The Renaissance
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Renaissance
“rebirth”; from 1300s to 1500s
Attitudes:
People want to make own era
New era = rebirth
Emphasis on individual goals
Wanted other human experiences
Values:
Monks + scholars = classical heritage
Latin language survived in church
Medieval scholars (Euclid = math; Ptolemy = astronomy; Aristotle)
Causes of the time period
the cause was…
the plague
trying to rebuild themselves
Old Order
the time when the church was in full power
Greco-Roman culture
philosophy
education
arches + domes
architecture
Patron
a financial supporter
Significance: Lorenzo (grandson of Cosmo; a politician; held Florence together)was this which helped support people that enjoyed art
The Medici Family
family of Florence organize banking business
Extended to wool manufacture + mining
Richest merchants/ bankers
Money = cultural + political power
Cosmo de’ Medici
Control Florence govt + was a uncrowned ruler
Florence
Symbolize energy of Italian renaissance
Had lots of poets, artists, architects scholars, + scientists
in the middle of trade between the east and west which allowed them to have money and people started to promote capitalism.
Humanism
A lifestyle that focuses on worldly subjects rather than on the religious issues; believed = using wisdom from ancestors to increase their knowledge of times
Humanities
the subjects taught in ancient Greek and Roman Schools; studies = grammar, poetry, history on Greek + roman texts; asked lots of questions;
Secularism
a movement towards the separation of religion and government, often termed the separation of church and state.
Perspective
making distant objects smaller than closer objects = view painting 3-dimensional
Used shading = make objects real
Studied human anatomy = wanted to portray the human body accurately
linear perspective - you don’t see the lines but they are the to draw your attention to a specific part of the painting
Chiarascuro
Strong contrast between light & dark forces the eye to a certain place
Sfumato
Subtle blending or smokiness used to transition between light to dark
Makes images more realistic
Francesco Petrarch
“The Father of Humanism”
Wrote sonnets to Laura (love poems inspired by a woman from a distance)
1300s Florentine- An early Renaissance humanist
Assembled a library of Greek and Roman manuscripts
Developments and writing influence later writers
Pieter Bruegel
A famous painter in the Northern Renaissance; valued realism and detail in people; would paint peasant daily life such as weddings, dances, and harvest; used rich colors + balance in the space —> sense of life and feeling
Leonardo da Vinci
Mono lisa + Last supper
portrayed the apostles (one person not reacting + the others in distress)
depicted the apostles in reacting as real people
The quintessential “Renaissance Man”
Music, art, architecture, engineering, inventor
Freshness & realism emphasized in his work
Studied & emphasized the human body
Michelangelo
Painter, architect, engineer, poet, etc.
created: statue of David:
Before sculpting
studied anatomy by dissecting human corpses
non-religious
the Sistine chapel
la pieta (the pity)
Baldassare Castiglione
Discusses the ideal man and woman; humanism
The Book of the Courtier - describes the manners, skills learning that a person at the court should have
Machiavelli
florentine diplomat(works and travels for rulers) with experience in observing rulers; was attacked giving “cruel advice”
Features of Northern Renaissance art
Details, realism > idealism; Greater focus on religion than the Italian Renaissance;
Vernacular
language or dialect spoken by the ordinary people in a particular country or region.
Shakespeare
he revolutionizes communication in the English language, invented 1700 words; wrote poems and plays; valued English language + wanted to understand human beings
Miguel de Cervantes
A famous author; wrote Don Quixote —> a poor Spanish nobleman who went crazy after reading too many books on knights; book may be idealistic of a person or he was making fun of chivalry
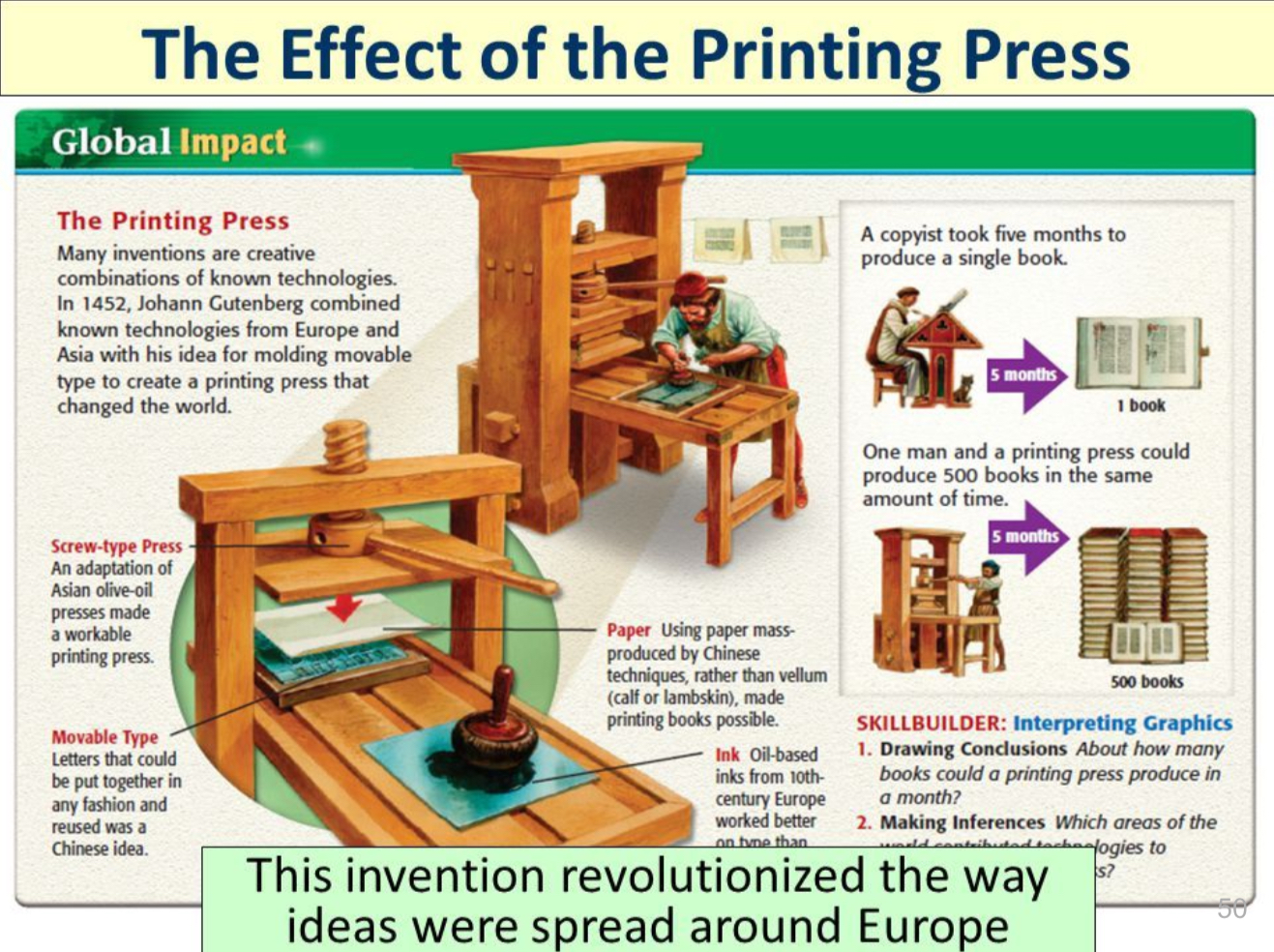
Johann Gutenberg
German; used metal letters instead of wood + redesigned wine press = printing press; first book completed was the Latin bible named, Gutenberg Bible; printed more books=replacing the hand-copied manuscripts + printing writings of Greek and Roman authors = inspired classical learning; Religious texts printed;
Erasmus
wanted a major change for the church; made big request —> wants the Bible to be printed in the vernacular (thought this would improve society)
Utopia
the idea of a perfect and ideal society; Thomas More fixes society with book his idea —> no money needed, no idea of property, no laws are needed)
Effects of the Renaissance
manufacture increase
books printed
Education increase
More art —> realism + humanism
Which factors were responsible for causing the Renaissance?
increase in trade
Why did the Renaissance emerge in the Italian city-states?
center of Roman empire
Survived through middle ages
many cities (Milan, Florence, Venice) for trade + manufacturing
Home of the renaissance is in Florence; wealthy merchants bc lots of trade is happening; Italian city states have rich historical items; humanism
What were the features of the Renaissance?
What themes and techniques did the Renaissance writers and artists explore?
Renaissance artist explored:
realism
Religion
Humanism
How are aspects of the Renaissance reflected in art/literature of the day?
The acts of the Renaissance were reflected on art by
Art becoming more personal than religeous —> a change in perspective of wanting personal gain
Books about stories
What impact did the printing press have on Europe and the world?
This invention allows…
allowed literature
Curiosity
Leads to manufacturing era
What were the contributions of the writers and artists in the Northern Renaissance?
Which change that occurred during the Renaissance was the greatest break with society of the Middle Ages? (A Revival of Europe, A focus on the non-religious, or A emphasis on the individual)
How did the Renaissance change European culture and society?
Raphel
Learns from Michelangelo & Da Vinci
Combines Christian & classical styles
created: Transfiguration + school of Athens
The Bubonic Plague
a disease that was transmitted from fleas on rats; killed lots of people
The Plague’s Origins & Impact
Origin: can from fleas off rats (rats came from boats that were used for trade)
Impact:
quarantine was created (40 days of staying away from everyone)
Many died —> less labor
People asked for higher wages since there were few survivors
People praying for god to forgive them
Pope could not help stop plague —> less faith in religion
God: God was punishing them → beat themselves with whips to show repent for sins
Scapegoats: Christians blame Jews (revenge: poisoning wells)
The Babylonian Captivity
a time when ancient Isrelites’’ were held captive by Babylon
Pope Clement V
Moved papal court to avignon (border of south france)
Remained for 70 yr
Reformers wanted to end captivity
Reformers elected pope to rule Rome
Revolt: french cardinals chose own pope as well
schism(split) church in two for years → 1417: church council at constance enter rivalry
The Western Schism
The Babylion Captivity caused this; The revolt of electing many popes at once;
John Wycliffe
a teacher at Oxford; attacked church corruption
Insisted bible was source for Christian truth
Followers translated bible to English people can read rather than rely on clergy
Czech students at Oxford followed ideas
Church response: persecuted Wycliffe + followers + suppressed Hussites
Found guilty = burned at stake (idea survived)
Jan Hus
Persecuted him for translating the Bible in English which would weaken the church bc people wouldn’t need Pope to teach them the ways of the lord
The Hundred Years’ War Cause and Effects
England + France fought fought; Cause of this war… = English been fighting French for years abt Norman ancestors
Edward III of England took throne of France → chaos
Fighting economic rivalry + national pride = hard for either side to give up
Joan of Arc
a 17 yr woman; told Charles VII God sent her to save France → persuaded king to let her lead army against English
inspired troops to fight against English
victories
taken captive by allies of English + turned to enemies for trial → English want to discredit her + tried for witchcraft = burned at the stake (later declared a saint)
Execution made French mad = took canon and attacked English castles → English had only port of Calais in North western France
Long bow
six feet long; discharge 3 arrows in time a man fired one; arrows pierced heaviest armor
Cannons
A weapon when a ball out of iron and steel would be put in a thing and shot out