Biomaterials Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
1
New cards
Diffusion by which mechanism occurs more rapidly in metal alloys?
\
A) Vacancy diffusion
B) Interstitial diffusion
\
A) Vacancy diffusion
B) Interstitial diffusion
B) Interstitial Diffusion
\
In metal alloys, interstitial diffusion takes place more rapidly than vacancy diffusion because the interstitial atoms are smaller and are more mobile. Also, there are more vacant adjacent interstitial sites than there are vacancies.
\
In metal alloys, interstitial diffusion takes place more rapidly than vacancy diffusion because the interstitial atoms are smaller and are more mobile. Also, there are more vacant adjacent interstitial sites than there are vacancies.
2
New cards
Self-diffusion is atomic migration in pure metals. Interdiffusion is diffusion of atoms of one metal into another metal.
\
True or False
\
True or False
True
3
New cards
As temperature decreases, the fraction of total number of atoms that are capable of diffusive motion
\
Increase or Decrease
\
Increase or Decrease
Decrease
\
As temperature decreases, the fraction of the total number of atoms that are capable of diffusive motion decreases
\
As temperature decreases, the fraction of the total number of atoms that are capable of diffusive motion decreases
4
New cards
If \[m\] atoms of helium pass through a \[a\] square meter plate area every \[t\] hours, and if this flux is constant with time, compute the flux of helium in units of atoms per square meter per second.
A) J = At/M
B) J = A/(Mt)
C) J = M/(At)
D) J = Mt/A
A) J = At/M
B) J = A/(Mt)
C) J = M/(At)
D) J = Mt/A
C) J = M/(At)
5
New cards
*Calculate the diffusion coefficient for copper in aluminum at 600°C.* \n *Preexponential and activation energy values for this system are 6.5 x 10–5 m2/s and 136,000 J/mol, respectively.*
*(A) 5.7 x 10-2 m2/s (C) 4.7 x 10-13 m2/s*
*(B) 9.4 x 10-17 m2/s (D) 3.9 x 10-2 m2/s*
*(A) 5.7 x 10-2 m2/s (C) 4.7 x 10-13 m2/s*
*(B) 9.4 x 10-17 m2/s (D) 3.9 x 10-2 m2/s*
C) 4.7 x 10-13 m2/s
6
New cards
After an edge dislocation has passed through some region of a crystal, the atomic arrangement of
that region is disordered.
\
True or False
that region is disordered.
\
True or False
False
\
Before and after an edge dislocation has passed through some region of a crystal, the atomic
arrangement is ordered and perfect. It is only during the passage of the extra half-plane that there is
disorder.
\
Before and after an edge dislocation has passed through some region of a crystal, the atomic
arrangement is ordered and perfect. It is only during the passage of the extra half-plane that there is
disorder.
7
New cards
The process by which plastic deformation is produced by dislocation motion is called ____.
Slip
8
New cards
Relative to the direction of an applied shear stress, the direction of motion of an edge dislocation’s line is
\
Parallel or Perpendicular
\
Parallel or Perpendicular
Parallel
\
The direction of motion of an edge dislocations’ line is parallel to the direction of applied shear stress.
\
The direction of motion of an edge dislocations’ line is parallel to the direction of applied shear stress.
9
New cards
The atoms surrounding a screw dislocation experience what kind(s) of strain(s)?
\
A) Shear strains
B) Compressive strains
C) Tensile strains
\
A) Shear strains
B) Compressive strains
C) Tensile strains
A) Shear Strains
\
The atoms surrounding a screw dislocation experience only shear strains.
\
The atoms surrounding a screw dislocation experience only shear strains.
10
New cards
Dislocations move with the same degree of ease on all crystallographic planes of atoms and in all crystallographic directions?
\
True or False
\
True or False
False
\
Dislocations do not move with the same degree of ease on all crystallographic planes of atoms and in all crystallographic directions. Crystallographic planes and directions along which dislocations move are those that are most closely packed with atoms.
\
Dislocations do not move with the same degree of ease on all crystallographic planes of atoms and in all crystallographic directions. Crystallographic planes and directions along which dislocations move are those that are most closely packed with atoms.
11
New cards
Reducing the grain size of metal improves toughness.
\
True or False
\
True or False
True
\
Reducing the grain size of a metal improves its toughness.
\
Reducing the grain size of a metal improves its toughness.
12
New cards
Most metals strain harden at room temperature.
\
True or False
\
True or False
True
\
Most metals strain harden at room temperature.
\
Most metals strain harden at room temperature.
13
New cards
Grain growth must always be preceded by recovery and recrystallization.
\
True or False
\
True or False
False
\
Grain growth does not always need to be preceded by recovery and recrystallization; it may occur in materials that have not been cold worked.
\
Grain growth does not always need to be preceded by recovery and recrystallization; it may occur in materials that have not been cold worked.
14
New cards
If %CW of low carbon steel increases, yield strength decreases.
\
True or False
\
True or False
False
\
Yield strength (*σ****y***) increases.
\
Yield strength (*σ****y***) increases.
15
New cards
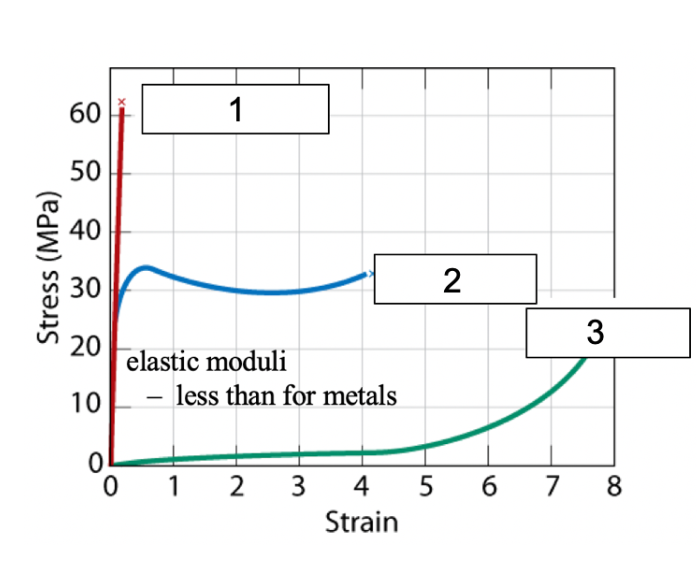
1) brittle
2) plastic
3) elastomer
2) plastic
3) elastomer
16
New cards
Ductility of a material depends on which of the following factors
\
A) room temperature, weight of material
B) angle of impact, duration of induced force
C) temperature of the material, strain rate and stress state
D) all of the above
\
A) room temperature, weight of material
B) angle of impact, duration of induced force
C) temperature of the material, strain rate and stress state
D) all of the above
C) temperature of the material, strain rate and stress state
17
New cards
Brittle fractures are characterized by prominent deformation of the material with low probability of crack propagation.
\
True or False
\
True or False
False
18
New cards
Fractures that are innate to crystalline materials that have cracks propagating along the grain boundaries are called.
A) intergranular fractures
B) crystallographic fringes
C) transgranular fractures
D) boundary line faults
A) intergranular fractures
B) crystallographic fringes
C) transgranular fractures
D) boundary line faults
C) transgranular fractures
19
New cards
The presence of inherent defects such as cracks and microscopic flaws does not affect the fracture strength of the material.
\
True or False
\
True or False
False
20
New cards
Critical stress for crack propagation in brittle materials depend on:
A) length of the internal crack
B) elastic modulus of material
C) specific surface energy
D) all of the above
A) length of the internal crack
B) elastic modulus of material
C) specific surface energy
D) all of the above
D) all of the above
21
New cards
The measure of a materials resistance to brittle fractures in the presence of cracks, known as ______________, depends on critical stress for crack propagation and crack length.
A) elasticity
B) fracture toughness
C)surface strain
D) flaw length
A) elasticity
B) fracture toughness
C)surface strain
D) flaw length
B) fracture toughness
22
New cards
If stress level and plane strain fracture toughness are fixed by the design situation, then the maximum allowable flaw size is inversely proportional to the imposed stress.
\
True or False
\
True or False
True
23
New cards
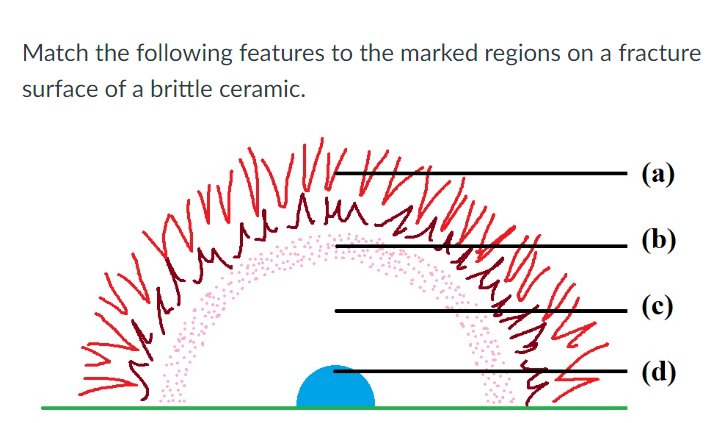
**A)** Hackle region
**B)** Mist region
**C)** Smooth mirror region
**D)** Source of failure
**B)** Mist region
**C)** Smooth mirror region
**D)** Source of failure
24
New cards
Thermoplastic polymers endure a phenomenon called __**( a )**__. This is associated with localized __**( b )**__ which leads to the formation of interconnected __**( c )**__ which grow and coalesce to form __**( d )**__.
**A)** crazing
B) plastic deformations
C) microvoids
D) cracks
B) plastic deformations
C) microvoids
D) cracks
25
New cards
The number of cycles required to cause failure of a material at a specific stress level, calculated through specimen mechanical testing is called ___________.
A) fatigue limit
B) fatigue strength
C) fatigue life
D) fracture toughness
A) fatigue limit
B) fatigue strength
C) fatigue life
D) fracture toughness
C) fatigue life