AP Psychology - Biological Psychology
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards based on key concepts and vocabulary from the lecture notes on Biological Psychology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Genome
Our common set of genes shared by all humans, which accounts for about 95-99% of genetic material.
Eugenics
The concern for the genetic quality of humans, involving the promotion of reproduction among individuals with desirable traits.
Heredity
The genetic transfer of characteristics from parents to offspring, functioning through DNA.
Epigenetics
The study of how environmental factors can cause genes to be triggered or blocked, potentially leading to permanent changes.
Behavior Genetics
The study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior.
Monozygotic Twins
Identical twins that develop from a single fertilized egg and share the same genetic material.
Fraternal Twins
Twins that develop from two separate eggs fertilized by different sperm, sharing genetic similarities like ordinary siblings.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
The part of the nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord and is responsible for decision making.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
The part of the nervous system that connects the CNS to the rest of the body, consisting of sensory and motor neurons.
Somatic Nervous System
The division of the PNS that controls voluntary movements by connecting to the skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System
The system of the PNS that regulates involuntary functions such as heartbeat and digestion.
Sympathetic Nervous System
The division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, preparing it for 'fight or flight' responses.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy.
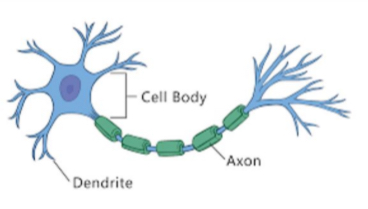
Neuron
A nerve cell responsible for the communication within the nervous system, the building blocks of the nervous system.
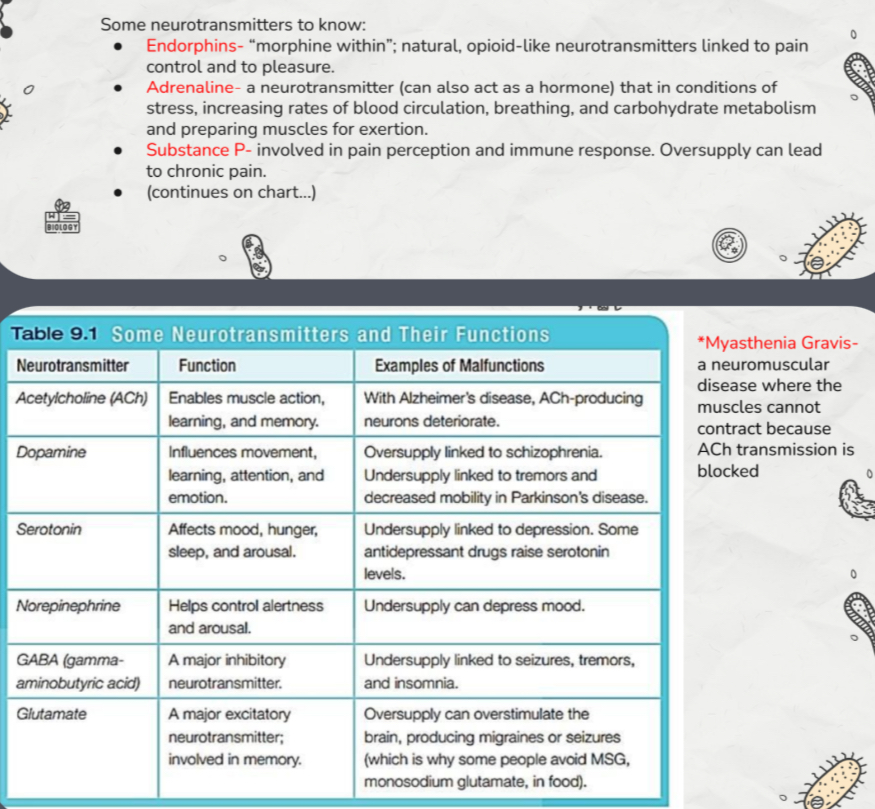
Neurotransmitters
Chemicals that transmit signals across synapses between neurons. Excitatory: continue the action. Inhibitory : block or prevent the message from moving farther.
Reuptake
The process by which neurotransmitters are reabsorbed by the sending neuron after they have performed their function.
Myelin Sheath
A fatty tissue layer that encases the axons of some neurons, enabling faster transmission of neural impulses. When the myelin sheath degenerates its a disease called Multiple Sclerosis
Action Potential
A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon when a neuron fires.
Reflex Arc
A simple spinal reflex pathway that includes a sensory neuron and a motor neuron, allowing for quick responses.
Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum, responsible for higher-level functions such as thinking and processing information.
Amygdala
A neural structure in the limbic system associated with anger and fear responses.
Hippocampus
A neural center in the limbic system involved in the processing and storage of explicit memories.
Wernicke's Area
A brain area involved in language comprehension and expression, typically located in the left temporal lobe.
Broca's Area
A region in the frontal lobe responsible for the production of speech.
Aphasia
A disorder characterized by impaired language ability, typically caused by damage to Broca's or Wernicke's area.
Sensory neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the body’s tissues and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
Motor neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
Interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord, they communicate internally and process information between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
Reflex
a simple automatic response to sensory stimulus such as a knee jerk response
Parts of neurons
Cell body (contains the nucleus)
Dendrite (a neurons branching extensions that receive and integrate messages conducting impulses towards the cell)
Axon (the neurons extension that passes messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands)
Synapse (the junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to another)
Glial Cells
Cells un the nervous system that support nourish and protect neurons. (They also play a role in learning, thinking, and memory)
Resting potential
positive - outside/ negative- inside state of an axon.
Depolarization
The process by which the neuron's membrane potential becomes less negative (more positive), leading to the generation of an action potential.
threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger an action potential in a neuron.
refractory period
The time following an action potential during which a neuron is temporarily unable to fire another action potential until the axon returns to its resting state
all or nothing response
The principle that a neuron either fires an action potential at full strength or does not fire at all, depending on whether the threshold is reached.
Examples of neurotransmitters
Hormones to know
