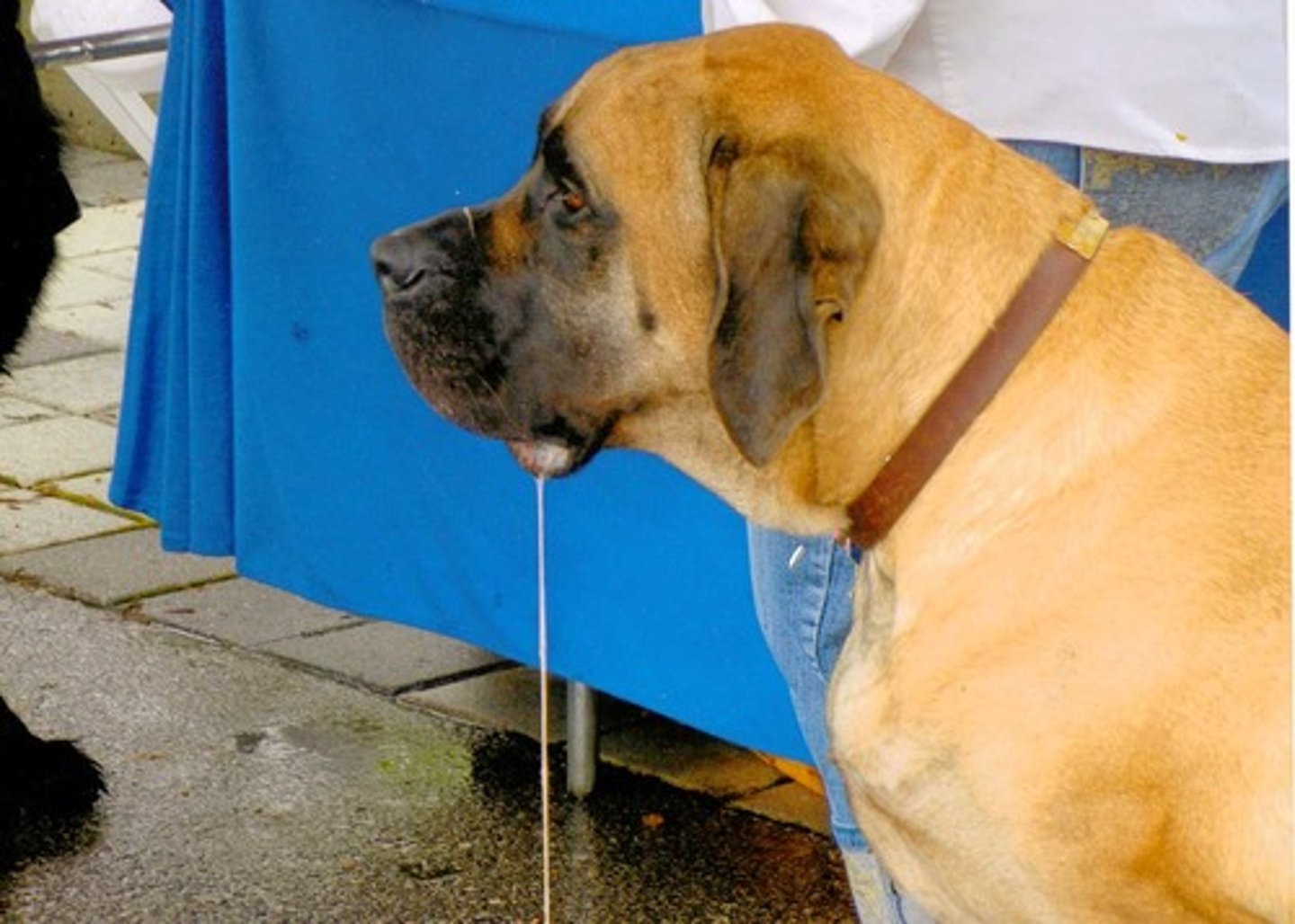
conditioned response
a learned response to a conditioned stimulus

Extinction
the diminishing of a conditioned response
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance, after a pause, of an extinguished conditioned response
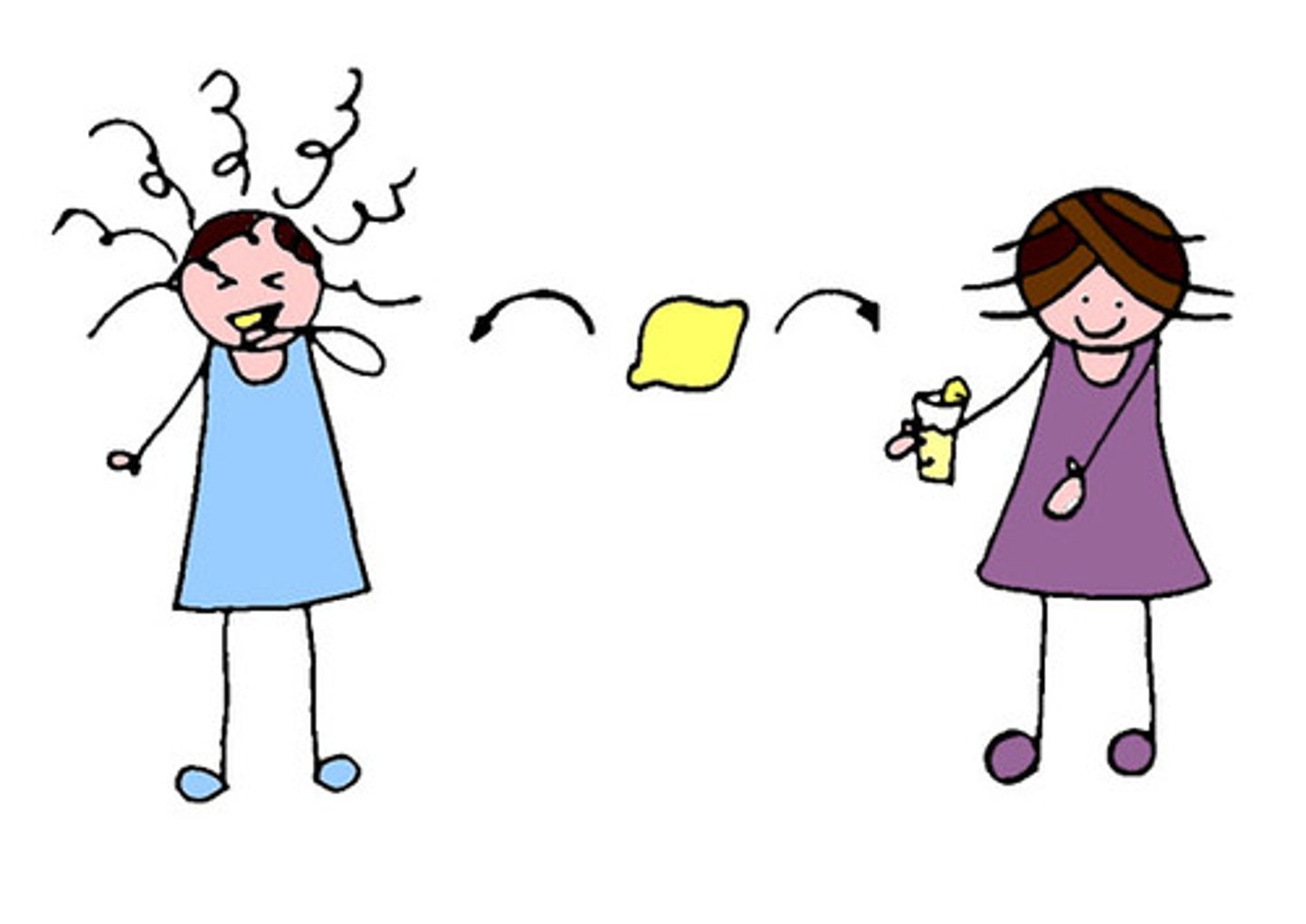
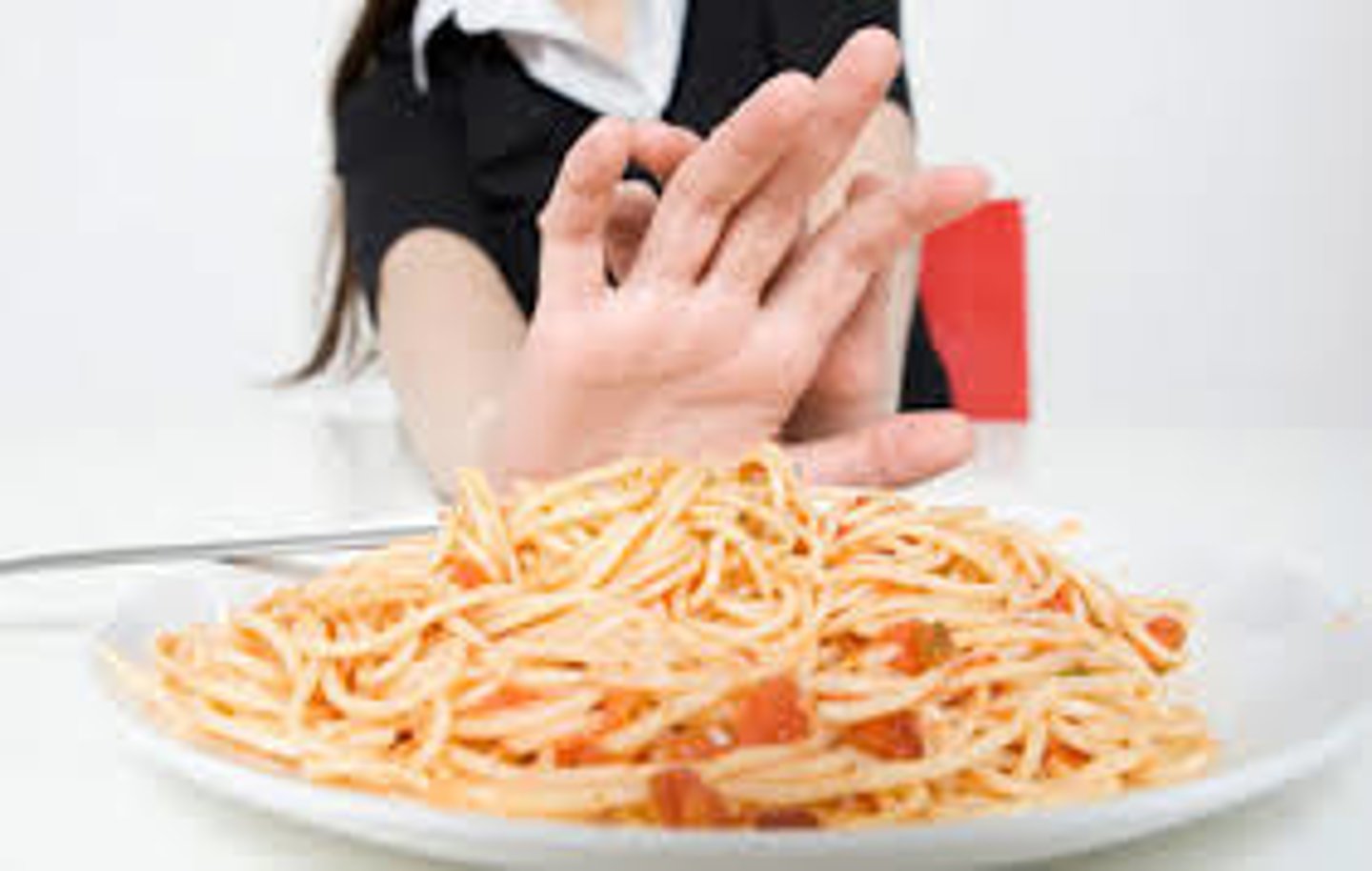
taste aversion
a learned avoidance of a particular food

higher-order conditioning
A procedure in which a neutral stimulus becomes a conditioned stimulus through association with an already established conditioned stimulus.
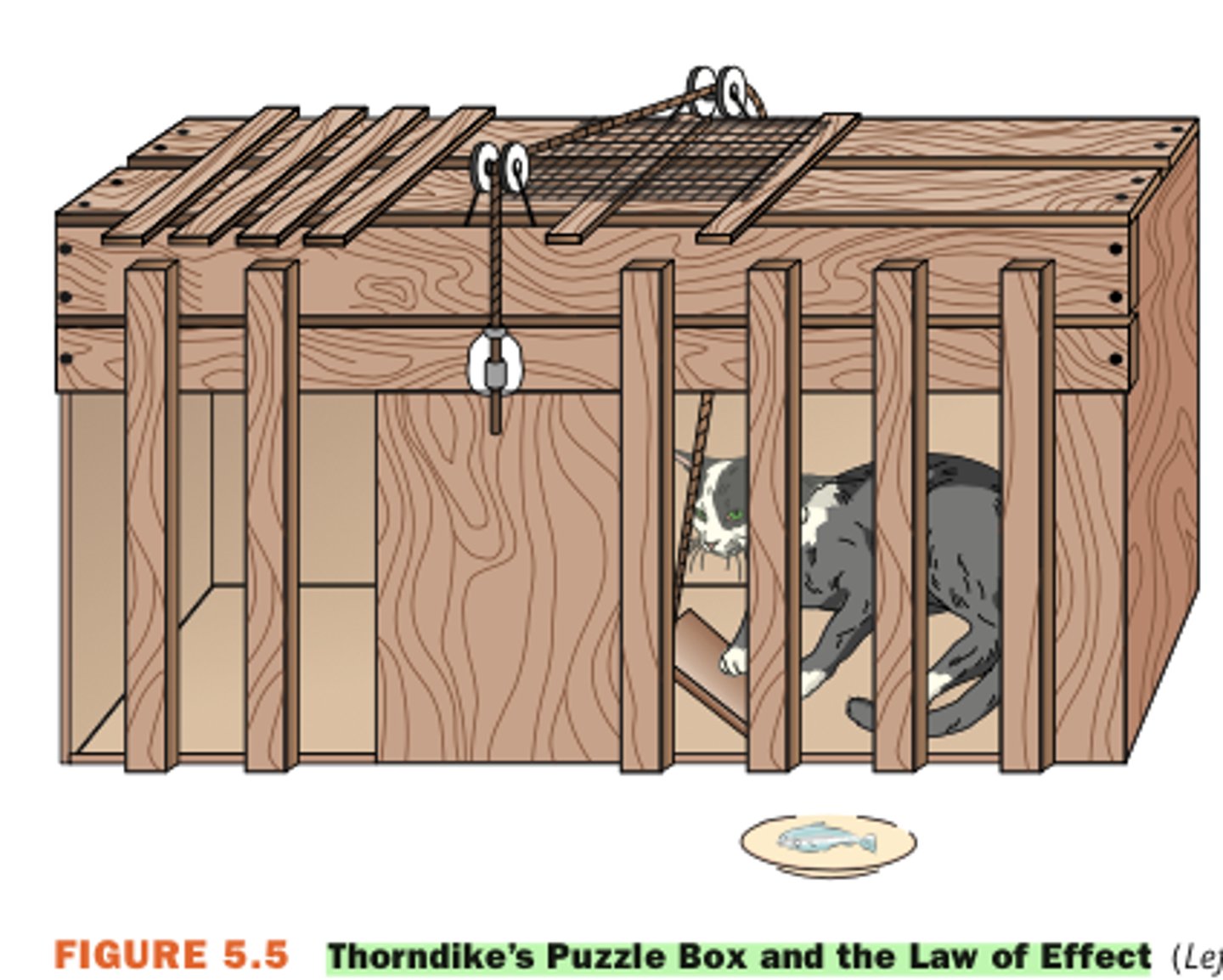
law of effect
Thorndike's rule that behaviors which have positive outcomes tend to be repeated
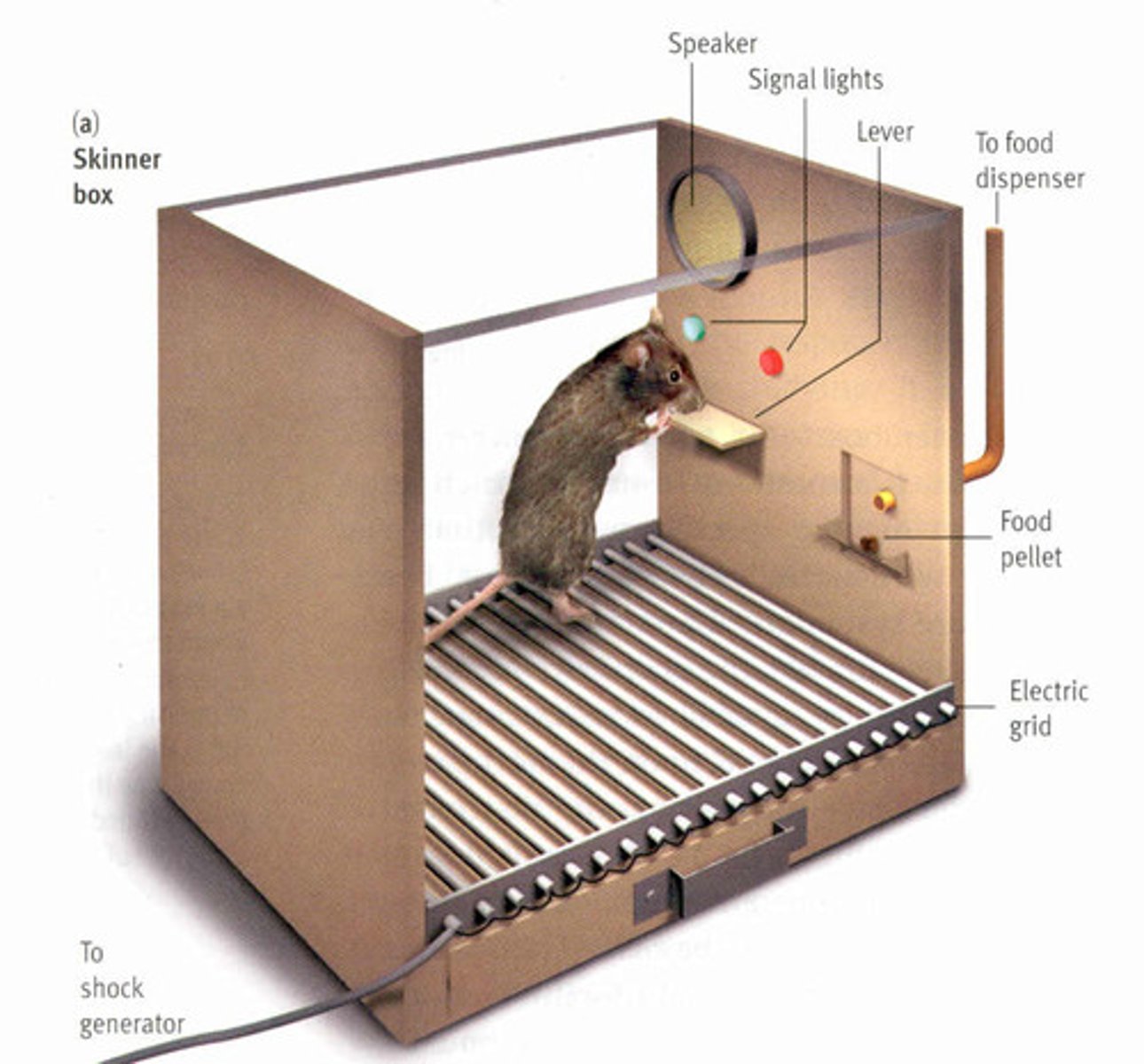
operant chamber
in operant conditioning research, a chamber (also known as a Skinner box) containing a bar or key that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; attached devices record the animal's rate of bar pressing or key pecking.
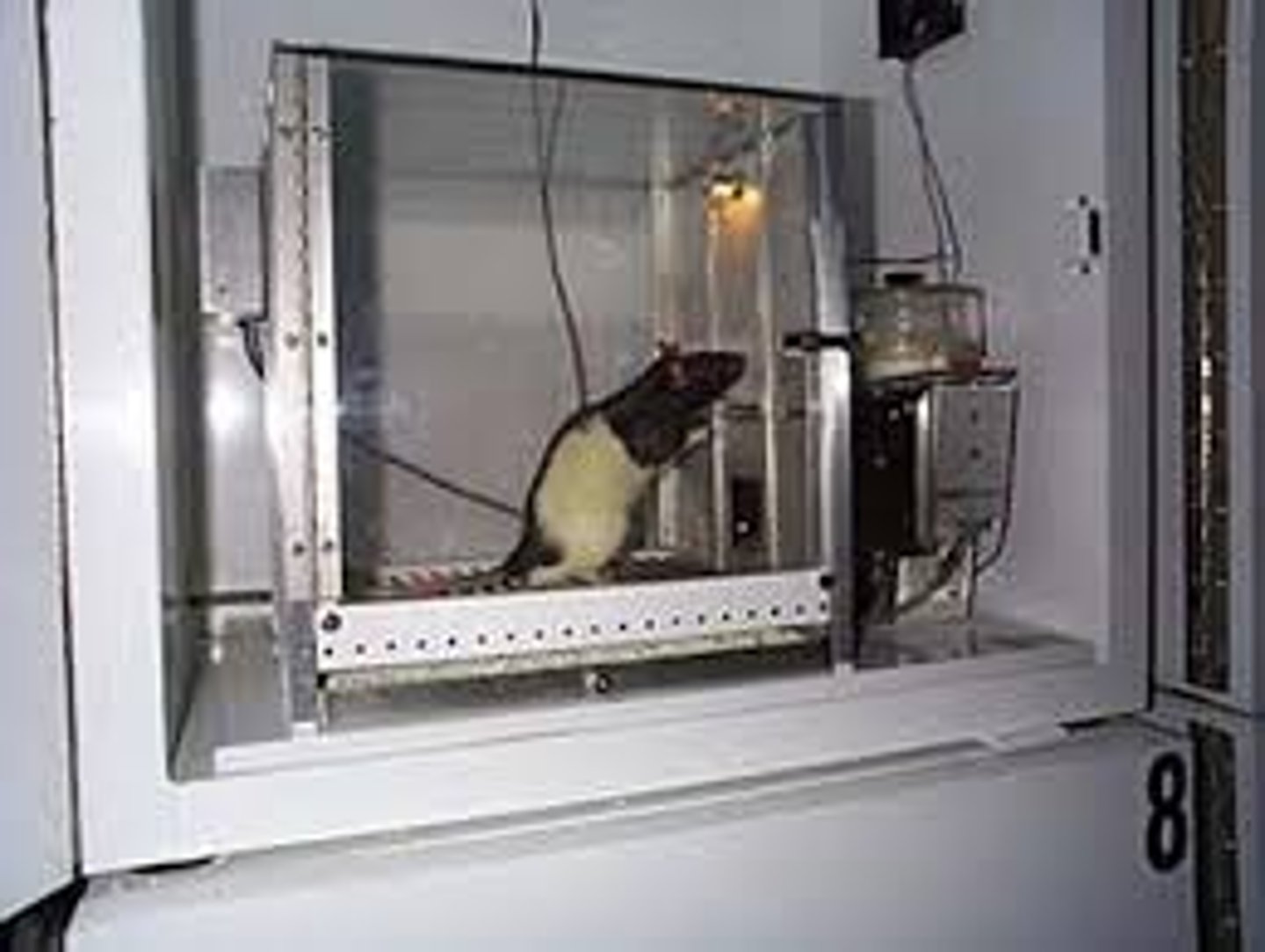

punishment
an event that decreases the behavior that it follows

Reinforcement
any event that strengthens the behavior it follows

postive
adding stimulus
negative
take away stimulus
primary rienforcer
stimulus that is naturally rewarding, such as food or water

secondary rienforcer
stimulus such as money that becomes rewarding through its link with a primary reinforcer
shaping
The reinforcement of closer and closer approximations of a desired response.

instinctive drift
In animals, its been shown that certain behaviors can be shaped through reinforcement

superstitious
having faith in magic or chance

learned helplessness
the hopelessness and passive resignation an animal or human learns when unable to avoid repeated aversive events

vicarious reinforcement
Learning that occurs by observing the reinforcement or punishment of another person.

continuous reinforcement
the reinforcement of each and every correct response

partial reinforcement
reinforcing a response only part of the time

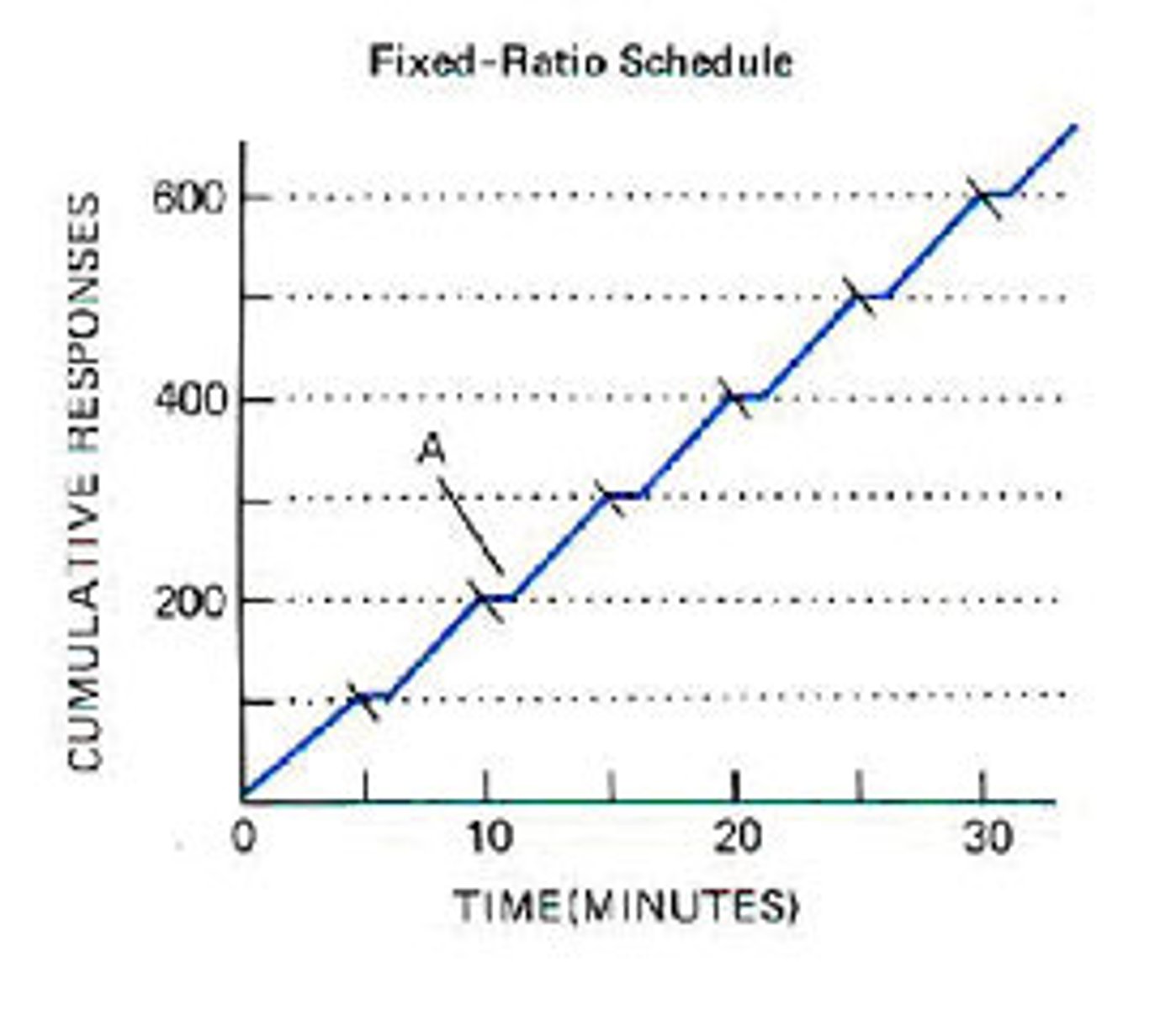
ratio
number of repetitions between reinforcement
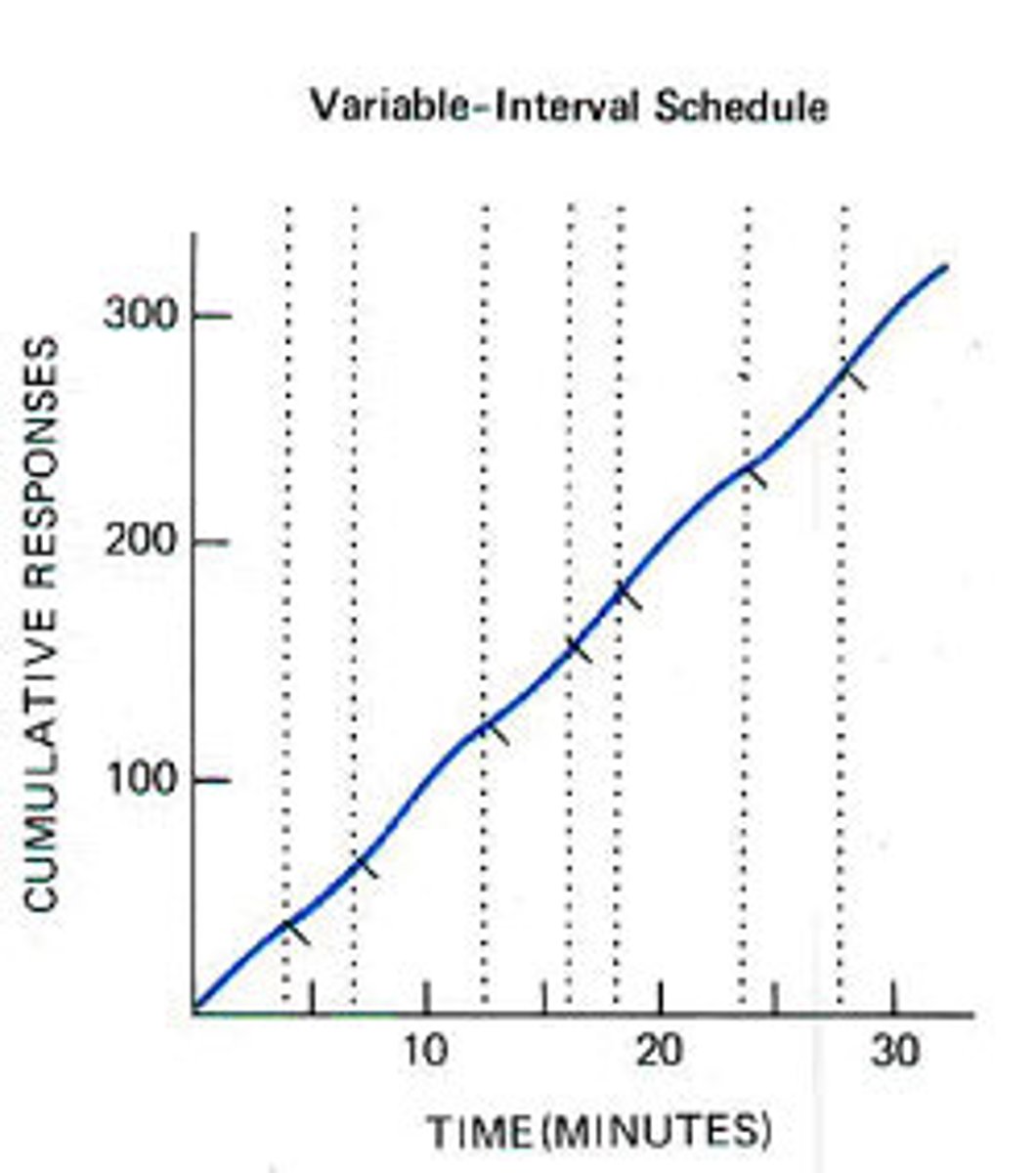
interval
time between reinforcement

fixed reinforcement
A reinforcement schedule that allows students to predict when the reinforcement will follow the desirable behavior
quickest learning
variable reinforcement
An unpredictable reinforcement schedule
slower extinction
Modeling
the process of observing and imitating a behavior

pattern of learning (benura)
learning occurs through
-attention
-encoding
-motivation
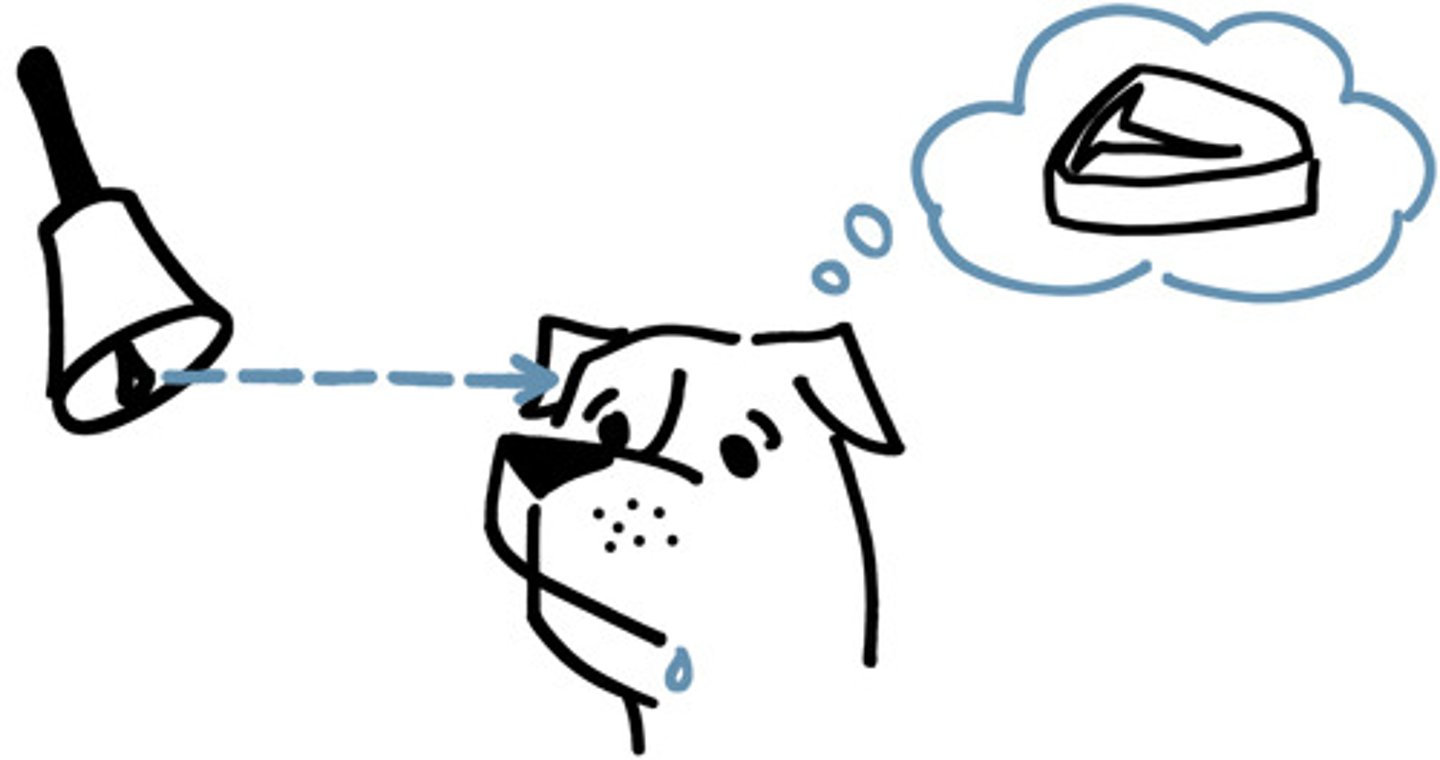
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events, INVOLANTARY
operant conditioning
a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher, VOLANTARY