Kohler Illumination
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
What is the purpose of koeller illumination
It finds the best compromise between contrast, depth of field and resolving power
What does the stage adjuster do?
Moves the stage around so the slide is in the correct spot under the microscope
What does the condenser height control do?
Positions the condenser lens as close as possible to the bottom of the slide without touching it
What does the field diaphragm do?
Makes the source of light smaller and bigger
What do the condenser centering screws do?
Center the light hexagon
What does the aperture diaphragm lever do?
Adjusts the contrast and resolution
What is blastulation?
Formation of a ball of cells
What is gastrulation?
Formation of three germ layers
What are the three distribution patterns that organisms can be distributed in?
Uniform
random
clumped
Does a high mean automatically indicate evenness between samples?
No
What does the simpsons diversity index measure?
measure of diversity that quantifies both the richness (number of species) and the evenness (relative abundance of species) in a community
Why is there n-1 in the simpsons diversity index
part of the formula that calculates the probability that two randomly selected individuals are the same species:
Are tapeworm truly segmented?
No
Why aren’t tapeworms truly segmented?
Because their body consists of proglottids which are individual units
How does a hydrostatic skeleton work?
Uses a fluid filled cavity to allow an organism to change shape and apply force
How to tell if a squid is male
You will see a spermatophoric gland to the side or just below the branchial heart. The testes will be a white mass at the posterior end of the squid
How to tell if a squid is female
You will have a large yellow gelatinous mass at the posterior end of the squid
In what order does water enter the water vascular system in echinodermata?
Madreporite → stone canal → ring canal → radial canal → ampullae → podia (tube feet)
Is the mesoglea a germ layer?
No because it is found in diploblastic animals with an endoderm and ectoderm
what stages do jellyfish undergo during development?
Polyp asexually makes medusa → Medusa sexually makes gametes → Gametes fuse to planula larvae → Planula settles to make new polyp
What aspect of jellyfish biology allows their bodies to float?
Their mesoglea in the bell
How did jellyfish blooms arise?
When there is something wrong with the ocean:
warmer waters allow them to mature faster
overfishing removes their natural predators
How do Ctenophores eat?
Catch food on tentacles and wipe across mouth—some species swallow whole
Are all worms cephalized?
Some parasitic flatworms like the flatworms (Cestoda) aren’t
What is the equation for a scale bar length?
Drawing size/Actual size = X(physical length of scale bar)/size scale bar represents
How big should the scale bar be on the paper?
Between 10-50% of the actual drawing size
What are the four cephalopod groups?
Nautiloids
Cuttlefish
Squid
Octopus
Which group of Cephalopods has shell coiling?
Nautiloids
How is the shell coiling in nautiloids different than gastropods
Nuatiloids coiling is the same on both sides and less tight
Why have bivalves lost cephalization?
An adaption to their filter feeding lifestyle
Which valve is larger in an oyster?
The left valve
In what direction are oysters elongated?
Dorsoventrally
In what direction are scallop shells elongated?
Dorsal-ventral
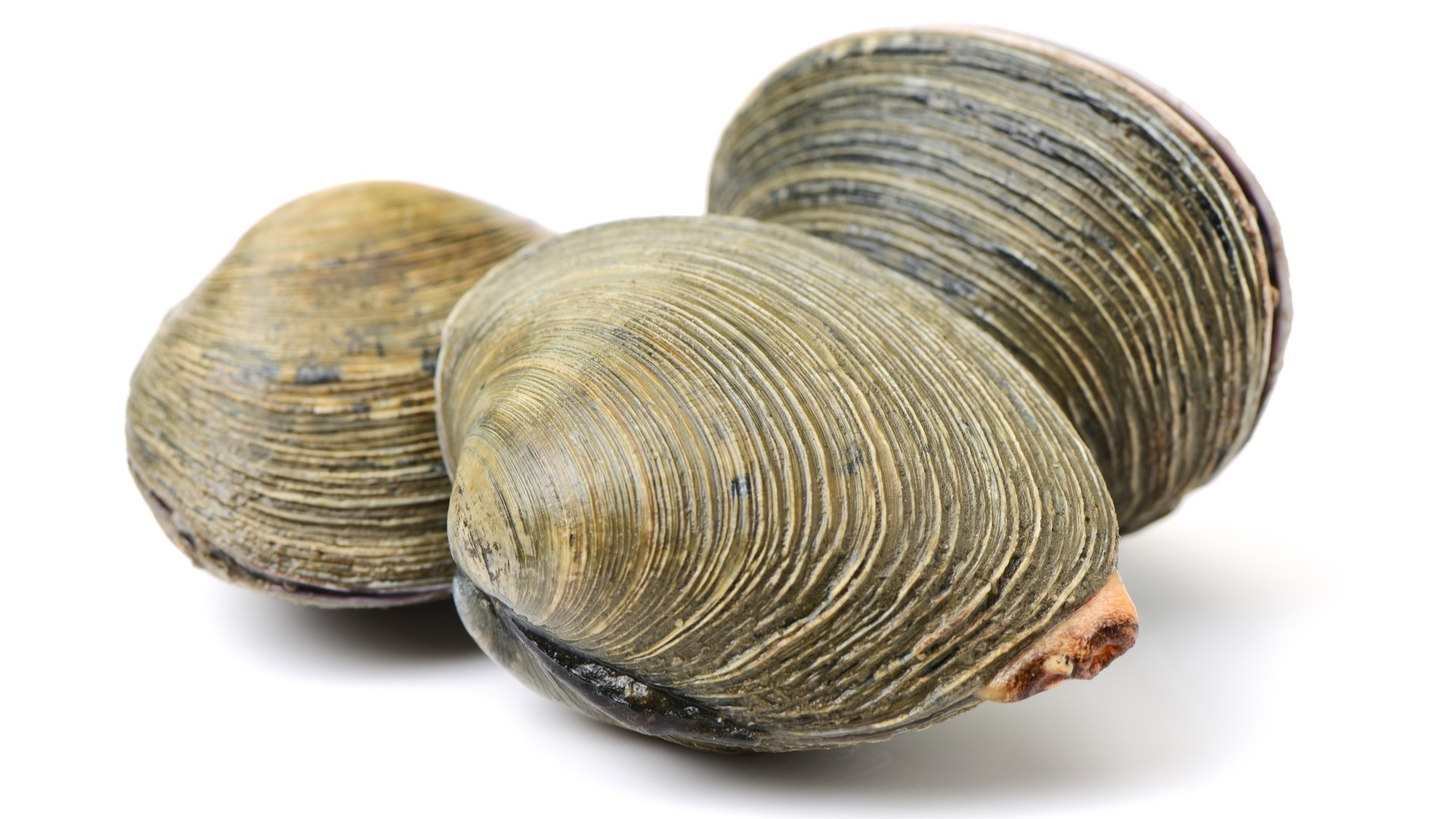

In what direction are clams elongated?
Anterior-posterior
In what direction are mussels elongated?
Anterior-posterior axis
How would you tell blue mussels apart from horse mussels
The blue mussel is quite blue while the horse mussel has a tinge of purple to it
How does collecting seashells harm the beach?
Increased erosion
Habitat loss for animals that use them
Reduced biodiversity
What kind of skeleton is found in arthropods?
A chitinous exoskeleton
Name an insect group that undergoes homometabolous metamorphosis (egg→larva→pupa→adult)
Butterflies
Name an insect group that undergoes hemimetabolous metamorphosis (egg→nymph→adult)
Dragon flies
What is an advantage of complete metamorphosis?
Protection during the pupa stage
What is the 5th subphyla of Arthropoda that only includes extinct animals?
trilobitomorpha
What two tagmata do crustaceans have?
Cephalothorax and abdomen
What two tagmata do myriapoda have?
Head and trunk
What two tagmata do Chelicerata have?
Cephalothorax and abdomen
What three tagmata do hexapoda have?
Head, thorax, abdomen
Carpace vs cephalothorax
Cephalothorax is head and thorax while carpace is protective shell covering cephalothorax
What type of skeleton is found in echinoderms?
Calcium carbonate endoskeleton made of ossicles
Which classes of echinodermata have secondary bilateral symmetry?
Echinoderm larvae—starfish and sea urchins
Where does water leave the water vascular system in echinodermata?
The podia or tube feet
What structure secretes the pen in squid?
The mantle
What are the five chordate characteristics?
Notochord
Dorsal hollow nerve cord
Pharyngeal pouches and slits
Endostyle or thyroid gland
Post-anal tail
What subphyla does amphioxus belong too?
Cephalochordata
How to distinguish between Asterias and Leptasterias sea stars?
Asterias are much more standard with the typical look while Leptasterias are much thicker and spiky
How to distinguish between Asterias Forbesi and Asteria Ruben
Asterias Forbesi are smaller and less colorful
How to tell apart Leptasterias littoralis and leptasterias tenera
Leptasterias littoralis are the green slender armed
In fish dissection, which structure is the paired pale pink if female and red if male?
Gonad
In fish dissection which structure is the silver tube?
Swim bladder
In fish dissection which structure is the pink tube
Stomach and intestine
Which structure looks like fingers attached to the stomach?
Pyloric ceca
Which structure is at the anterior end of the stomach and is deep red, mushy?
Liver
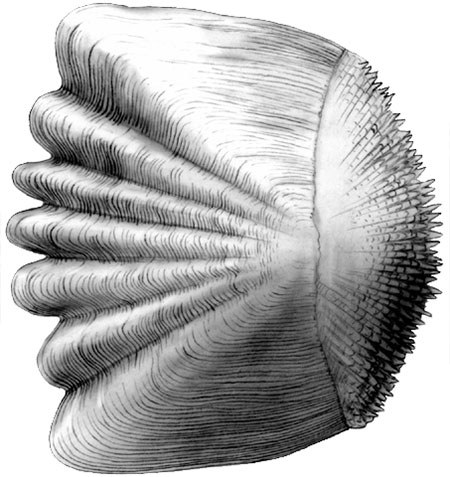

Which scale is this?
Ctenoid
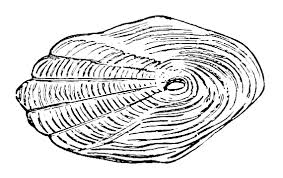
Which scale is this?
Cycloid
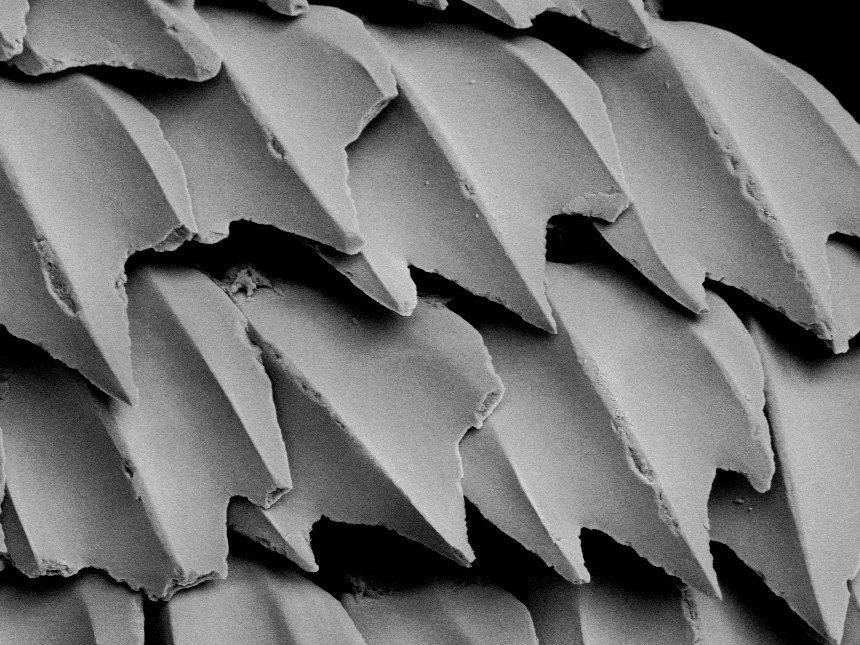
Which scale is this?
Placoid

Which scale is this?
Ganoid
What kind of caudal fin do myxini and petromyzontida have?
Protocercal (if not an option, diphycercal)
What kind of caudal fin do chondrichthyes have?
heterocercal tail
What kind of caudal fin do actinopterygii have?
Homocercal tail
What kind of caudal fin do sarcopterygii have?
Diphycercal
Do hagfish and lampreys have a pectoral fin?
No
Do hagfish and lampreys have an anal fin
No
What is viviparous?
Live birth, fed by placenta
What is oviparous?
Hatched from laid egg
What is ovoviviparous?
Live birth—fed by egg
What kind of young do sharks lay?
Ovoviparous
What is a mermaids purse?
Empty case of egg hatched by shark, skate, or ray
Catadromous migration
FW → SW → FW
Anadromous migration
SW → FW → SW
What is the common example given for anadramous migration?
Salmon; lampreys
What is the common example given for catadromous migration
Eels
What is cutaneous respiration?
Gas exchange occurs through the skin
Why are reptiles not monophyletic
They don’t include all recent common ancestors which includes birds
Tetrapods evolved from what fish ancestral group
Sarcopterygii or tetrapodamorphs
What are the layers in the amniotic egg
Chorion
Allantois
Amnion
Yolk sac
What is the function of the Chorion in the amniotic egg?
Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
What is the function of the allantois in the amniotic egg?
Gas exchange and stores waste products
What is the function of the amnion in the amniotic egg?
Hydrates and cushions/protects
What is the function of the yolk sack in amniotic egg?
Provides nourishment (feeds)
What is the function of the temporal lobes in amniotes?
Allow muscles to expand and lengthen especially the jaw
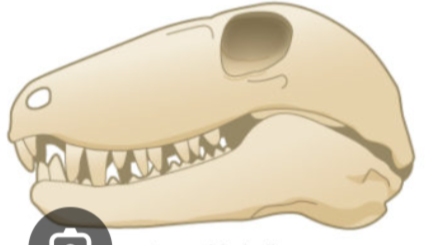
Which skull is this?
Anapsid
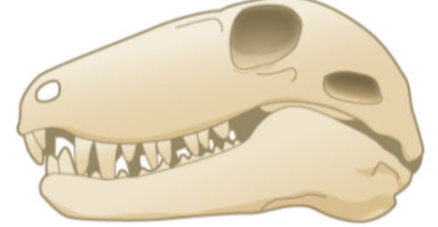
Which skull is this?
Synapsid
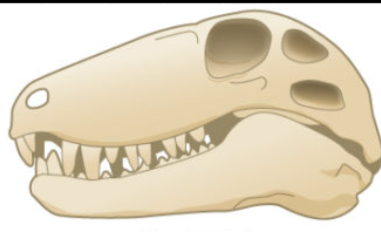
Which skull is this?
Diapsid
Are there living examples of anapsids?
Only turtles
Key features of mammals:
Warm-blooded
Four chambered heart
Diaphragm
Lower jaw
What kinds of glands do mammals have?
Mammary glands—produce milk
Hair glands/sebaceous glands
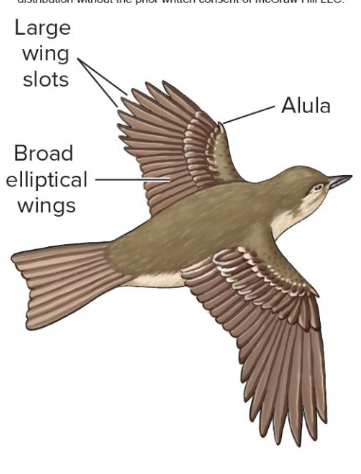
What are these kinds of wings for?
Forest flying
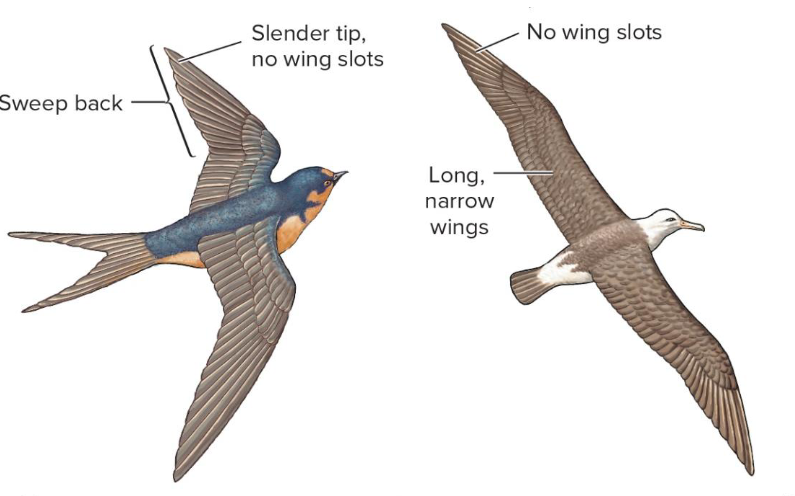
What are these kinds of wings for?
Long distance flying
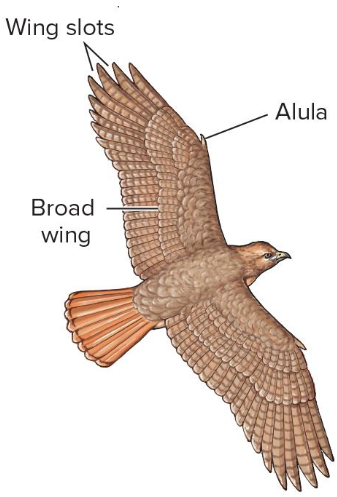
What are these kinds of wings for?
Soaring
What are the parts of a feather?
Quill, shaft, vanes
Why aren’t snakes ecdysozoan?
They are part of chordates with a vertebrate and are deuterostomes