Anemias due to RBC destruction or loss
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
hemolytic anemia definition
-premature destruction of RBC (<120 days)
-caused by hemolysis
hemolytic anemia classification
intrinsic defect: abnormality with RBC itself
extrinsic defects: normal RBC destroyed by external factors
hemolytic anemia clinical manifestation
signs that suggest hemolysis
-jaundice/scleral icterus
-dark urine (intravascular)
-splenomegaly (extravascular)
hemolytic anemia common diagnosis
CBC- low H/H
RI- elevated
bilirubin- elevated
haptoglobin- decreased
LDH- elevated
DAT
hemolytic anemia common treatment
-folic acid supplementation
-RBC transfusion
-iron chelation
-other thing specific to disease
hemolytic anemia common complications
-iron overload
-gallstone of bilirubin
-folate deficiency
-hemolytic crisis (ton RBC erupt)
-aplastic crisis
inherited hemolytic anemias
-Hereditary spherocytosis
-Hereditary elliptocytosis
-G6PD deficiency
-Pyruvate kinase deficienc
hereditary spherocytosis epidemiology
-intrinsic hemolytic anemia
-most common RBC membrane disorder
-autosomal dominant inheritance
hereditary spherocytosis pathophysiology
-genetic mutation > defect in RBC membrane proteins > loss of membrane surface area > produced spherical RBC > spherocytes trapped and destroyed in spleen
hereditary spherocytosis etiology
-genetic mutation: autosomal dominant pattern
hereditary spherocytosis risk factors
-family history
-physiological stressors: pregnancy, infection, surgery can lead to hemolytic crisis
hereditary spherocytosis symptoms
-varies from asymptomatic to severe
-basic anemia symptoms
-hemolytic symptoms: jaundice
-hemolytic/aplastic crisis with parvovirus B19 infection
hereditary spherocytosis signs
-vital sign abnormalities if severe
-pallor
-jaundice/icterus
-splenomegaly
-right upper quadrant pain if gallstones
hereditary spherocytosis diagnosis
CBC: normal
Reticulocyte count: elevated
PBC: spherocytes
DAT: distinguish from hemolytic anemia

hereditary spherocytosis treatment
avoid oxidative stressor
-splenectomy
-vaccination key in asplenic patients
-daily folic acid supplementation
-transfusion as needed
hereditary elliptocytosis epidemiology
-more common in malaria epidemic regions
-autosomal dominant inheritance
-most mild or asymptomatic
hereditary elliptocytosis pathophysiology
genetic mutation > defect in spectrin protein used to make RBC skeleton > abnormal skeleton leds to elliptical/elongated RBC shape > variable degree of hemolysis
hereditary elliptocytosis etiology
-genetic mutation
- alpha-spectrin (SPTA1) most common
hereditary elliptocytosis risk factors
-family history
-physiologic stressors
hereditary elliptocytosis symptoms
-most patients are asymptomatic or have mild anemia
Severe forms present with:
-anemia symtpoms
-hemolytic symptoms
hereditary elliptocytosis signs
-normal in mild cases
Severe cases:
-vital signs abnormal
-pallor
-jaundice
-splenomegaly
hereditary elliptocytosis diagnosis
CBC: normal
Reticulocyte count: normal or +
PBS: >25% elliptocytes (cigar shape)
Direct coombs: negative
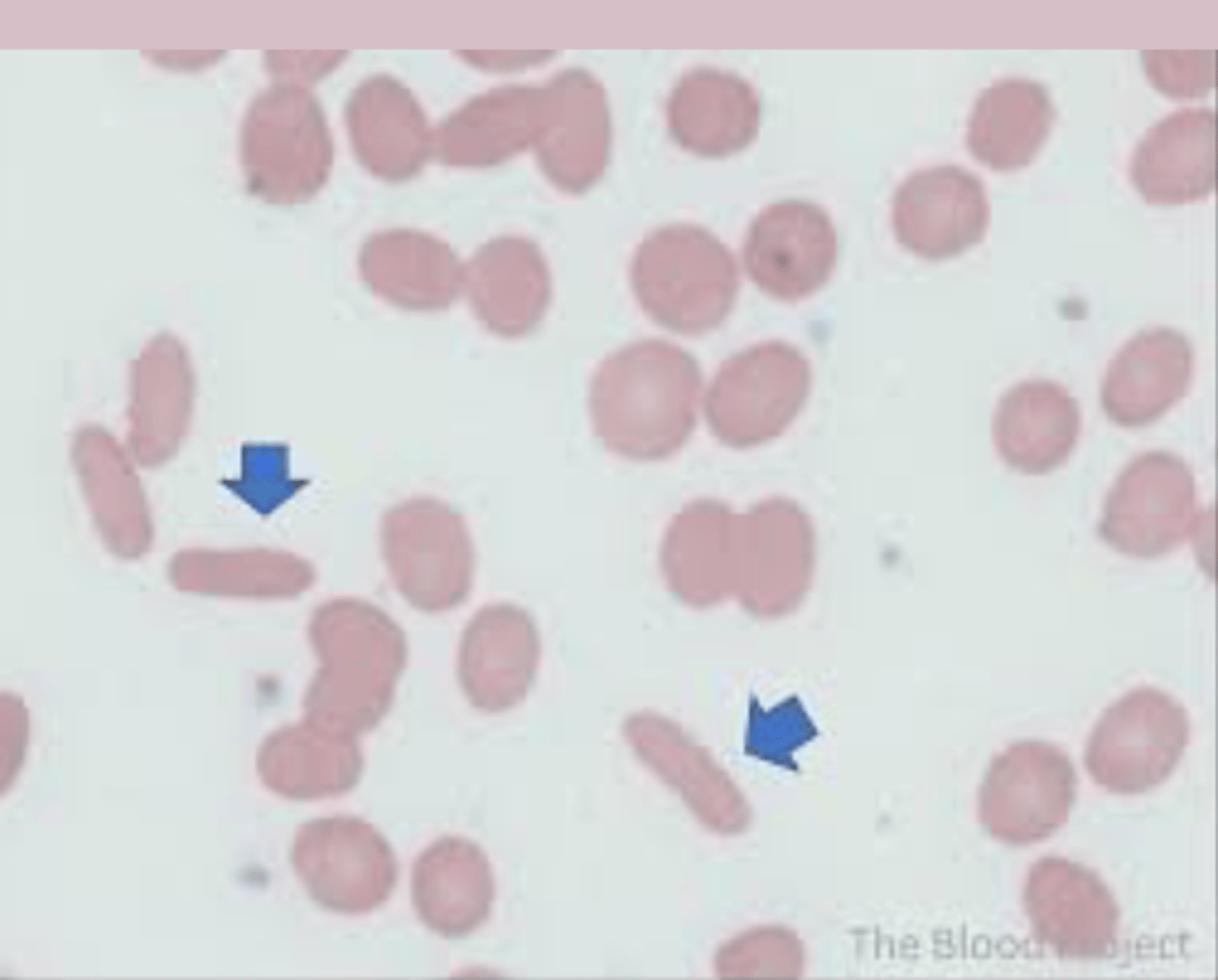
hereditary elliptocytosis treatment
-observation from most cases
-severe may need to do more
G6DP deficiency epidemiology
-most common deficiency worldwide
-x linked recessive inheritance
-africa
G6DP deficiency pathophysiology
-G6PD: produces NADPH
-NADPH protects RBC from damage
genetic defect of G6PD > less NADPH > cant neutralize oxidative stress > RBC membrane damage > intravascular and extravascular hemolysis during time of oxidative stress
G6DP deficiency etiology
-genetic mutations in G6PD
-400 variants
G6DP deficiency risk factors
-males
-african
Exposure oxidative stress:
-sulfonamides, nitrofurantoin, vitamin K, diphenhydramine,
isoniazid, acetaminophen
-fava beans
-infections
G6DP deficiency symptoms
-most patients chronic compensated hemolytic anemia with episodic acute hemolysis
-triggered by hemolytic stress
-signs of anemia
-hemolysis: dark urine, jaundice, pain
G6DP deficiency signs
usually catching during hemolytic episode: jaundice, mild splenomegaly, dark urine
G6DP deficiency diagnosis
-most appear normal when not in acute phase
-CBC: down during acute episode
-reticulocyte count: elevated during acute episode
-PBS: bite cells, heinz bodies
-Urinalysis: hemoglobinuria
-G6DP enzyme activity assay: tests patients levels = low
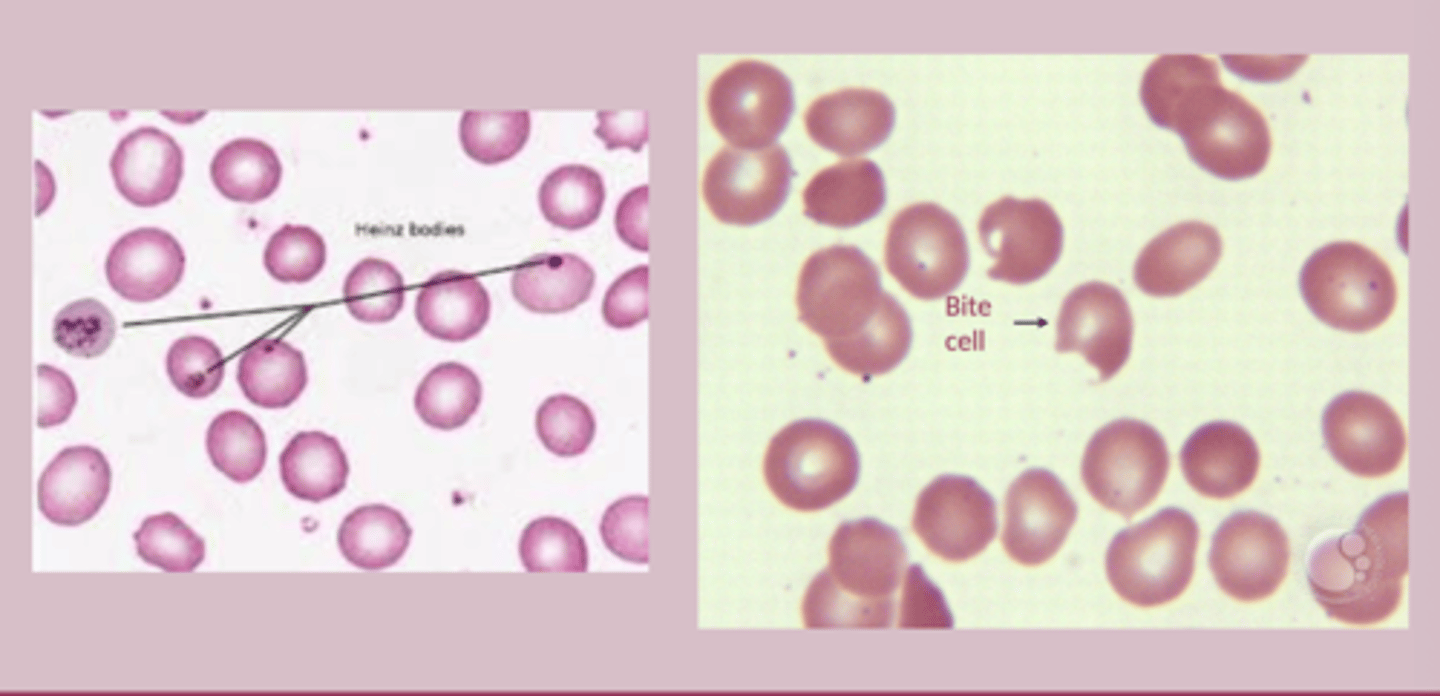
G6DP deficiency treatment
-removal/avoid triggering stressors
-supportive care
-severe= transfusion
pyruvate kinase deficiency epidemiology
-autosomal recessive inheritance
pyruvate kinase deficiency pathophysiology
genetic mutation in PKLR gene > decreased pyruvate kinase activity > reduced ATP production > ATP depletion > impaired RBC membrane > RBC become rigid and dehydrated > RBC destruction in spleen (extravascular hemolysis)
pyruvate kinase deficiency etiology
-mutation in PKLR gene (chromosome 1q21)
-many mutations
pyruvate kinase deficiency risk factors
-family history
-parental consanguinity
-certain ethnic backgrounds
pyruvate kinase deficiency symptoms
-variable
-hemolysis is chronic
-anemia symptoms
-hemolysis symptoms fluctuate
pyruvate kinase deficiency signs
-can be normal
-pallor, jaundice, splenomegaly
-frontal bossing in severe cases (children more prominent)
pyruvate kinase deficiency diagnosis
CBC: normal
reticulocyte count: elevated
PBS: Burr cells, acanthocytes
hemolysis marker: elevated
DAT: negative
PK enzyme activity assay: test PK enzyme = reduced
pyruvate kinase deficiency treatment
-avoid oxidative stressors
-depends on severity
-monitoring
-folic acid supplement
acquired hemolytic anemias
-Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (intrinsic)
-Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (extrinsic)
-Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia (extrinsic)
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria epidemiology
-rare acquired clonal hematopoietic stem cell disorder
-30-40 years
-association with bone marrow failure
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria pathophysiology
acquired mutation in PIG-A gene B > abnormal sensitivity of RBC membrane to lysis by complement > intravascular hemolysis
-acquired mutation will also come from thrombosis, bone marrow failure
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria etiology
-acquired somatic mutation in PIG-A gene
-immune mediated bone marrow injury
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria risk factors
-history of anemia or bone marrow failure
-immune disorders
-immunosuppressive therapy
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria symptoms
-classic triad: intravascular hemolysis, venous thrombosis, cytopenias
-anemia symptoms
-hemolysis symptoms: dark urine, jaundice
-thrombosis
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria signs
-pallor, jaundice
-thrombosis
-petechiae, purpura id thrombocytopenia
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria diagnosis
CBC: normal
reticulocyte count: elevated
PBS: nonspecific
hemolysis marker: elevated LDH
Urinalysis: Hemoglobinuria
DAT: negative
FLOW Cytometry: gold standard
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria treatment
-folic acid supplement
-transfusion
stem cell transplant only curative option
-anticoagulation for thrombosis
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria education/prognosis
thrombosis is main cause of mortality
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) epidemiology
-extrinsic
-warm AIHA: more common female
-cold AIHA: when they are colder
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) pathophysiology warm
IgG auto auto-antibodies bind to RBC membrane > RBC undergo extravascular hemolysis within the spleen
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) pathophysiology cold
IgM auto-antibodies bind to RBC at low temp > complement activation > intravascular hemolysis of RBC
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) etiology
-primary idiopathic 50%
-secondary: other autoimmune disorders
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) risk factor
-autoimmune disorder
-older
-female
-cold exposure
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) symptoms warm
-gradual onset of anemia and hemolysis symptoms
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) symptoms cold
-similar to warm but worsen when cold
-acrocyanosis
-hemoglobinuria after exposure
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) signs
warm- splenomegaly
cold- acrocyanosis
-other classic symptoms for both
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) diagnosis
CBC: normal
reticulocyte count: elevated
PBS: spherocytes, polychromasia
RBC agglutination in cold AIHA
DAT: positive
Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia (AIHA) treatment
-treat underlying condition
-warm: corticosteroids (prednisone 1-2mg/kg/day)
-cold: avoid cold, DMARDS (Rituximab)
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia epidemiology
-extrinsic
-RBC damage by circulation then lysis
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia pathophysiology
RBC in perpherial blood due to trauma > damaged/activated endotherlium > platelet adhesion/thrombi > intravascular hemolysis of RBC, form clots
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia etiology
many
-TTP, HUS, DIC
-anything that causes direct mechanical damage to RBC
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia risk factors
-underlying cause
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia symptoms
-acute onset of anemia and hemolysis symptoms
- features of underlying cause
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia signs
-pallor, jaundice
-dark urine, petechiae, purpura
-specific to underlying cause
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia diagnosis
CBC: normal
reticulocyte count: elevated
PBS: schistocytes
hemolysis marker: elevated LDH
DAT: negative
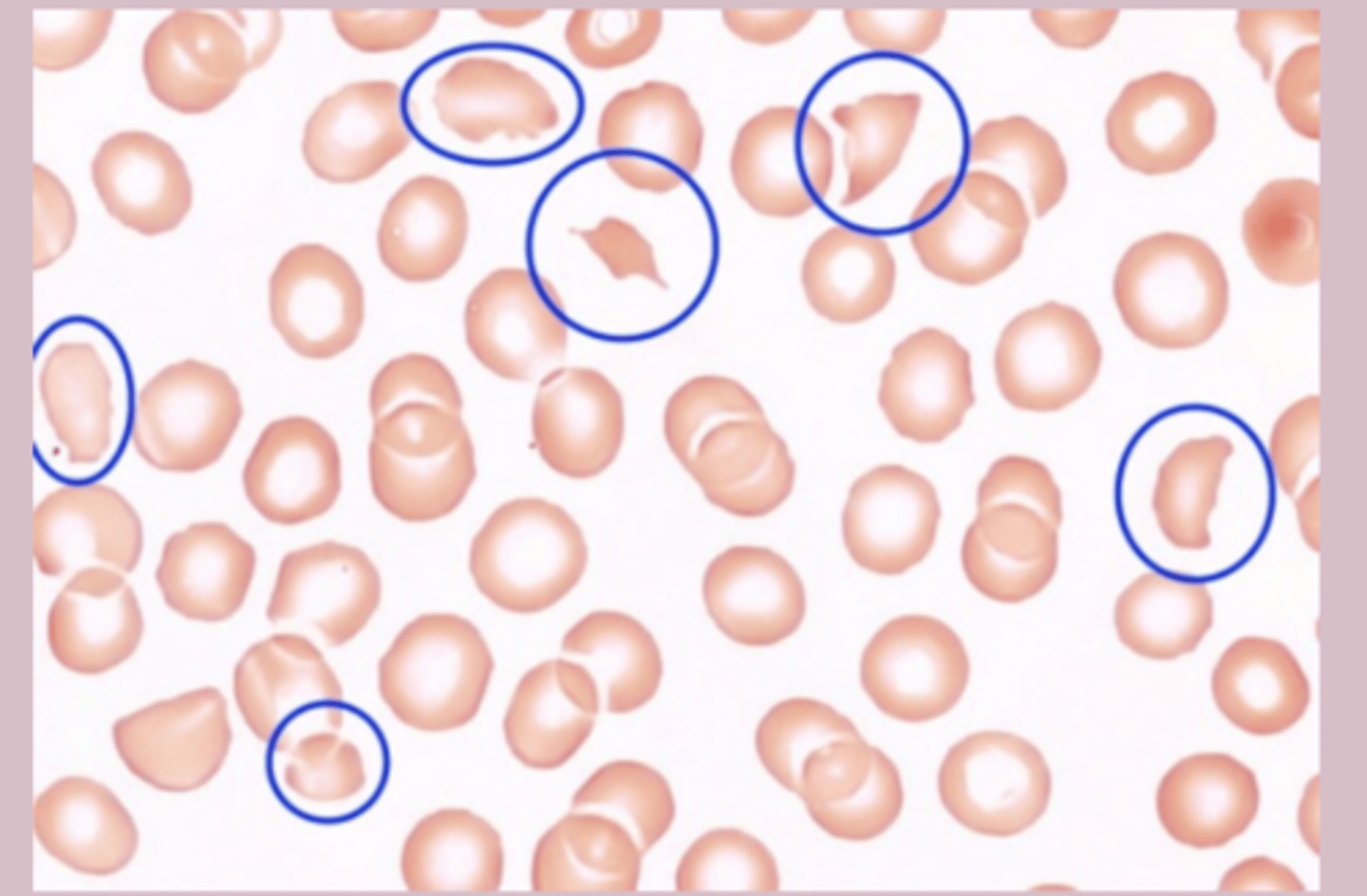
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia treatment
-management of underlying cause
-supportive care
hemorrhagic anemia
caused by acute blood loss
-treatment aimed to stop hemorrhage
Acute Posthemorrhagic Anemia (APHA) Epidemiology
-common from due to acute blood loss
-trama is leading cause
-GI bleeding
Acute Posthemorrhagic Anemia (APHA) pathophysiology
some sort of trauma that leads to bleeding > acute blood loss leads to anemia
-hypovolemia (min to hr)
- conversion to anemia (hr to day)
-bone marrow responds (days to weeks)
Acute Posthemorrhagic Anemia (APHA) etiology
-some form of acute blood loss
-external bleeding: trauma
-internal bleeding: HI, OB
Acute Posthemorrhagic Anemia (APHA) risk factors
-trauma
-antiplatelet meds
-GI
-OB
Acute Posthemorrhagic Anemia (APHA) symptoms
-symptoms depend on rate of blood loss
-mild <15% minimal symptoms
-moderate 15-30% tachy, hypotension, weak
-severe 30-40% tachy, hypotension, confusion
-critical >40% shock
Acute Posthemorrhagic Anemia (APHA) diagnosis
initially: CBC and reticulocyte count =normal
Type and screen in preparation for transfusion
Acute Posthemorrhagic Anemia (APHA) treatment
-control bleeding
-IV fluids
-transfusion