Physics ✿ forces
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
what should happen in order to cause an object to stretch, bend or compress?
2 forces must act on the object
the extension of an elastic object is _______ proportional to the force applied
directly
Hooke’s law
the extension of an elastic object is directly proportional to the force applied
directly proportional
when one variable changes, the other one changes by same amount
limit of proportionality
the length a spring can be stretched before it can no longer return to its original length
elastic deformation
when a spring is stretched and can return to its original length
inelastic deformation
when a spring is stretched and cannot return to its original length
distance
a scalar quantity that measures how far an object moves
displacement
a vector quantity that measures how far out of place place A is from place B
velocity
speed in a given direction
acceleration
the rate of change of velocity
equation for acceleration (on a graph)
change in velocity / time taken
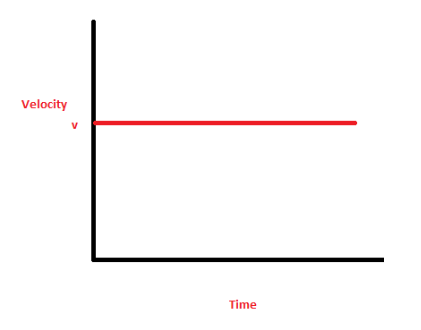
what does this graph show?
constant velocity
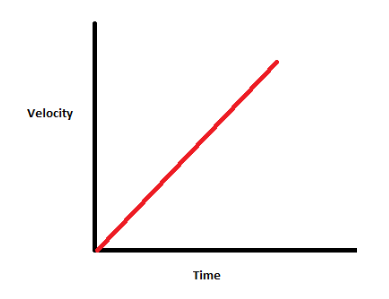
what does this graph show?
constant acceleration
terminal velocity
what is it caused by?
the maximum speed objects reach when falling
air resistance
how do you find the speed on a distance time graph?
change is y values / change in x values
if an object is moving in a circular motion, what happens to the velocity?
it is always changing and is perpendicular to the acceleration
what is the typical speed of a person walking?
1.5m/s
what is the typical speed of a person running?
3m/s
what is the typical speed of a person cycling?
6m/s
what is the typical speed of a car?
25m/s
what is the typical speed of a train?
30m/s
what is the typical speed of a plane?
250m/s
what happens to terminal velocity when an object has..
a large surface area?
a small surface area?
and why?
large surface area:
has a lower terminal velocity as more air resistance acts on it
small surface area:
has a higher terminal velocity as less air resistance acts on it
uniform acceleration
when an object's speed is increasing at a constant rate
briefly describe an experiment you could do to compare people’s reaction times
have a person sit with their hand open ready to catch a ruler
hold the ruler vertically with the 0 cm aligned with the top of the person’s finger
drop the ruler
record the measurement at the point where the ruler was caught
state how a person with a parachute enters terminal velocity [3]
weight makes person accelerate downwards
acceleration causes air resistance to increase until it reaches same size as weight
this causes person to fall at constant speed (terminal velocity)
state how a person with a parachute can land safely [3]
opening parachute increases surface area making air resistance greater than weight
resultant force upwards causes deceleration
air resistance decreases until it balances the weight (slow terminal velocity)
newtons first law
objects will stay at rest or move at constant speed unless a net resultant force is acted on it
newtons second law
the acceleration is proportional to the resultant force
and inversely proportional to the object’s mass
newtons third law
whenever 2 objects interact the forces they exert on each other are equal but opposite
give an example of newtons third law in action
a bird flying →
bird’s wings push downwards
air pushes upwards on bird
bird flies up
stopping distance
thinking distance + braking distance
what is the typical driver’s reaction time?
0.2 - 0.9 seconds
state 3 factors affecting reaction time
drugs/ alcohol
distractions e.g. animals
tiredness
state 4 factors affecting braking distance
wet or icy roads
poor vehicle condition
fast speed of vehicle
friction from brake and wheel reduced kinetic energy
momentum
a measure of how difficult it is to stop a moving object
conservation of momentum
in a closed system, total momentum before an event is equal to total momentum after the event
closed system
no external forces
scalar
a quantity that has a magnitude only
vector
a quantity that has a magnitude and direction which is usually represented as an arrow
name 2 forces
push and pull
non contact forces
a force made when objects are physically separated
contact forces
a force made when objects are physically touching
what are forces measured in?
newtons (N)
the weight and mass of an object are __________ proportional
directly
what is the difference between mass and weight?
mass → amount of matter in an object
weight → force of gravity acting on an object
what happens to an object if forces are balanced?
the resultant force is zero
the object stays at rest or moves at constant speed
resultant force
overall force on an object
when a force causes an object to move through a distance, ______ is _______ on the object
work is done
1 newton meter =
1 joule
work done against friction
when an object is moved along a rough surface
what does work done against friction produce?
heat (thermal energy)
equation for work done
force applied (n) x distance (m)
mechanical work
a force which causes an object to move
transferring energy to the kinetic energy store of the object
gravitational work
a force which lifts up an object
transferring energy to the gravitational potential store of the object
vectors
a quantity that has a magnitude and a direction
scalars
quantities that only have a magnitude