Interlude B
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Which of the following best describes the term sediment?
a. loose fragments of rocks and minerals broken off bedrock or precipitated from water
b. blocks of bedrock separated by large fractures
c. dissolved chemical constituents in groundwater and surface waters
d. modified bedrock that can support the growth of vegetation and other organisms
a. loose fragments of rocks and minerals broken off bedrock or precipitated from water
The accumulation of sediments that are found on top of the Earth's bedrock is known as
a. hydrosphere.
b. soil.
c. cover.
d. horizons.
c. cover.
Sediment formation is the result of __________ at the Earth's surface.
a. igneous activity
b. metamorphic activity
c. weathering
d. hydration
c. weathering
Why does physical weathering speed up the processes of chemical weathering?
a. Physical weathering requires abundant water, as does chemical weathering.
b. Physical weathering produces more surface area for chemical weathering to attack.
c. Chemical weathering can occur only on small surfaces, not large ones.
d. Chemical weathering requires salt, which is provided by salt wedging.
b. Physical weathering produces more surface area for chemical weathering to attack.
Weathering results in
a. larger, less-rounded pieces.
b. larger, more-rounded pieces.
c. smaller, less-rounded pieces.
d. smaller, more-rounded pieces.
d. smaller, more-rounded pieces.
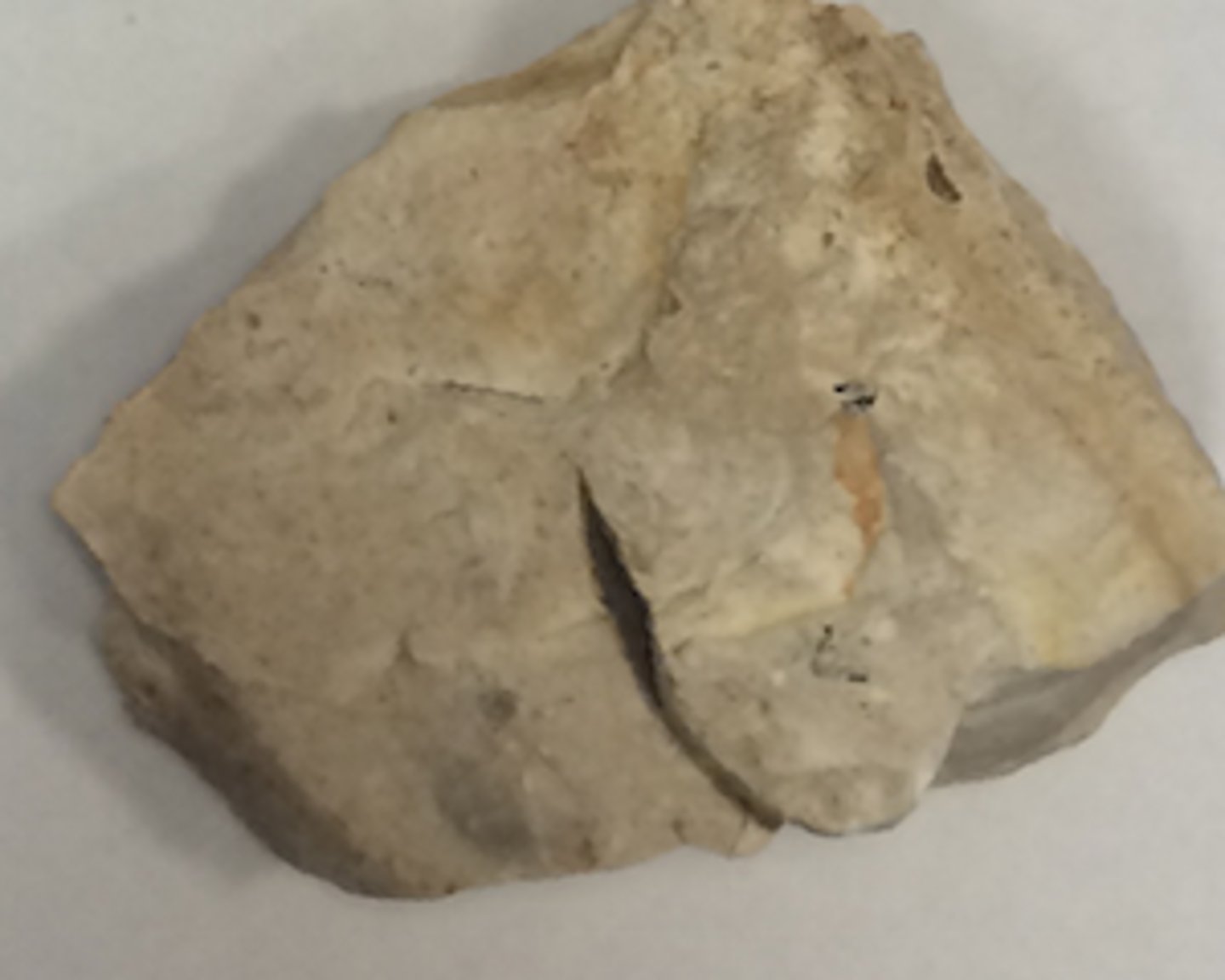
What type of phenomenon is demonstrated by the vertical lines in this picture?
a. jointing
b. exfoliation
c. chemical weathering
d. hydration
a. jointing
What type of weathering has produced the honeycomb-like features shown in the following photo?
a. salt wedging
b. frost wedging
c. dissolution
d. hydration
a. salt wedging
What type of weathering has created the onion-like layers in the rocks in the below picture?
a. jointing
b. hydration
c. dissolution
d. oxidation
Which of the following is a type of physical weathering?
a. rocks breaking apart into smaller pieces along joints and other fractures
b. minerals in bedrock dissolving into stream water
c. minerals in bedrock reacting with oxygen in rainwater
d. slowly adding water into certain minerals' structure
What type of weathering are you most likely to find occurring in areas with cold climates?
a. hydrolysis
b. frost wedging
c. salt wedging
d. dissolution
b. frost wedging
What type of weathering are you most likely to find occurring near an ocean?
a. dissolution
b. thermal expansion
c. salt wedging
d. root wedging
c. salt wedging
Chemical weathering involves the breakdown of material due to
a. mechanical breakdown of rock.
b. baking in the hot sun.
c. interaction with ice.
d. interaction with water or air.
d. interaction with water or air.
Dissolution occurs when minerals
a. are dissolved into water.
b. are turned into rust.
c. absorb water and expand.
d. are removed by frost.
a. are dissolved into water.
Hydration occurs when minerals
a. are dissolved into water.
b. are turned into rust.
c. absorb water and expand.
d. are removed by frost.
c. absorb water and expand.
Which type of weathering process is happening to materials when they rust?
a. hydrolysis
b. hydration
c. oxidation
d. dissolution
c. oxidation
Which types of minerals are most likely to experience oxidation during chemical weathering?
a. evaporite minerals such as halite
b. carbonate minerals such as calcite and aragonite
c. silicate minerals such as quartz and feldspar
d. iron minerals such as biotite and pyrite
d. iron minerals such as biotite and pyrite
The zone of leaching is the area in which
a. weathered bedrock forms a soil horizon.
b. organic matter gathers to create a soil horizon.
c. minerals are precipitated and added to soil.
d. minerals are dissolved and removed from soil.
d. minerals are dissolved and removed from soil.
Climate, substrate, slope, time, and organisms are all factors that influence _______.
a. mountain uplift
b. soil formation
c. sediment color
d. regolith temperature
b. soil formation
The Dust Bowl of the 1930s is an example of what hazard to soils and the roles they play in society?
a. soil accumulation
b. soil erosion
c. soil percolation
d. soil leaching
b. soil erosion
Below is a photo of an outcrop where bedrock, unconsolidated sediments, and soil are all visible. Which of the three materials is youngest?
A
B
C
All are the same age
A
FEEDBACK: The bedrock breaks down to form unconsolidated sediment. Once organic material is added to the unconsolidated sediment, soil is formed. Consequently, the soil is younger.

The following image shows a natural outcropping of bedrock, soil, and unconsolidated sediment. Match the letter on the image with the appropriate term.
a. A - soil, B - bedrock, C - unconsolidated sediment
b. A - soil, B - unconsolidated sediment, C - bedrock
c. A - unconsolidated sediment, B - soil, C - bedrock
d. A - bedrock, B - soil, C - unconsolidated sediment
b. A - soil, B - unconsolidated sediment, C - bedrock
FEEDBACK: The modern soil is found at the top of the section. Coherent bedrock makes up the basement material. Partially weathered and broken bedrock comprise unconsolidated sediments.

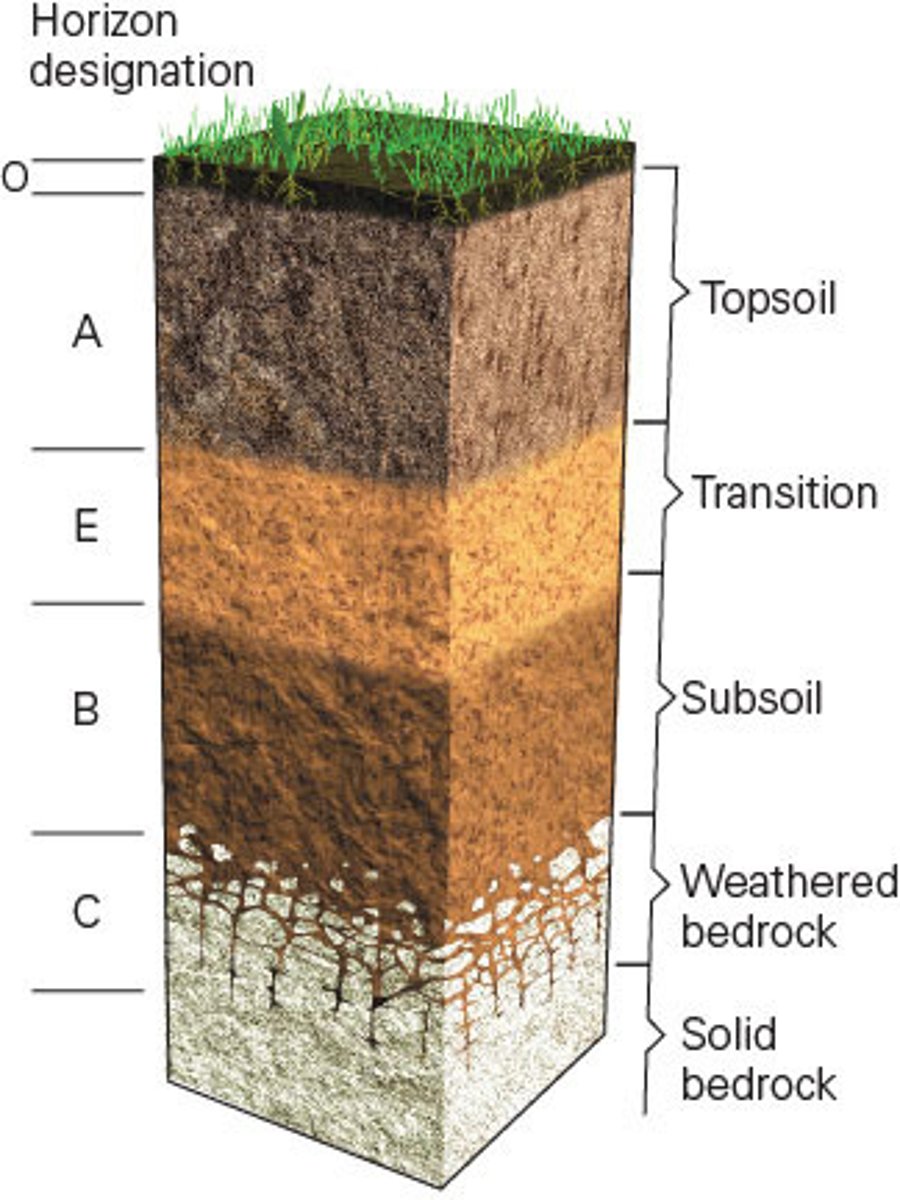
The image below shows an idealized soil profile divided into soil horizons. Where in the horizon is caliche or calcrete found?
a. Horizon A
b. Horizon E
c. Horizon B
d. Horizon C
c. Horizon B
FEEDBACK: Caliche is the calcite-based concrete that can cement the B-horizon. One origin of caliche is calcite precipitation from water percolating downwards through the soil profile.
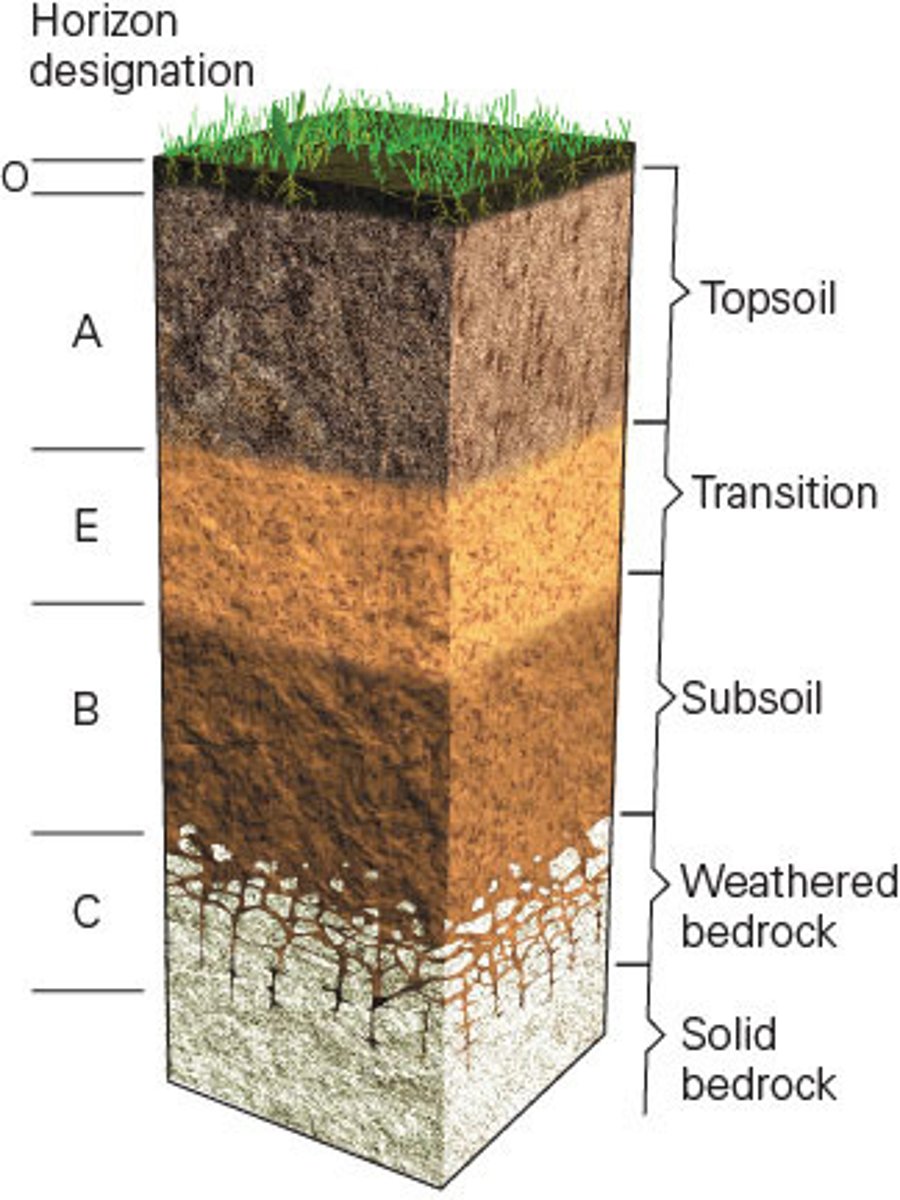
The image below shows an idealized soil profile divided up into soil horizons. Where in the horizon is extensive leaching found?
a. Horizon O
b. Horizon E
c. Horizon B
d. Horizon C
b. Horizon E
FEEDBACK: Leaching can begin at the base of the A horizon, but the E horizon is dominated by leached sediments. Leaching occurs as downward moving water removes fine clays and soluble chemicals. These are then deposited in the zone of accumulation.
This image shows a chemical reaction that is primarily responsible for the chemical deterioration of limestone. Which form of chemical weathering does the figure show?
a. dissolution
b. hydrolysis
c. oxidation
d. hydration
a. dissolution
FEEDBACK: Dissolution occurs when water molecules pluck ions off grain surfaces. This process physically alters the surface texture and affects primarily carbonate materials, like limestone.
