Chem 100 Lec: EXAM 1 PRACTICE (Without Combine)
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHEM100 LEC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
What is the Smallest Unit to Largest Unit according to their Magnitude
Microliter
Milliliter
Centiliter
Deciliter
Liter
Kiloliter
What is the Definition of Specific Heat?
The amount of heat required to increase the temp of 1g of a substance by 1 °C
What are the Names for Diatomic Elements?
Bromine
Hydrogen
Iodine
Fluorine
Nitrogen
Oxygen
Chloride
What are the Chemical Formulas for Diatomic Elements?
Br2
H2
I2
F2
N2
O2
Cl2
Would the properties change when a solid like dry ice is transformed to gas?
The Mass is
Same
Would the properties change when a solid like dry ice is transformed to gas?
The Composition is
Same
Would the properties change when a solid like dry ice is transformed to gas?
The Density is
Changes/Different
Would the properties change when a solid like dry ice is transformed to gas?
The Physical State is
Changes/Different
Is N2 an Element or a Compound?
Element
Is CO2 an Element or a Compound?
Compound
Is O2 an Element or a Compound?
Element
Is He an Element or a Compound?
Element
Is NO2 an Element or a Compound?
Compound
When you have Dissolved a Small Amount of Sugar in Water, you have prepared What?
A Mixture
Is Sugar Dissolved in Water Homogeneous or Heterogeneous?
Homogeneous
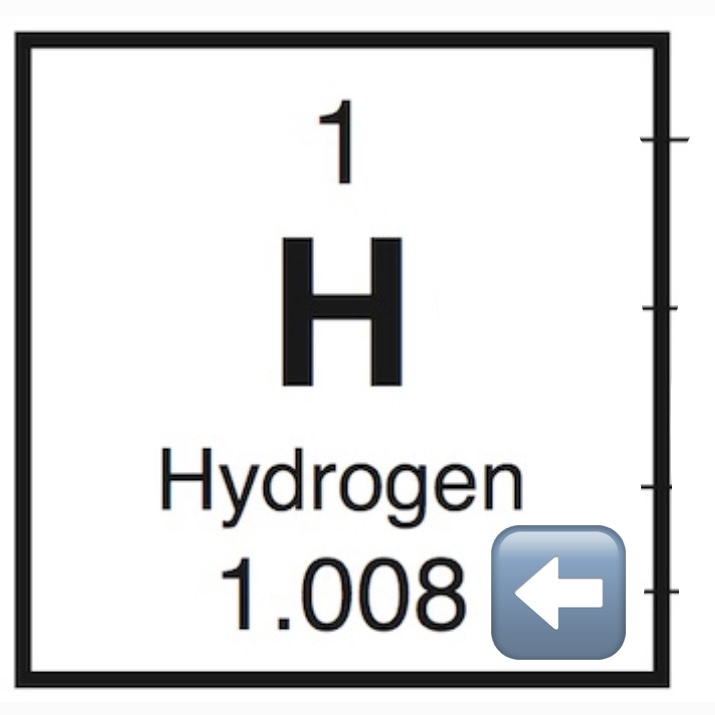
Atomic Mass
The Kinetic Energy of the Particles Increases as the Temperature blanks
Increases
True or False: The pressure exerted on the inner wall of a vessel containing a sample of gas is due to the collisions of the gas particles with the inner wall
True
True or False: H3PO4 is a molecule of a compound
True
True or False: H3PO4 is a homogeneous mixture
False
True or False: H3PO4 is a heterogeneous mixture
False
True or False: H3PO4 is an element
False
True or False: H3PO4 is a compound
True
True or False: A compound is a pure substance made of elements which are combined chemically
True
True or False: A compound is a pure substance that can be decomposed into components (That is, into simpler substances) by chemical means only
True
True or False: A compound is a pure substance that can be decomposed into components (That is, into simpler substances) by physical means only
False
When Heat is Added to a Mixture of Ice and Water at 0 °C, we expect the Temperature of the Mixture to:/ Explain your Answer
Remain the same. Heat is used to break the bonds (Energy) between the particles in ice. The temperature will increase only after all the ice has melted.
True or False: Compounds cannot be decomposed into simpler substances
False
True or False: Compounds can be decomposed by physical means into simpler substances
False
True or False: Compounds can be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical means
True
True or False: Mixtures cannot be decomposed into simpler substances
True or False: Mixtures can be decomposed by physical means into simpler substances
Energy due to Position or Composition is Called
Potential Energy
Energy due to Motion is Called
Kinetic Energy
Give the Names of Any Transition Elements (Name Three)
Scandium
Titanium
Vanadium
Chromium
Manganese
Iron
Cobalt
Nickel
Copper
Zinc
Yttrium
Zirconium
Niobium
Molybdenum
Technetium
Ruthenium
Rhodium
Palladium
Silver
Cadmium
Hafnium
Tantalum
Tungsten
Rhenium
Osmium
Iridium
Platinum
Gold
Mercury
Give the Chemical Symbols of any Transition Elements (Name Three)
Sc
Ti
V
Cr
Mn
Fe
Co
Ni
Cu
Zn
Y
Zr
Nb
Mo
Tc
Ru
Rh
Pd
Ag
Cd
Hf
Ta
W
Re
Os
Ir
Pt
Au
Hg
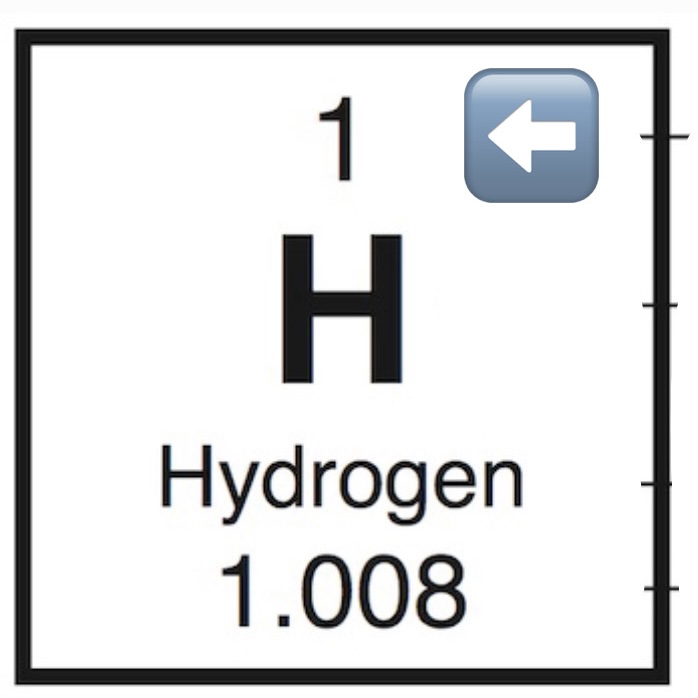
Atomic Number
Physical or Chemical Change: A red solution turns green
Chemical Change
Physical or Chemical Change: Bubbles form when baking soda is mixed with lemon juice
Chemical Change
Physical or Chemical Change: Sulfur is melting
Physical Change
Physical or Chemical Change: Oil is freezing
Physical Change
Name an Element in the Same Period as Copper
Potassium
Calcium
Scandium
Titanium
Vanadium
Chromium
Manganese
Iron
Cobalt
Nickel
Zinc
Gallium
Germanium
Arsenic
Selenium
Bromine
Krypton
What is the Definition of Boiling Point?
The temp at which the vapor pressure is equal to the external pressure (Pressure of atmosphere)
Will the Composition of a Substance Change when it Undergoes a Chemical Change?
Yes
Will the Composition of a Substance Change when it Undergoes a Physical Change?
No
How will the volume of a certain sample of gas change at constant pressure if the temperature is increased?
The Volume Increase
How will the pressure of a certain sample of gas change at constant volume if the temperature is increased?
The Pressure Increase
How will the volume of a certain sample of gas change at constant temperature if the pressure is increased?
The Volume Decrease
If the Number of Gas Particles are Increased at a Constant Temperature, the Volume of the Gas will blank to maintain Constant Pressure.
Increase
The Lower the Atmospheric Pressure, the blank the Boiling Point of a Liquid
Lower
The Atmospheric Pressure in Big Bear Mountain is blank in the San Fernando Valley
Lower than
The Higher the Attractive Forces between the Molecules of a Liquid, the blank the Vapor Pressure of the Liquid
Lower
What is the Definition of the Law of Definite Composition?
The percent by mass of the elements in a compound that is fixed
A Technique used for Separating Solid from Liquid using Filter Paper is called
Filtration
The Liquid that goes through the Filter Paper during Filtration is called
Filtrate
The Solid that remains on the Filter Paper is called
Residue
Elements that are Members of the Same Horizontal Row on the Periodic Table are said to belong to the Same blank
Period
Elements that are Members of the Same Vertical Column on the Periodic Table are said to belong to the Same blank
Family
When Atoms of the Same or Different Elements are combined chemically to form a unit, the Unit is called a
Molecule
A blank is composed of particles made of different elements combined chemically in a fixed proportion (Fixed ratio) by mass
Compound
Name all Alkali Metals
Lithium (Li)
Sodium (Na)
Potassium (K)
Rubidium (Rb)
Cesium (Cs)
Francium (Fr)
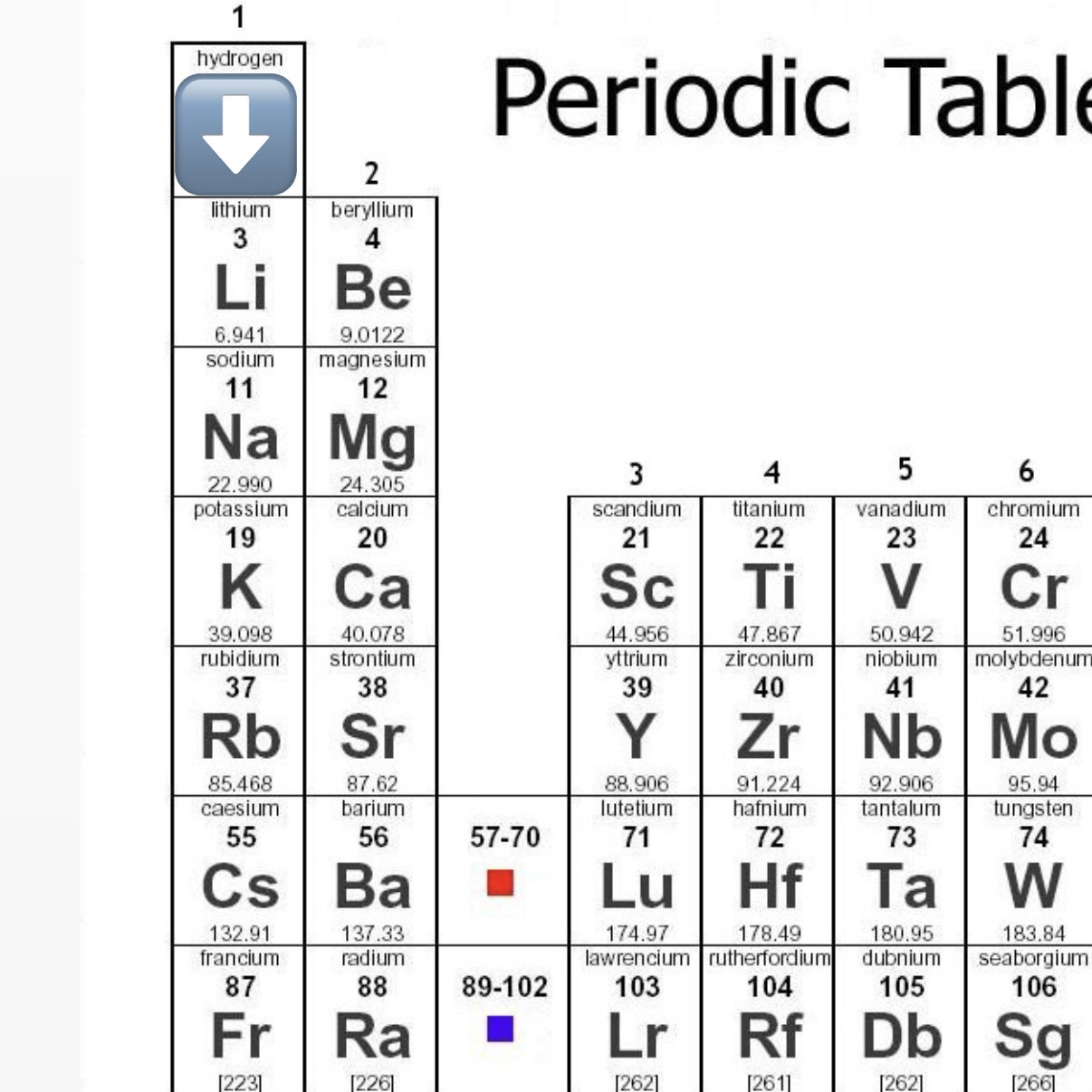
Alkali Metals
Name all Alkaline Earth Metals
Beryllium (Be)
Magnesium (Mg)
Calcium (Ca)
Strontium (Sr)
Barium (Ba)
Radium (Ra)
Name all Halogens
Fluorine (F)
Chlorine (Cl)
Bromine (Br)
Iodine (I)
Astatine (At)
Name all Noble Gases
Helium (He)
Neon (Ne)
Argon (Ar)
Krypton (Kr)
Xenon (Xe)
Radon (Rn)
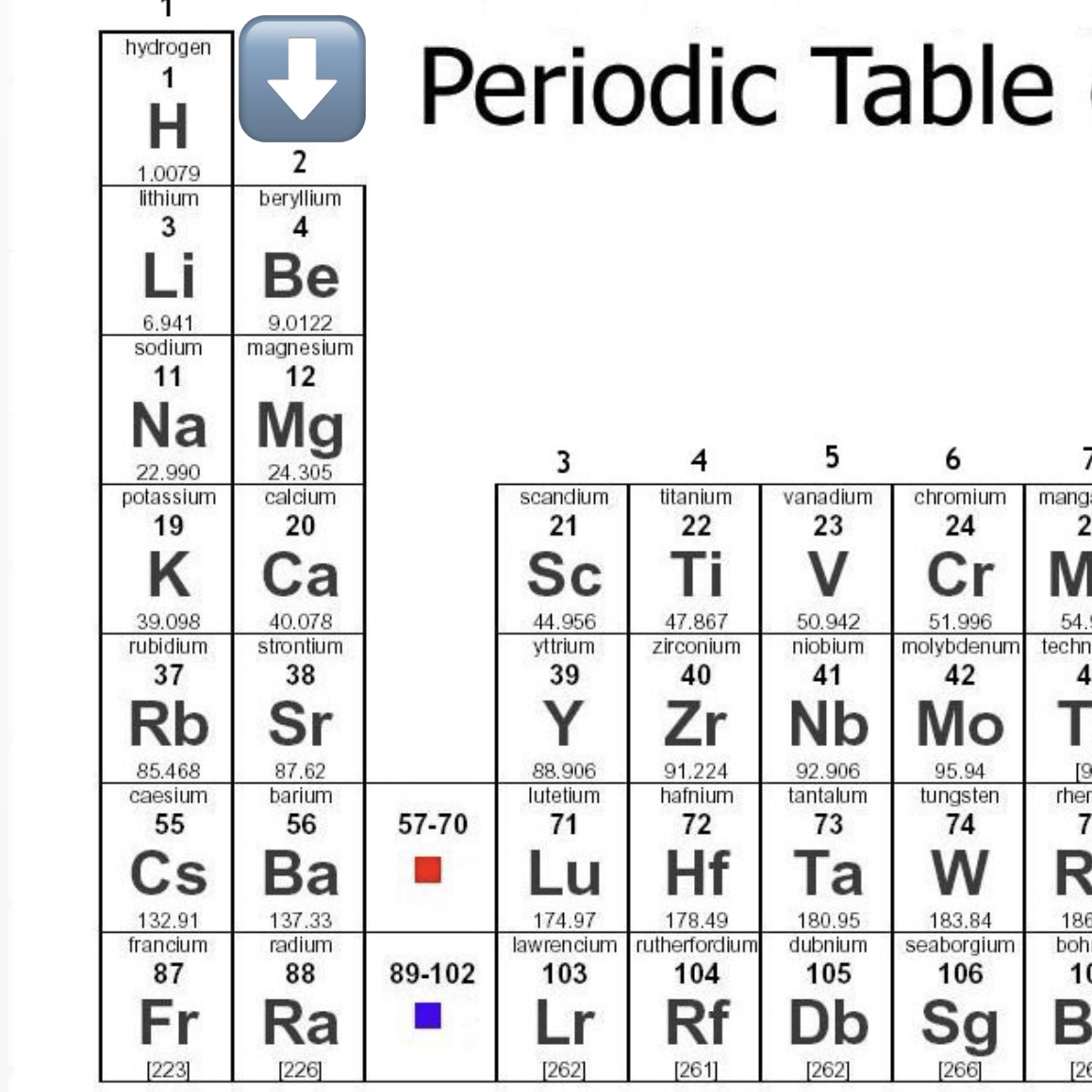
Alkaline Earth Metals
Transition Metals
Halogens
Noble Gases