Cross Sectional Anatomy I Final Exam
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
What is letter e?
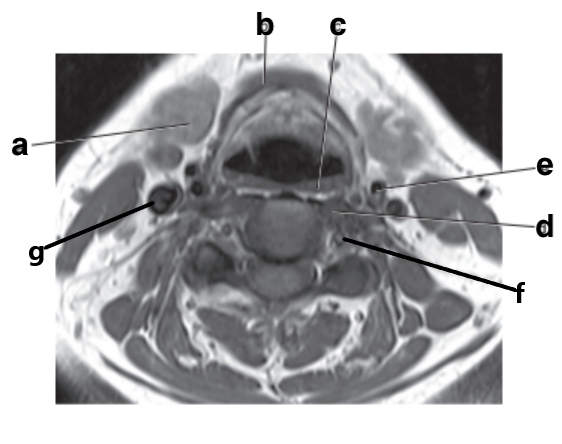
Subclavian artery
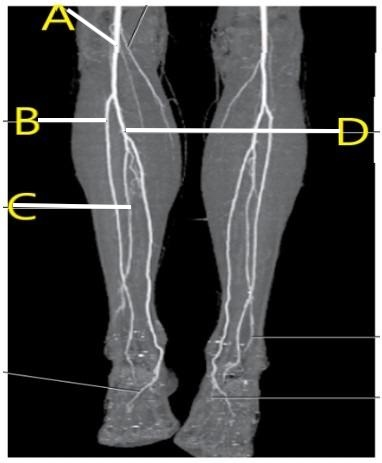
Which letter is the popliteal artery?
A
What is letter f?
Vertebral artery
The gallbladder is in the:
right upper quadrant
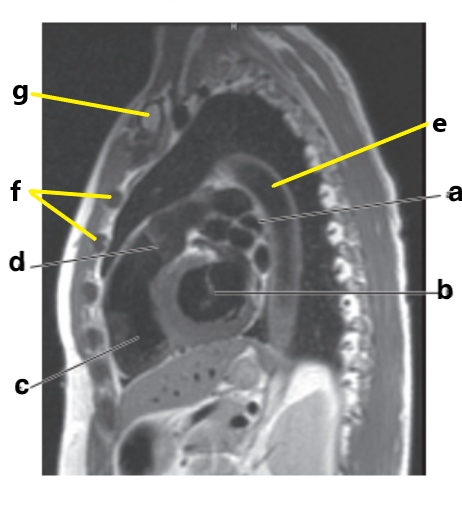
What is letter b?
Left ventricle
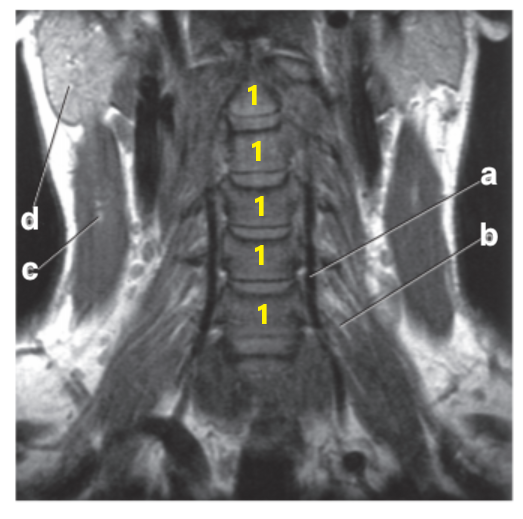
What is letter a?
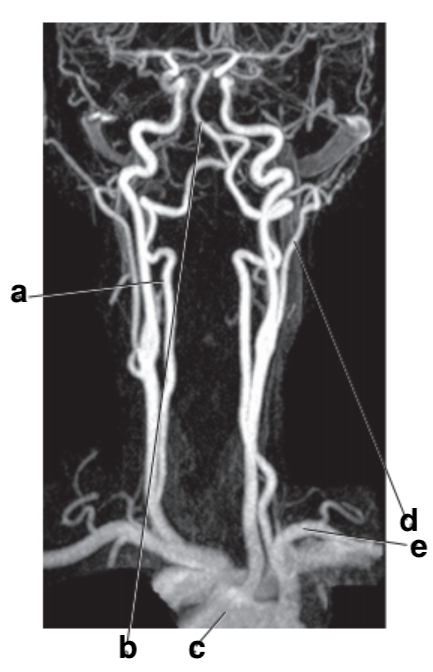
Vertebral artery
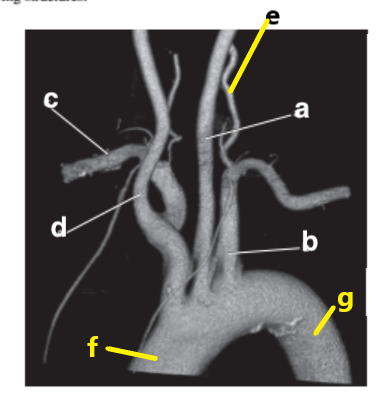
Which letter is the ascending aorta?
f
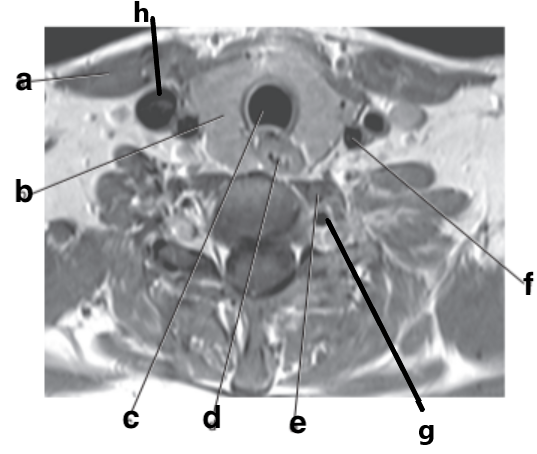
What is letter b?
Thyroid gland
_____________ is the typical cryogen used in a superconducting magnet of an MRI system.
Liquid Helium
___________ substances have strong magnetic properties and can be pulled into the magnetic field.
Ferromagnetic
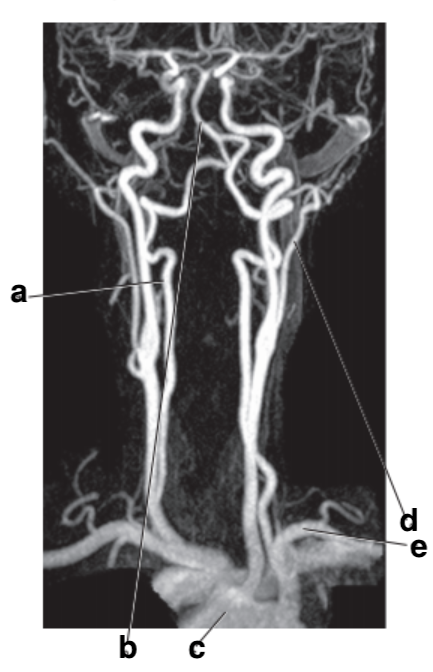
What is letter c?
Aortic arch
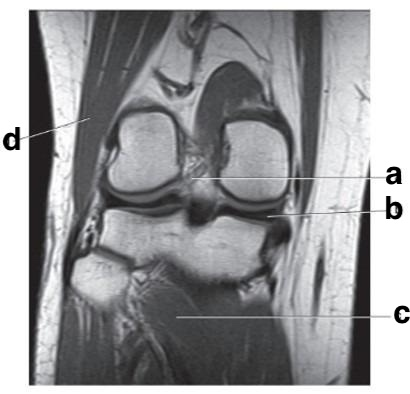
What is letter b?
Medial meniscus
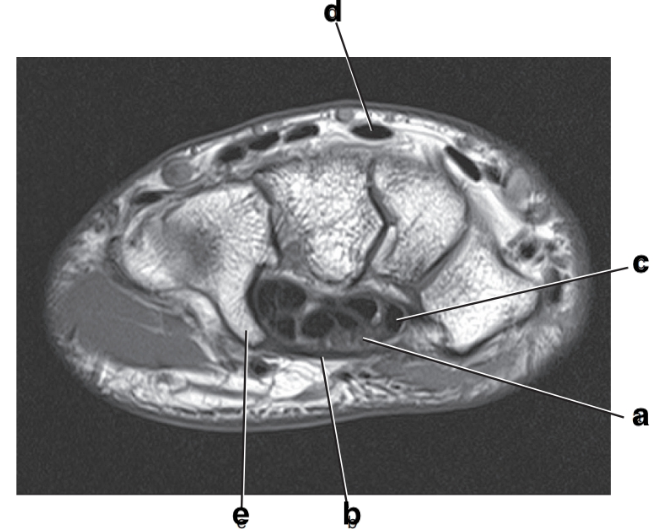
What is letter e?
Hook of the hamate
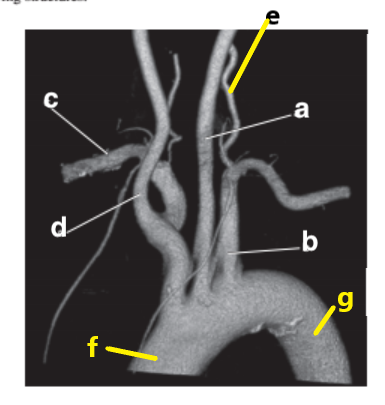
Which letter is the left common carotid?
a
What is the major stabilizing mechanism for the distal radioulnar joint?
Triangular fibrocartilage complex
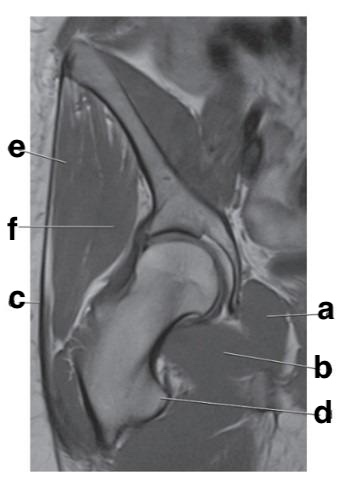
What is letter d?
lesser trochanter
What structure cushions the articulation between the femoral condyles and the tibial plateaus?
Menisci
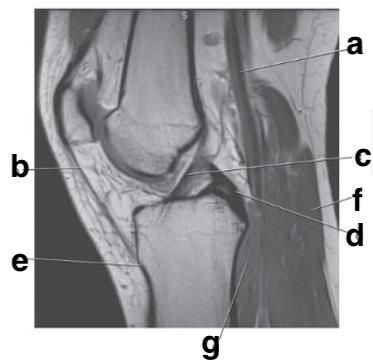
What is letter d?
posterior cruciate ligament
The femoral artery is an extension of which artery?
External iliac
What is the largest peripheral nerve in the body?
Sciatic
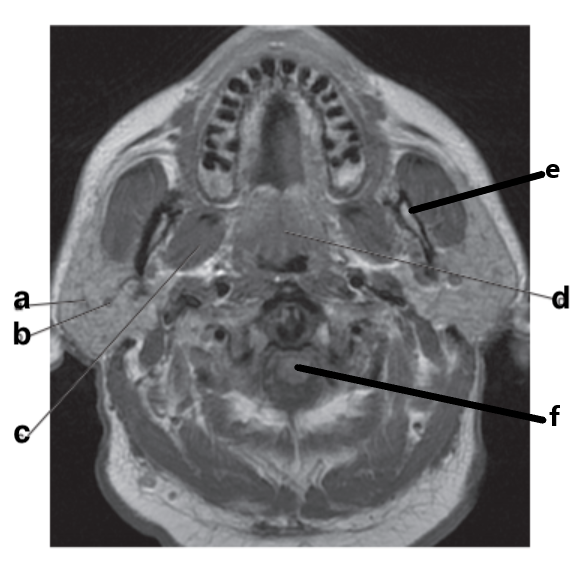
What is letter e?
Mandible
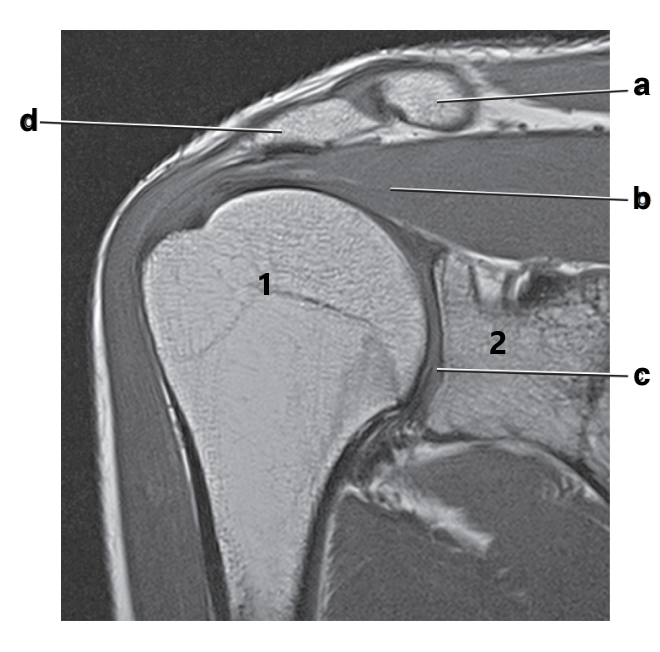
What is letter d?
Acromion
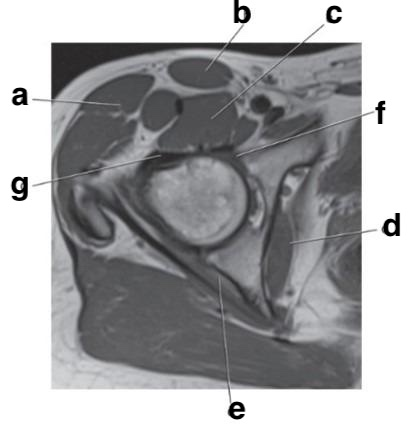
Which letter is the Anterior acetabular labrum?
f
The simplest and least expensive means of preventing problems associated with acoustic noise is to _______________.
use disposable foam earplugs.
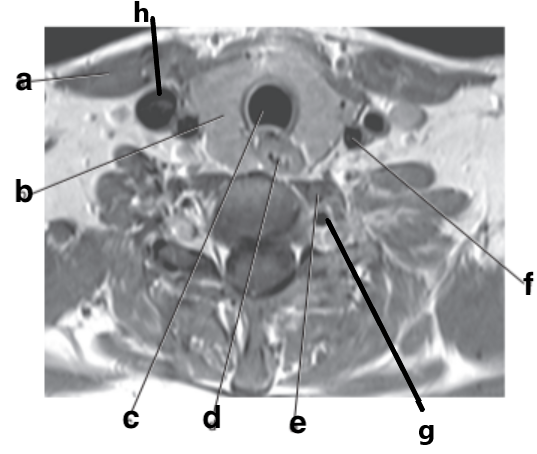
What is letter d?
Esophagus
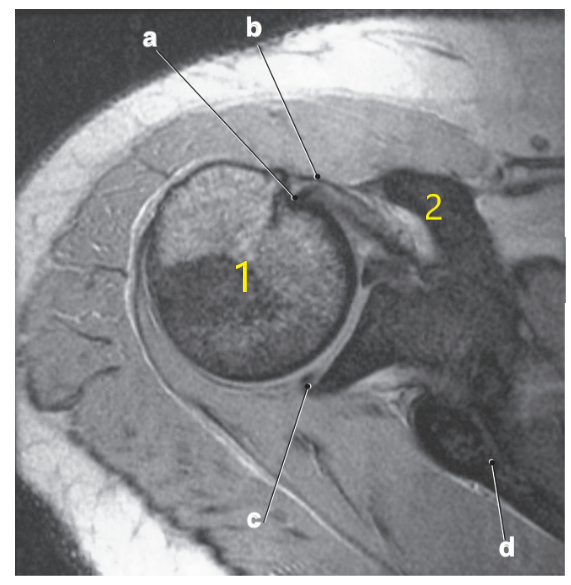
What is letter d?
Scapular spine
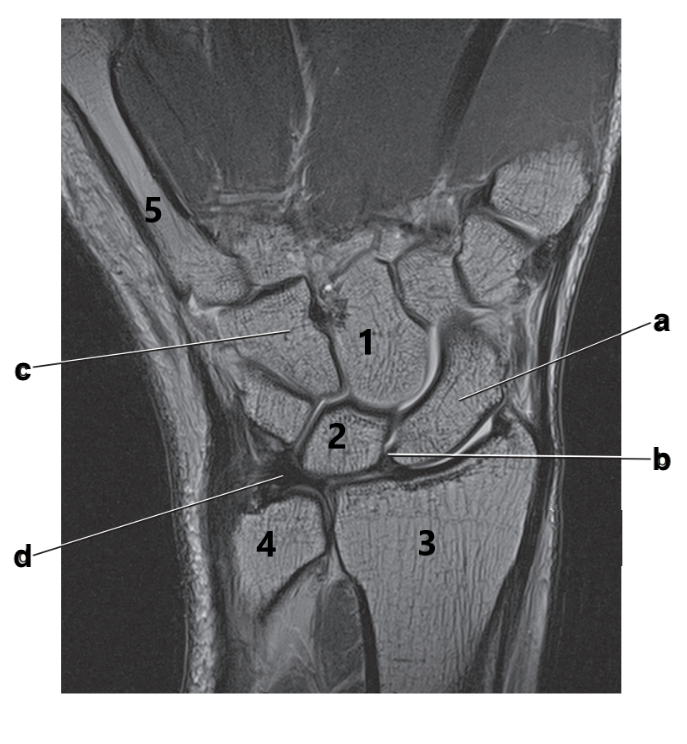
What is # 4?
Ulna
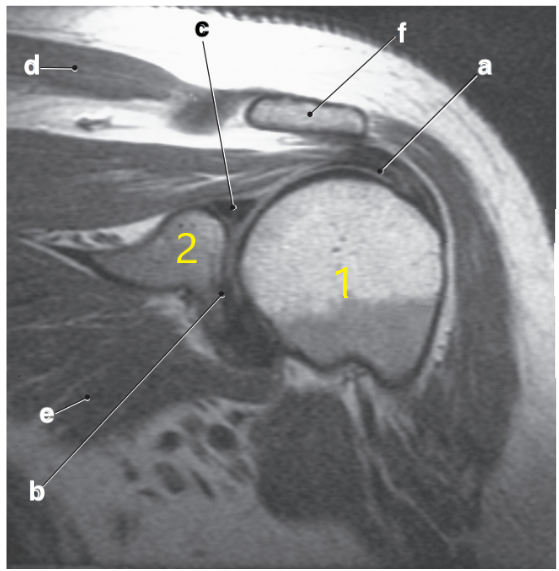
What is letter a?
Supraspinatus tendon
Which of the following is NOT a method to help control access to the MRI environment?
Use a flashing yellow “warning” sign
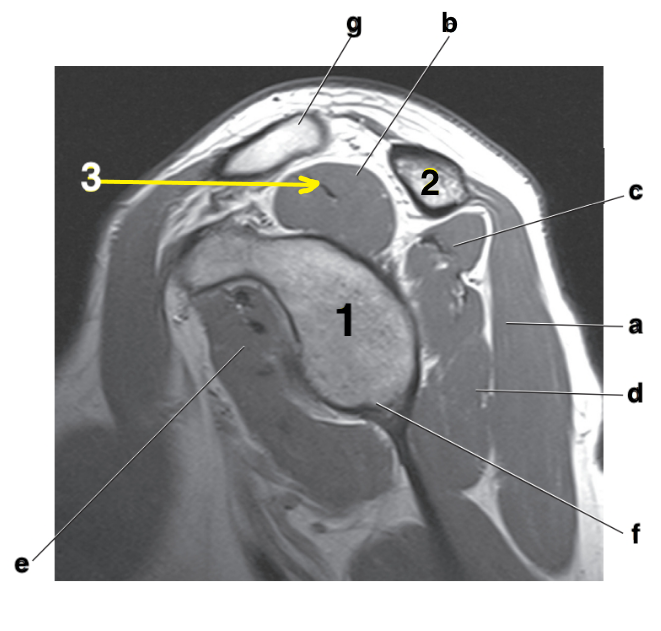
What is letter b?
Supraspinatus muscle
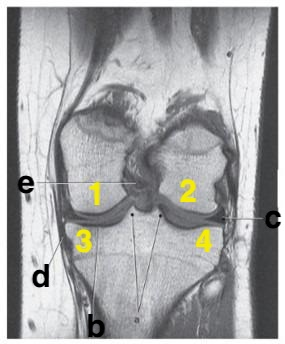
Which letter is pointing to the posterior cruciate ligament?
e
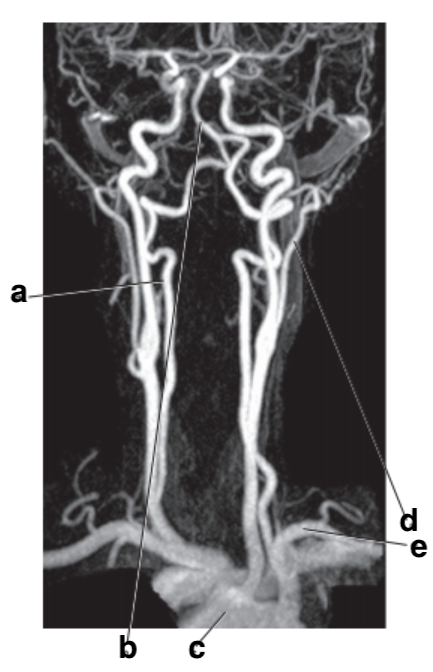
What is letter a?
Vertebral artery
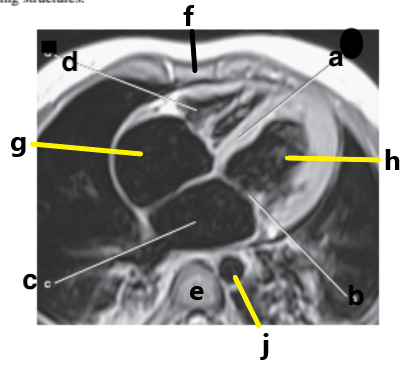
What is letter G?
Right atrium
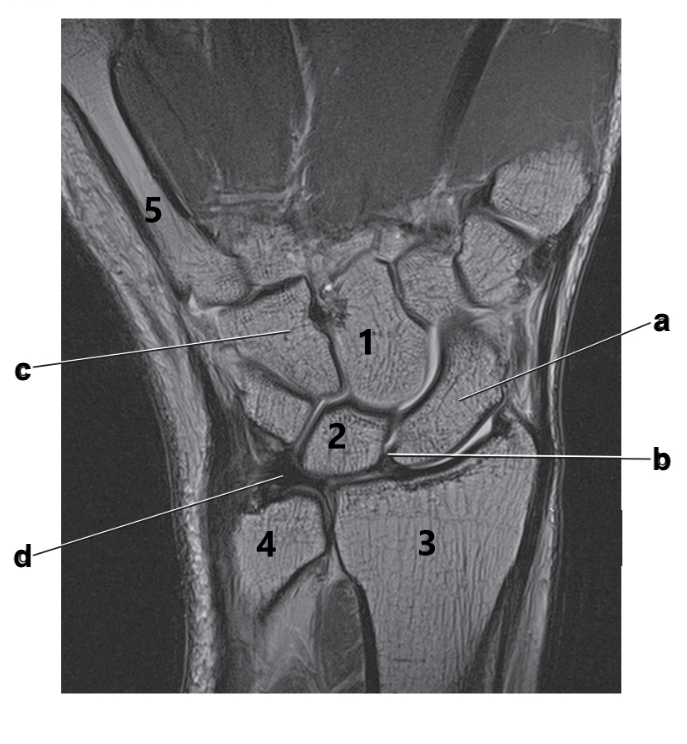
What is letter d?
Triangular fibrocartilage complex
The “missile effect” during which a ferromagnetic object may become a projectile, is related to the ________ field of the MRI system.
static magnetic
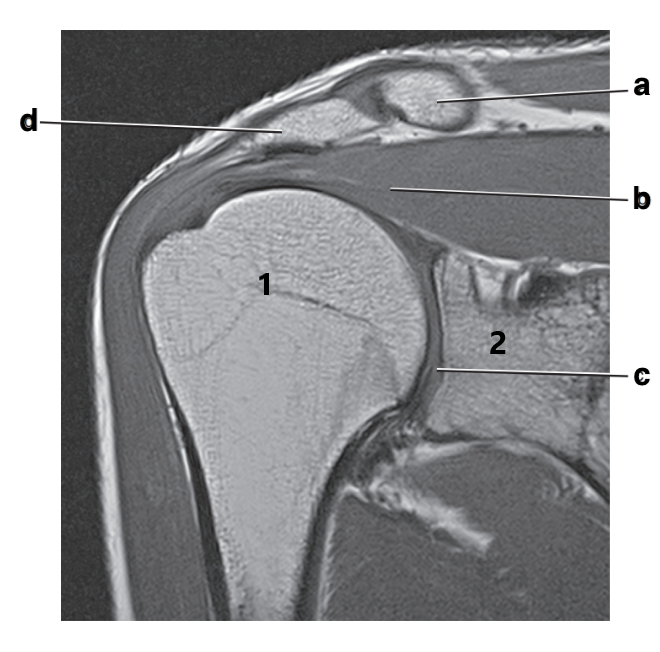
What is letter b?
Supraspinatus muscle
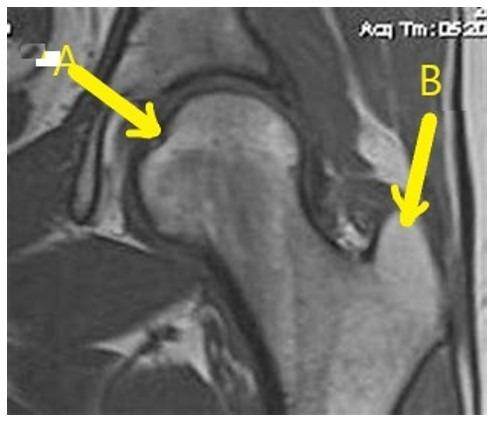
What anatomy is letter B?
Greater trochanter
The aorta arises from the:
Left ventricle
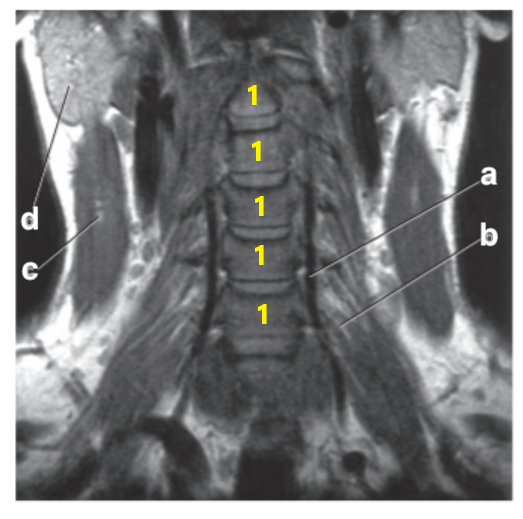
What is letter d?
Parotid gland
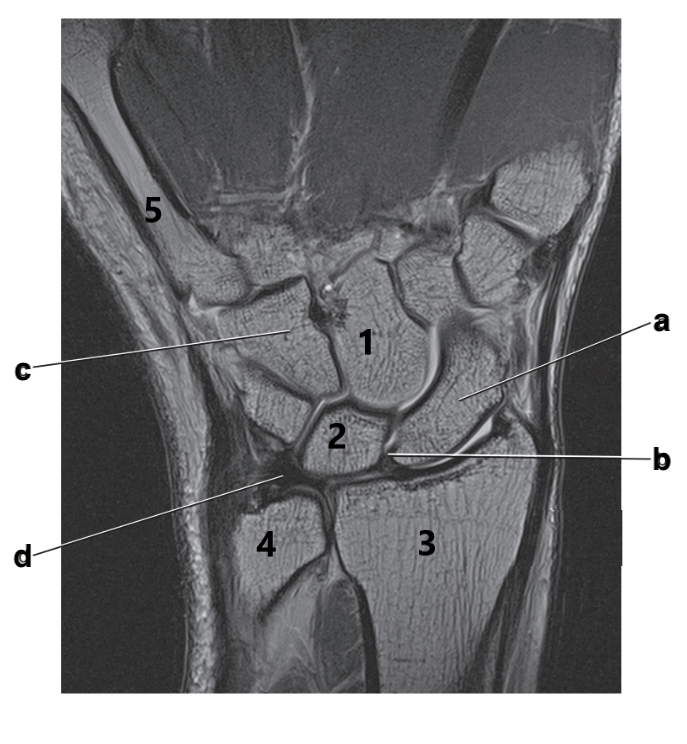
What is letter a?
Scaphoid
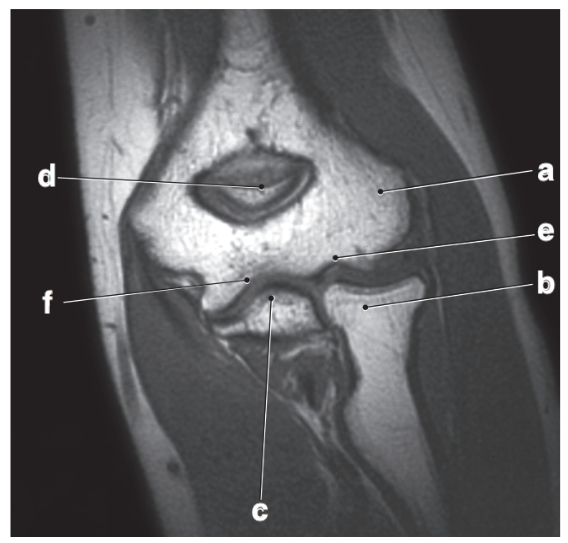
What is letter b?
Radial head
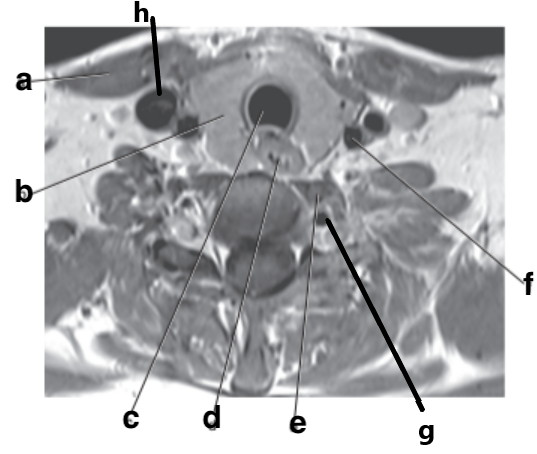
What is letter c?
Trachea
The common carotid artery bifurcates at the level of:
C3-C4
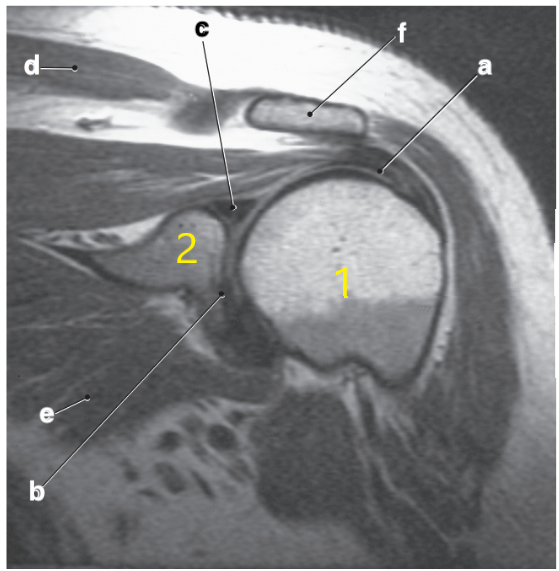
What is letter c?
Superior glenoid labrum
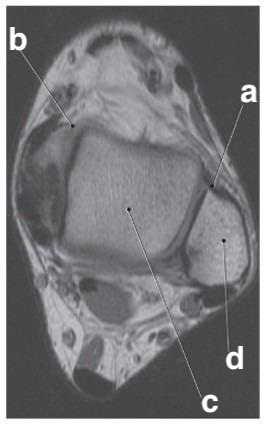
Which letter is the talus?
c
Which one of the following is CORRECT regarding the static magnetic field of an MRI system?
Safety issues associated with the static magnetic field are always present.
According to the “zone” method described by the American College of Radiology, the area that all persons should be monitored by a level 2 safety trained MRI personnel, is designated by which zone/s?
3 & 4
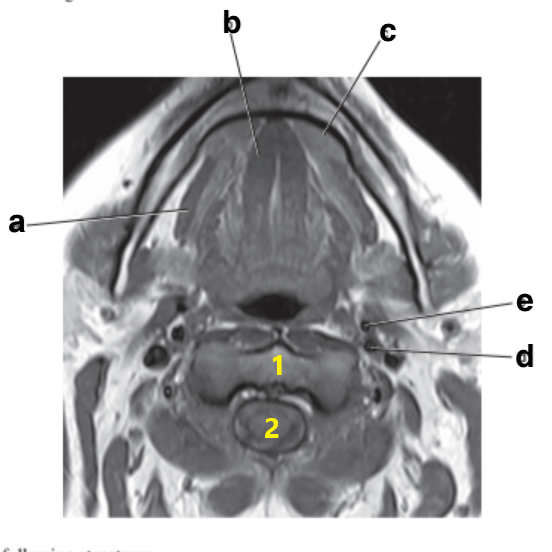
What is letter d?
Internal carotid artery
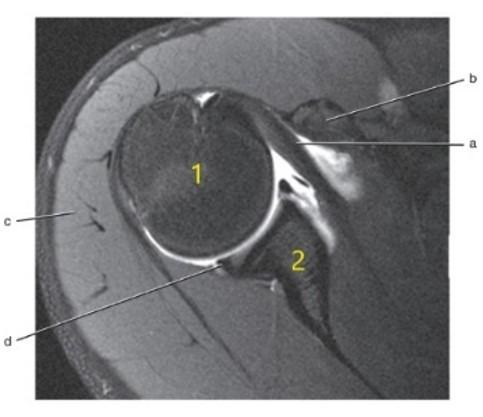
What is letter d?
Posterior glenoid labrum
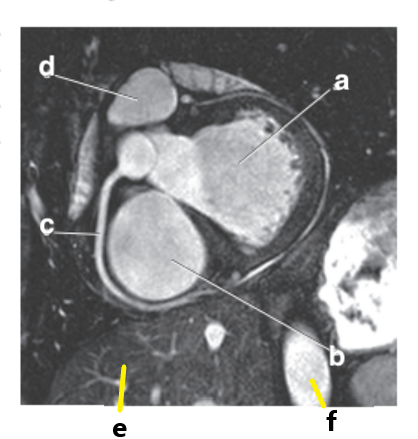
What is letter e?
Liver
Because of its superficial location, the ___________ nerve is the most frequently injured nerve of the body.
ulnar
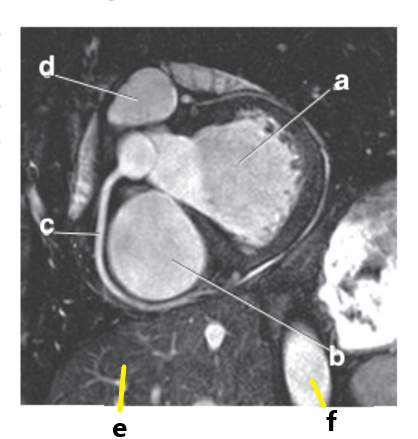
What is letter f?
Abdominal aorta
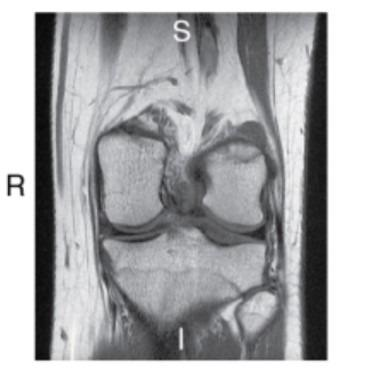
What imaging plane is this?
coronal
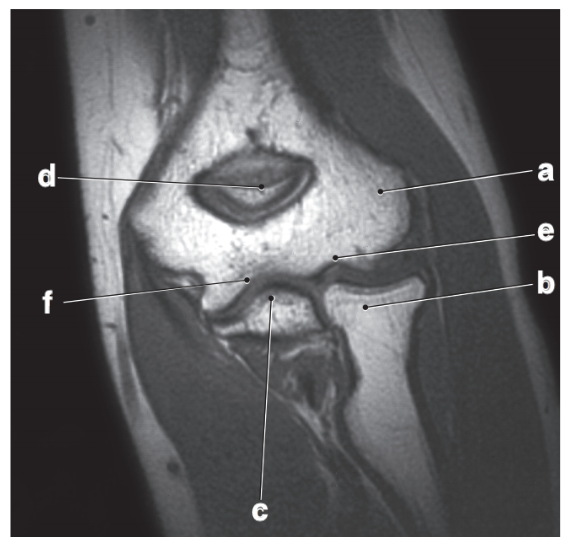
Letter D is the:
Olecranon process
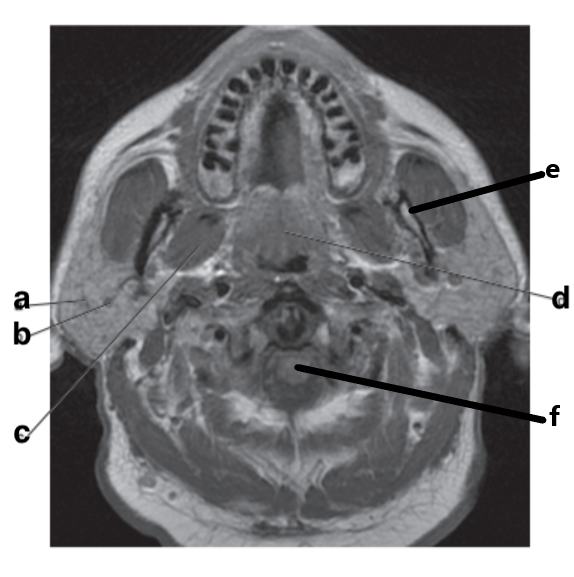
What is letter f?
Cervical Spinal cord
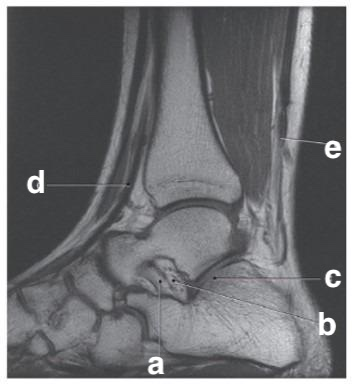
What is letter e?
Achilles tendon
The MRI static magnetic field is _______________?
is always on
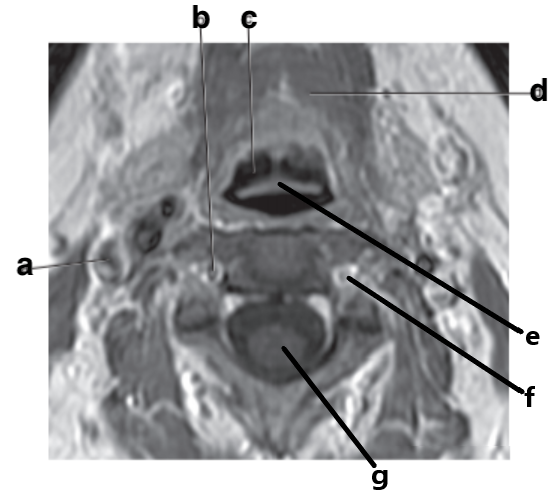
What is letter e?
Epiglottis
Which of the following is typically the largest vascular structure located in the neck?
Internal jugular vein
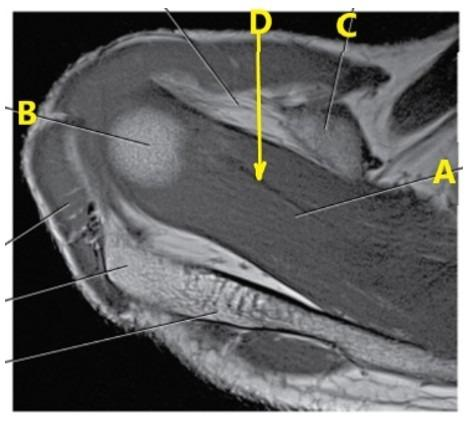
What is letter D arrow pointing to?
Supraspinatus tendon
Toward the midsagittal plane:
medial
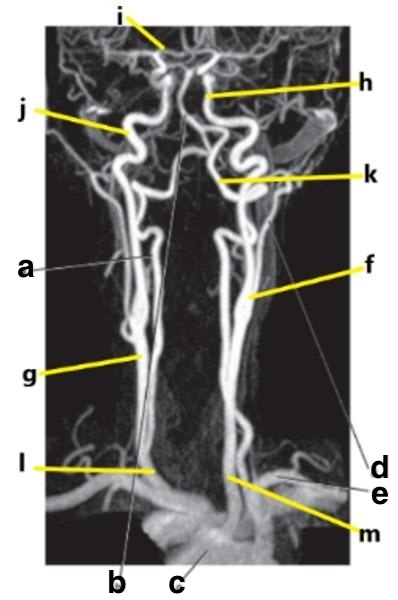
What is letter k?
Vertebral artery
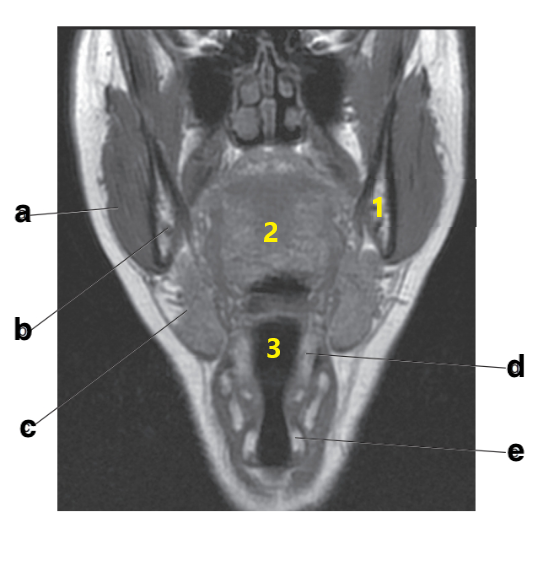
What is letter c?
Submandibular gland
The oblique coronal views for an MRI of the shoulder need to be oriented ---
Parallel to the supraspinatus tendon
The fringe magnetic field:
Can cause nearby medical devices to malfunction
The first vessel to branch off the aortic arch is the:
Brachiocephalic trunk
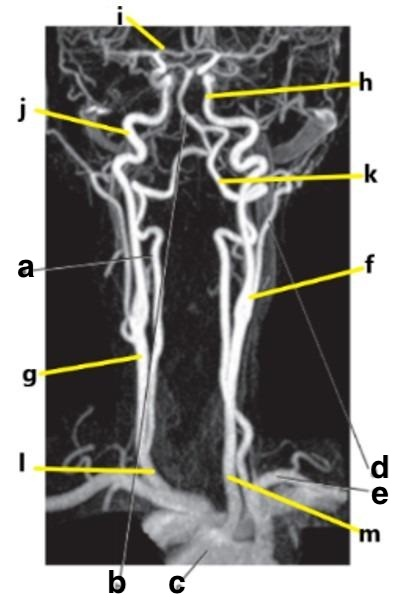
What is letter h?
Internal carotid artery
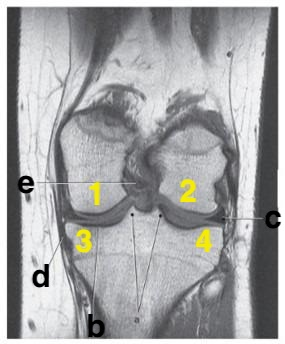
Number 2 is on the __________ side of the patient.
lateral
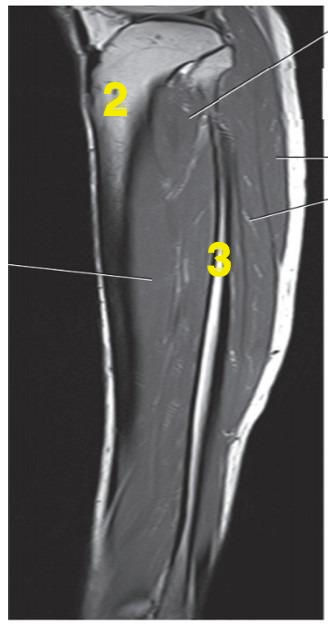
What anatomy is # 3?
fibula
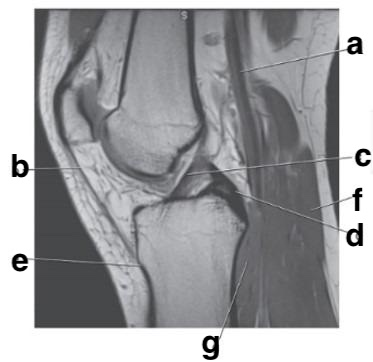
Which letter is pointing to the patellar ligament?
b
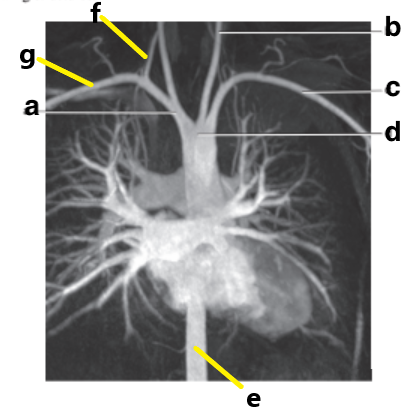
Which letter is the Right vertebral artery?
f
The appendix is in the:
right lower quadrant
Which rotator cuff tendon is the most frequently injured?
Supraspinatus
Which imaging plane is a vertical plane that passes through the body, dividing it into anterior (ventral) and posterior (dorsal) portions?
coronal
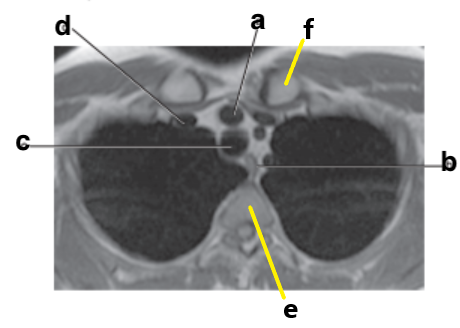
What is letter c?
Trachea
Which nerve courses through the carpal tunnel?
Median
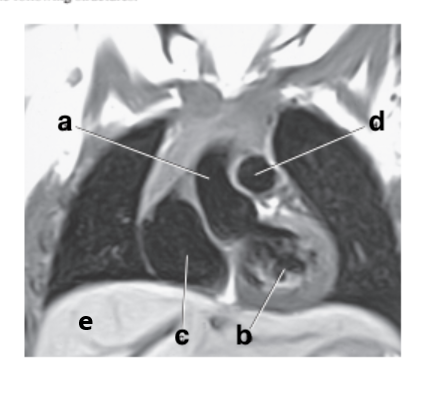
What is letter a?
Ascending aorta
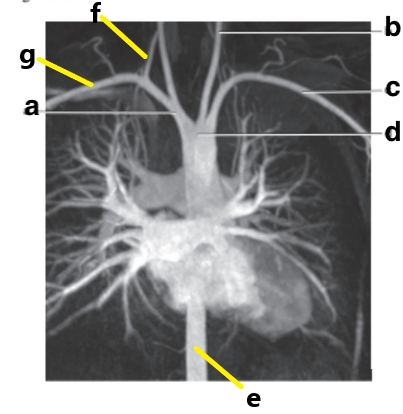
What is letter e?
Descending aorta
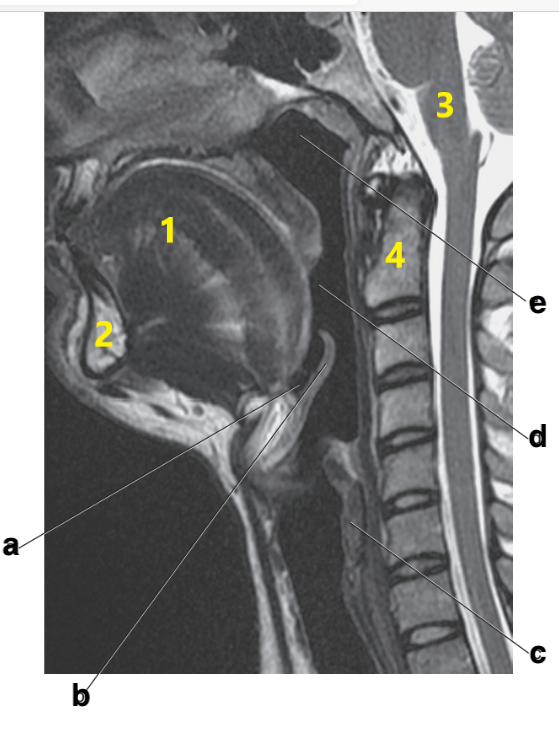
What is # 2?
Mandible
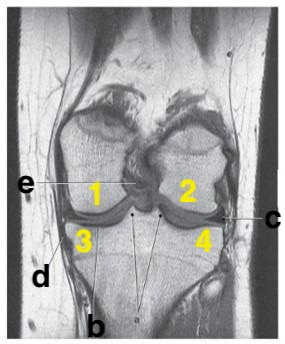
What is letter d?
medial collateral ligament
What is the safety issue related to the gradient magnetic fields?
peripheral nerve stimulation
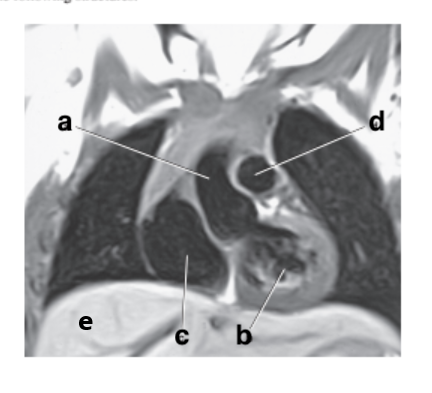
What is letter b?
Left ventricle
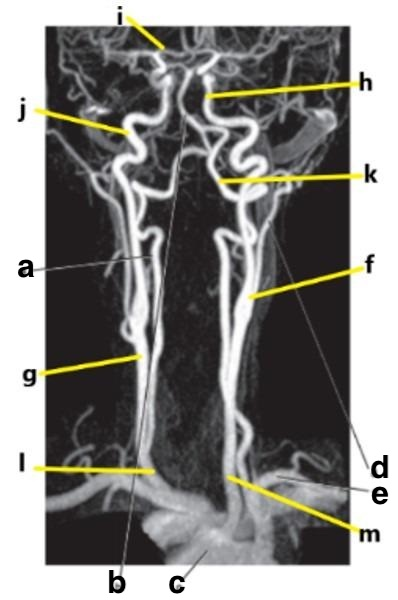
What is letter f?
Carotid bifurcation
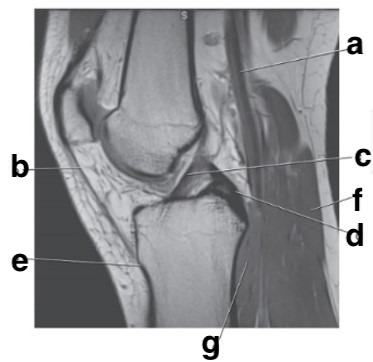
Which letter is pointing to the anterior cruciate ligament?
c
If a quench occurs, you must ____________
Answers A and B above
According to the “zone” method described by the American College of Radiology, the area that is identified as the waiting/reception area, is designated by which zone/s?
2
What ligamentous structure spans the wrist to create an enclosure for the passage of tendons?
Flexor retinaculum
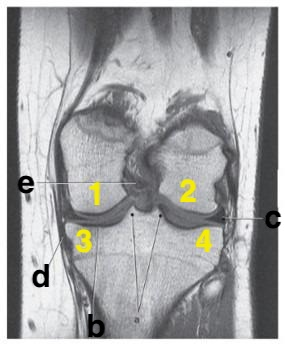
Where is the tibial plateau?
3 and 4
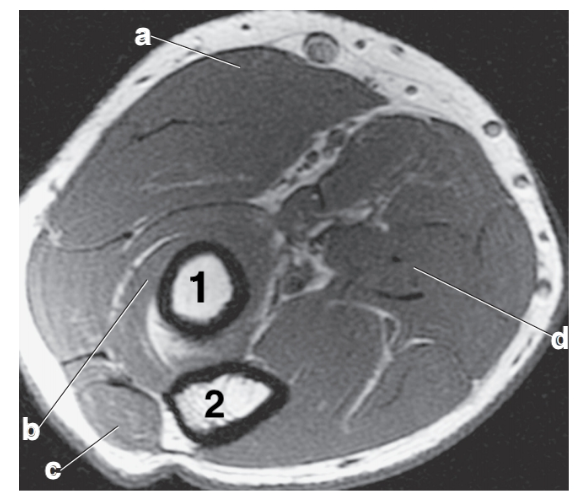
What anatomy is # 2?
Ulna
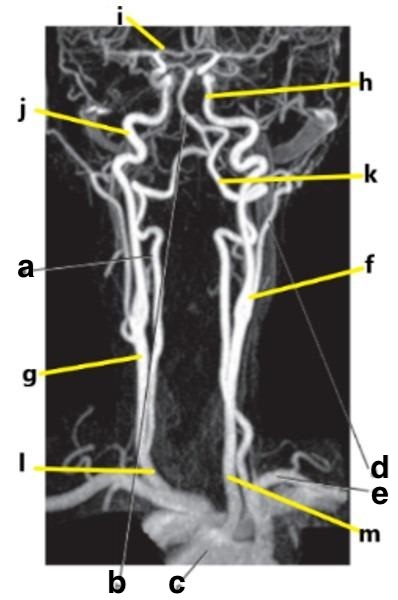
What is letter m?
Common carotid artery
The thickest, strongest muscle in the heart is located in the:
Left ventricle
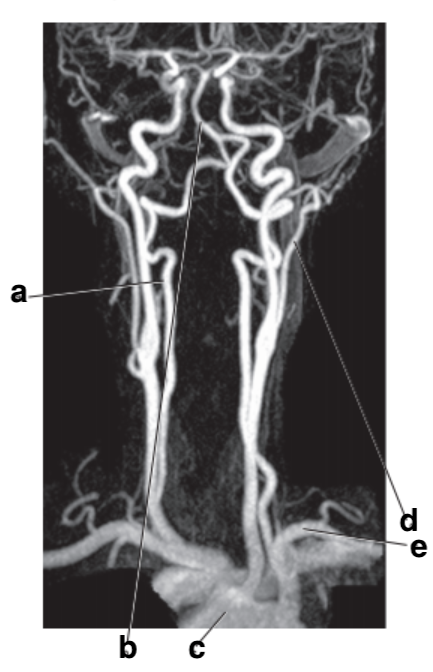
What is letter d?
External carotid artery
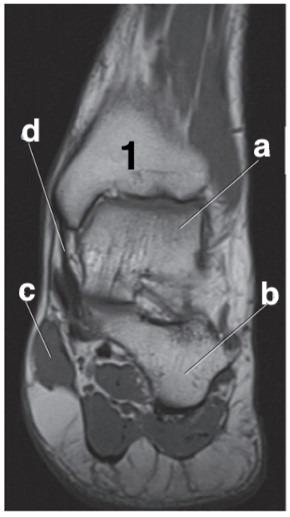
Which letter is the talus?
a
According to the “zone” method described by the American College of Radiology, the area that contains the MRI system (i.e., the potentially most dangerous area) is designated by which zone?
Zone 4
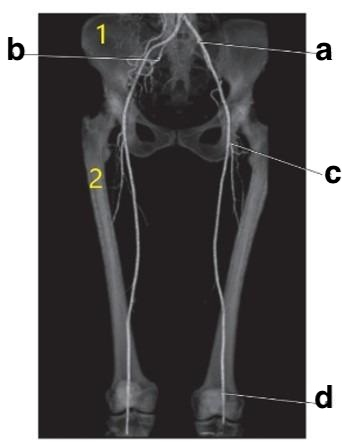
What is letter d?
left popliteal artery
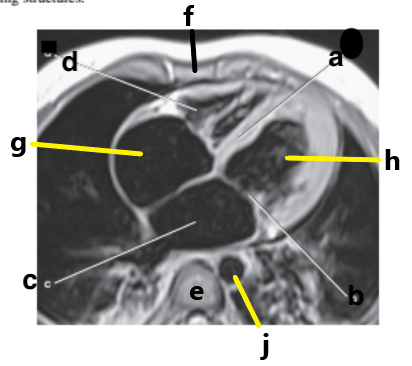
What is letter a?
Interventricular septum
What is the safety issue related to RF?
tissue heating
What structure deepens the acetabulum to increase stability of the hip joint ?
Acetabular labrum
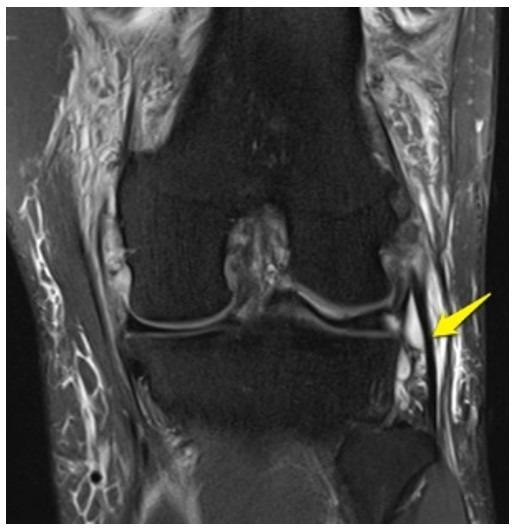
What anatomy is the arrow pointing to?
lateral collateral ligament
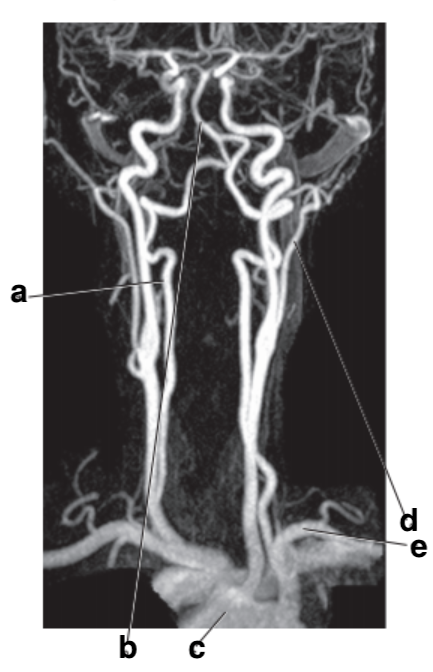
What is letter b?
Basilar artery