the polymerase chain reaction and gel electrophoresis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what is the polymerase chain reaction
a manipulation technique that amplifies DNA by making multiple identical copies.
Used by scientists when there is an insufficient amount of DNA sample for testing
focus on certian genes through primers or restricition endonucleases
after each cycle DNA present is doubled
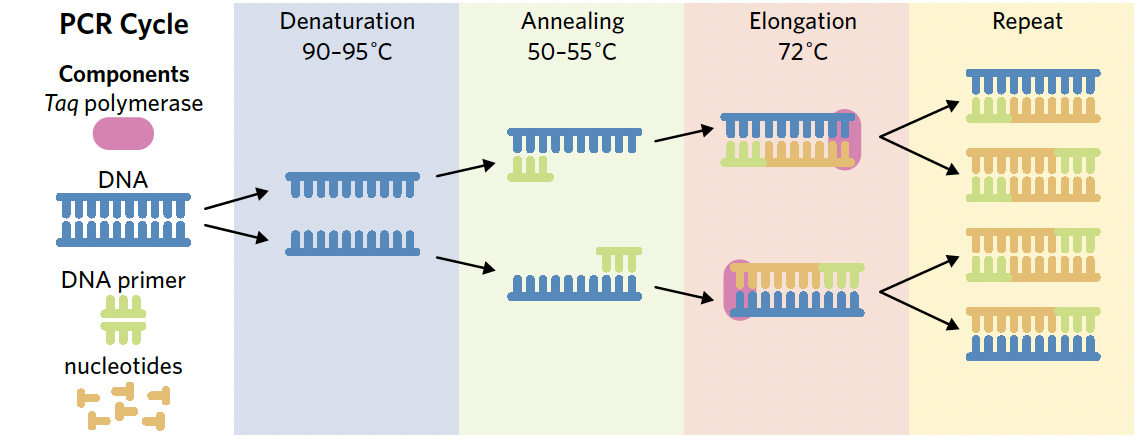
step by step process of polymerase chain reaction
denaturation - the DNA stramd is heated to approx 90-95 to break the hydrogen bonds between the bases and seperate the strands forming a single stranded DNA
annealing - the single stranded DNA is cooled to approx 50-55 to allow the primers to bind to complementary sequences on the single stranded DNA
elongation - DNA is heated again to 72 which allows taq polymerase to work. Taq polymerase binds to the primer which acts as a staring point, and begins synthesing a new complementary strand of DNA
repeat - the process is repeated multiple times to create more copies of DNA
what is taq polymerase
a heat resistant DNA polymerase enzyme which amplifies a single strandted molecue by attaching com nucleotides
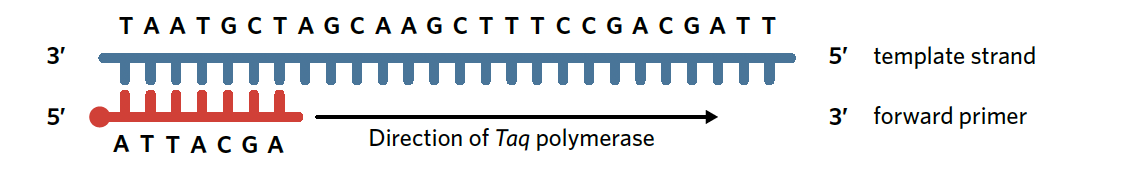
forward primer
the forward primer will bind to the start codon at the 3’ end of the template strand. This causes taq polymerase to synthesis a new DNA strand in the same direction that RNA polymerase would function
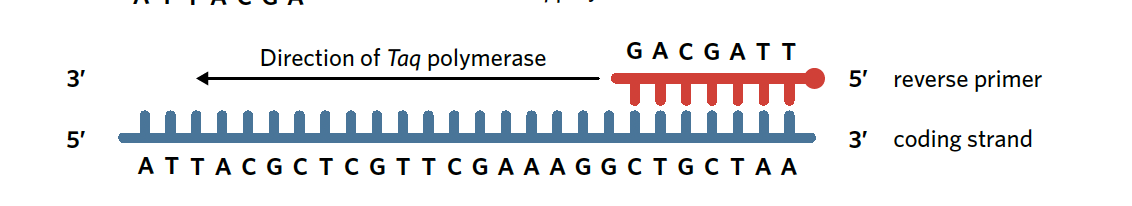
reverse primer
the reverse primer will bind to the stop codon at the 3’ end of the coding strand. This causes taq polymerase to synthesis a new DNA strand in the reverse direction that RNA polymerase would function
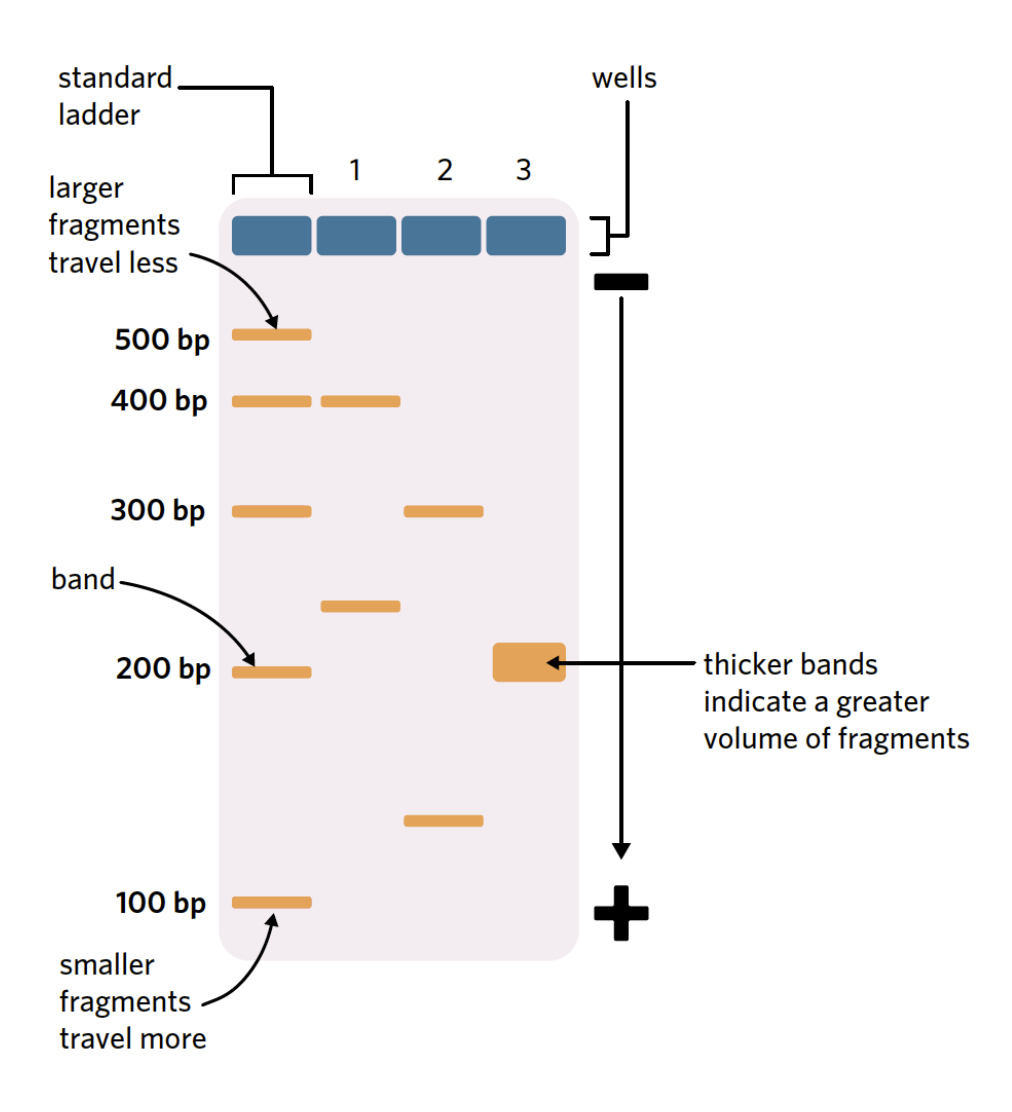
what is gel electrophoresis
a lab technique that seperates prepared DNA fragments (from restriction endonuclease or pc) based on molecule size
reading gel electrophoresis
a standard ladder contains a number of DNA fragments with a known molecular size
molecular size indicates the length of a nucleic acid sequence
short tandem repeats
STRs are segments of DNA that contain repeats of 2-6 nucleotides found in the non-coding regions of DNA
everyone has two copies of each STR region (one from mum and one from dad)
there are many fixed locations where STRs are located on our chromosome