50. Neurologic examination & other diagnostic procedures
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is the aim of a physical examination in neurological cases?
To rule out other disorders that mimic neurological symptoms
What does a complete neurological examination follow?
Physical examination
What is the purpose of a neurological examination?
To confirm a neurological condition and localise the lesion
What are the steps in a neurological examination?
Mentation
Posture & gait
Cranial nerve examination
Postural reactions
Spinal reflexes
Palpation
Nociception
What is mentation?
Observation of the patient's behaviour and consciousness
What do alterations in mentation indicate?
Intracranial disease
What are the different mentation states?
Normal, excitement, depression (apathy, stupor), coma
What are some abnormal postures?
Kyphosis: dorsal curvature of spine
Lordosis: ventral curvature of spine
Scoliosis: lateral deviation
Torticollis: head tilt, vestibular system, brain stem
Opisthotonus: dorsoflexion of head & neck.
Wide-based stance: vestibular or cerebellar lesion
Schiff-Sherrington posture: Increased tone in forelimbs, paralysis in hindlimbs. T3-L3 lesion
What are some abnormal gaits?
Paralysis: complete and incomplete (paresis) loss of function of muscles
Ataxia: no paralysis, by lack of functional coordination
Spasm: pathologically exaggerated contraction of muscles
Tremor: rapid sequence of limited clonic muscular movement
Forced movements: repetition of muscle movements in the same pattern
How is gait evaluated?
On a non-slippery surface
What is the purpose of examining cranial nerves?
To detect abnormalities in cranial nerve function and localise lesions to specific locations in the brain or brianstem
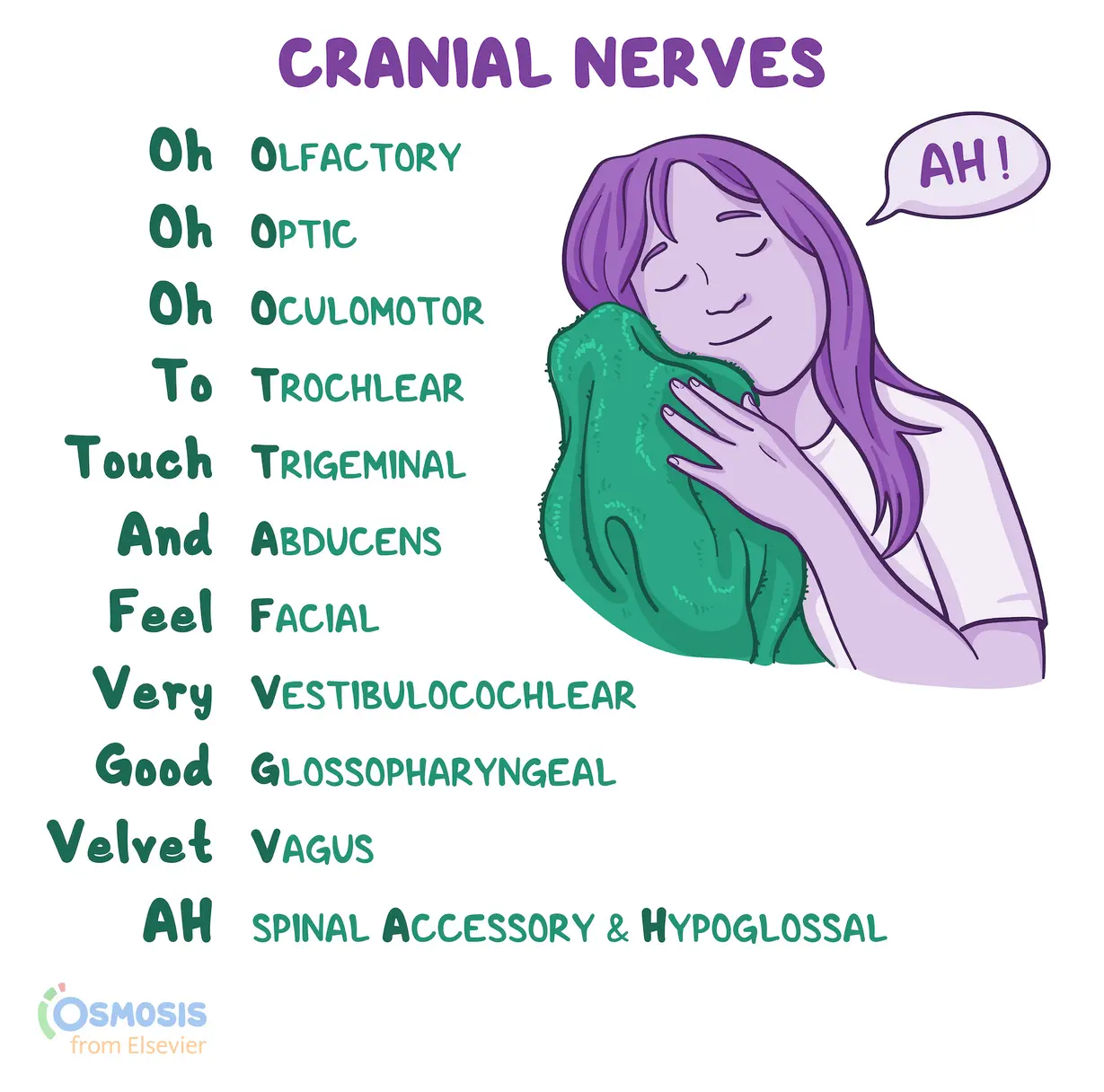
What are the cranial nerves?
I. Olfactory
II. Optic
III. Oculomotor
IV: Trochlear
V: Trigeminal
VI: Abducens
VII: Facial
VIII: Vestibulocochlear
IX: Glossopharyngeal
X: Vagus
XI: Spinal accessory
XII: Hypoglossal
What are some cranial nerve tests?
Olfactory: Olfactory nerve (CN I)
Menace response: Optic nerve (CN II), Facial nerve (CN VII)
Pupillary light reflex: Optic nerve (CN II), Oculomotor nerve (CN III), Abducens nerve (CN VI)
Vestibular eye movements: Optic nerve (CN II), Oculomotor nerve (CN III), Abducens nerve (CN VI)
Palpebral reflex: Trigeminal nerve (CN V), Facial nerve (CN VII)
Corneal reflex: Abducens nerve (CN VI)
Nasal mucosa: Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
What is nystagmus?
Jerking movements of the eyeball
What do postural reactions test?
Proprioceptive and motor systems
What do abnormalities in postural reactions indicate?
Lesion in peripheral or central nervous system
What is an early indicator of spinal cord compression?
Abnormal conscious proprioception
What are some postural reaction tests?
Knuckling correction: foot is manipulated w/ dorsal surface on table, animal should automatically correct position in 1-2 seconds
Placing response
Tactile: sensation of touch when blindly moved toward a table
Visual: when animal sees table, puts feet out to place on ground
Hopping reaction: slow to initiate w/ conscious proprioception abnormality. Dysmetria: inaccurate movement
Hemi-walking: lift two feet (one fore & one hind) look for balance on remaining feet.
Wheel-barrowing: Dog should compensate & perform walking movement.
What is dysmetria?
Inaccurate movement
What is the procedure for testing spinal reflexes?
Lateral recumbency, relaxation
What are some spinal reflexes tested?
Biceps reflex (C6-T1): knock biceps tendon → contraction of biceps muscle or twitch in toes
Triceps reflex (C7-T1): knock triceps tendon → contraction of triceps muscle
Patellar reflex (L4-L6): knock patellar tendon → kick w/ foot
Gastrocnemius reflex (L6-L7): knock Achilles tendon → contraction of semimembranosus & semitendinosus muscle
Withdrawal reflex (C6-T2, L4-S1, L5-L6, S1-S2): done by squeezing a digit → w/drawal of limb
Perineal reflex (S1-S3): touch skin around anus → contraction of sphincter
Panniculus reflex (C7-T2): pinch skin at level of tuber coxae along length of vertebrae
Which nerve is involved in the biceps reflex?
Musculocutaneous
Which nerve is involved in the triceps reflex?
Radial
Which nerve and muscle are involved in the patellar reflex?
Femoral nerve. Quadriceps muscle
Which muscles contract when testing the gastrocnemius reflex?
Semimembranosus and semitendinosus
Which nerves are involved in the withdrawal reflex?
C6-T2, L4-S1, L5-L6, S1-S2
Which nerve is involved in the perineal reflex?
Perineal nerve
Which nerves are involved in the panniculus reflex?
Lateral thoracic nerves
What does palpation detect in a neurological exam?
Swelling, atrophy, pain
What is nociception?
Perception of pain
What does loss of deep pain perception indicate?
Poor prognosis (last function to be lost)
How is superficial pain tested?
Cutaneous stimulation
How is deep pain tested?
Periosteal pressure: applying pressure to digits with haemostats/fingernails
What imaging techniques are used in neurological diagnosis?
Radiography, CT scan, MRI, myelography
What does radiography detect?
Spinal fractures, osteophytes, bone loss, subluxations, disc space deviations
What are the advantages of CT scan over radiography in spinal injuries?
More accurate identification of fractures and bone problems
What are the limitations of CT scan in spinal injuries?
Less useful for soft tissue damage detection
What are the advantages of MRI in spinal injuries?
Better for soft tissue damage (spinal cord, discs, ligaments, nerve roots)
What is myelography?
Radiography (or CT) of the spinal cord after contrast medium injection
What does myelography detect?
Spinal canal stenosis
How can orthopaedic and neurological problems be differentiated?
Proprioception tests
What is the difference between coma and stupor?
Stupor means that only vigorous and repeated stimuli will arouse the individual, and when left undisturbed, the patient will immediately lapse back to the unresponsive state.
Coma is a state of unarousable unresponsiveness.