Introduction to Glaucoma: Part 2 - Anterior Segment & Ocular Disease Fall 2025
1/306
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
307 Terms
primary angle closure glaucoma
appositional or synechial closure of the anterior chamber angle
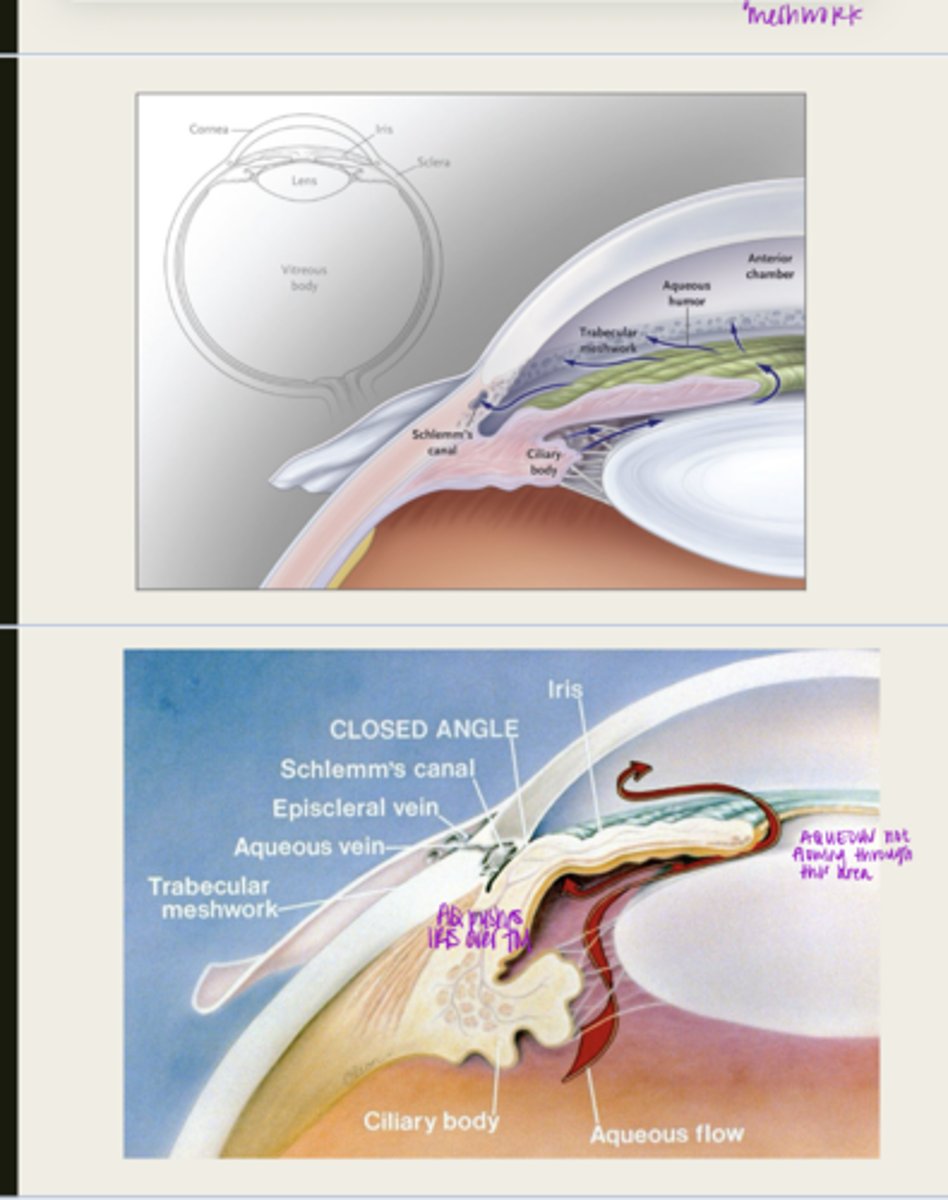
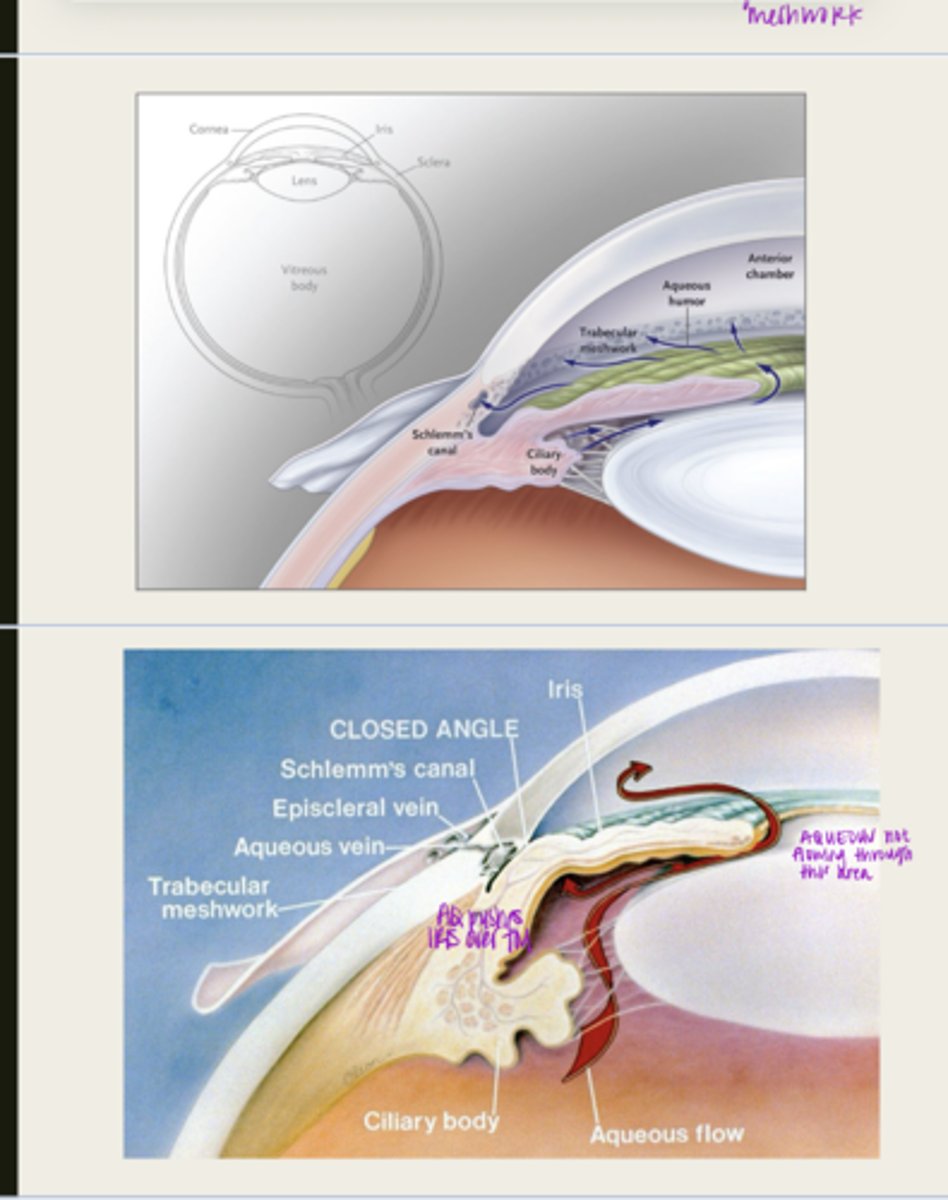
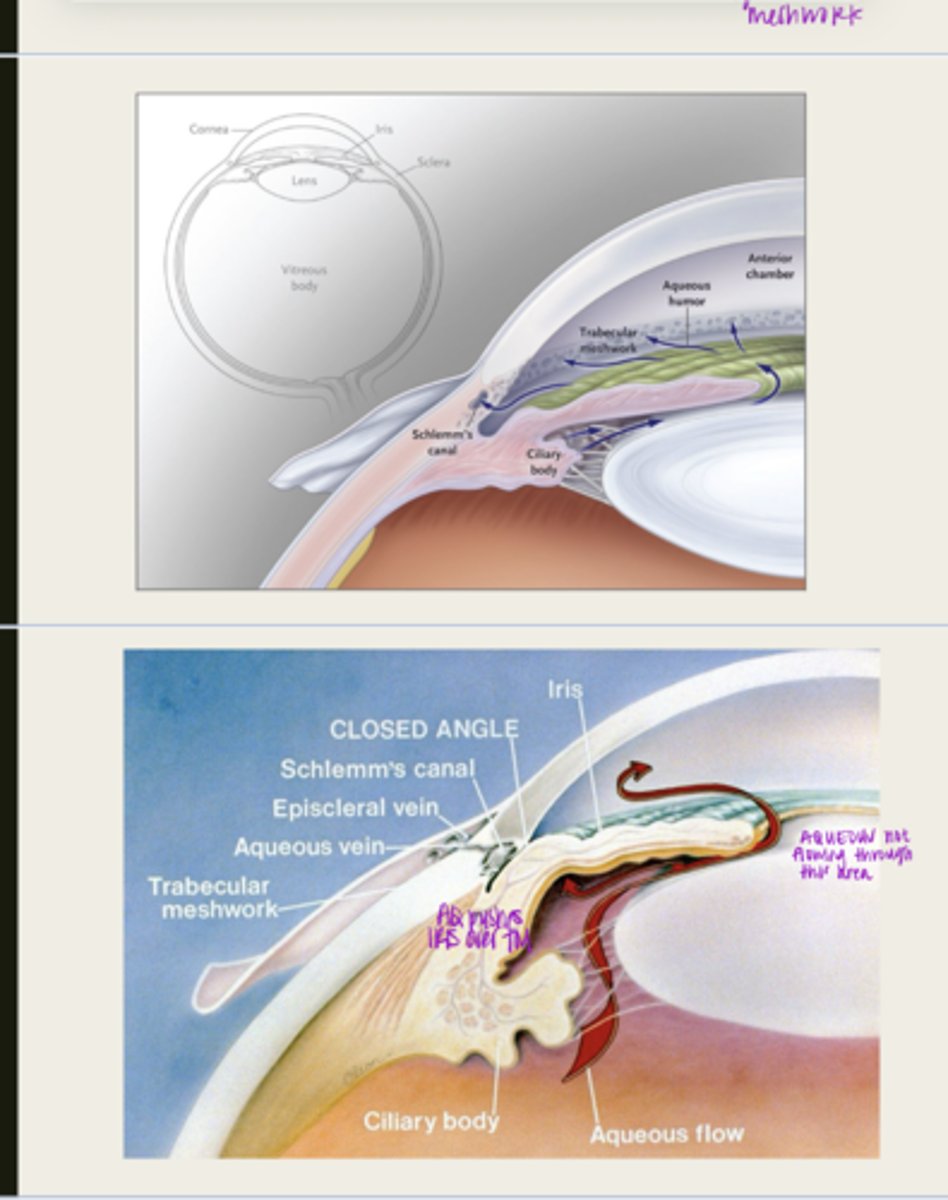
aqueous outflow will be reduced which will lead to an increase in IOP
What happens to aqueous flow during primary angle closure glaucoma?
50+ yo
What is the onset of primary angle closure glaucoma?
Asia -- higher incidence of myopes with flatter cornea and narrow anterior chamber
Where is primary angle closure glaucoma common?
females
Who is more affected by primary angle closure glaucoma?
Females or males
yes
Are there multiple mechanisms possible for the development of primary angle closure glaucoma?
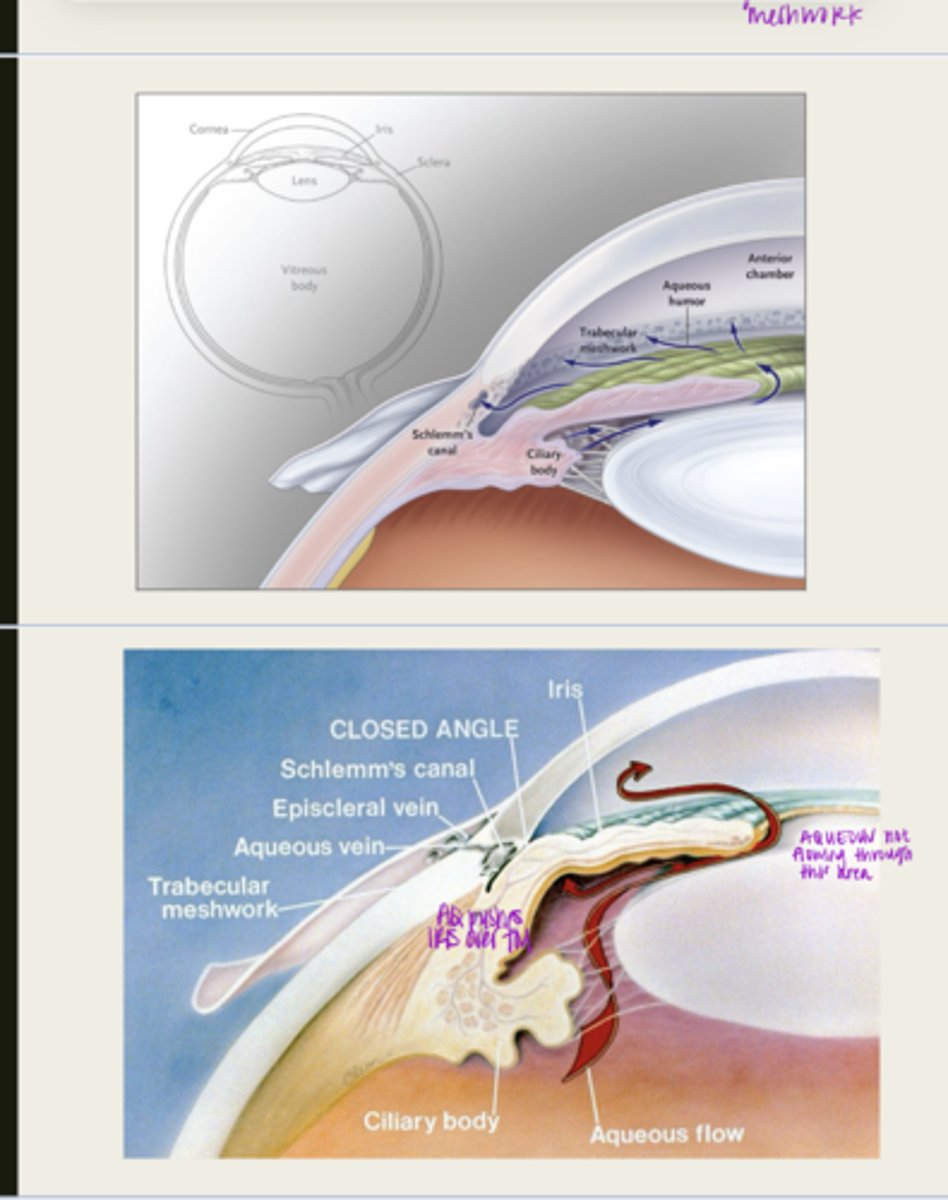
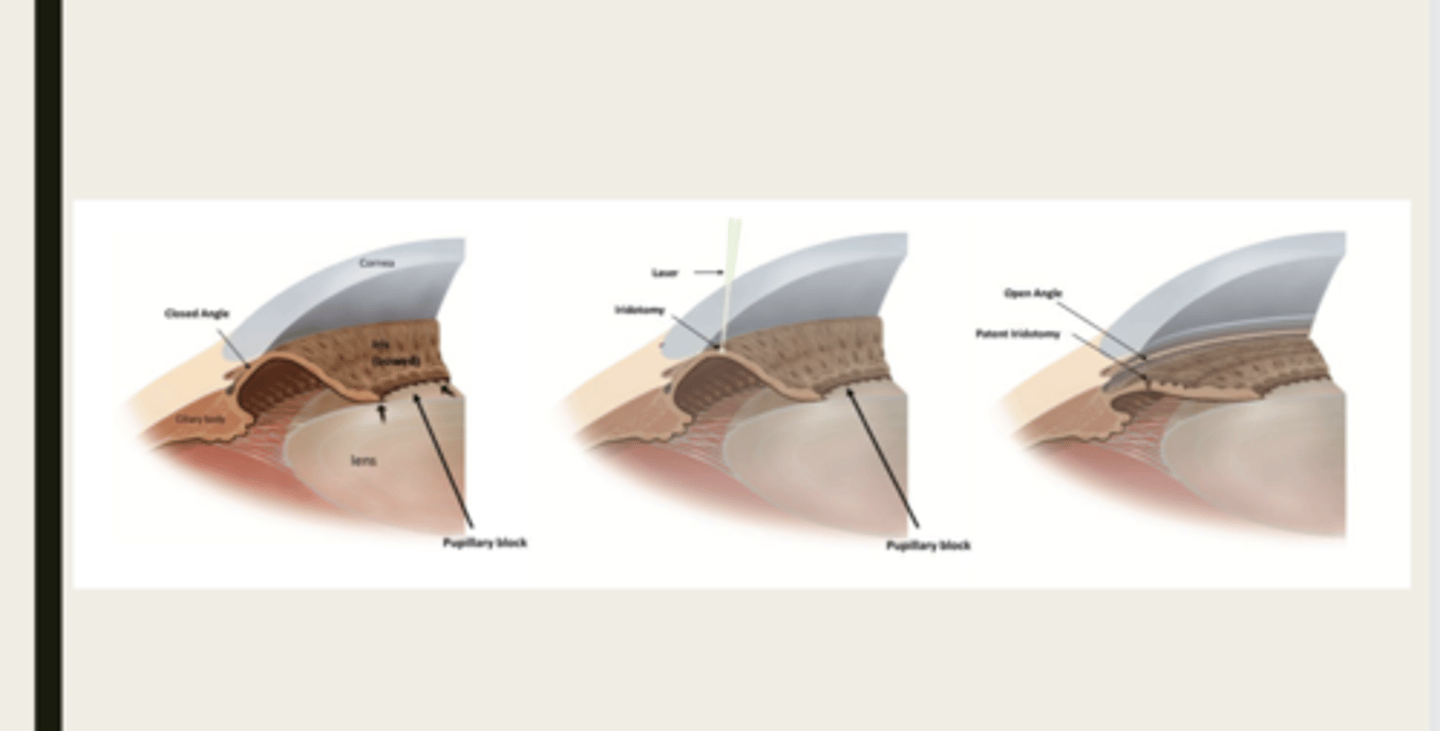
pupillary block
What is a key element in most variants of primary angle closure glaucoma?
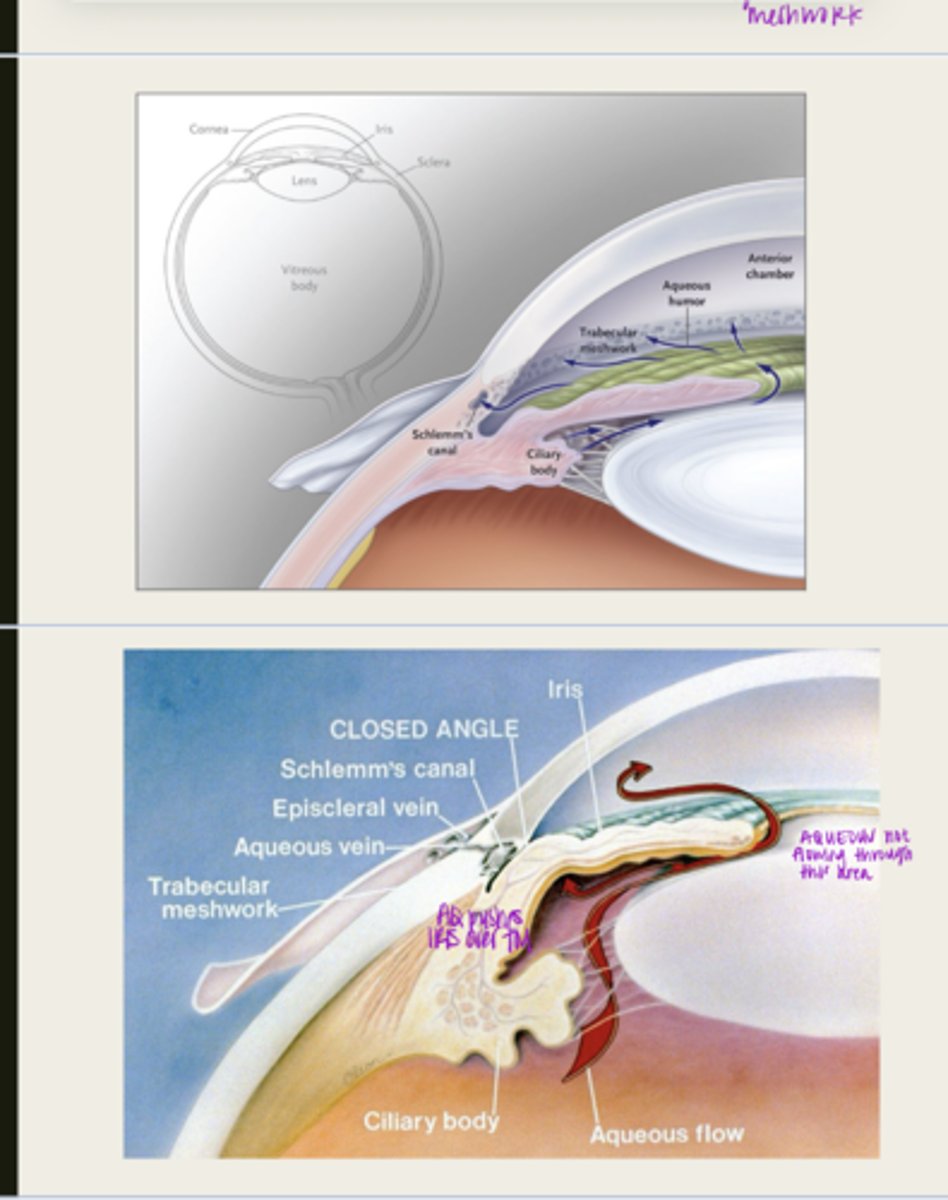
aqueous is blocked from traveling from the posterior chamber to the anterior chamber
What happens during pupillary block with primary angle closure glaucoma?
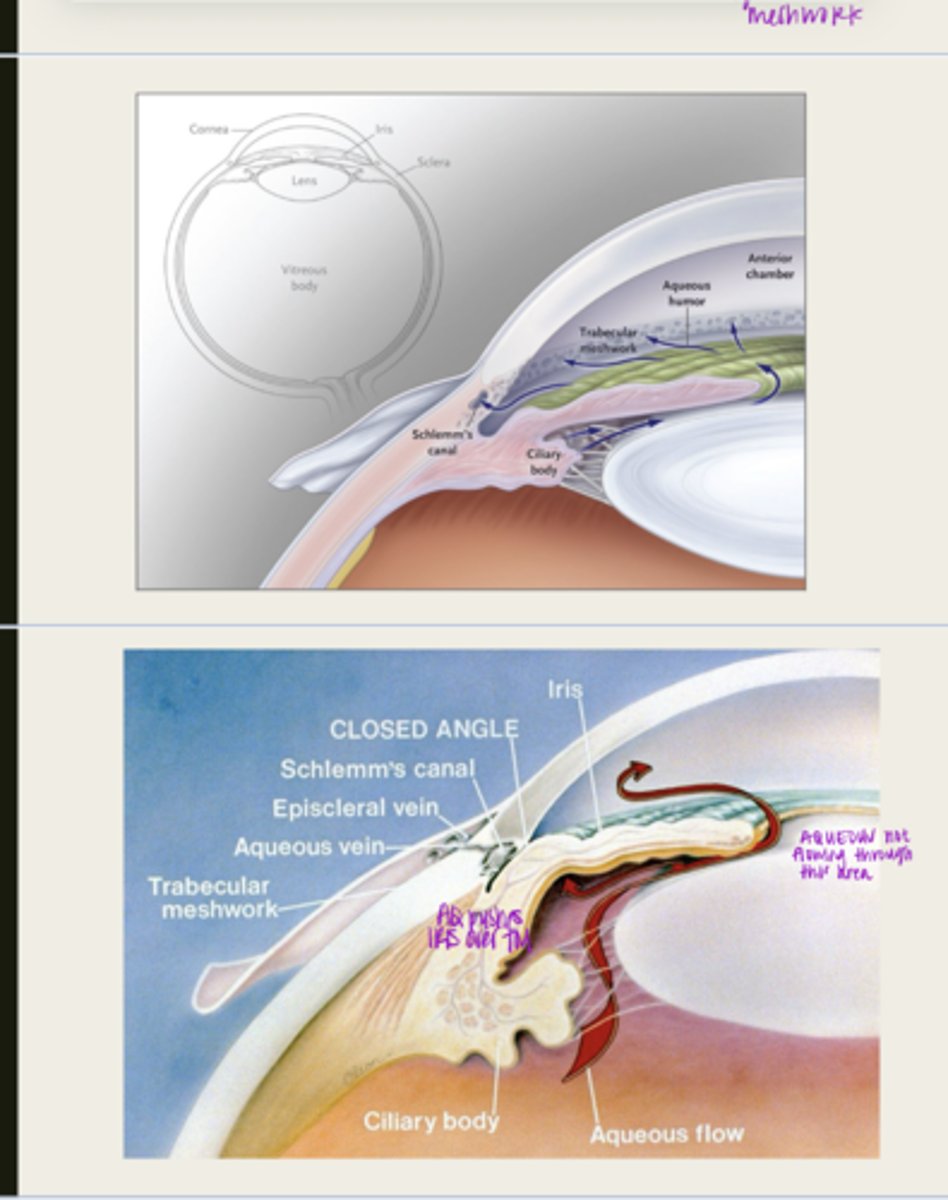
d/t posterior synechia
What is pupillary block usually d/t with primary angle closure glaucoma?
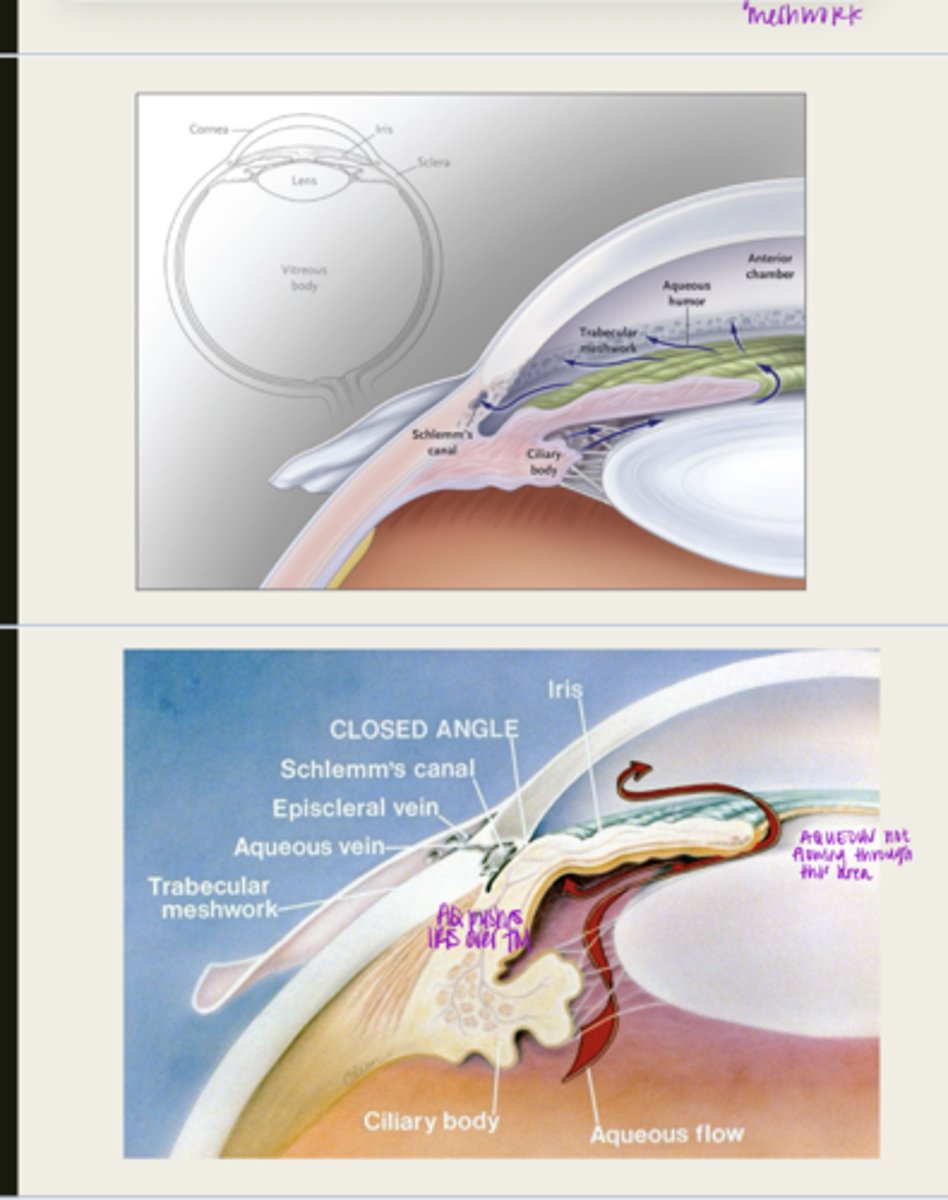
the iris will bow forward d/t the increase volume of aqueous in the posterior chamber
What happens to the iris with pupillary block?
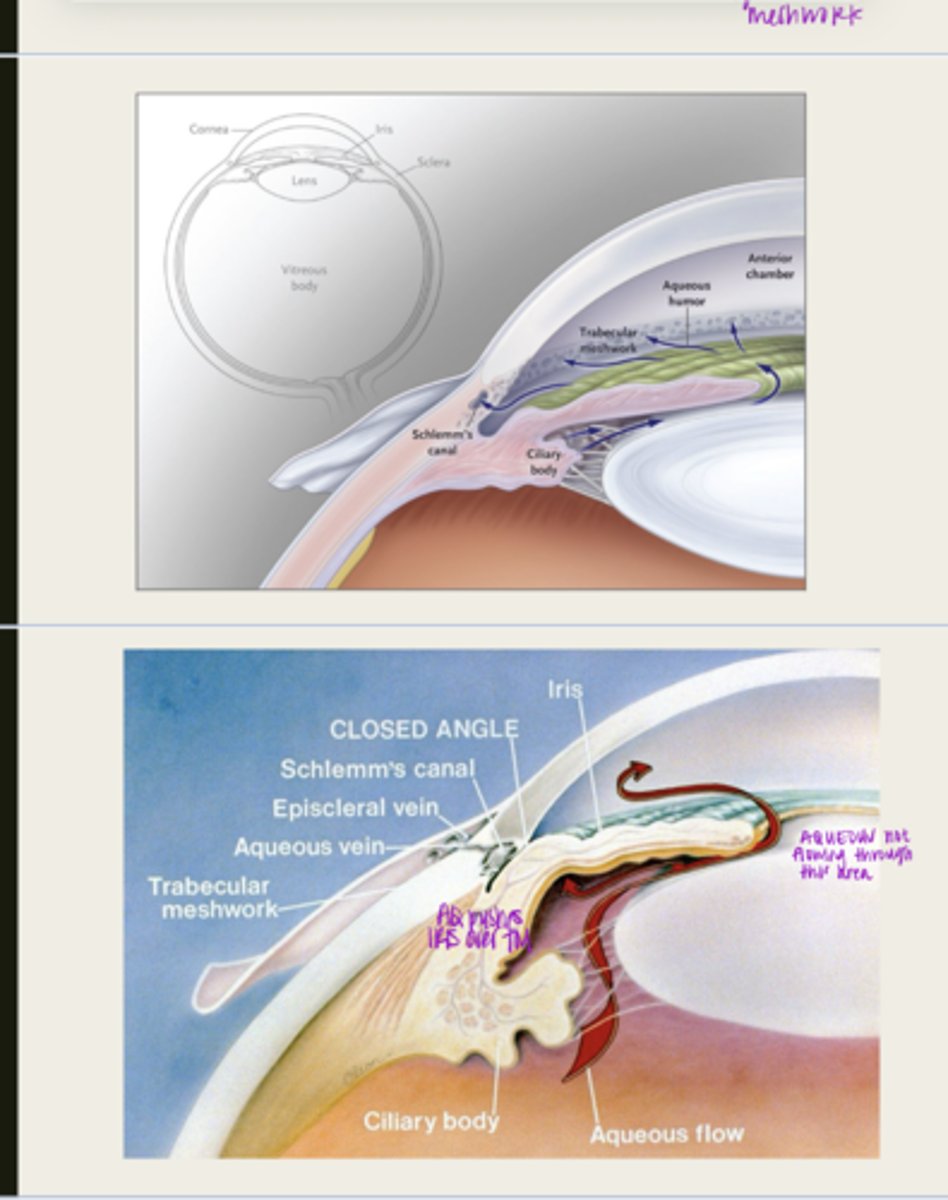
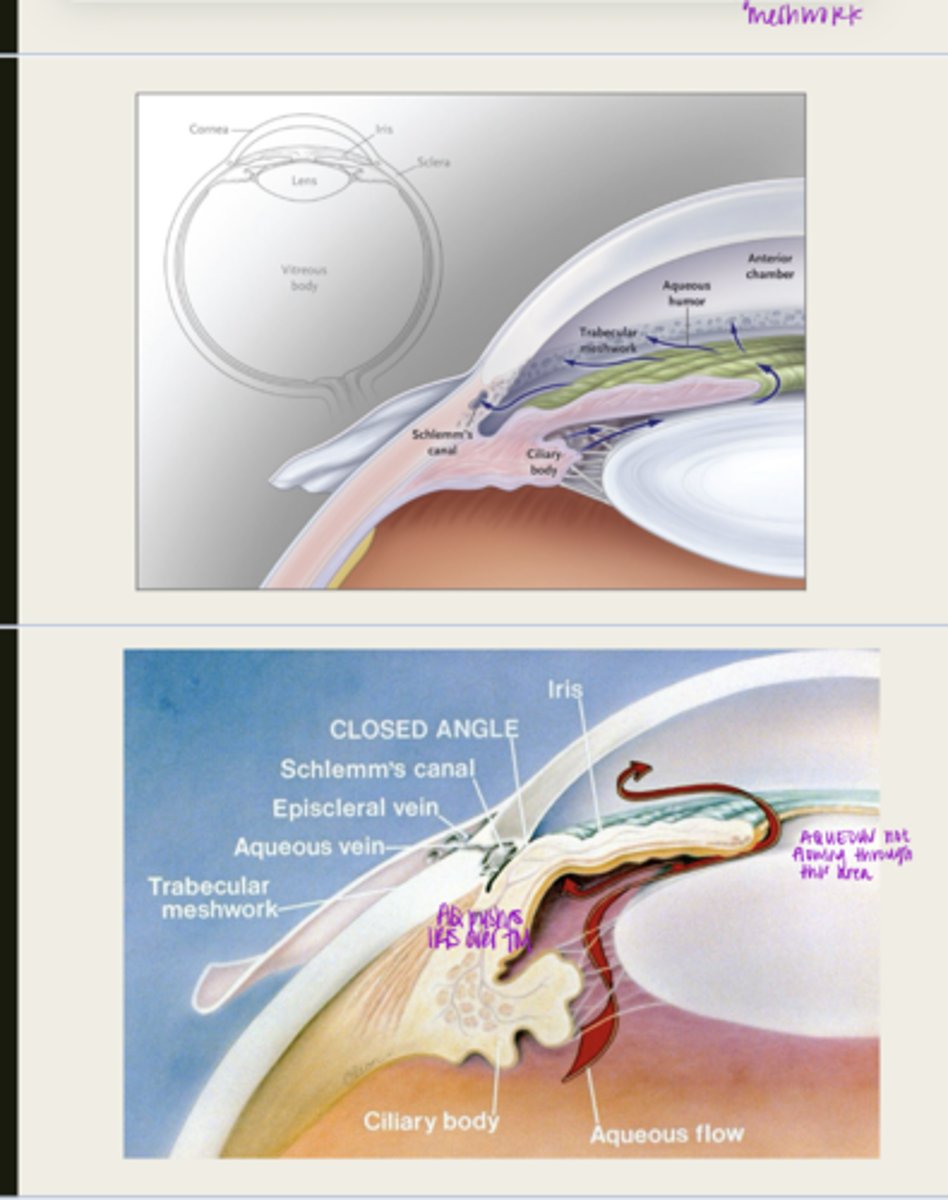
iris adheres to and blocks the TM, aqueous cannot flow through
What happens d/t iris bowing forward with pupillary block?
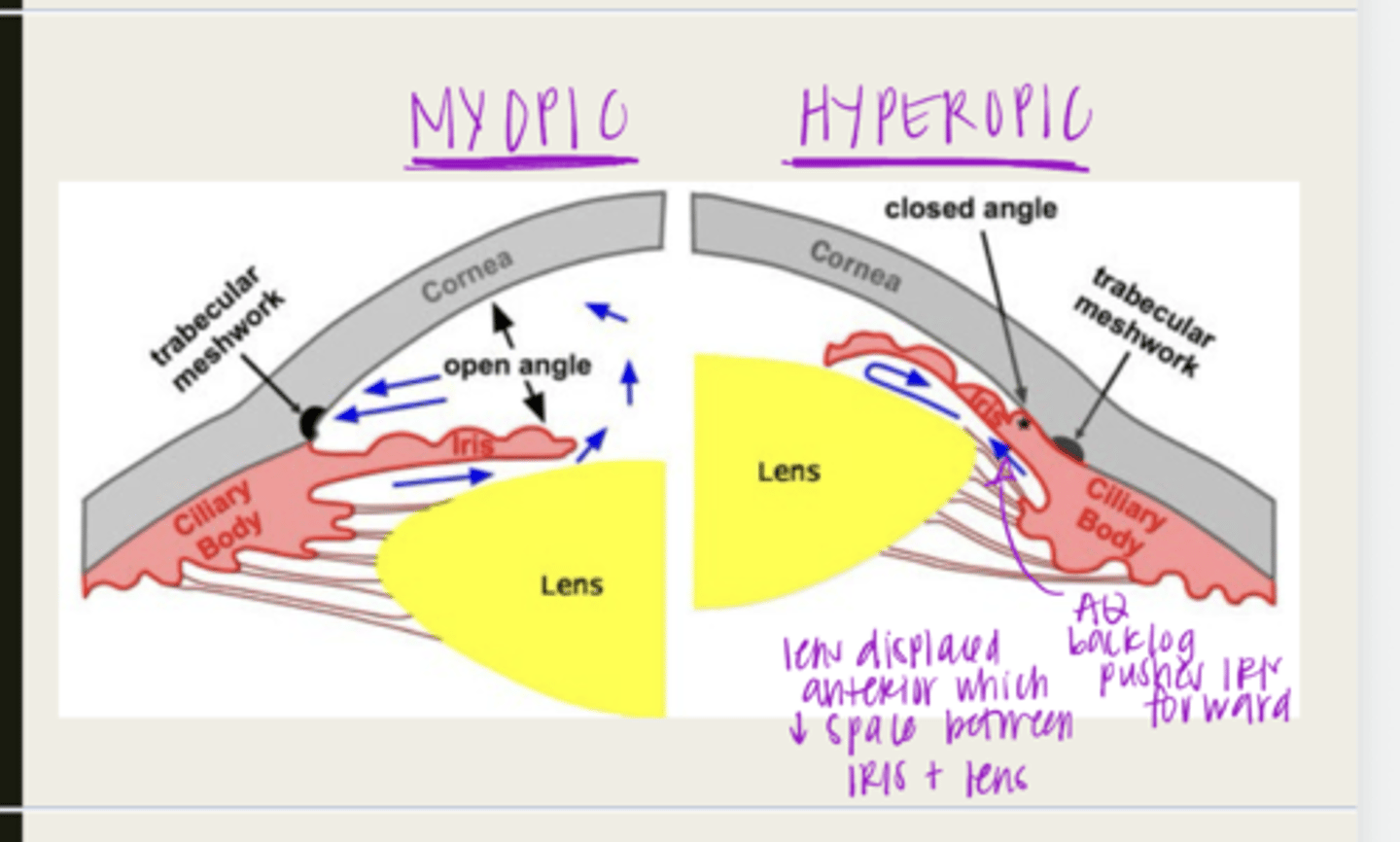
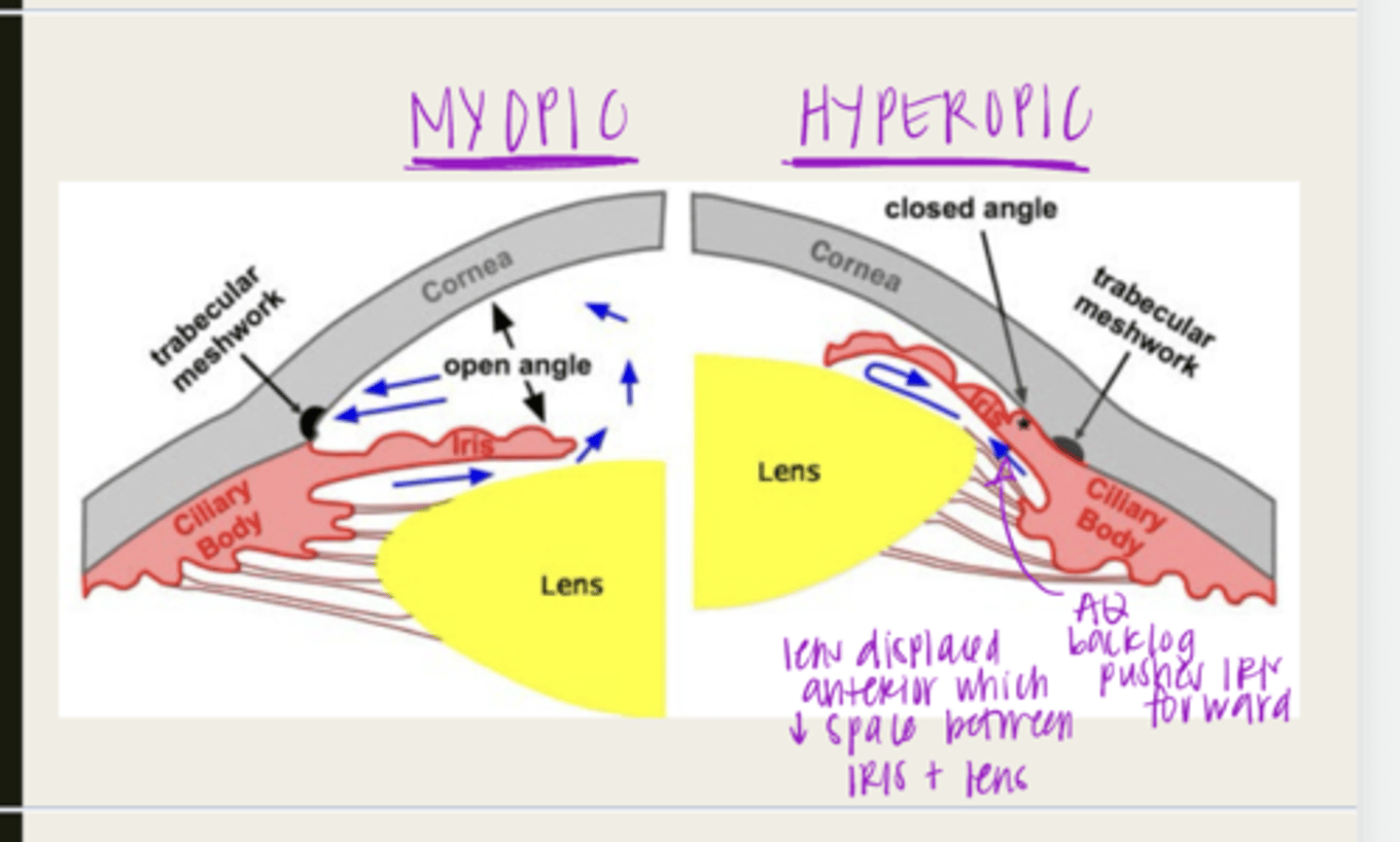
-hyperopia
-shorter axial length
-shallow anterior chamber
-family hx
-thicker crystalline lens
What are the risk factors for primary angle closure glaucoma?
-primary angle closure suspect
-primary angle closure
-primary angle closure glaucoma
**step wise progression, patients can present at any point
What are the possible types of primary angle closure glaucoma?
an individual with anatomically narrow angle width
What is the definition of primary angle closure suspect?
no symptoms
What are the symptoms of a primary angle closure suspect?
-narrow anterior chamber with LESS THAN 180º of iridotrabecular contact (ITC)
What is the presentation of a primary angle closure suspect?
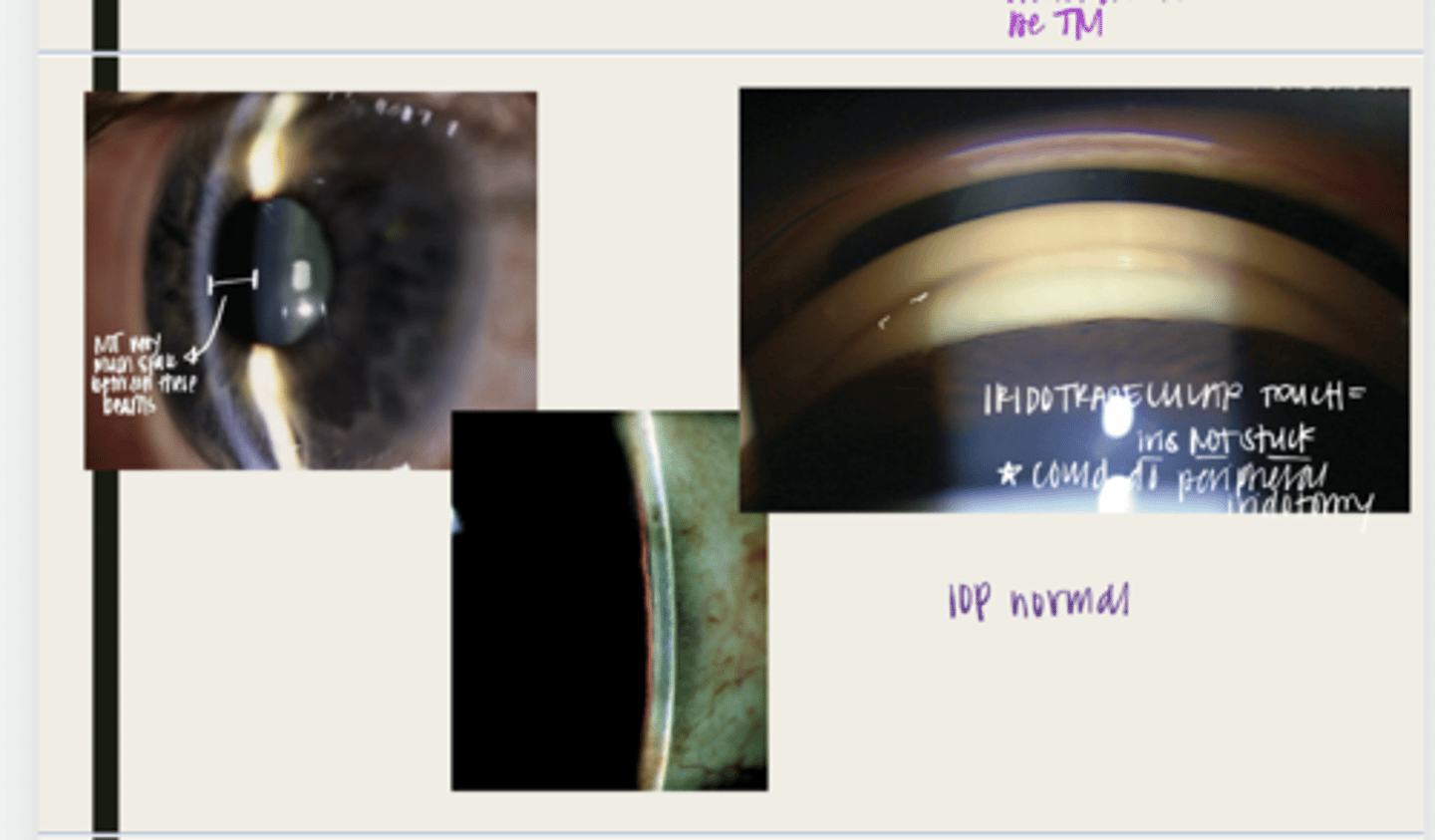
no peripheral anterior synechiae
With a primary angle closure suspect, will there be ANY adhesions of the iris and the TM?
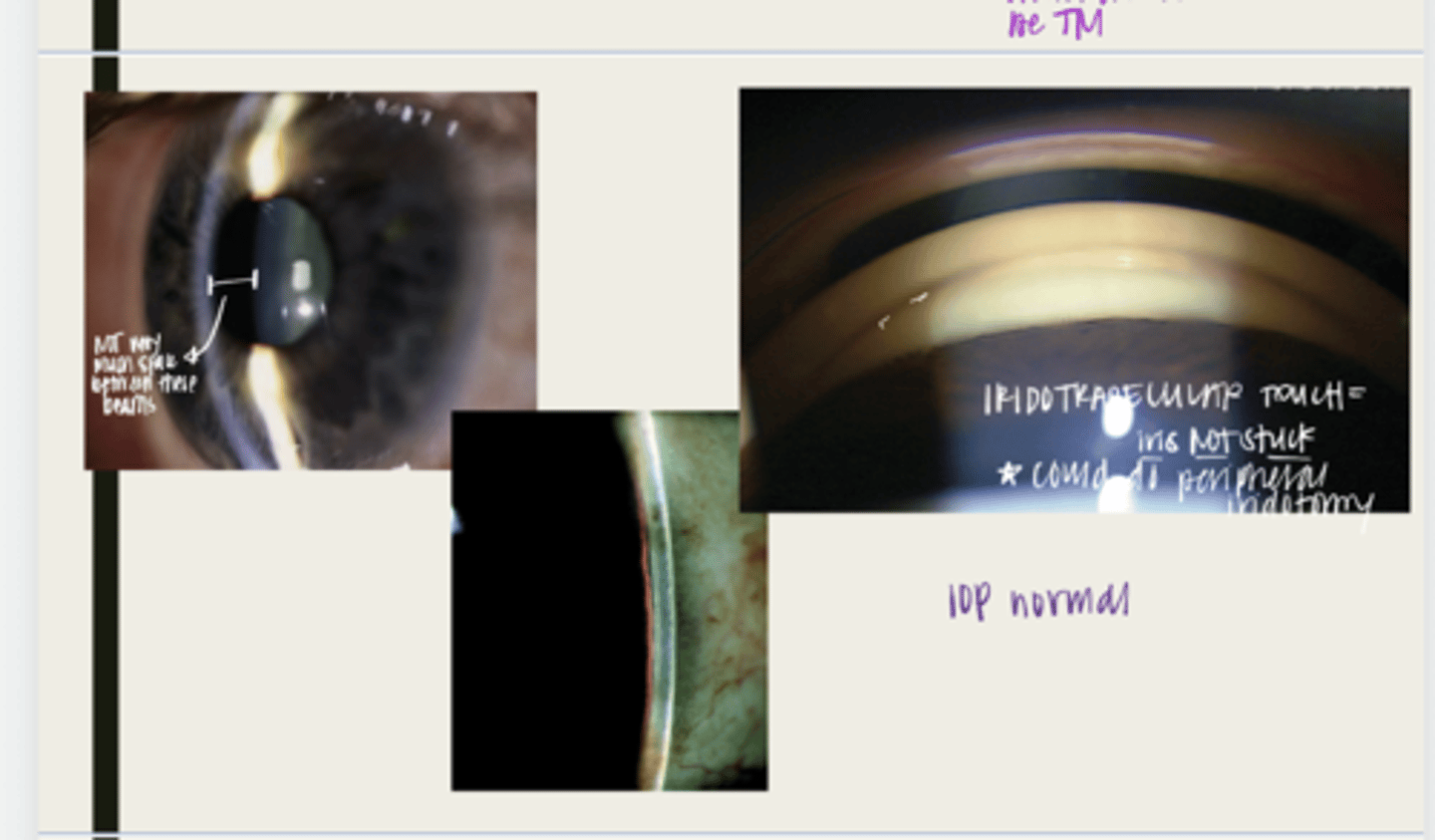
no -- they are all normal
With a primary angle closure suspect, are the IOP, optic nerve or VFs affected?
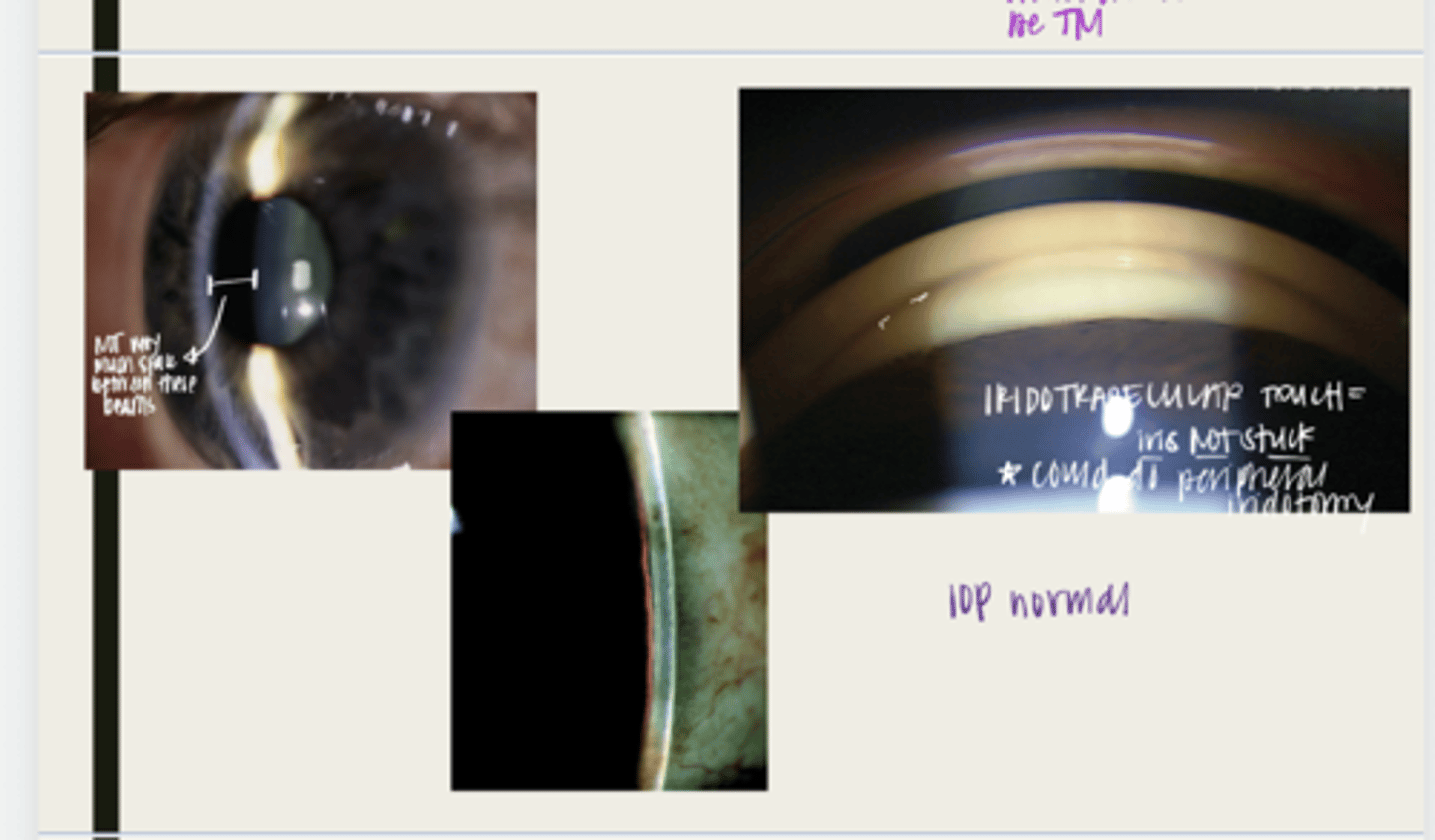
-subacute angle closure attacks
-progression into primary angle closure
What are the possible complications that can occur in a primary angle closure suspect?
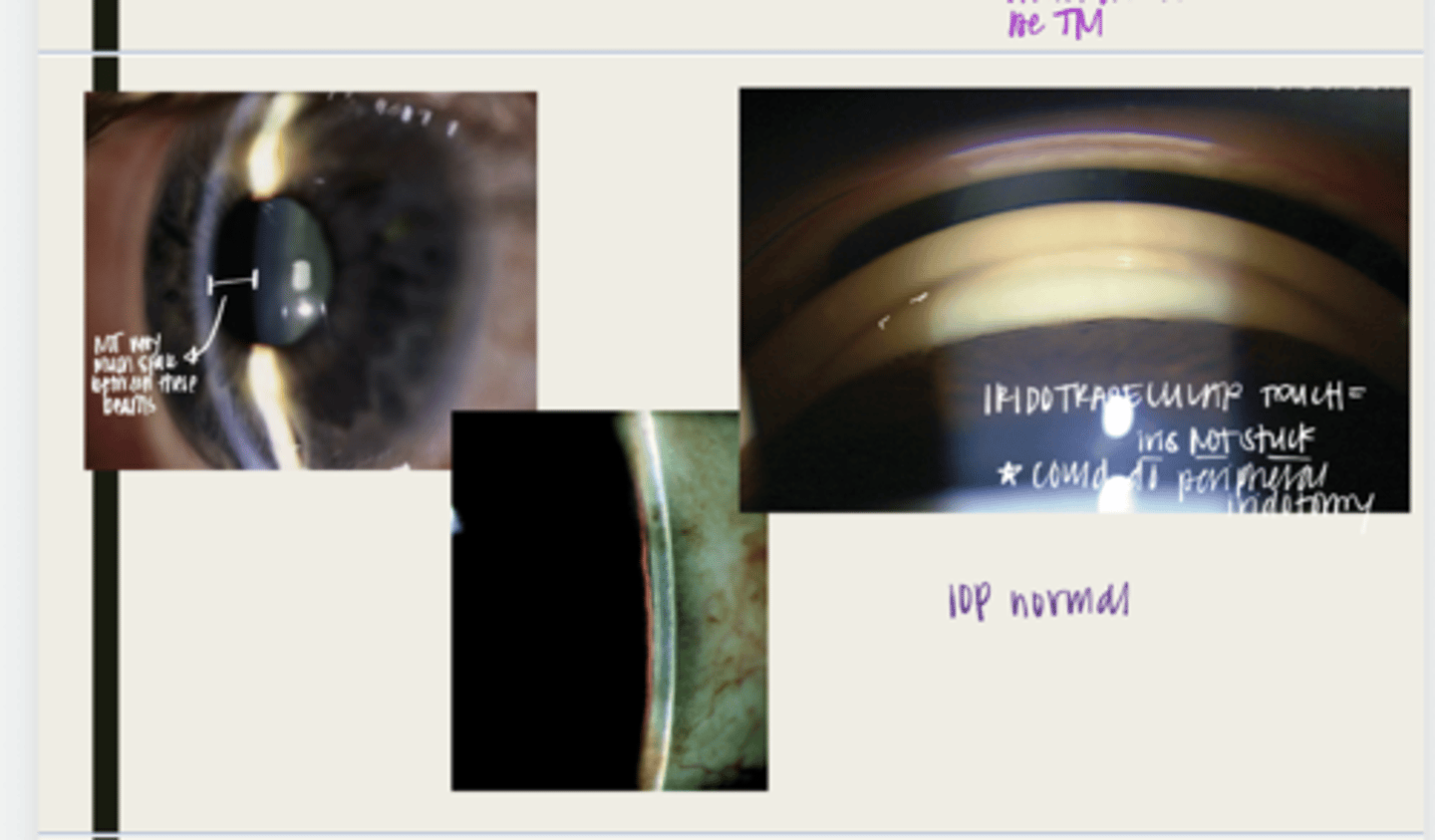
individual will sporadically go into and out of partial angle closure attacks
What happens when a patient experiences subacute angle closure attacks?
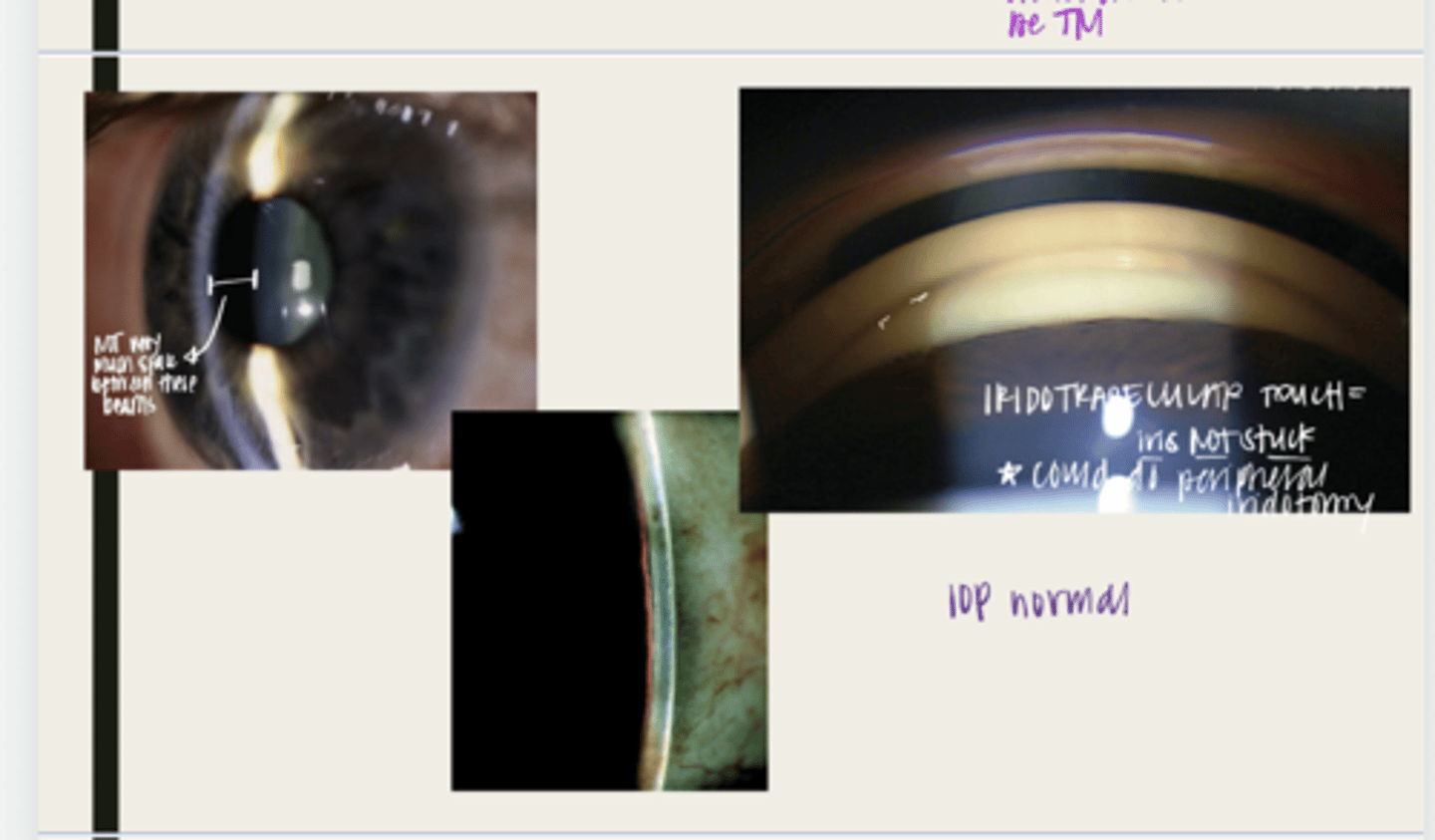
-will present with intermittent symptoms of blurred vision or halos due to mild corneal edema
-intermittent HAs in brow area
-intermittent elevations in IOP
How will a patient present during a subacute angle closure attack?
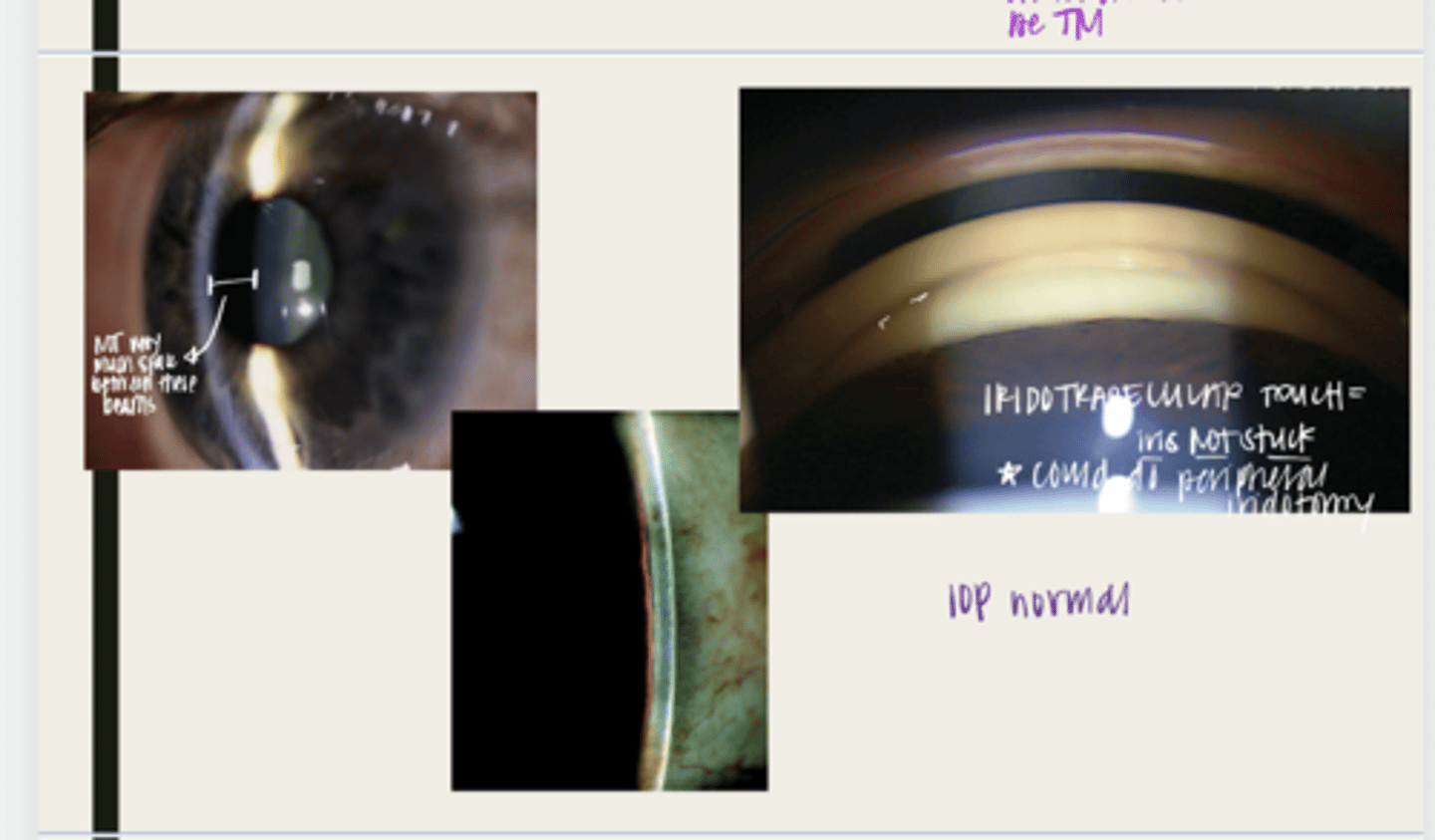
when in a dark room, with night driving, or with dilation
When do the symptoms of subacute angle closure attacks seem to be worse?
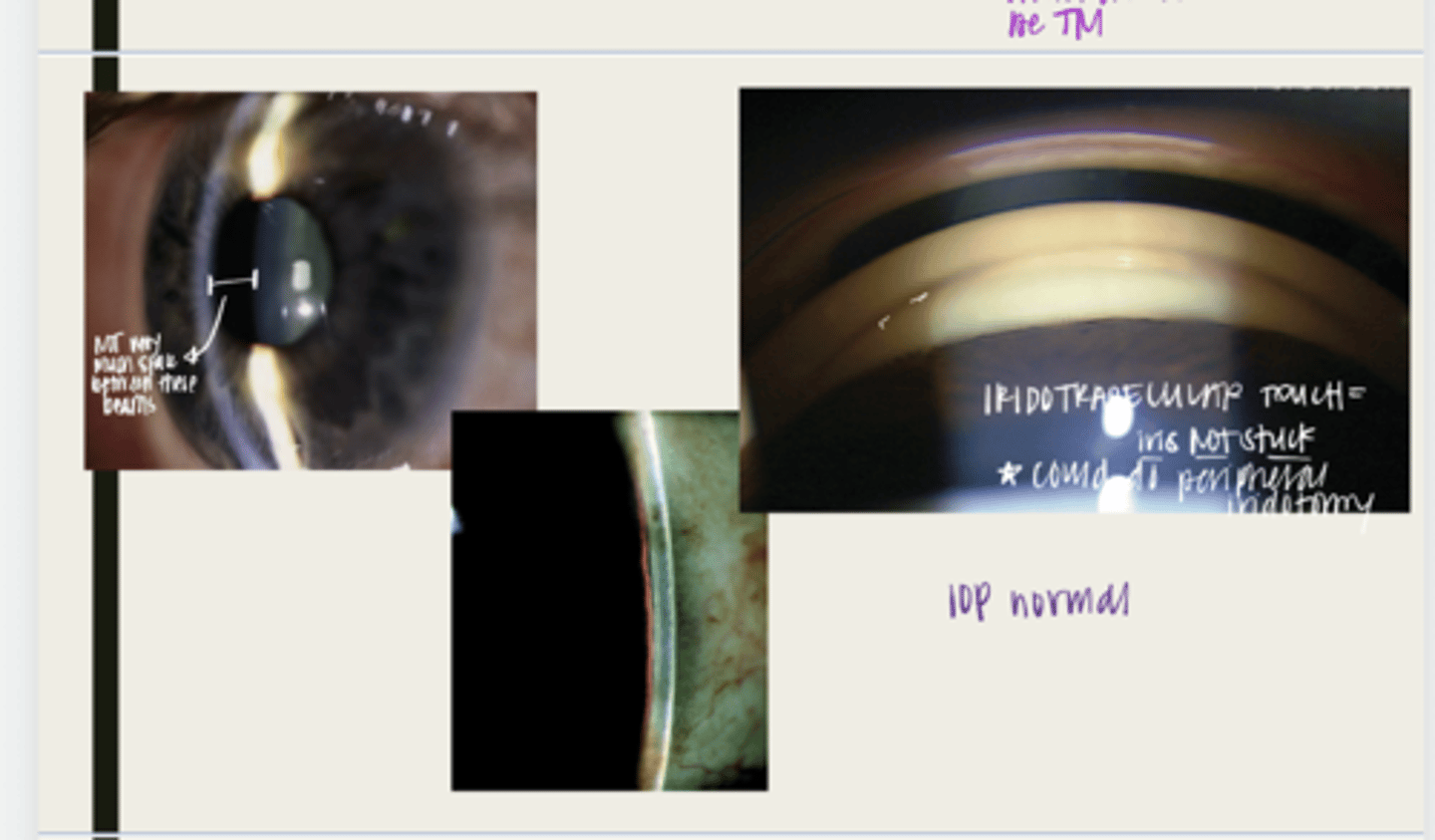
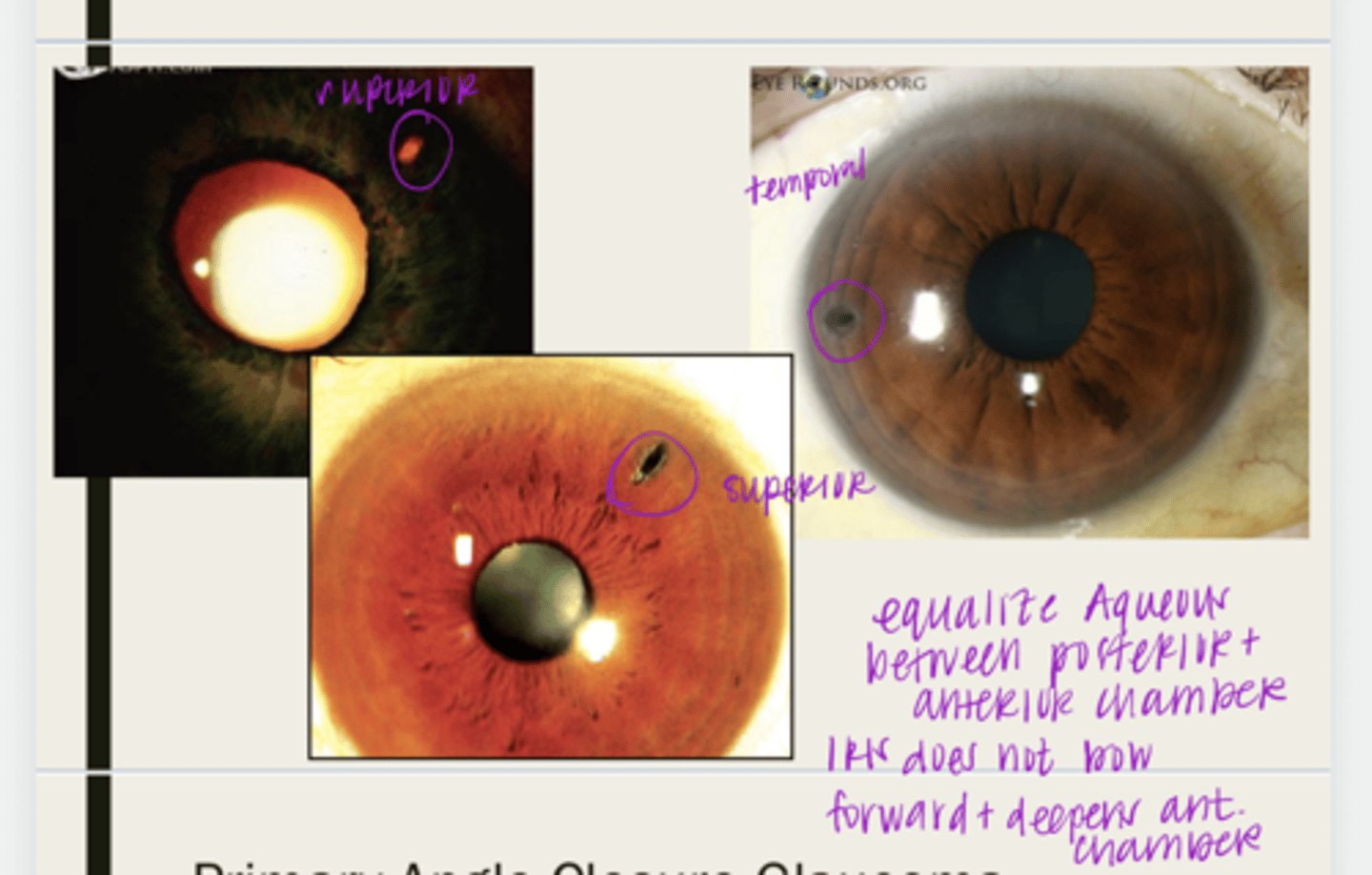
peripheral iridotomy (PI)
What is the treatment that we should present to a patient that is a primary angle closure suspect?
primary angle closure
individual with anatomical narrow angles with BLOCKAGE of the TM
none, unless experiencing acute angle closure crisis
What are the symptoms of primary angle closure?
-three qradrants of iridotrabecular contact (ITC)
-elevated IOP d/t less aqueous outflow
-peripheral anterior synechiae may be present
-normal retinal nerve fiber layer, optic nerve, and VF
What is the presentation of primary angle closure?
No -- cannot break these
Are peripheral anterior synechiae reversible?
peripheral iridotomy
What is the treatment for primary angle closure?
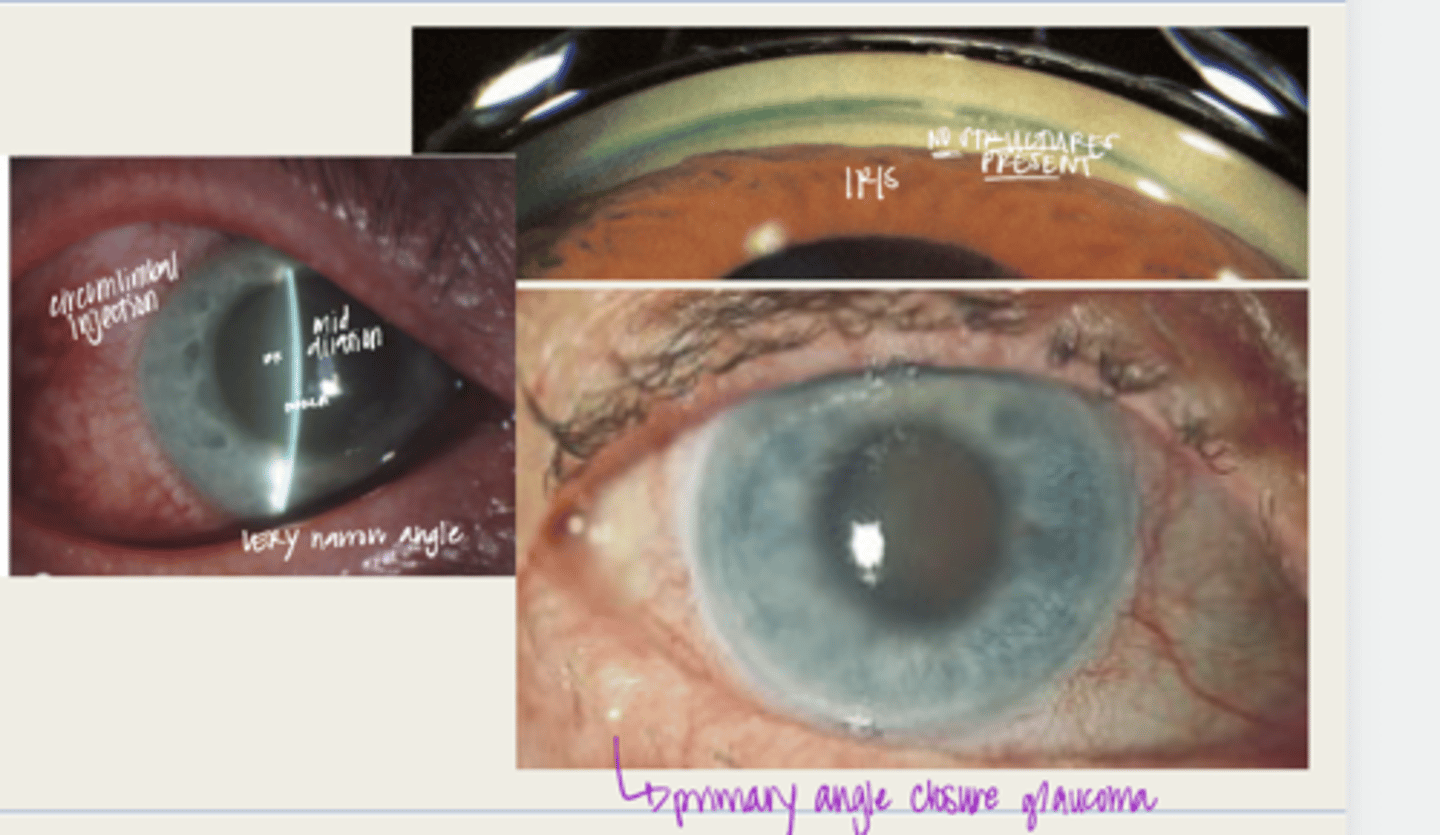
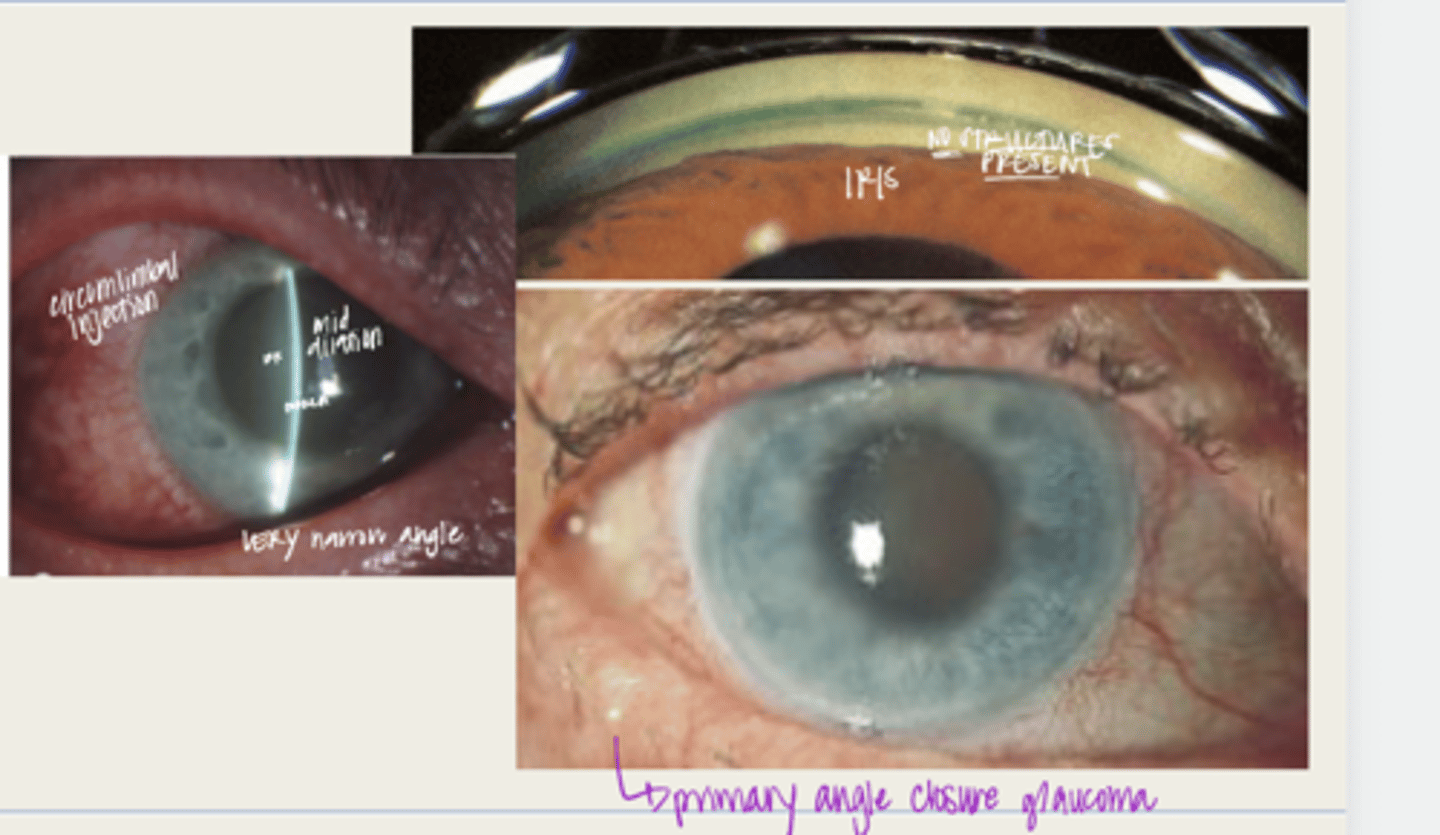
acute angle closure crisis
individual with anatomical narrow angles with blockage of the TM and an ACUTE INCREASE in IOP
primary angle closure glaucoma
What is acute angle closure crisis considered to be a complication of?
yes -- an ocular emergency
Is acute angle closure crisis an emergency?
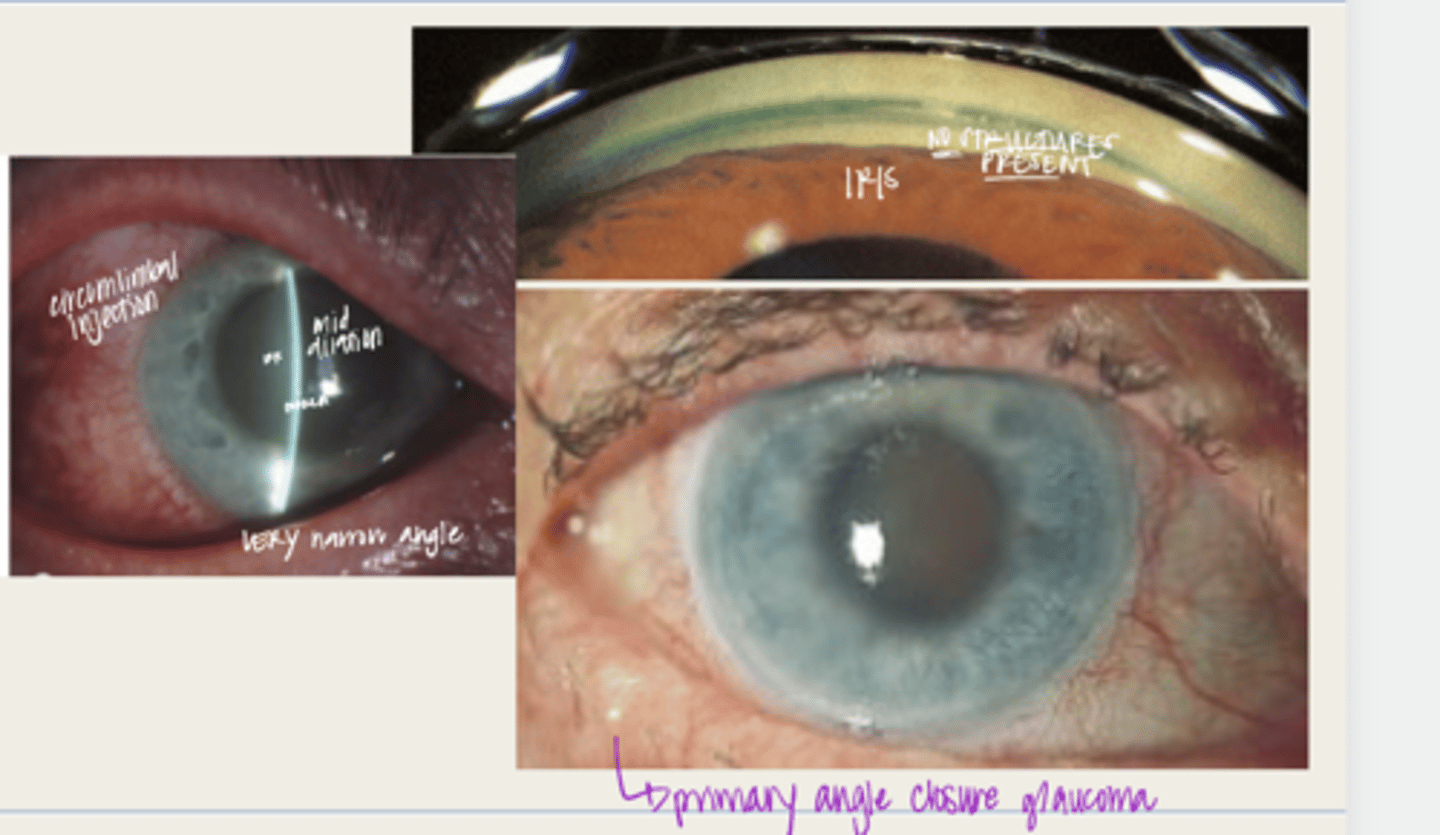
-significantly reduced VA
-glare or halos with lights d/t corneal edema
-gastointestinal symptoms (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting)
What are the symptoms of acute angle closure crisis?
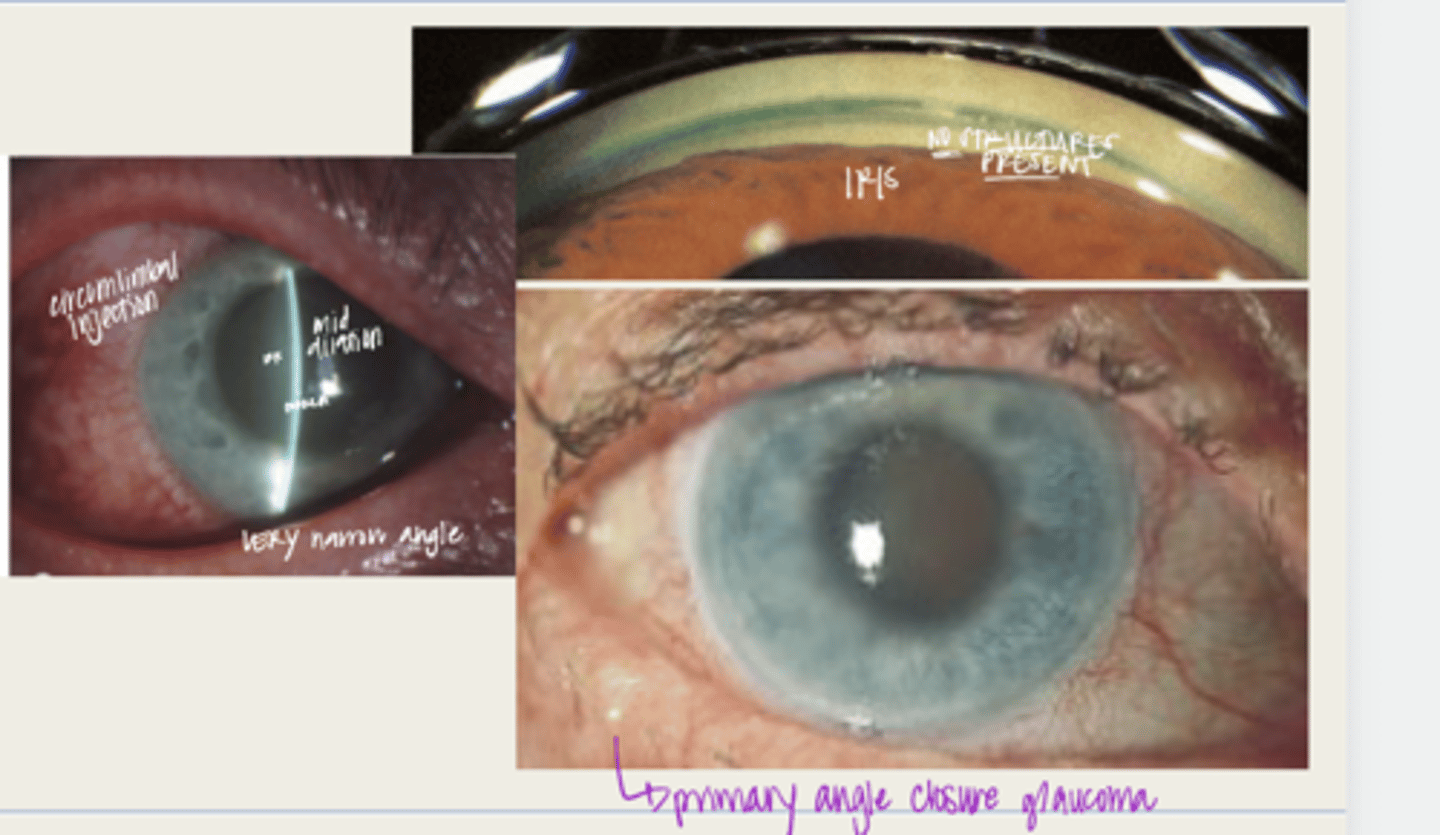
-narrow anterior chamber with iridotrabecular touch
-corneal edema
-circumlimbal conj hyperemia
-elevated IOP (50-80mmHg)
-anterior uveitis
-non-reactive, mid dilated vertically oval pupil
-fellow eye shows an occludable angle
What is the presentation of acute angle closure crisis?
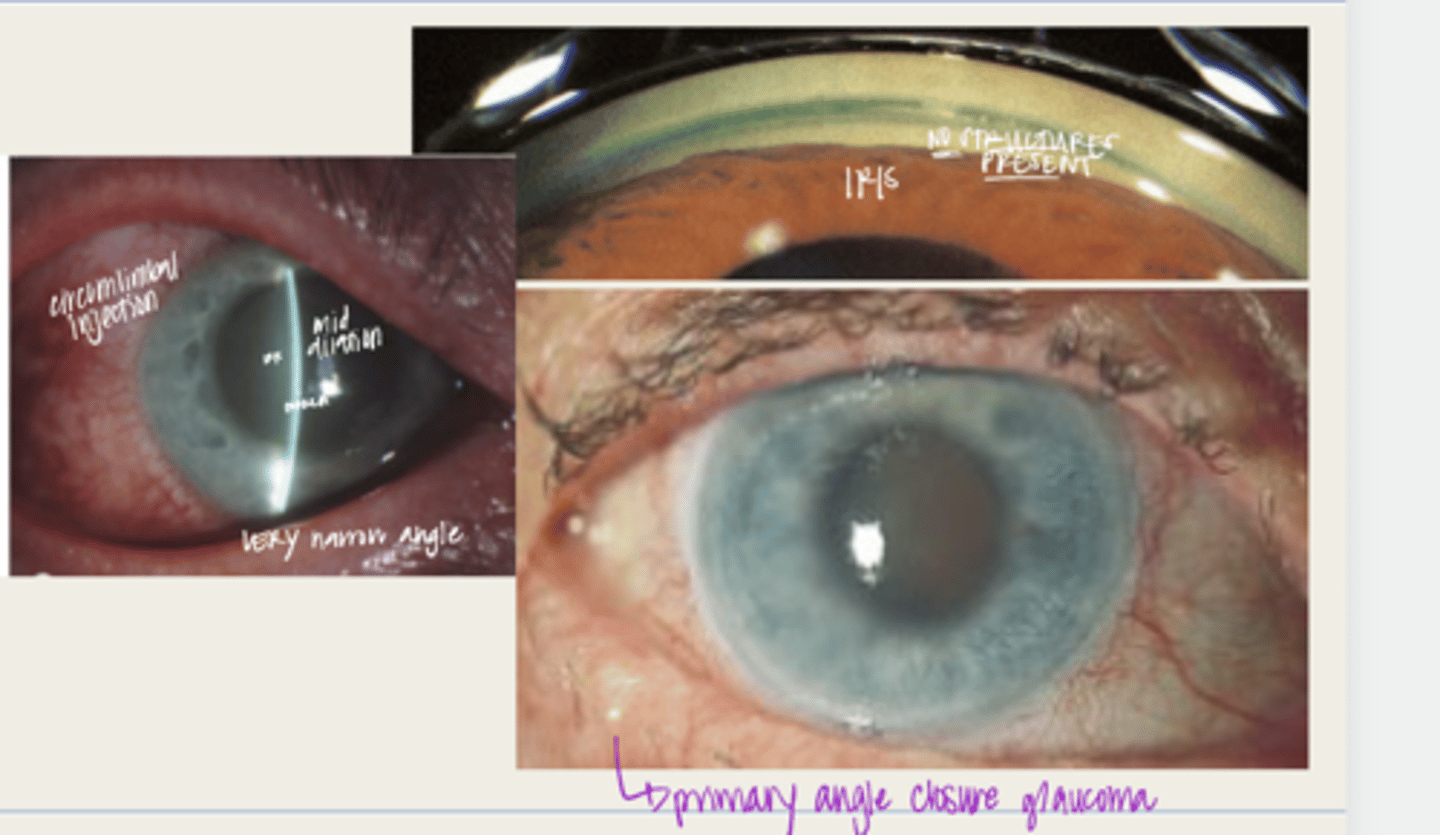
d/t sphincter ischemia
Why are the pupils nonreactive and mid dilated during acute angle closure crisis?
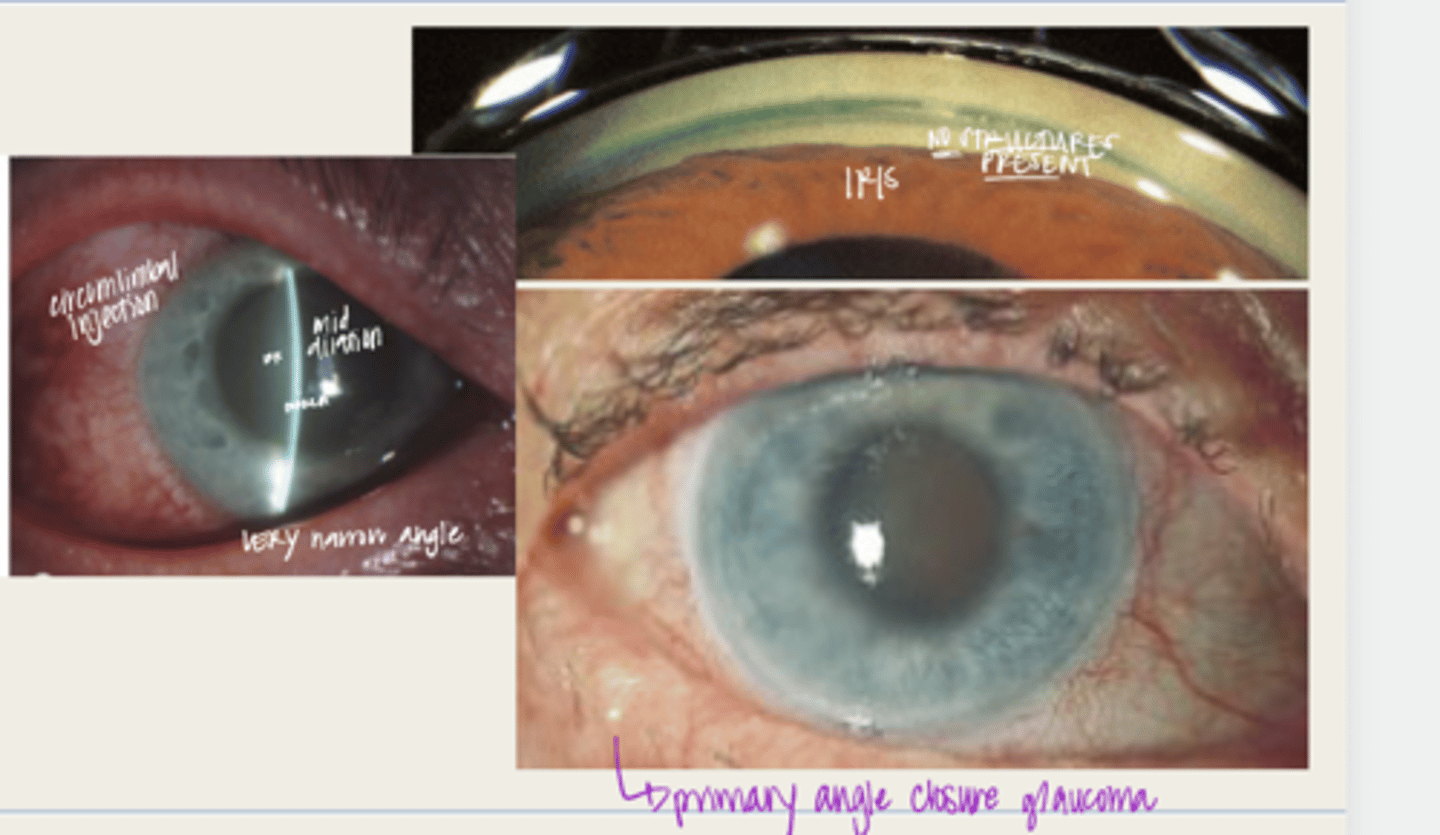
-development of primary angle closure glaucoma
-pupil distortion d/t iris sphincter damage
-glaukomflecken cataract
-peripheal anterior synechiae
-low IOP d/t ciliary body ischemia
What are the complications of acute angle closure crisis?
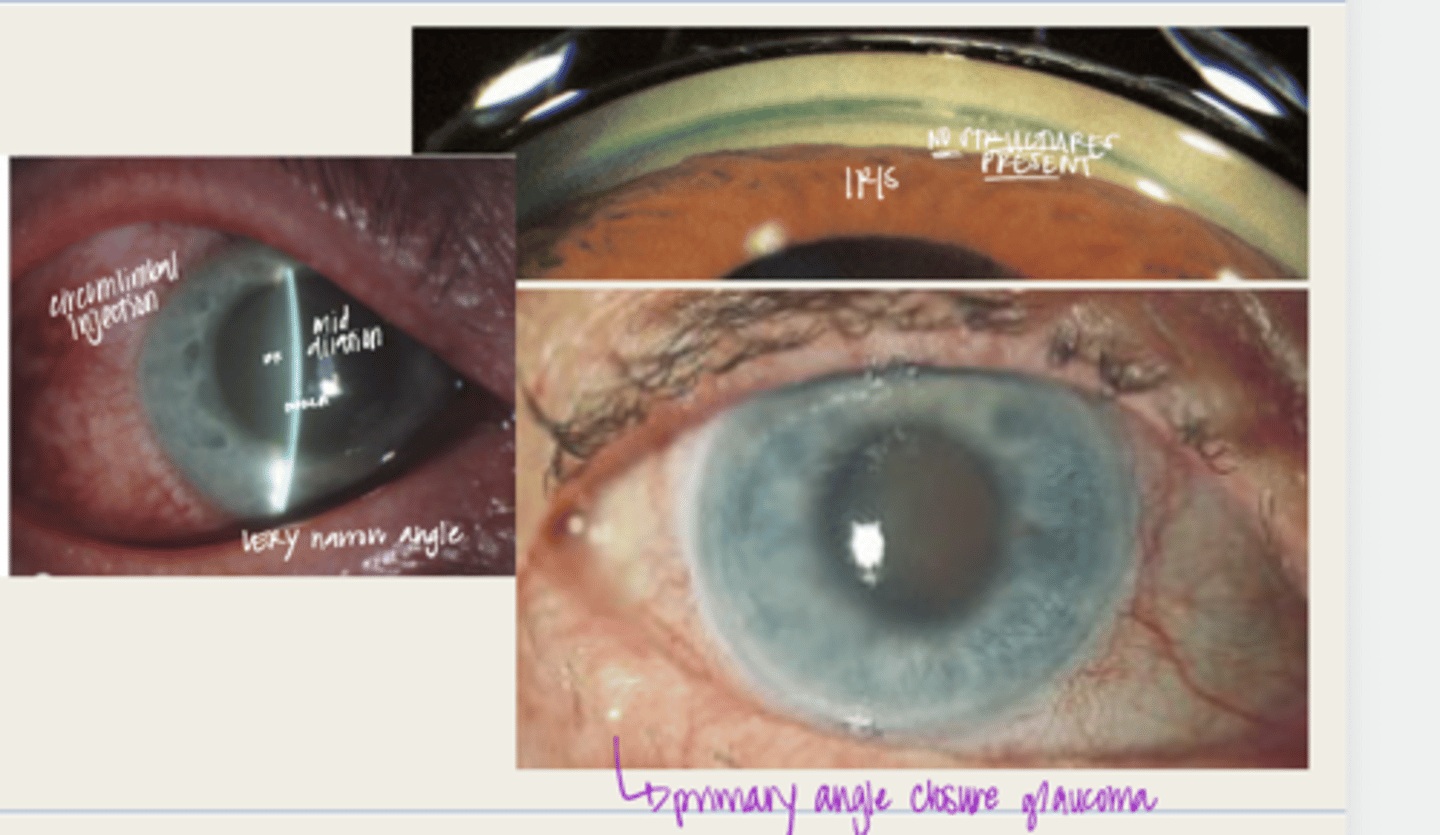
-acetazolamide
-topical beta blocker and topicla alpha-2 agonist
-topical corticosteroid
-topical pilocarpine
-oral pain meds/antiemetic meds
-Once IOP is controlled and corneal edema improved, peripheral iridotomy
What is the treatment for acute angle closure crisis?
given via IV
If IOP is greater than 50mmHg, how is acetazolamide given to patients in acute angle closure crisis?
orally
If IOP is less than 50mmHg, how is acetazolamide given to patients in acute angle closure crisis?
use caution with IOP is above 40mmHg as iris sphincter ischemia may occur
When is oral pilocarpine given to patients in acute angle closure crisis?
decrease aqueous production
What is the function of the beta blocker and alpha-2 agonist given to patients in acute angle closure crisis?
primary angle closure glaucoma
individual with anatomically narrow angles with BLOCKAGE of the TM and additional GLUACOMATOUS FiNDingS
decreased vision and reduction in peripheral vision
What are the symptoms of primary angle closure glaucoma?
-three quadrants of iridotrabecular contact
-elevated IOP
-retinal nerve fiber thinning
-glaucomatous optic nerve appearance
-glaucomatous visual field defects
What is the presentation of primary angle closure glaucoma?
topical glaucoma mediations and peripheral iridotomy
What is the treatment for primary angle closure glaucoma?
decreased vision and reduction in peripheral vision
What are the symptoms of primary angle closure glaucoma?
-three quadrants of iridotrabecular contact
-elevated IOP
-retinal nerve fiber thinning
-glaucomatous optic nerve appearance
-glaucomatous VF defects
What is the presentation of a patient with primary angle closure glaucoma?
topical glaucoma medications and peripheral iridotomy
What is the treatment for a patient with primary angle closure glaucoma?
chronic angle closure glaucoma
What is a possible complication of primary angle closure glaucoma?
none -- patient may develop blurred vision if IOP is high
What are the symptoms of chronic angle closure glaucoma?
-elevated IOP
-intermittent areas of iridotrabecular contact with peripheral anterior synechiae
-eventually entire angle will close 360º
-retinal nerve fiber thinning
-glaucomatous optic nerve
What is the presentation of chronic angle closure glaucoma?
-surgical
-peripheral iridotomy
-iridoplasty
-trabeculectomy
What is the treatment for chronic angle closure glaucoma?
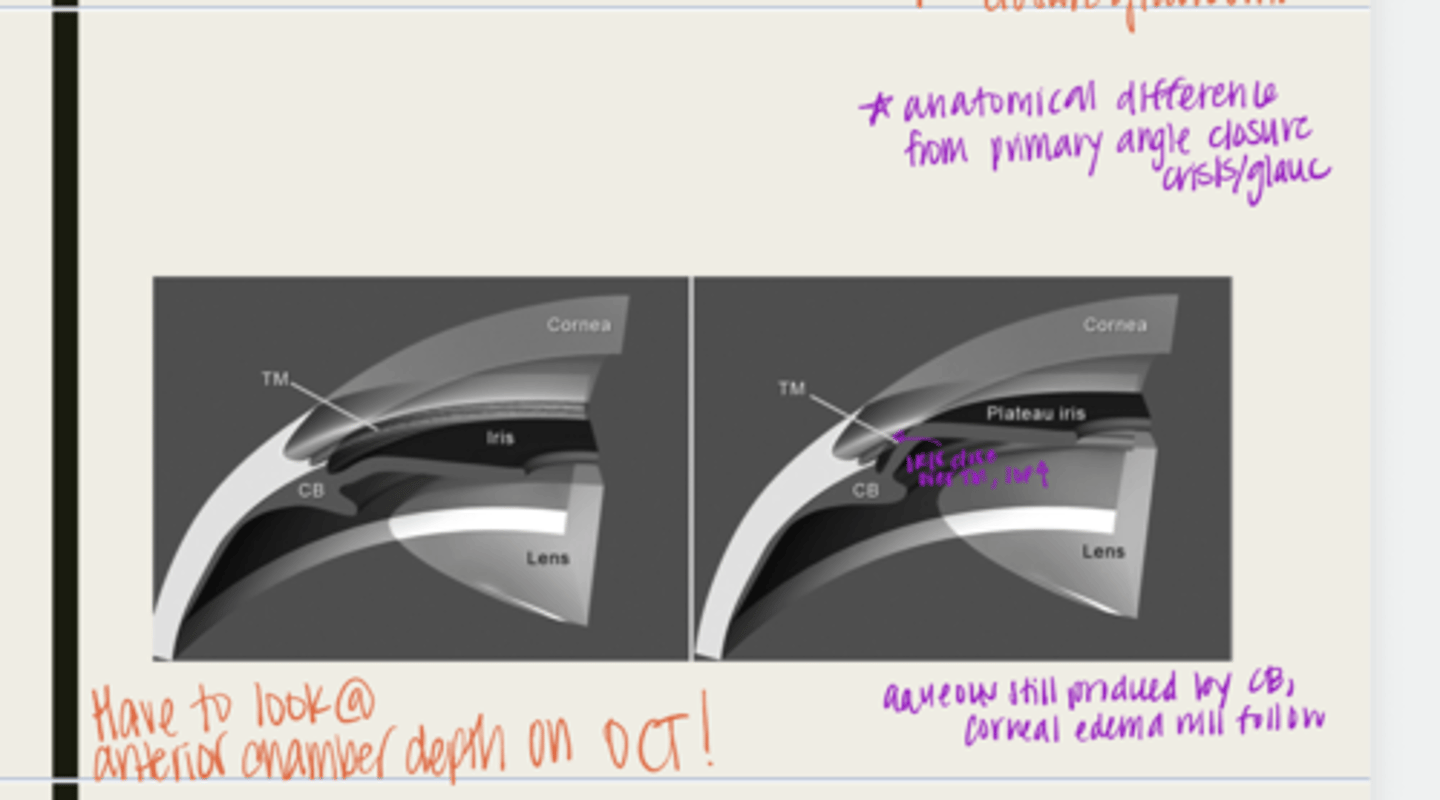
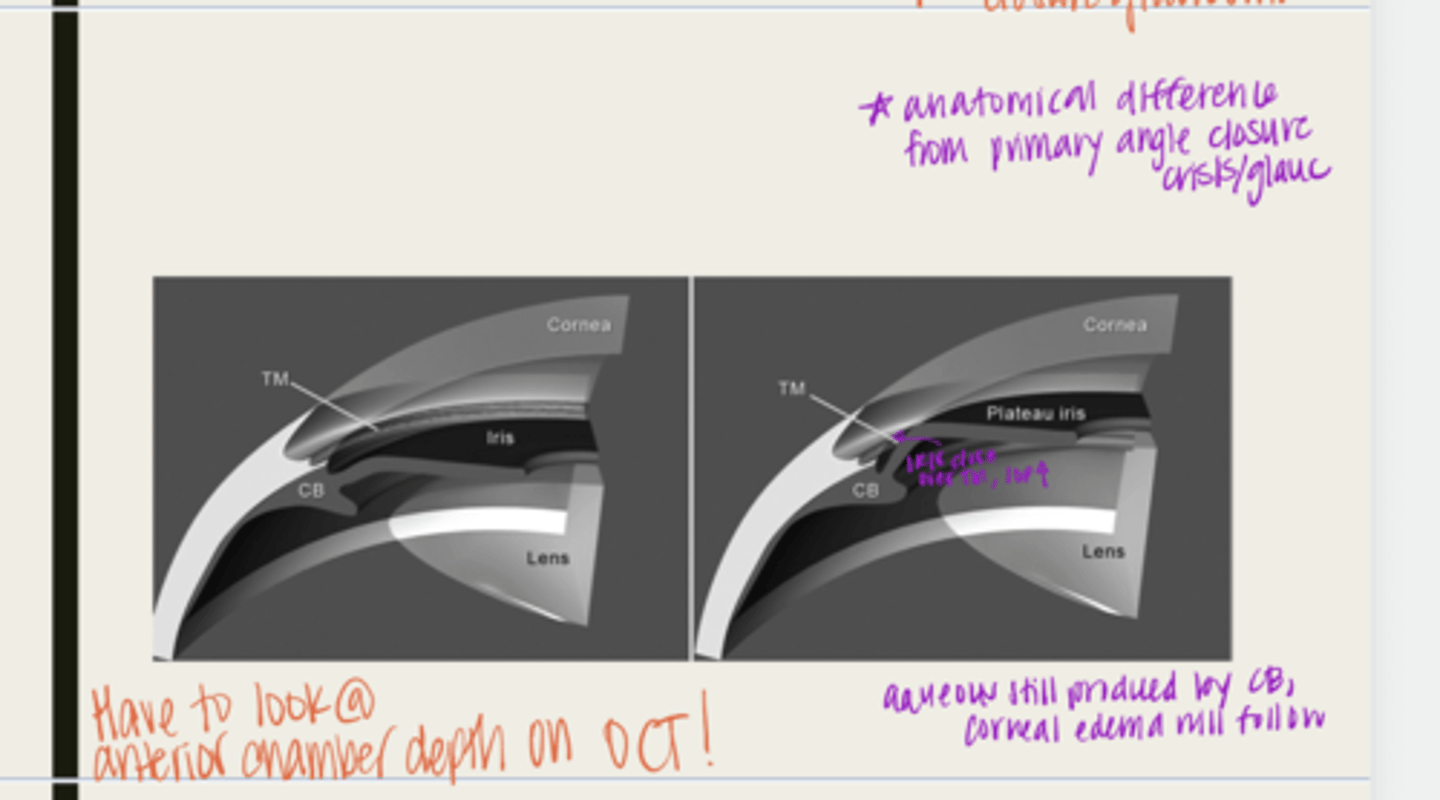
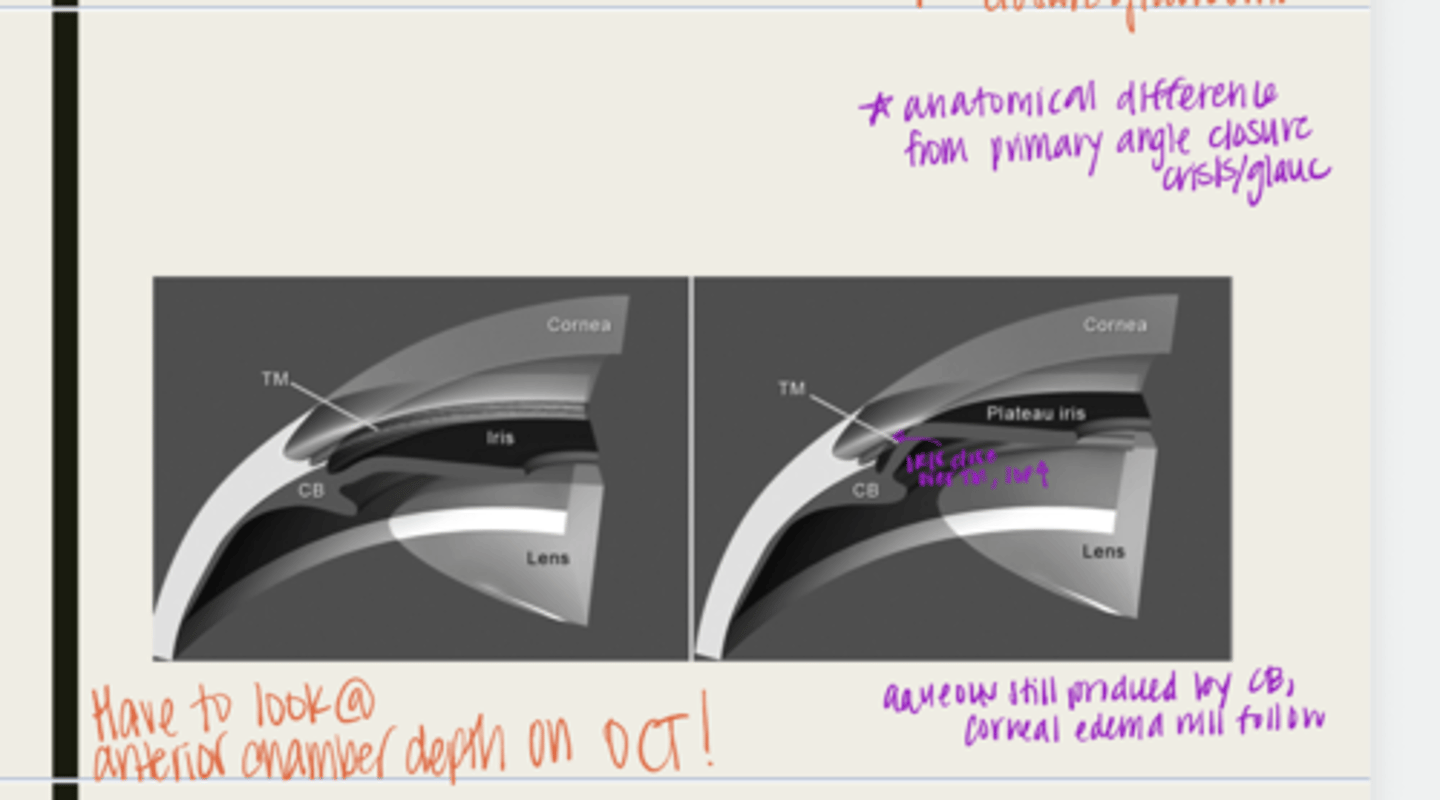
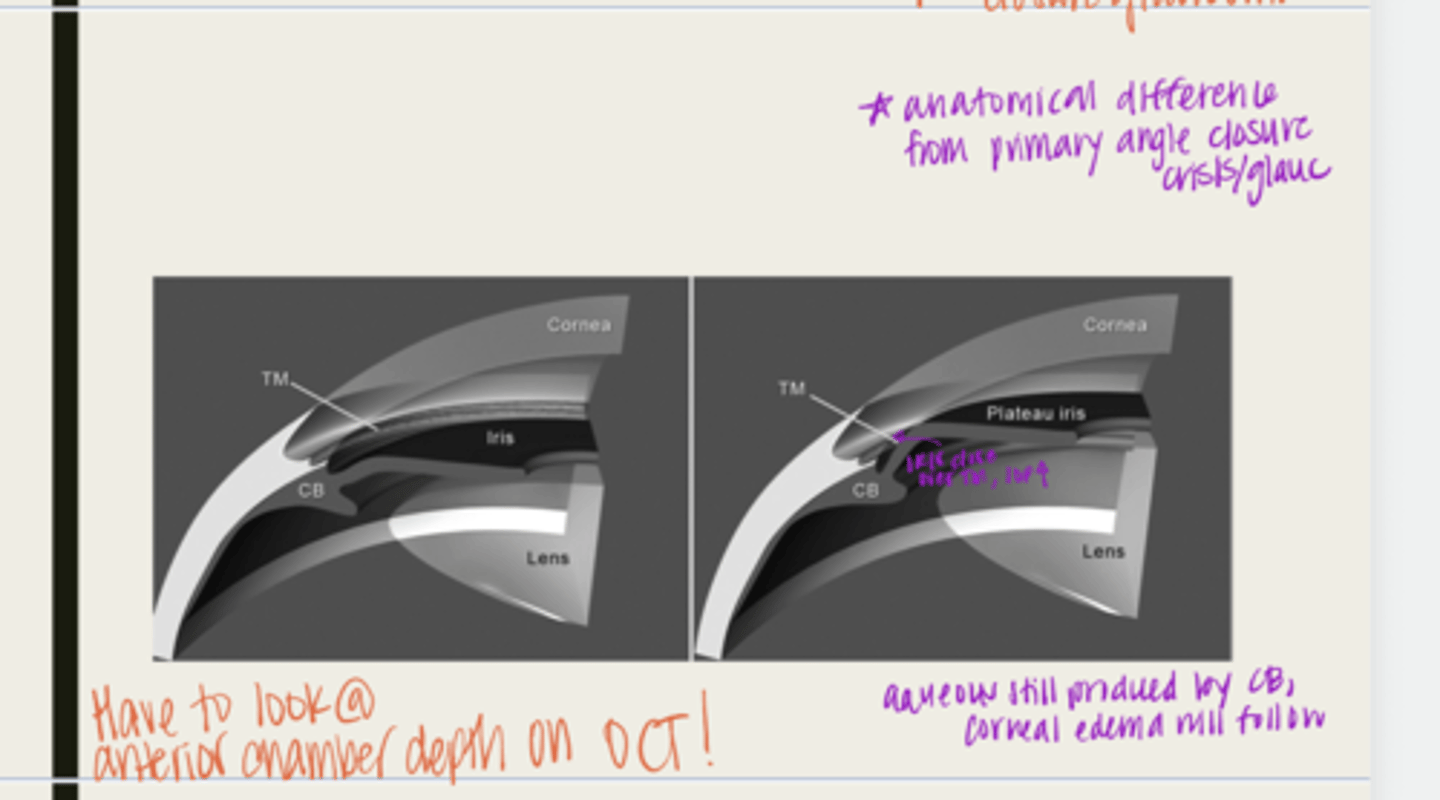
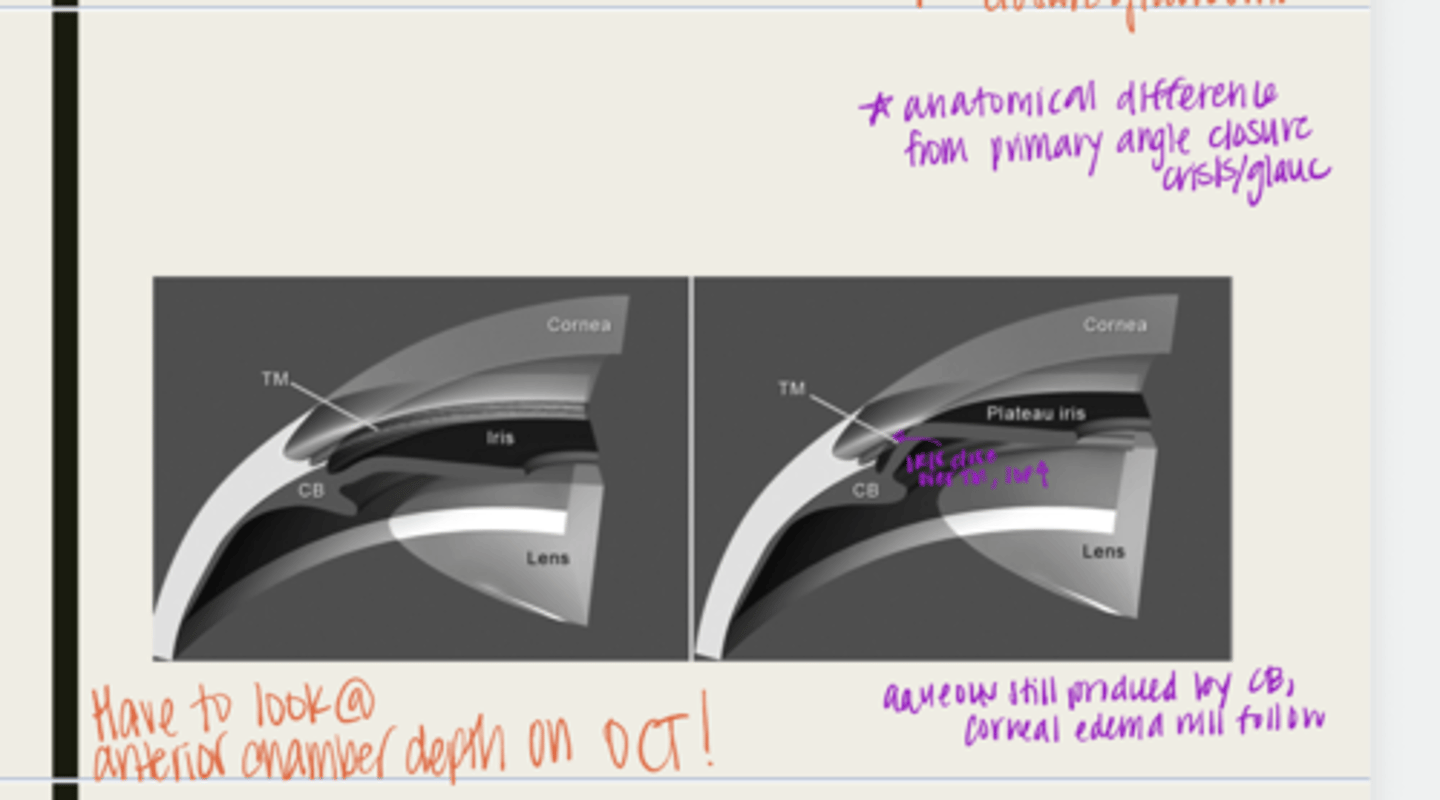
plateau iris configuration
form of angle closure by an anteriorly displaced ciliary body
30-50yo
What is the onset of plateau iris configuration?
females
Is plateau iris configuration more common in males or females?
-hyperopic
-fam hx of angle closure
What are the risk factors for plateau iris configuration?
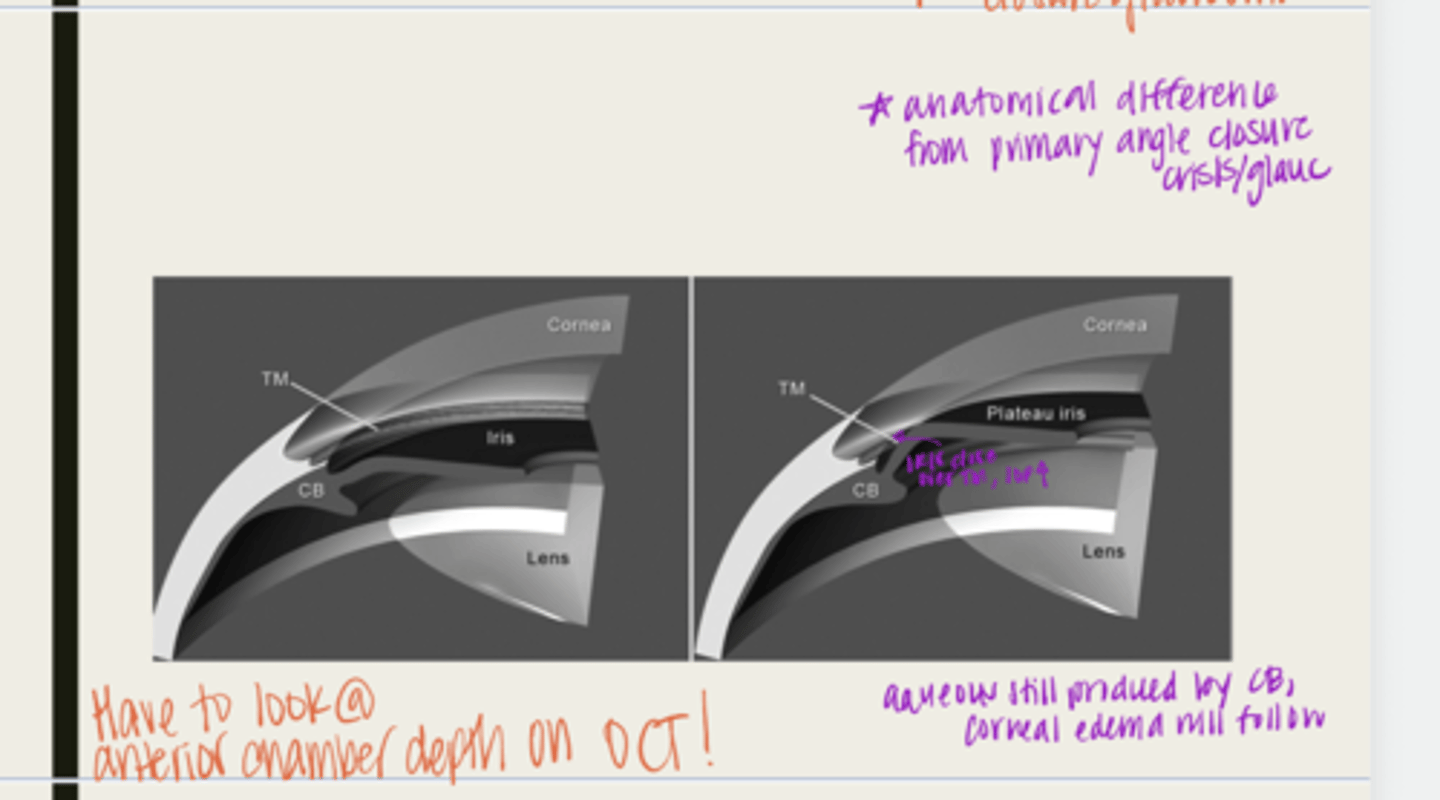
-ciliary body will be anteriorly displaced due to a short iris root
-peripheral iris will move forward
-when the pupil dilates, the iris will bunch together and block the TM
-IOP will rise
What is the pathophysiology of plateau iris configuration?
-blurry vision with halos
-eye pain
-HA
-vomiting/nausea
What are the symptoms of plateau iris configuration?
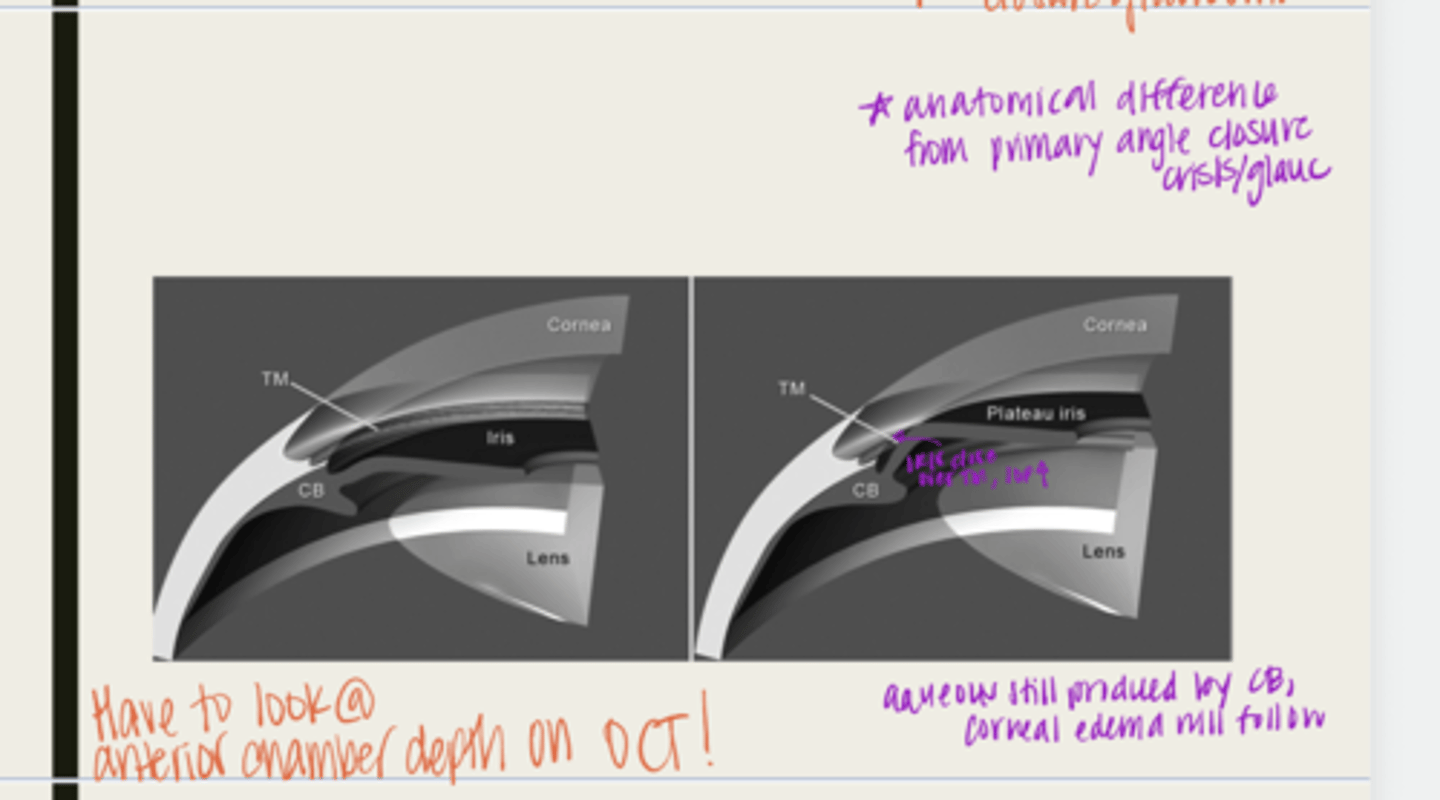
-normal anterior chamber depth
-flat iris surface
-narrow angle seen with gonioscopy
What is the presentation of plateau iris configuration?
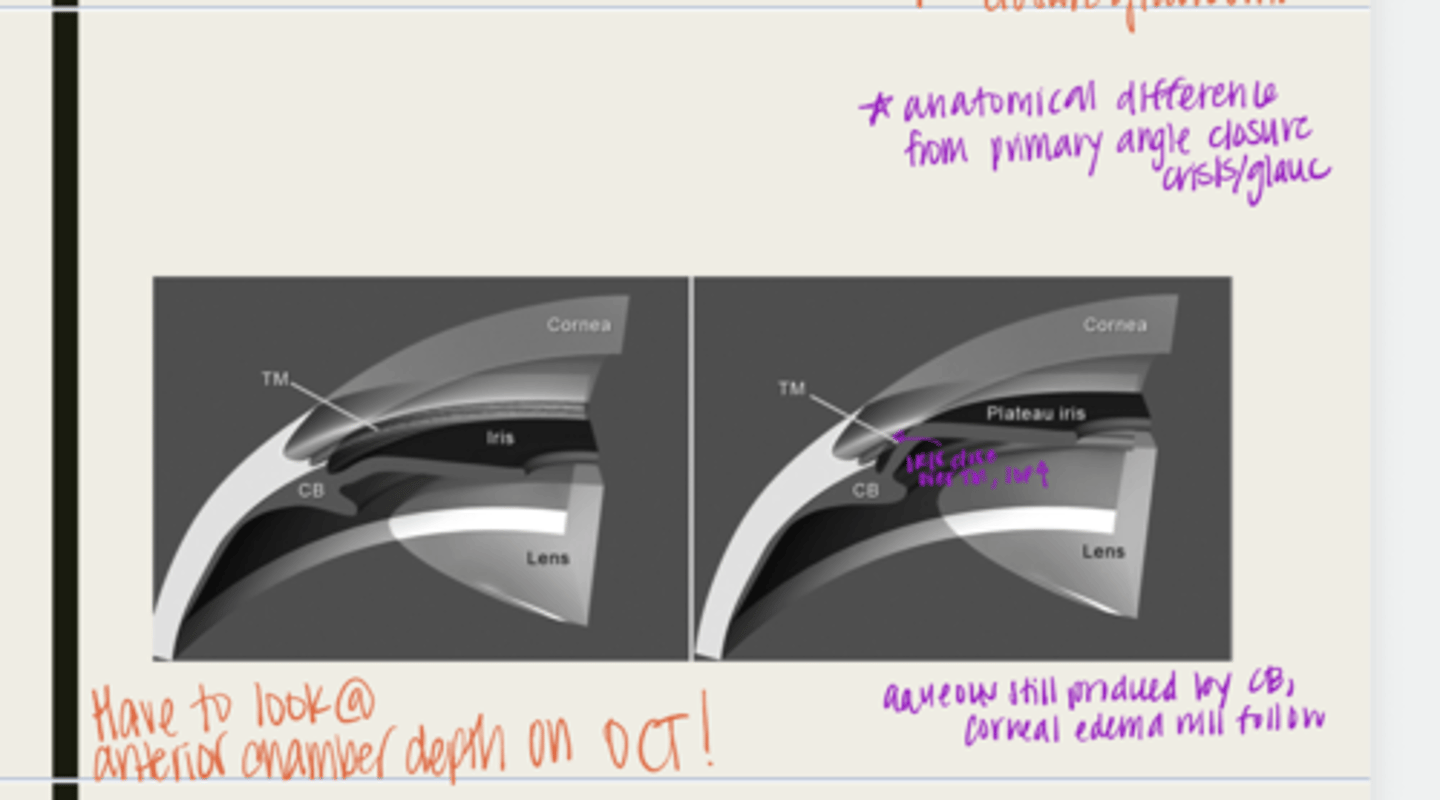
plateau iris syndrome
What is the possible complication of plateau iris configuration?
angle closure in the presence of a patent peripheral iridotomy
What is the definition of plateau iris syndrome?
-peripheral iridotomy
-iridoplasty
What is the treatment for plateau iris configuration?
secondary glaucoma
development of glaucoma as a consequence of another eye condition or systemic condition
-open angle
-closed angle
What are the 2 classifications of secondary glaucoma?
-pretrabecular
-trabecular
What are the subtype of open angle glaucoma?
blockage of the TM d/t a membrane
What is pretrabecular open angle secondary glaucoma?
blockage of the TM d/t obstruction or blockage
What is trabecular open angle secondary glaucoma?
-with pupillary block
-without pupillary block
What are the subdivisions of closed angle secondary glaucoma?
pseudoexfoliation
systemic condition in which there is an abnormal production or turnover of extracellular matrix in the basement membrane
50 yo with rapid increase in prevalence after 60yo
What is the onset of pseudoexfoliation?
females
Is pseudoexfoliation more common in males or females?
Scandinavia
Where is pseudoexfoliation most common?
hearing loss, cardiovascular disorders
What have been associated with pseudoexfoliation?
-grey-white fibrillary material is deposited on the lens capsule, zonular fibers, iris and TM
-fibrillary material is produced by iris, lens epithelium, ciliary body or TM
What is the pathogenesis of pseudoexfoliation?
-pseudoexfoliation syndrome
-pseudoexfoliation glaucoma
What are the 2 ocular manifestations of pseudoexfoliation?
no symptoms
What are the symptoms of pseudoexfoliation syndrome?
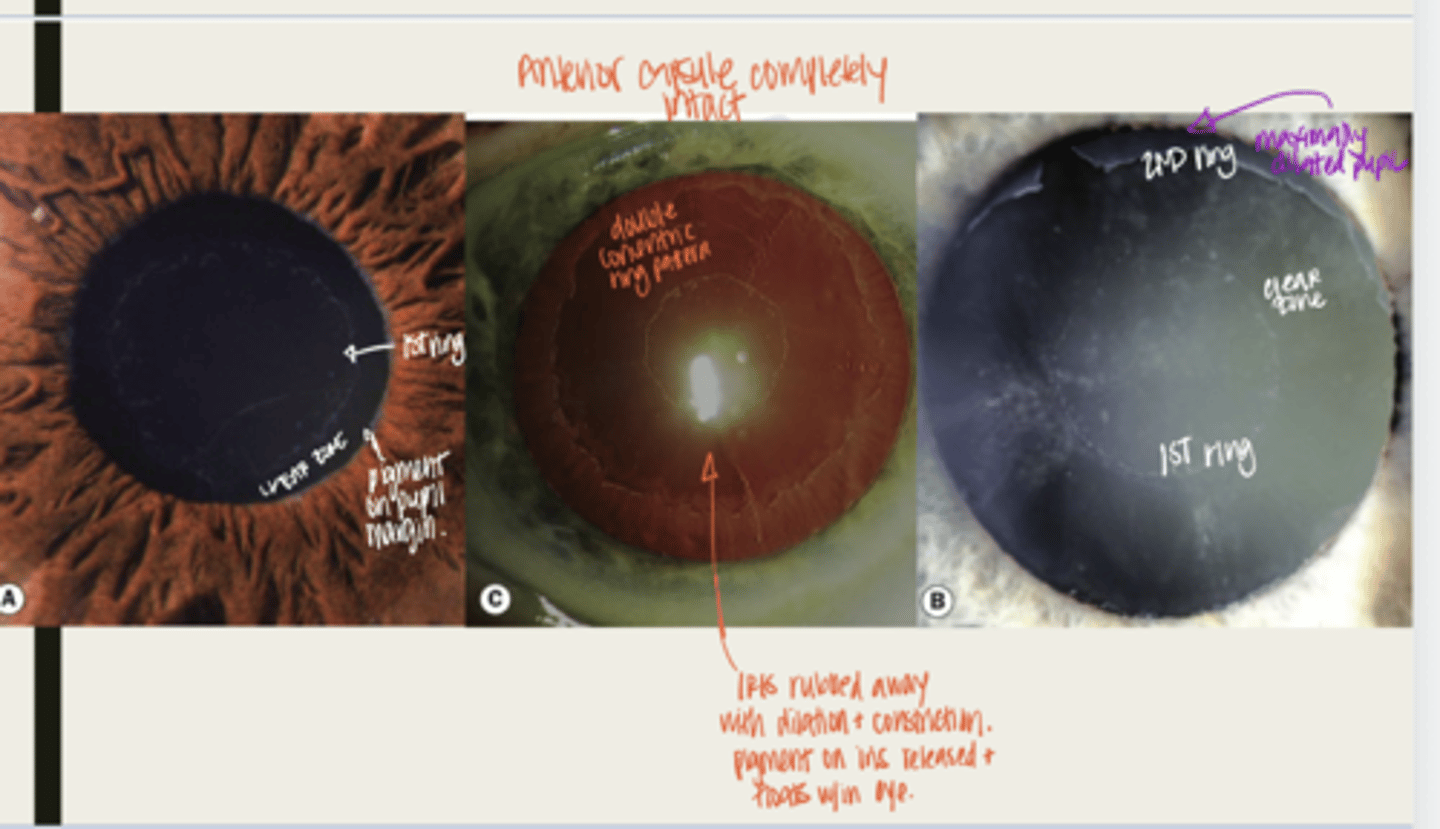
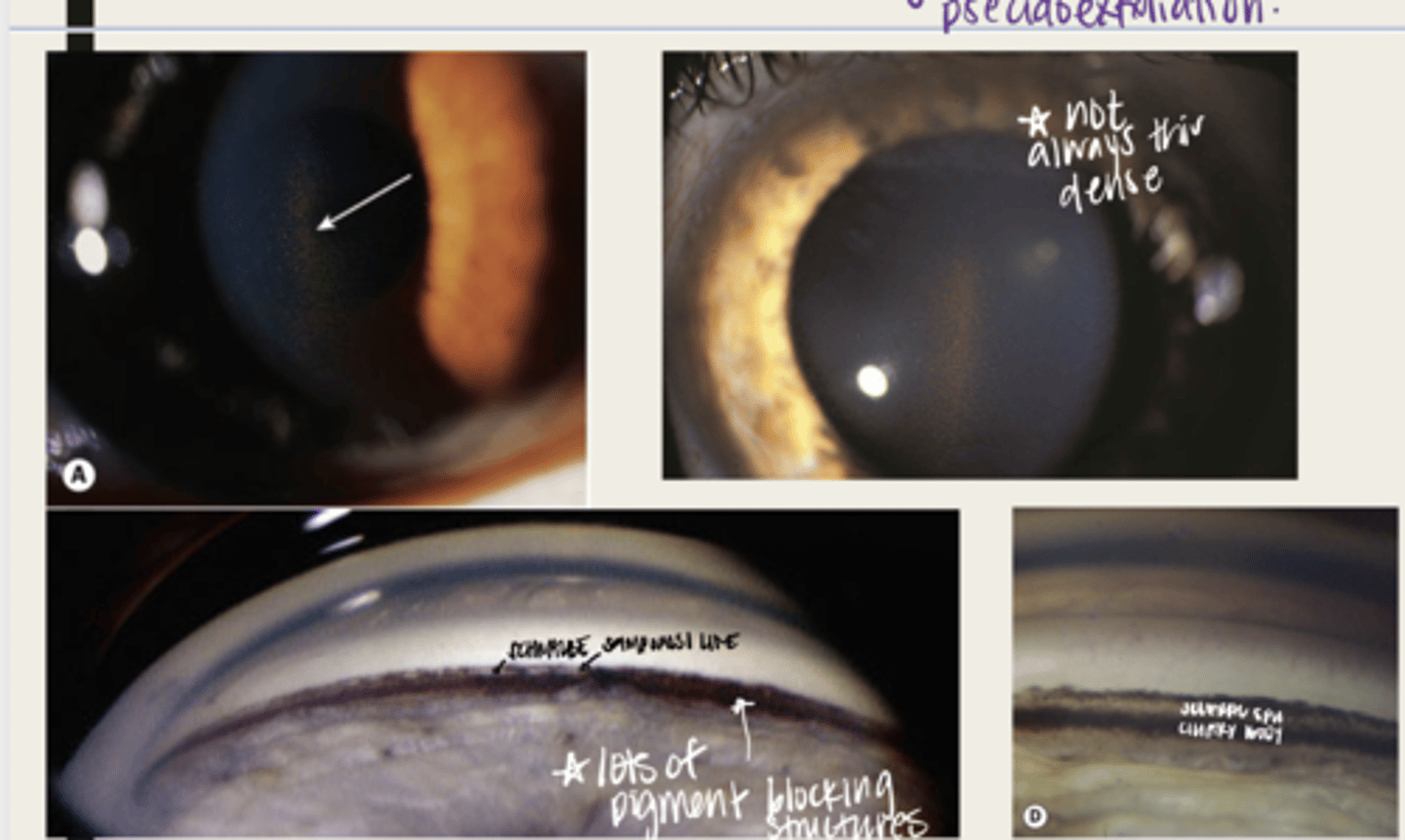
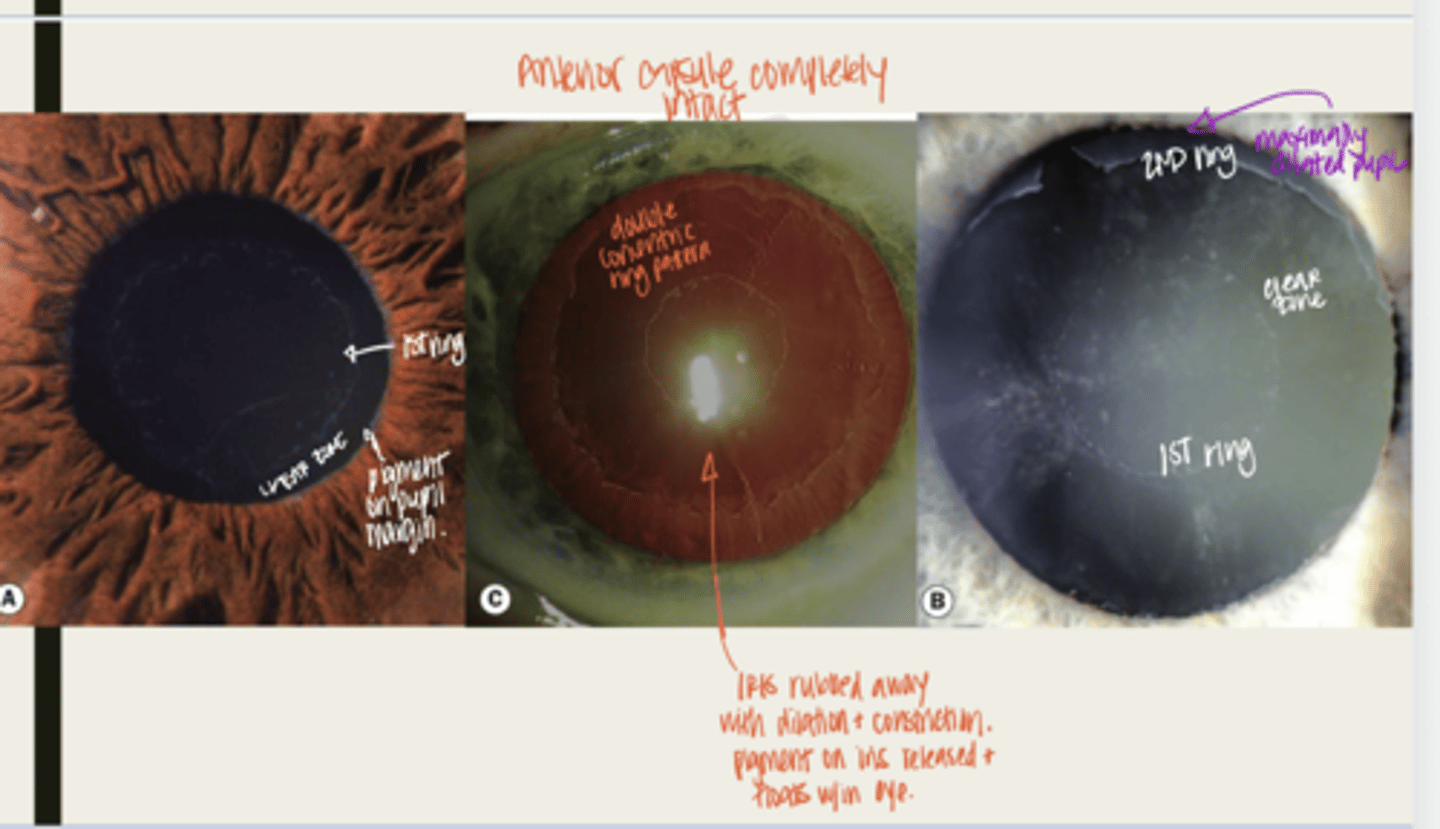
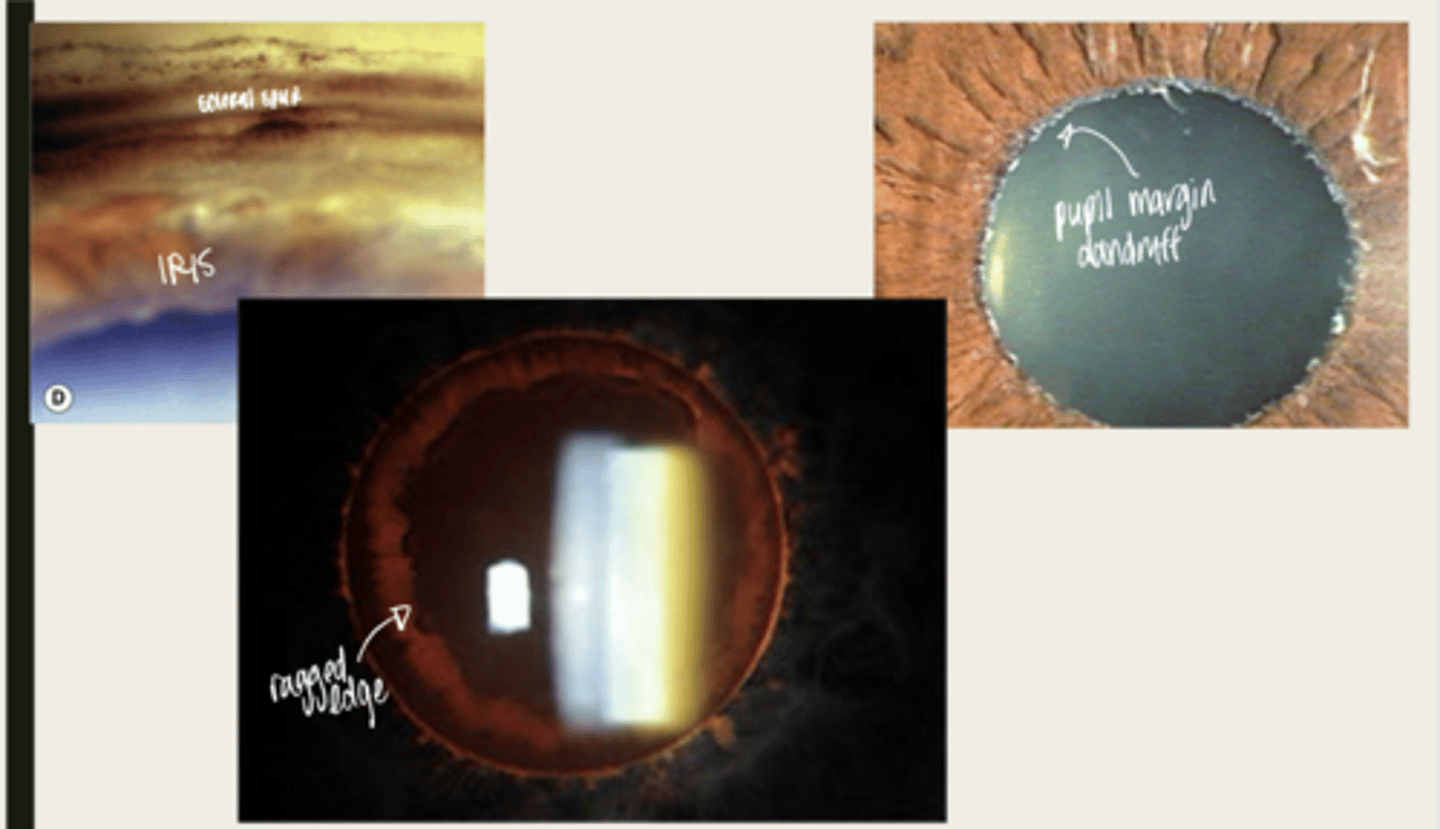
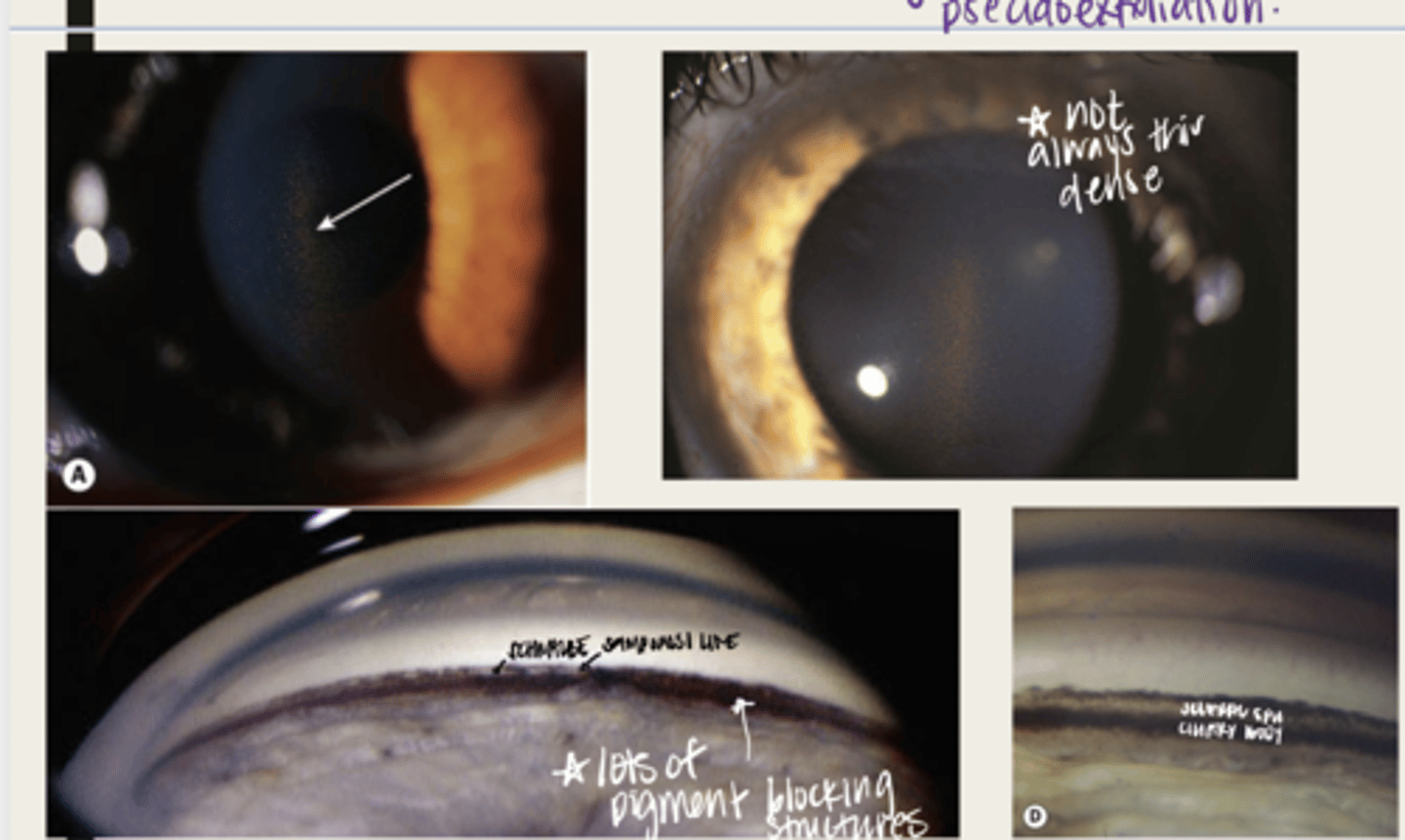
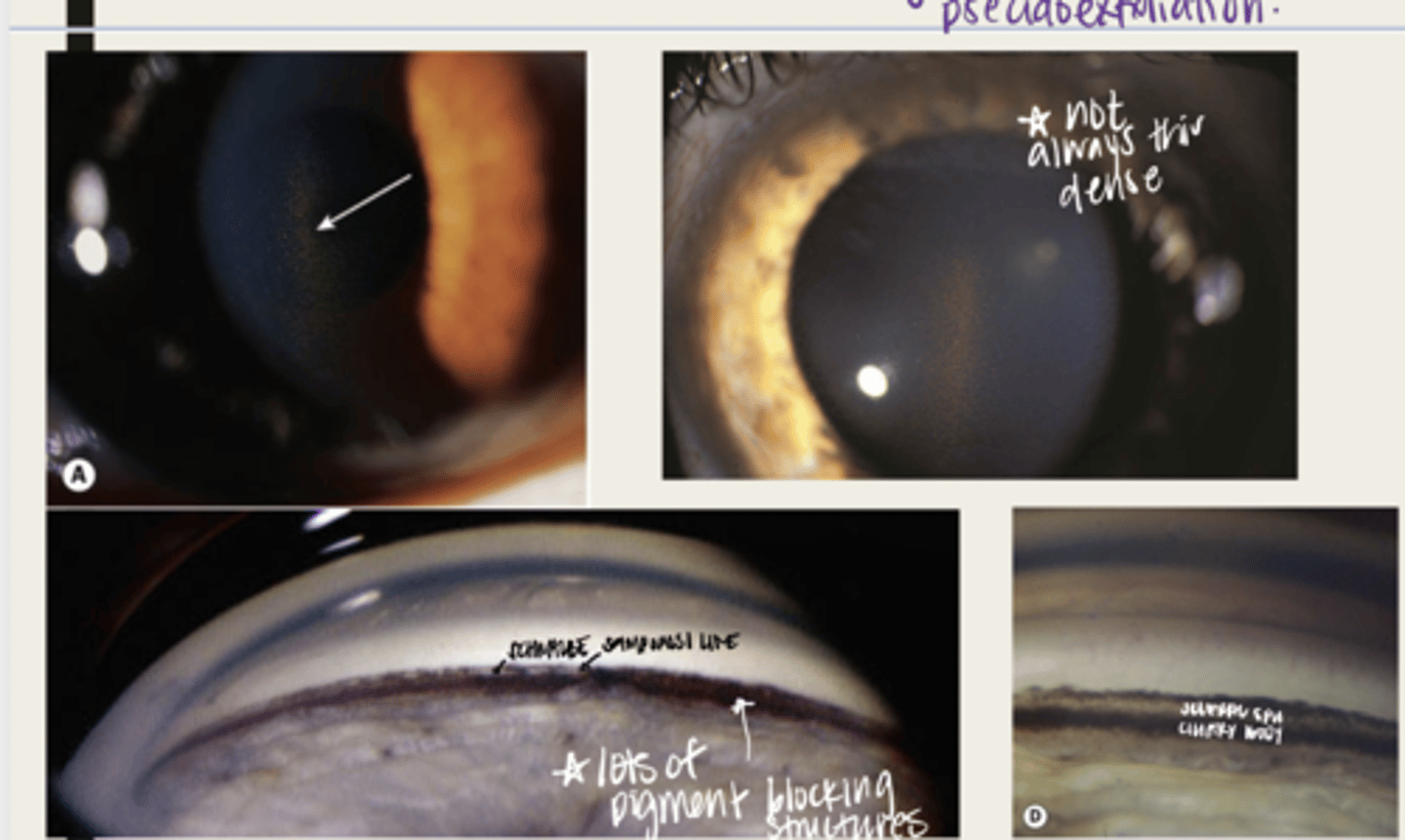
-dandriff like material deposited on lens, anterior chamber and iris
What is the presentation of pseudoexfoliation syndrome?
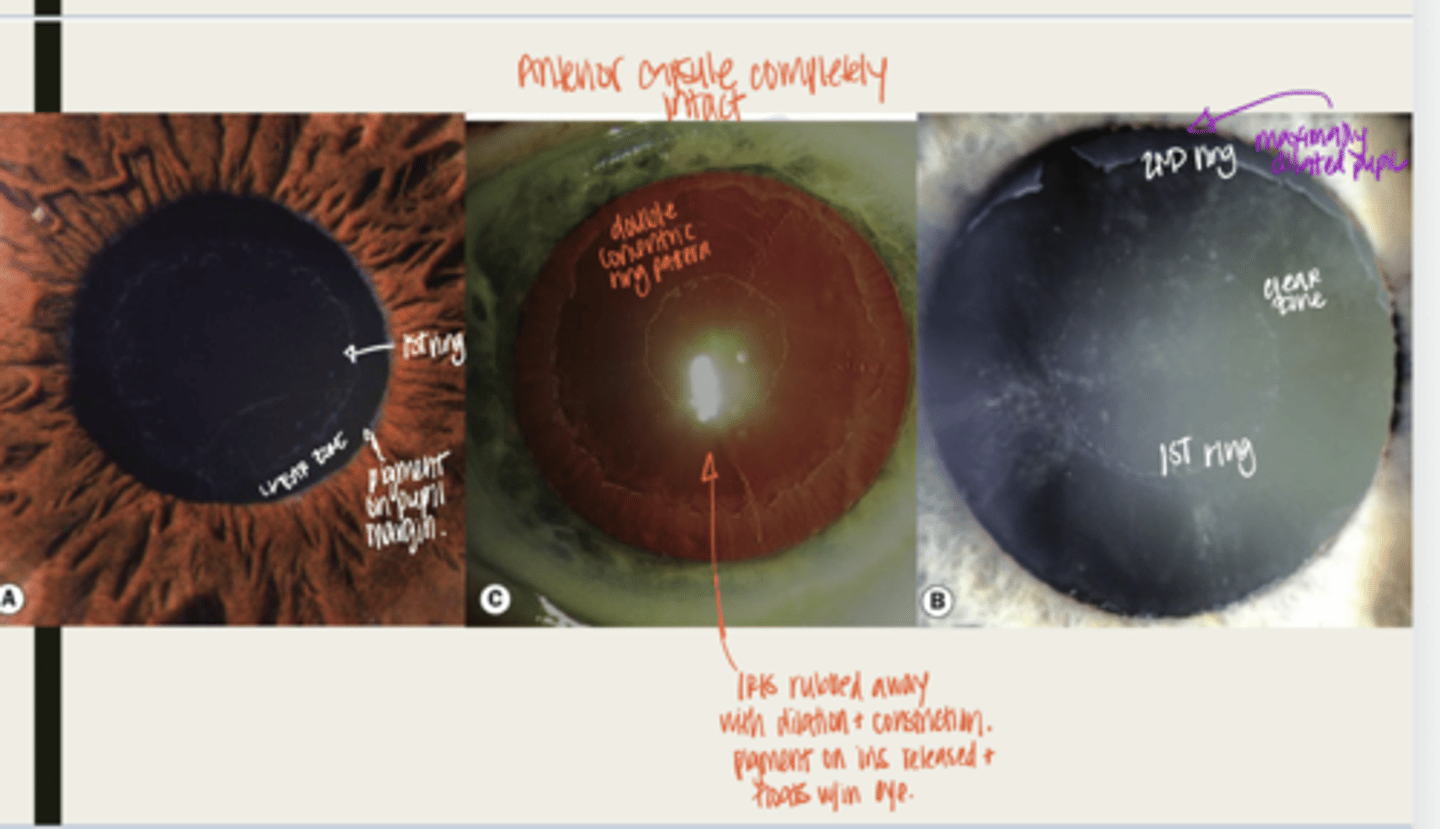
double concentric ring pattern -- separated by a clear zone
The dandruff like material deposited on the lens in pseudoexfoliation syndrome will look like what?
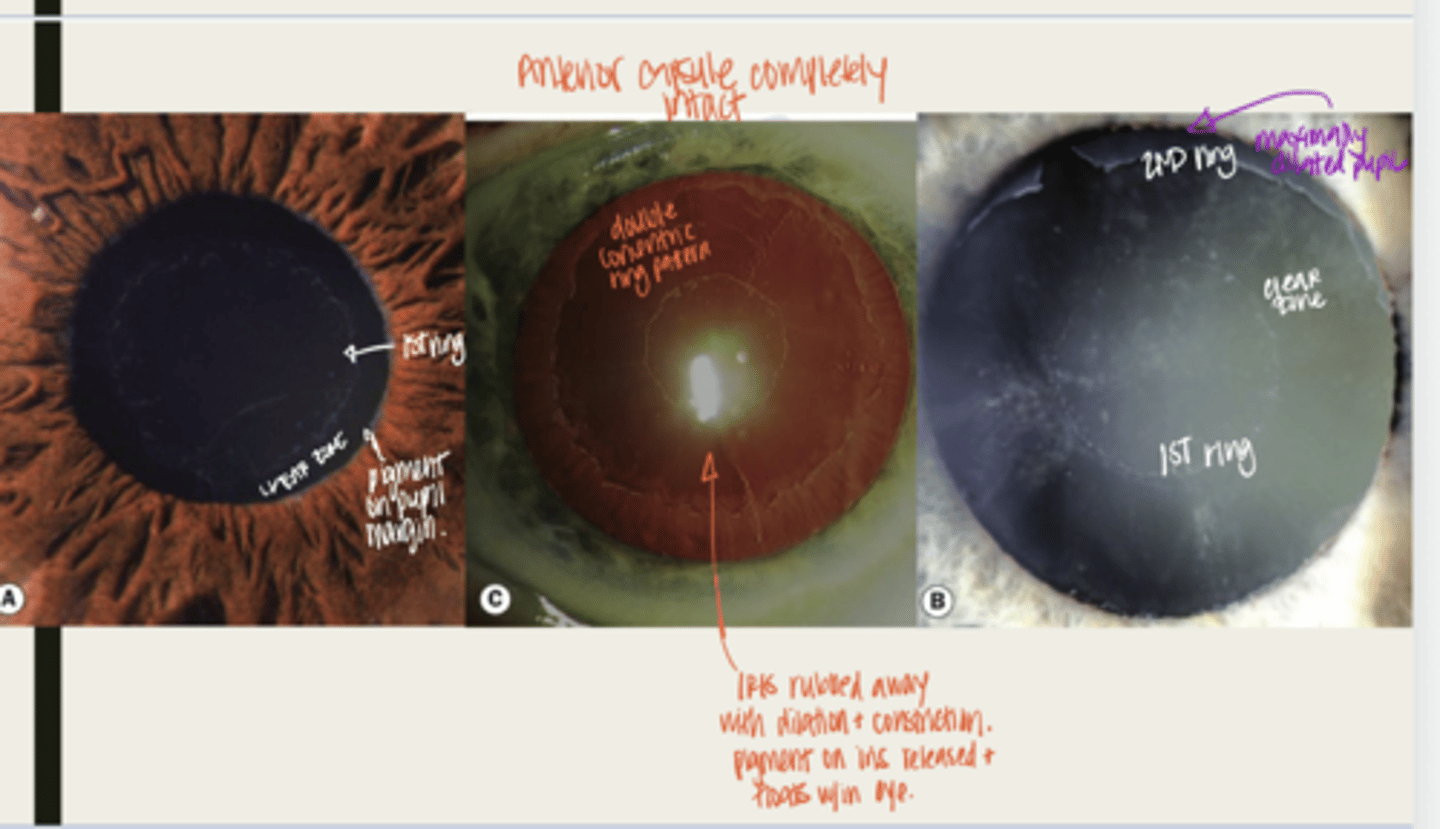
-seen near TM
-patchy areas of TM hyperpigmentation will also be seen
The dandruff like material deposited in the anterior chamber in pseudoexfoliation syndrome will look like what?
-seen at the pupillary ruff
-transillumination defects will be seen near pupillary ruff
The dandruff like material deposited on the iris in pseudoexfoliation syndrome will look like what?
pseudoexfoliation glaucoma
What are the complications of pseudoexfoliation syndrome?
true
True or False:
The risk of developing glaucoma increases the longer the patient has pseudoexfoliation syndrome
60
____% of patients with pseudoexfoliation syndrome are diagnosed with glaucoma at 5 years
increased IOP, retinal nerve fiber thinning, glaucomatous optic nerves, VF defects
Patients with pseudoexfoliation glaucoma will have what?
decreased VA and reduced peripheral vision
increased IOP, retinal nerve fiber thinning, glaucomatous optic nerves, VF defects d/t pseudoexfoliation syndrome can lead to what?
pseudoexfoliation glaucoma
Which has a more rapid progression?
pseudoexfoliation glaucoma or primary open angle glaucoma
no treatment is needed for pseudoexfoliation syndrome
What is the treatment for pseudoexfoliation syndrome?
-topical glaucoma meds
-surgical management with trabeculoplasty, trabeculectomy, tube shunt, or ciliary body destruction
What is the treatment for pseudoexfoliation glaucoma?
pigment dispersion syndrome
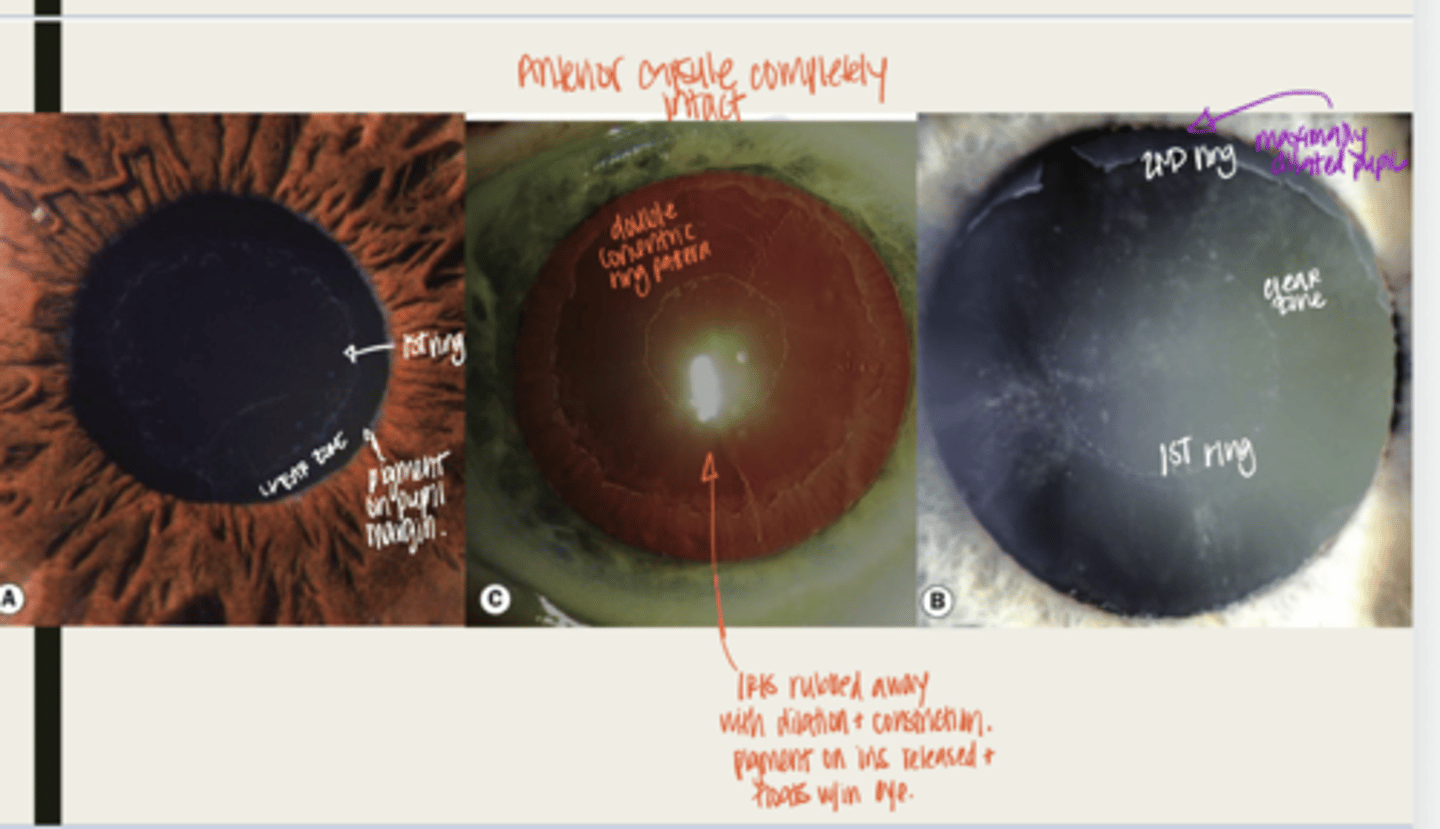
release of pigment granules from the iris pigment epithelium
throughout the anterior segment
Where will the pigment granules deposit in pigment dispersion syndrome?
white, young, myopic males
Who is pigment dispersion syndrome common in?
-excessive posterior bowing of the mid-peripheral portion of the iris
-bowing of the iris will cause posterior iris to rub against the zonules which will in the release of pigment granules
What is the pathogenesis of pigment dispersion syndrome?
decrease -- lens will thicken with accommodation
Does pigment dispersion in pigment dispersion syndrome increase or decrease with age?
-asymptomatic
-blurred vision with hals and acute increases in IOP
What are the common symptoms of pigment dispersion syndrome?
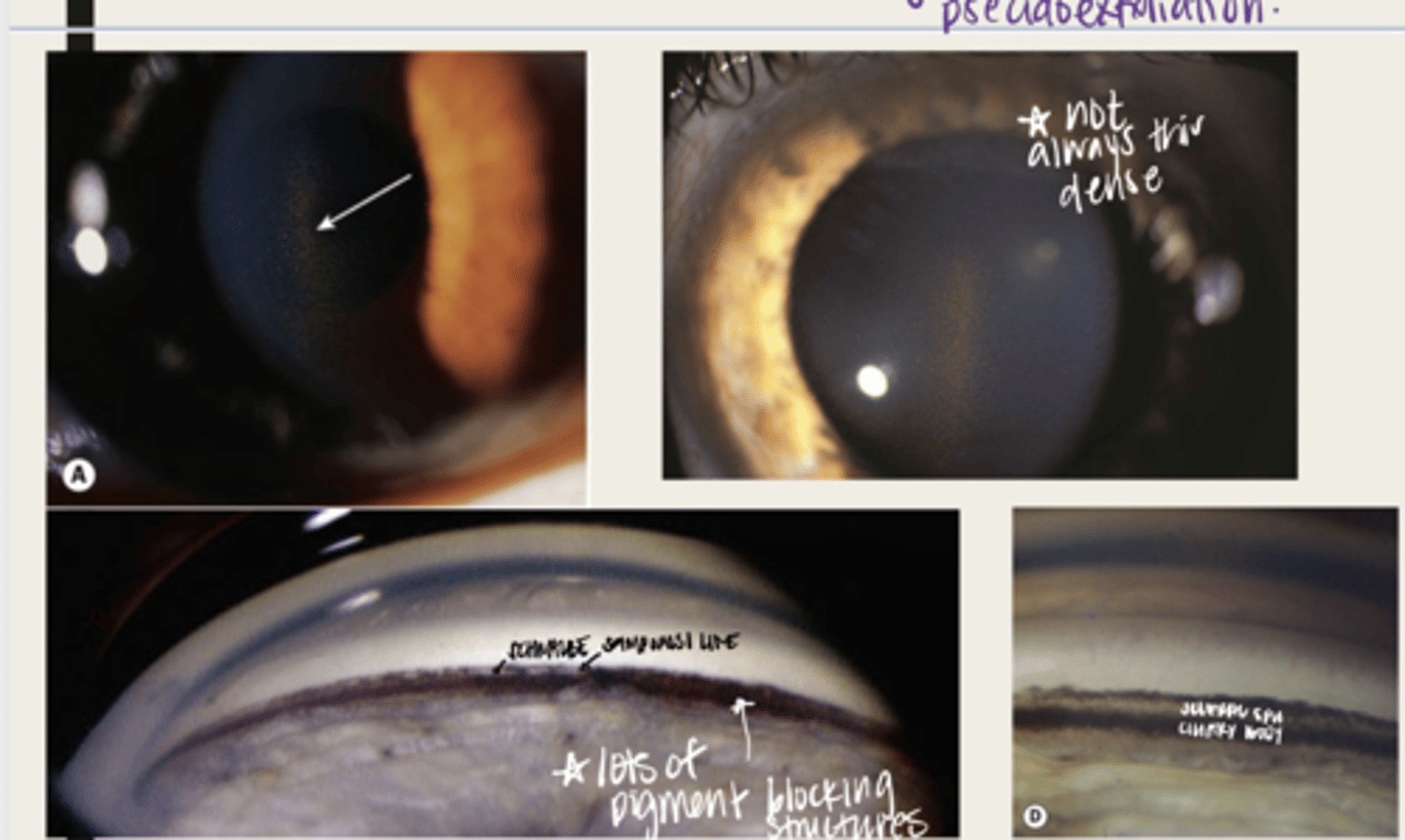
pigment deposition on the endothelium in a vertical spindle shape (Krukenberg spindle)
What is the presentation of pigment dispersion syndrome on the cornea?
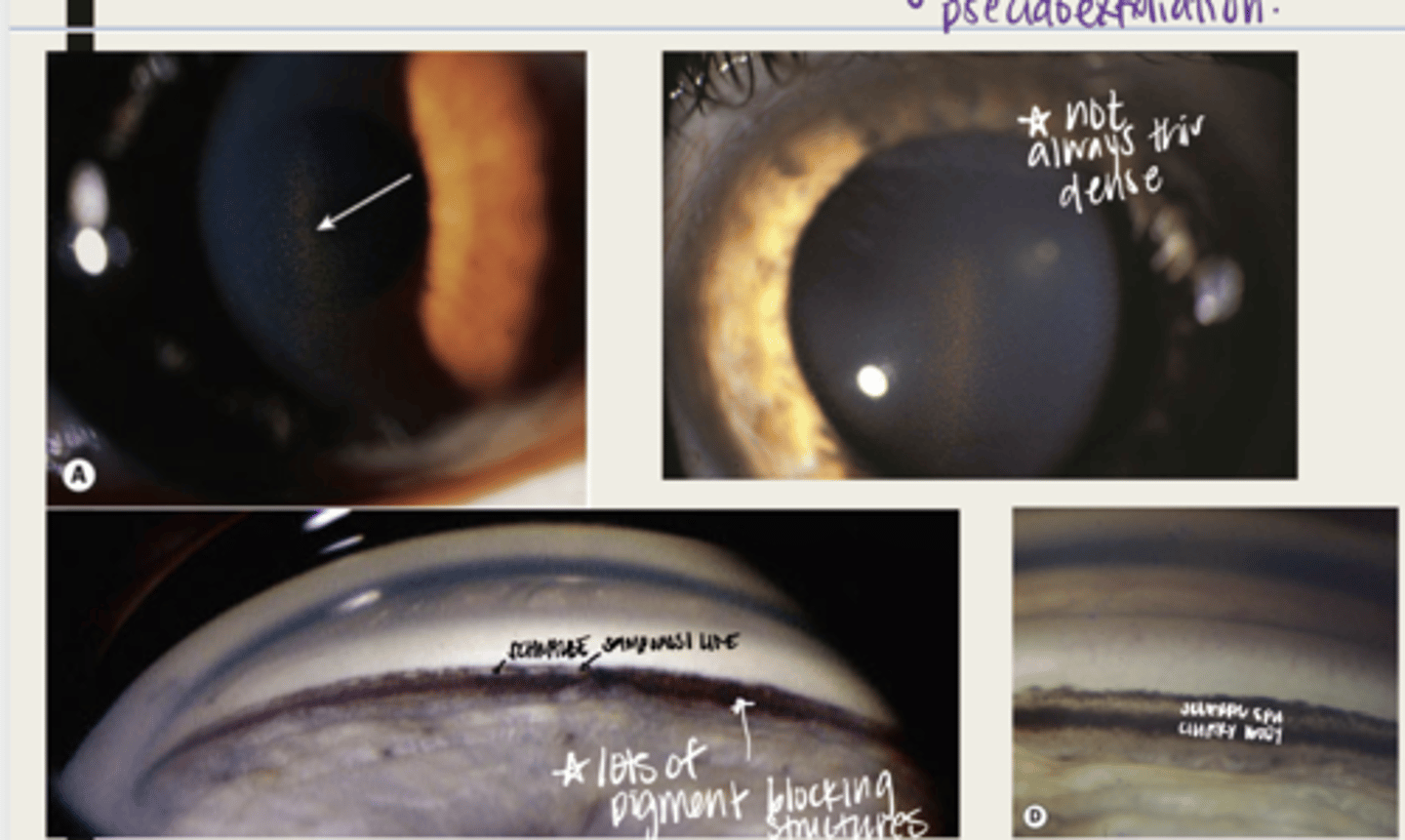
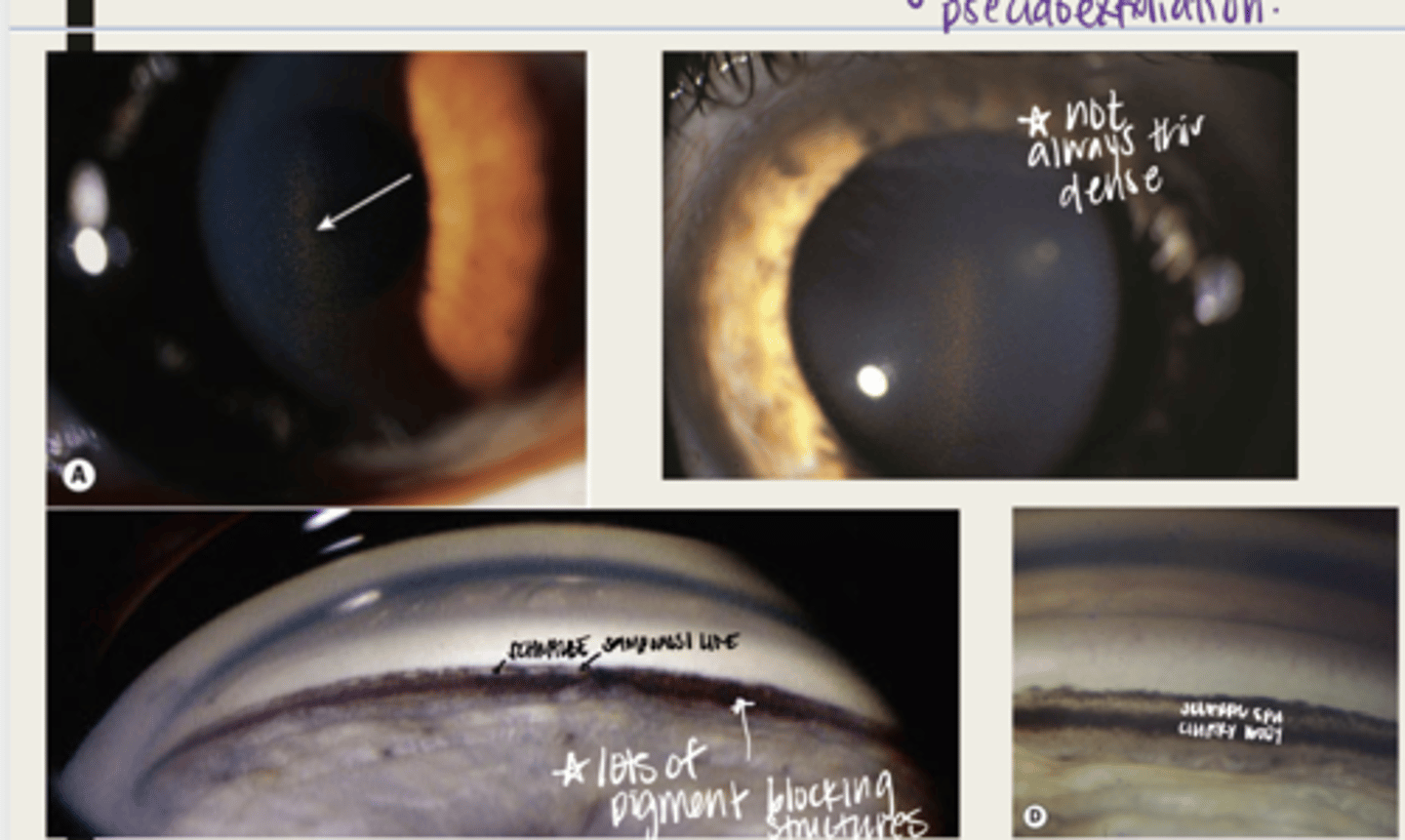
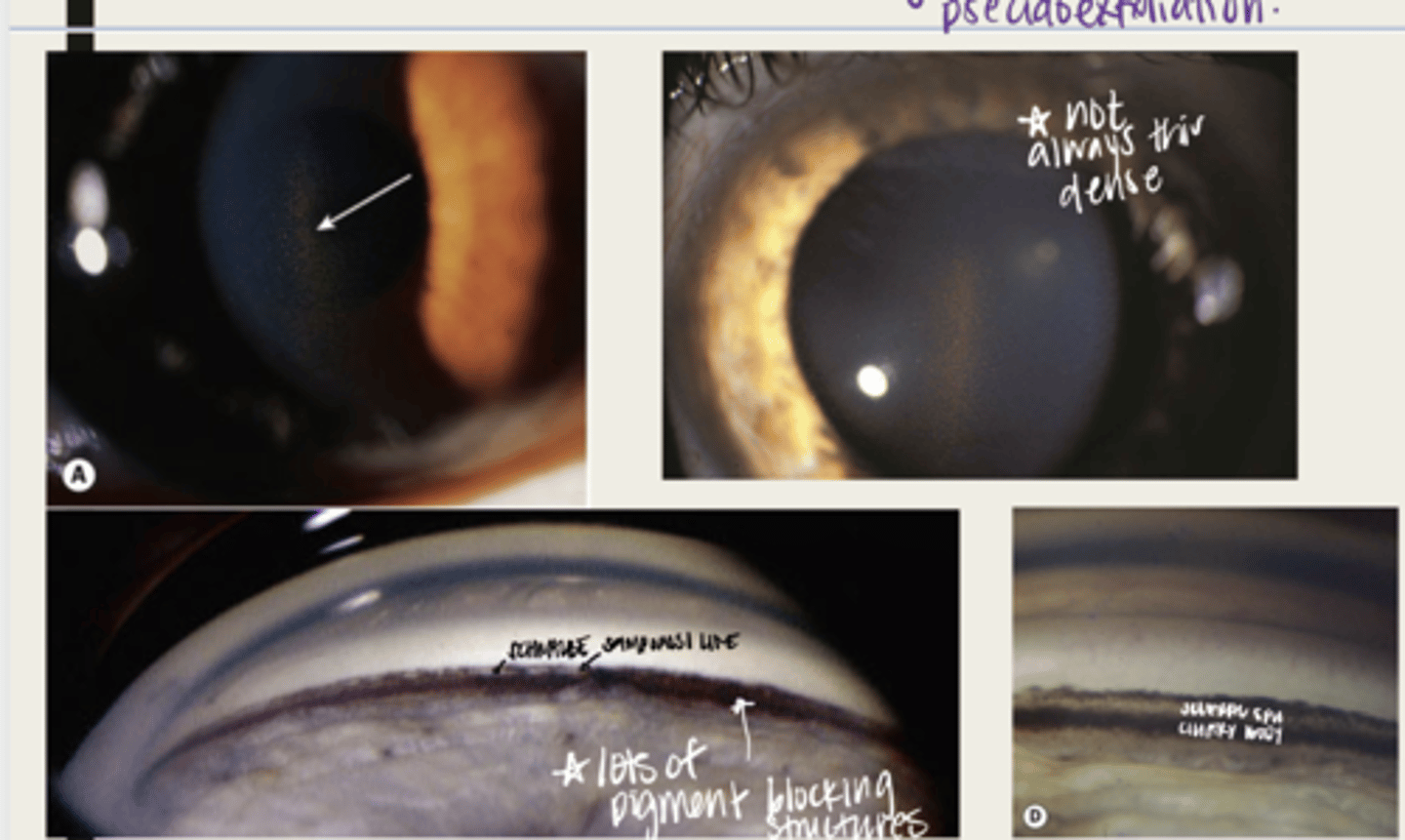
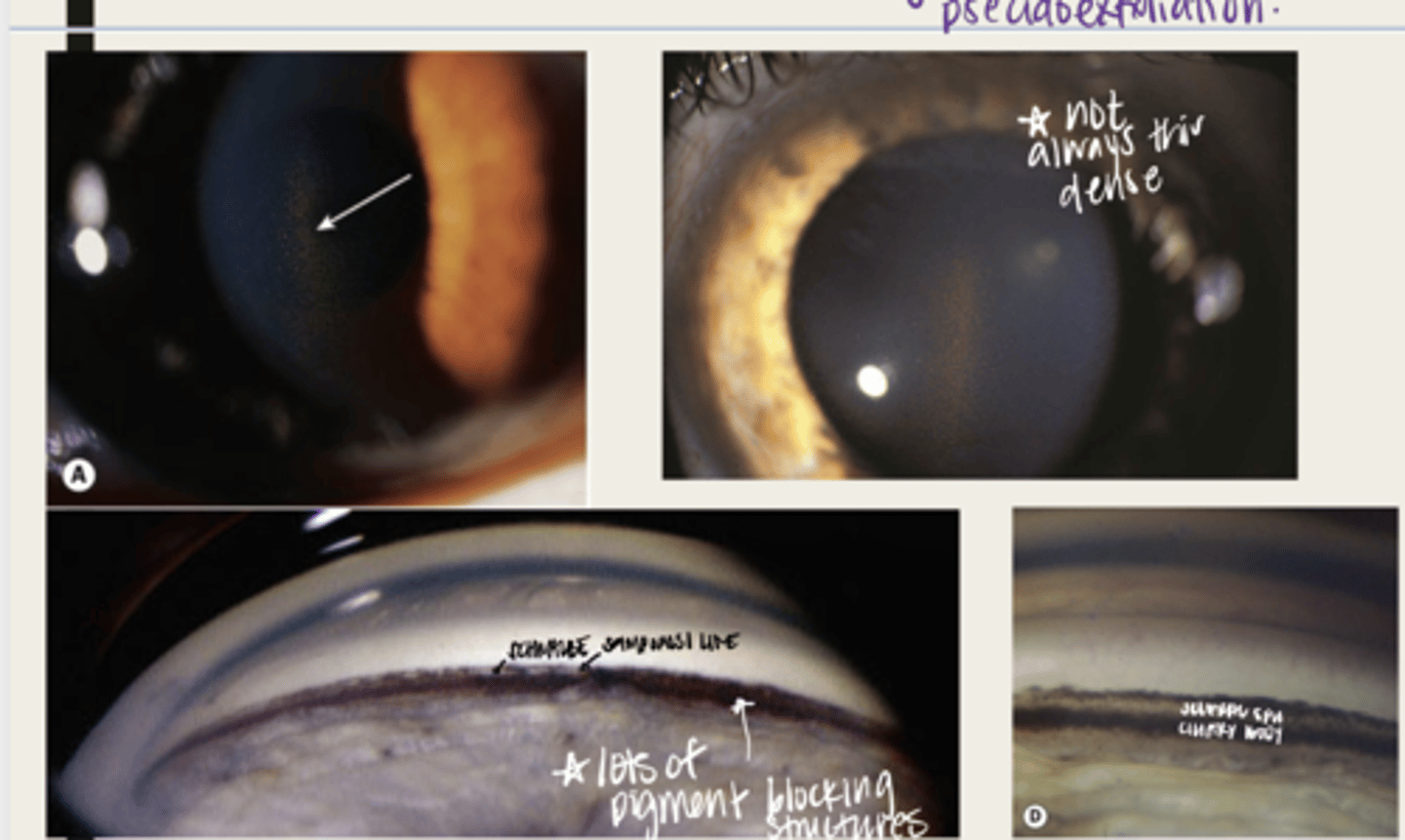
-open angles with heavily pigmented trabecular meshwork
-pigment can be anterior to Schwalbe's line (Sampaolesi line)
What is the presentation of pigment dispersion syndrome in the anterior chamber (seen with gonioscopy)?
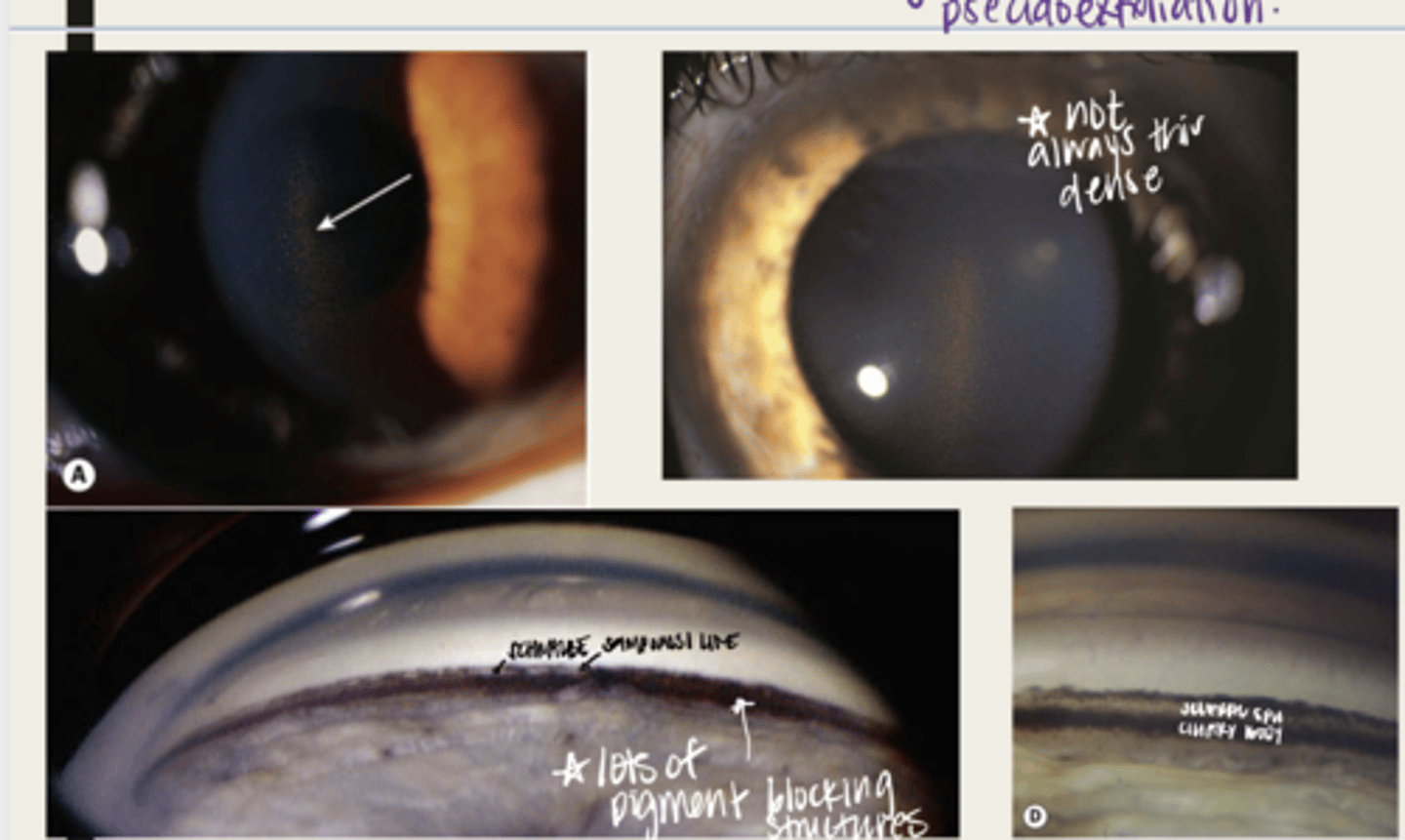
radial mid peripheral transillumination defects with pigment deposition on the anterior surface of the iris
What is the presentation of pigment dispersion syndrome on the iris?

pigment position can be seen on the anterior capsule and pigment can also be seen near the zonule insertion
What is the presentation of pigment dispersion syndrome on the lens?
increases in IOP can be seen
What is the effect of pigment dispersion syndrome on the acute intraocular pressure?
no effects
What is the effect of pigment dispersion syndrome on the optical nerve and VF?
pigment dispersion glaucoma
What is a possible complication of pigment dispersion glaucoma?