10.4 - Human effects on ecosystems
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What human activities have a very significant effect on the environment?
Farming & fishing
Hunting & deforestation
Building & pollution
Burning fossil fuels
What are the 3 levels that biodiversity can be divided into?
Genetic diversity: variety of alleles within a species
Species diversity: variety of species within a habitat
Ecosystem diversity: variety of habitats within an ecosystem
How are each of the 3 levels of biodiversity being reduced by human activities?
Genetic diversity: selective breeding & competition with humans
Species diversity: farming, hunting, habitat destruction & introduction of alien species
Ecosystem diversity: deforestation, mining & building
What is the definition of extinction?
The permanent loss of all members of a species:
can be localised → a species becomes extinct in one location
can be total → a species is completely lost from the world
What is the definition of conservation?
The attempt to conserve biodiversity worldwide
What is CITES?
An international agreement between governments, whose aim is to ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals & plants doesn’t threaten their survival
What rule does CITES enforce?
Only bans the act of international trading, not hunting:
however, trading is only allowed under government licence & licences are not granted for species that are threatened with extinction
How did the fishing industry change in the 20th century?
Large factory ships could sail to any part of the world, staying out for weeks & freezing their fish catch on board
They trawled deeper water with larger nets & used sonar to find shoals of fish
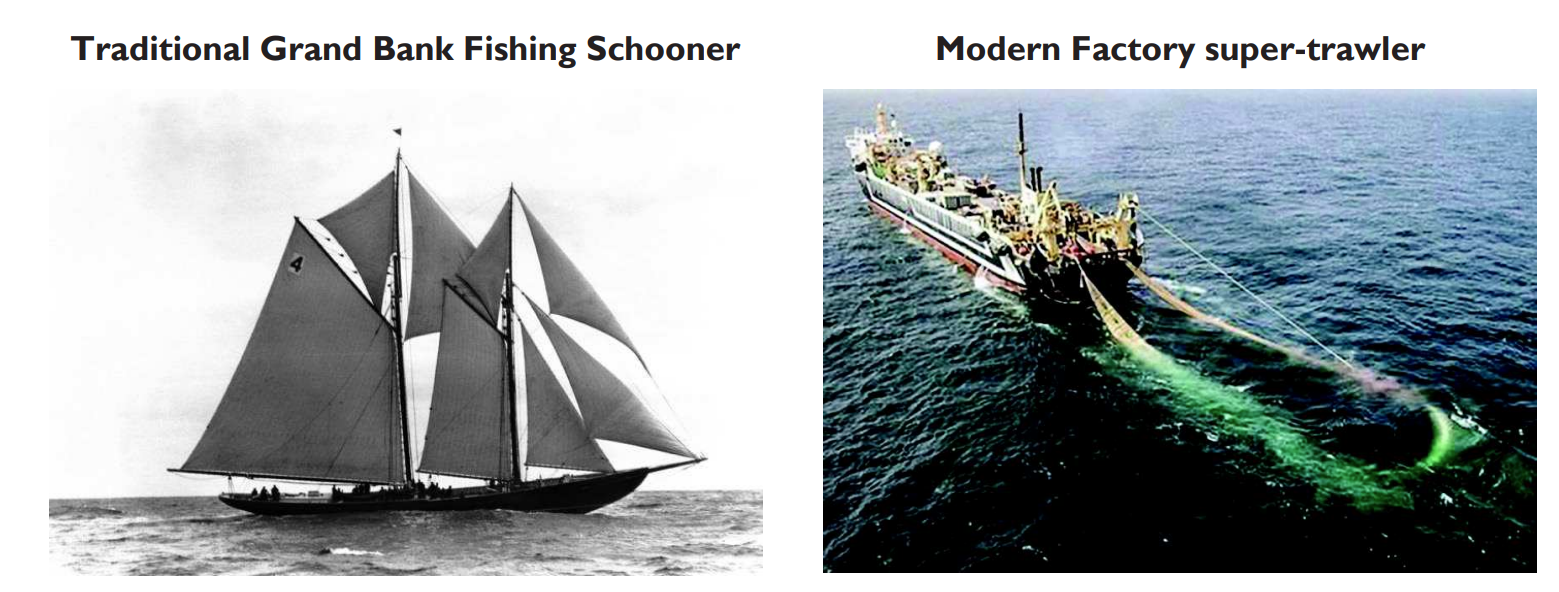
What are the effects of modern day fishing?
Fish are removed far faster than they can breed, so fish stocks decline
The fine-meshed trawl nets catch many species that can’t be sold & thus, are dumped back into the sea, forming detritus
Young fish are caught, so cannot breed to replace the fish stocks the next season
Bottom-trawling physically disturbs organisms & habitats on the ocean floor, destroying whole food webs
How have governments enacted various measures to try limit the impact of commercial fishing on fish stocks?
Setting & enforcing quotas to limit number of each species caught each year
Limiting certain types of fishing (e.g. bottom trawling)
Limiting size of mesh in fishing nets, so young fish aren’t caught
Limiting fishing seasons to avoid fish breeding seasons
Banning the fishing of specific species altogether
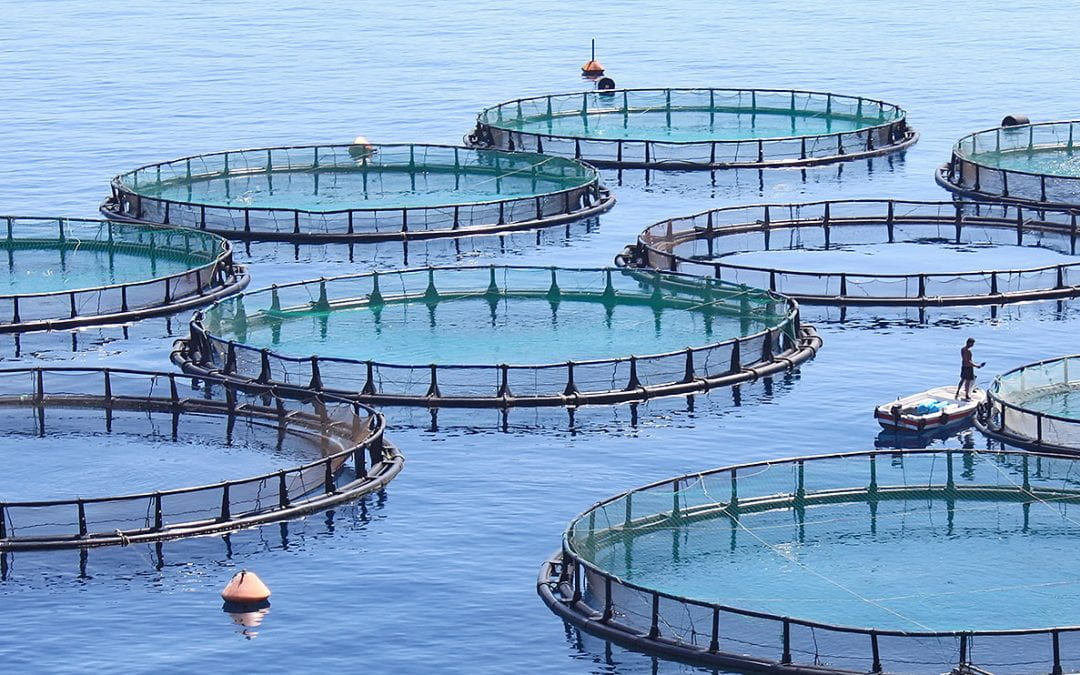
What are fish farms?
Fish are grown in netted areas in estuaries & bays:
reduces pressure on wild fish stocks, but can pollute the local environment with the waste from a dense fish population

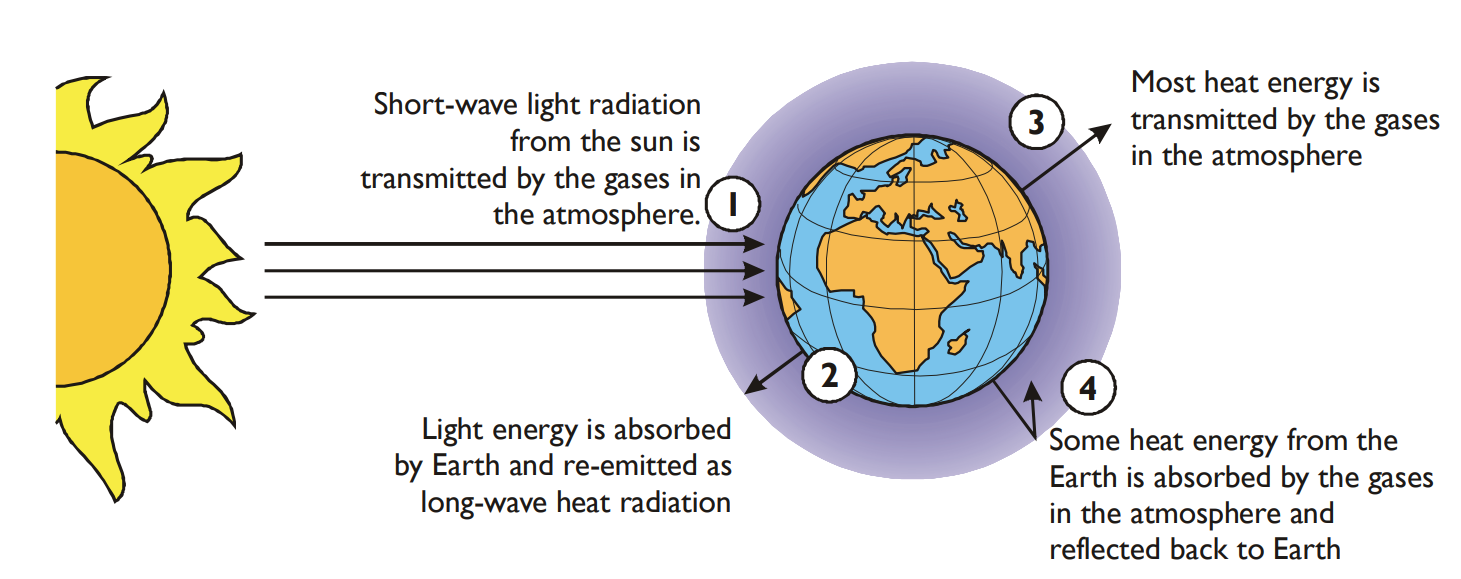
What is the greenhouse effect?
Infrared radiation from the sun is trapped by greenhouse gases (e.g. carbon dioxide & methane), leading to an increase in the temperature of the Earth’s surface & atmosphere → results in global warming
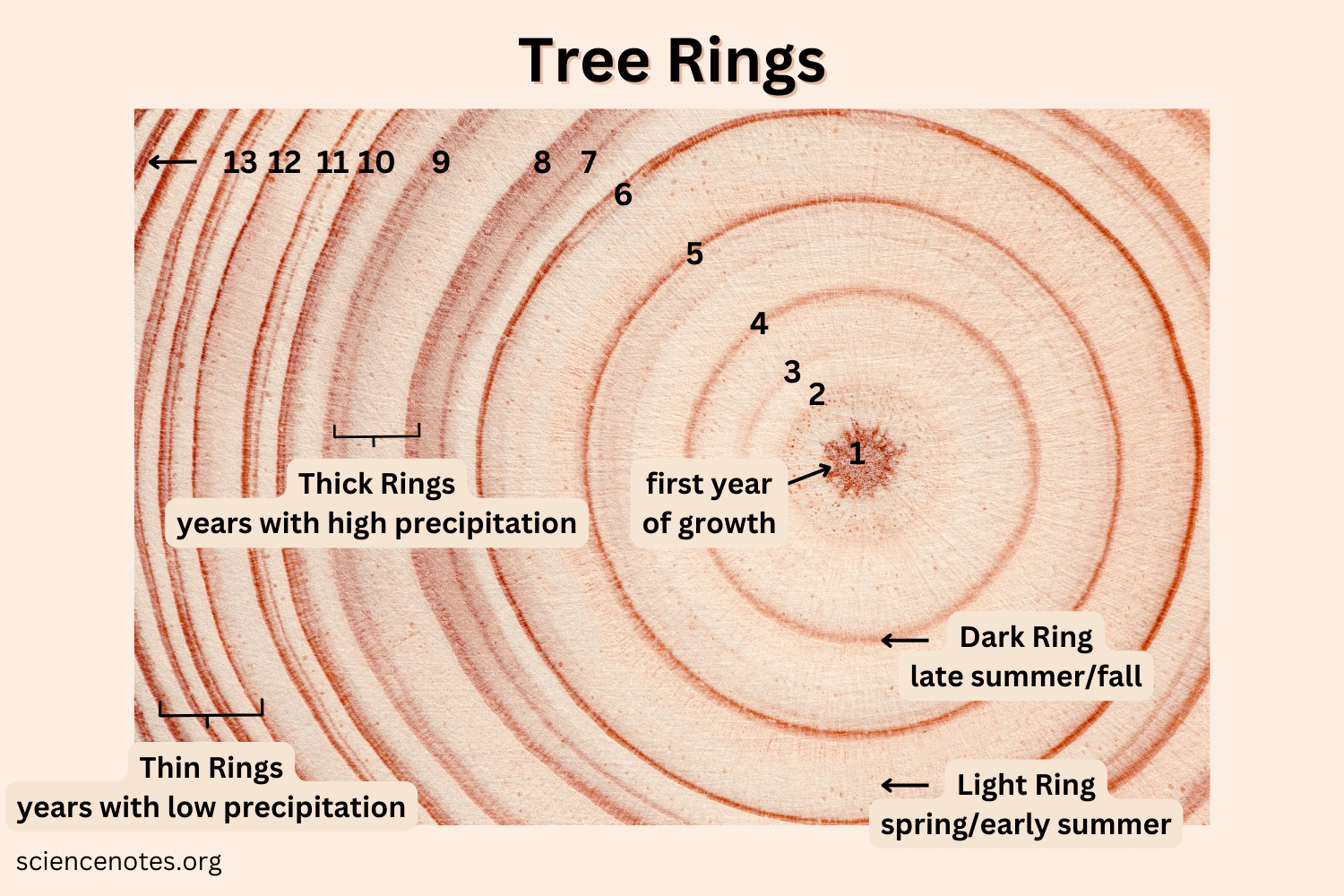
How can dendrochronology be used to provide evidence for global warming?
Tree trunks have annual rings due to seasonal patterns of growth (big rings in summer, followed by small rings in winter):
narrow annual rings mean that growth was slow → so temperature was colder
wider annual rings mean that growth was faster → so temperature was warmer
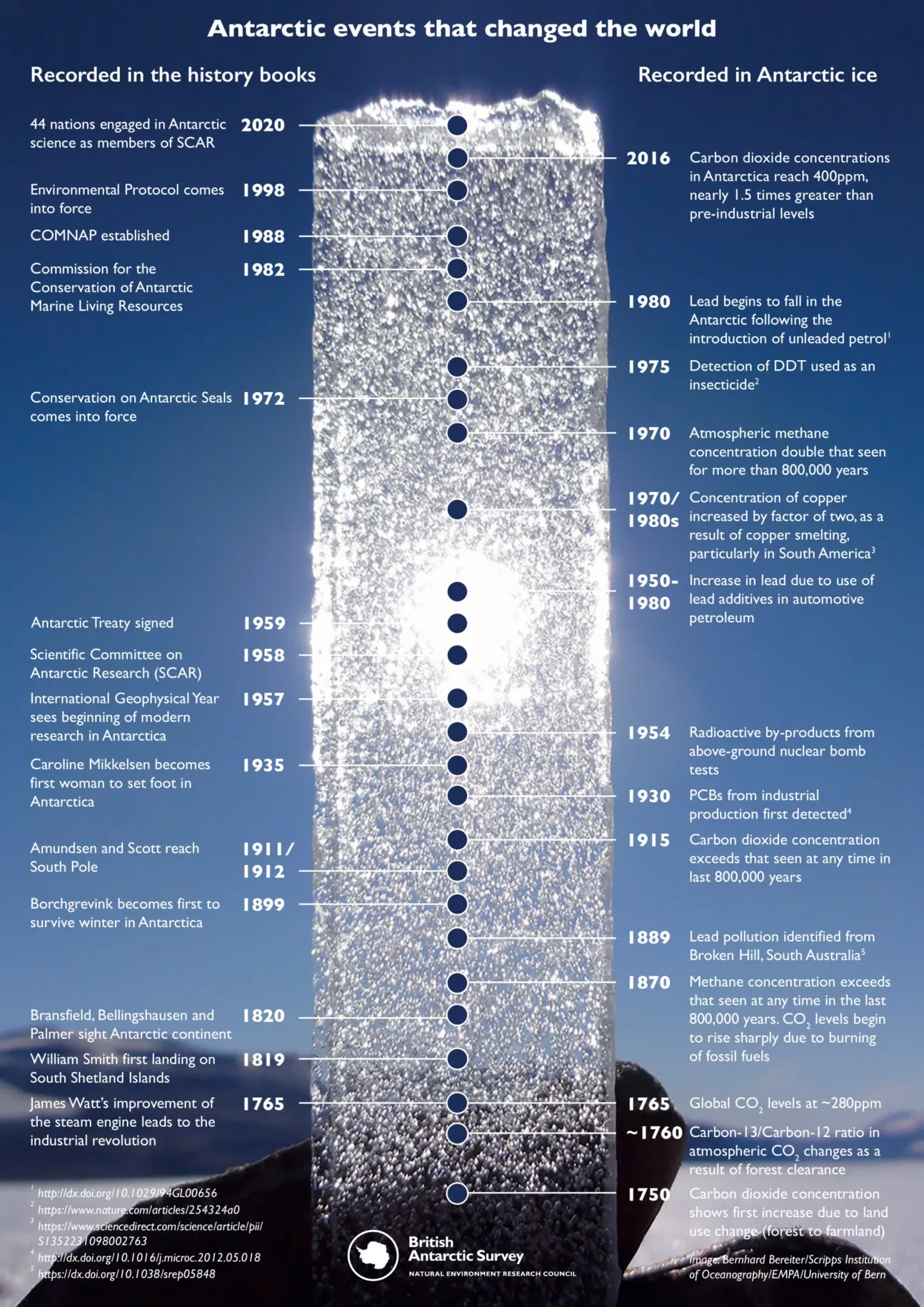
How can ice cores provide evidence for global warming?
Ice cores have annual rings, reflecting seasonal rainfall, so specimens from the cores can be dated
As each fresh layer of ice freezes, tiny air bubbles are trapped & using modern sensitive techniques, we can analyse the air bubbles for gas content
What are the main causes of global warming?
Anthropogenic changes → all linked to rising human population:
burning fossil fuels & deforestation
agriculture & landfill
What abiotic changes have occurred as a result of climate change?
Ice & glaciers: slowly shrinking, retreating & melting; meaning temporary flooding & less freshwater
Sea levels & ocean currents: rising levels means severe flooding in low-lying islands, countries & cities
Weather: increased temperatures & less rainfall in some countries
What effect has global warming had on metabolic rates?
Increasing environmental temperatures speed up enzyme activity, accelerating metabolic processes (e.g. respiration, photosynthesis, DNA replication)
Higher temperatures also increase evaporation & transpiration, which can lead to dehydration or overheating in some organisms
What effect has global warming had on distribution?
As their environment warms up, many animals & plants simply colonise new habitats with a more suitable climate
Many birds are starting their annual migrations earlier
What effect has global warming had on seasonal cycles?
Some animals & plants adapt to a warming environment by staying where they are but changing their life cycles:
plants flower earlier, insects emerge earlier, birds breed earlier & mammals wake from hibernation earlier
What effect has global warming had on farming?
Tropical regions may be unable to support their current crops as the climate becomes too warm & dry
African countries may struggle to feed their populations, as staple crops fail due to rising temperatures & decreased rainfall
What effect has global warming had on disease?
Mild winters mean that insects can now survive in areas where they couldn’t before
Insects (e.g. mosquitoes) are also vectors of human & animal pathogens
Tropical diseases could soon be found in more northern countries
How can the emission of carbon dioxide be reduced?
Burn less fossil fuels by cutting electricity use & using public transport
Use carbon scrubbers in power stations
Use alternative energy sources (e.g. carbon neutral biofuels)
Reduce deforestation & increase reforestation
How can the emission of methane be reduced?
Recycle waste to reduce landfill
Change livestock (e.g. cows) diet to reduce methane release
Reduce meat consumption
How is evidence related to climate change validated?
Papers are sent out to other experts for peer review to check for validity
If data & conclusion seem reasonable, results are published in scientific journals & may also be presented at conferences