Lecture 4 - DNA Damage and it's Repair - Part II
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 335 - Radiobiology. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Three types of DNA damage caused after ionizing radiation
damaged bases, single strand breaks, DSB (most lethal)
an average cell per day accumulates ____ lesions of DNA damage, while a cell receives ____ after 2 Gy of low LET ionizing radiation?
50 000, 3-4000
why are the 4000 lesions caused by radiation therapy more lethal than the 50 000 lesions caused normally
endogenous lesions are isolated and distributed anywhere in the body since they are random, but in radiaiton, the electron tracks deposity energy in clusters
also time span as huge impact: endogenous lesions happen over a long period of time while RT damage happens within microseconds
what type LET has a higher concentration cluster of ionization events?
high LET
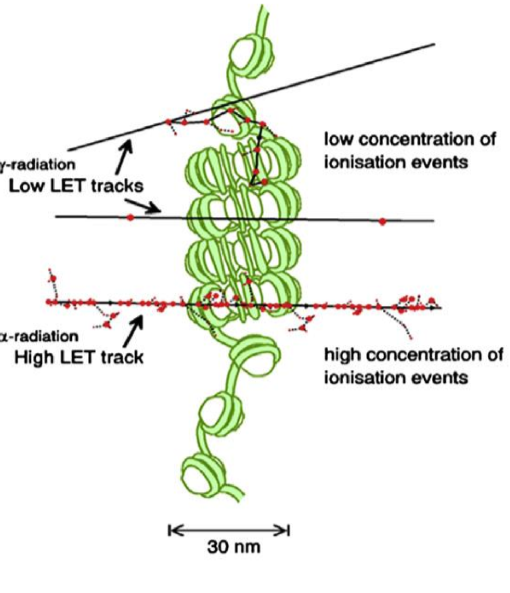
in low LET, what percent of damage is isolated DNA lesions, and what percent is damage clusters?
70% isolated DNA lesions
30% damage clusters
in high LET, what percent of damage is isolated DNA lesions, and what percent is damage clusters?
10% isolated DNA lesions
90% damage clusters
due to high amount of energy released in short time periods
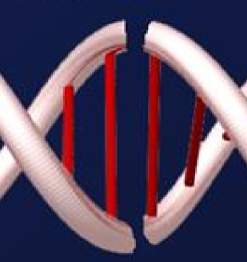
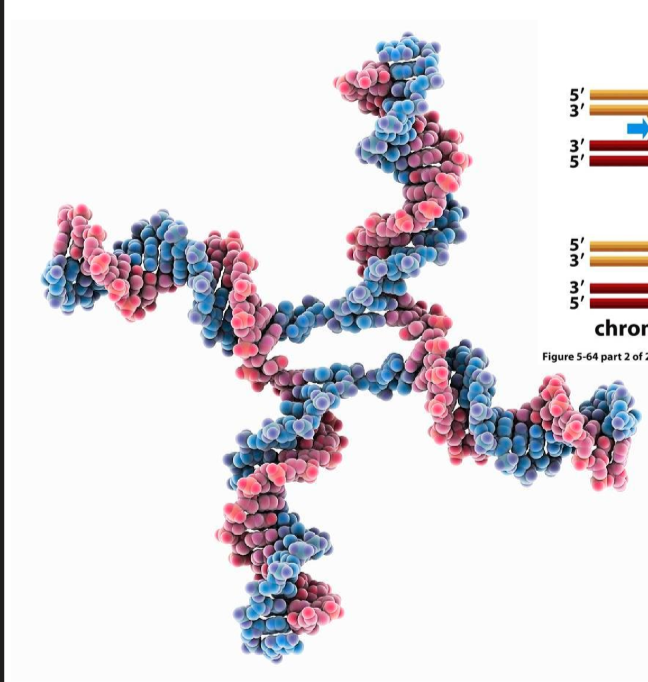
Do DSB breaks have ‘blunt’ perfect ends that we see in cartoon depictions?
no, rarely ever. instead they often have overhangs, that look like single strand breaks in opposite directions

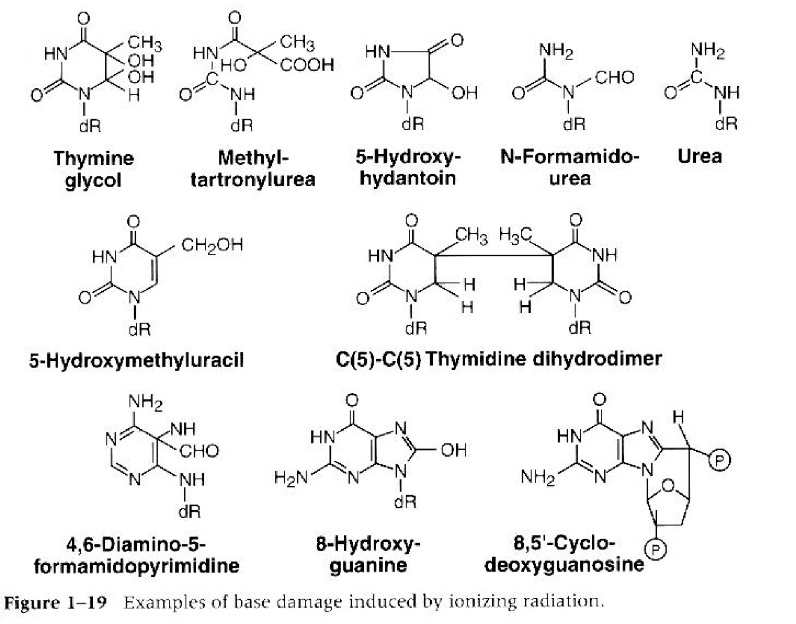
What leads to strongly modified base pairs as shown in the image below
radical chemistry that occurs to ionizing radiation
what are the two main DNA repair mechanisms?
Homologous recombination
Non-homologus end-joining
non-homologous end joining
the primary repair mechanism that is extremly fast and may lead to errors
cells clean up the break and put it back together
in addition to DNA damage repair, what else is NHEJ used for?
VDJ recombination —> leads to IgG diversity
when is NHEJ used?
before DNA replication, especially in G1 phase
What genes of the PIKK family are important for DNA damage signalling?
ATR, ATM, DNAPK, mTOR
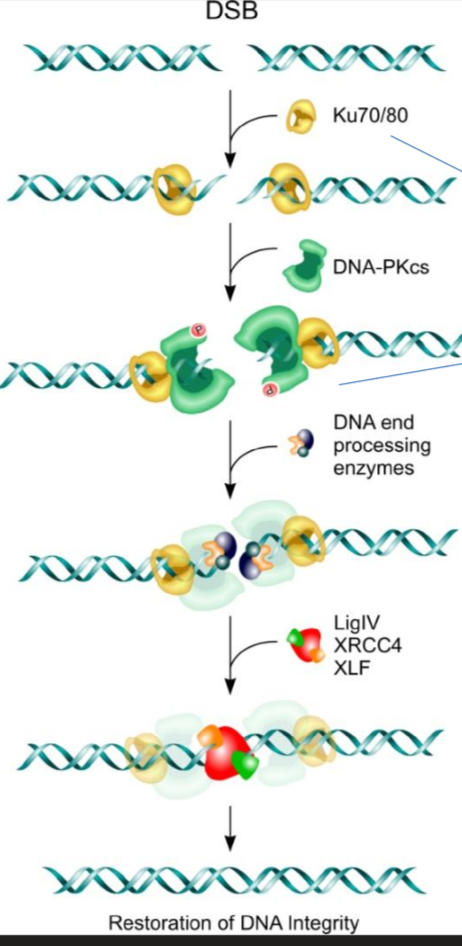
NHEJ Step 1 - Recognition
Damage is recognized by the Ku 70/80 dimer which forms a ring on the double stranded break
Ku 70/80 then recruits a DNAPK enzyme to phosphorylate the proteins for step 2
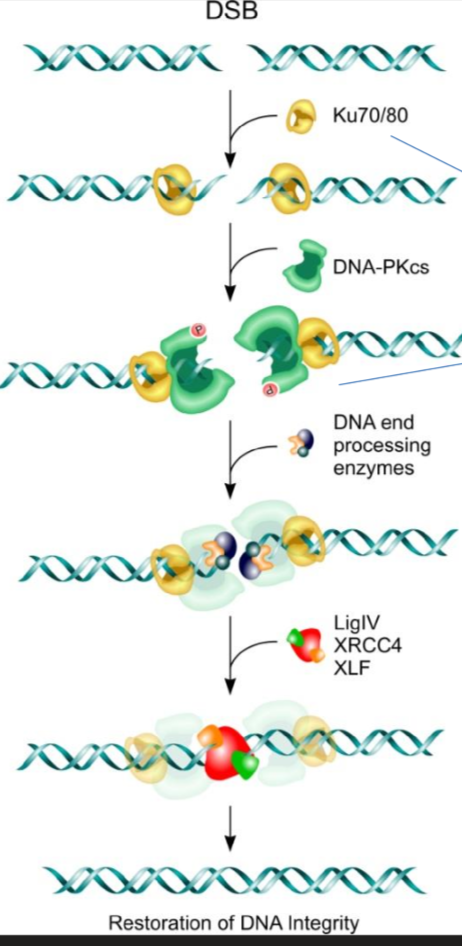
NHEJ Step 2 - Remove Damaged Nucleotides
DNA-protoein kinase activates (via phosphorylation) Artemis, which is a nuclease which cuts out nucleotides not needed in DNA damage repair
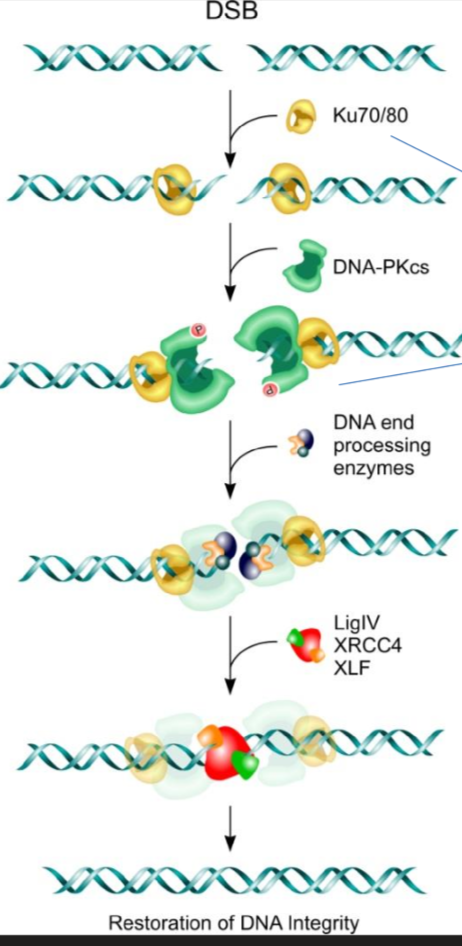
NHEJ Step 3 - Gap Filling/DNA synthesis
DNA polymerase mu or lambda are recruited to add base pairs back
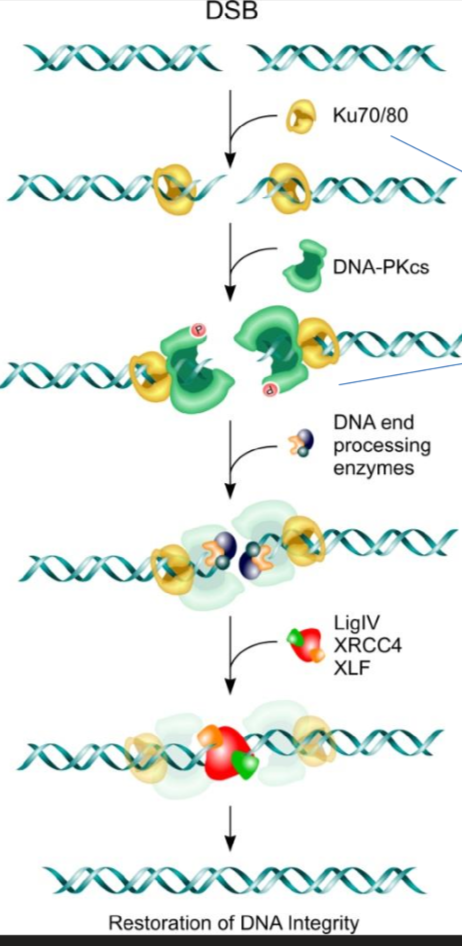
NHEJ Step 4 - Seal Gaps
Ku 70/80 recruit XRCC4 and XLF to form bridge and hold the ends of the DNA together
XRCC4 then recruits ligase IV to seal the nucleotides together
what happens when a person has an Artemis deficiency (the NHEJ nuclease)
they have SCID
severe combined immunodeficiency
Homologous Recombination
uses a sister chromatid template and is error free
when does HR repair occur?
must be after DNA synthesis: mid-S to G2
are DNA repair mechanisms active in M-phase?
no, both NHEJ and HR are shut down in mitosis
HR - Pre Step 1
Strand Resection: damaged strand searches for the complementary strand on the undamaged chromosome
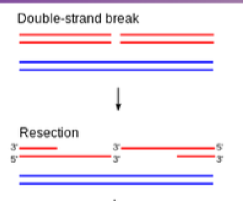
HR Step 1 - recognize DNA damage
The MRN complex recognizes the double stranded breaks and then recruit the next set of proteins via activating the kinase ATM
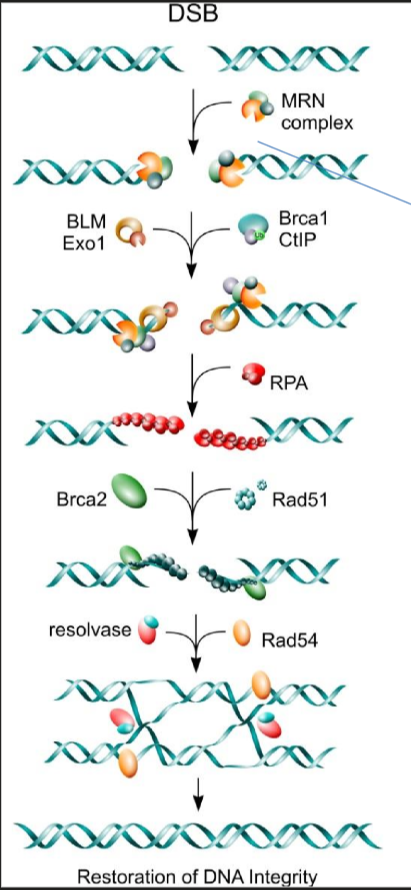
What are the three proteins that make up the MRN complex
MRE11
RAD50
NBS1
HR Step 2 - removal of damage nuclides
ATM then activates EXO1 nuclease and helicase to resect the damaged nuclides
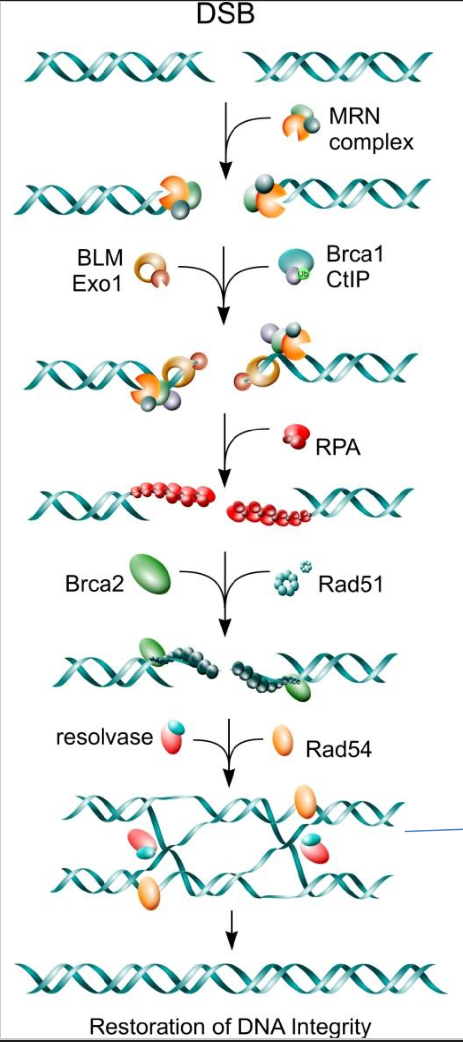
HR Pre Step 3 - RPA coating
RPA comes and bins to ssDNA to protect it so cell doesn’t attack it
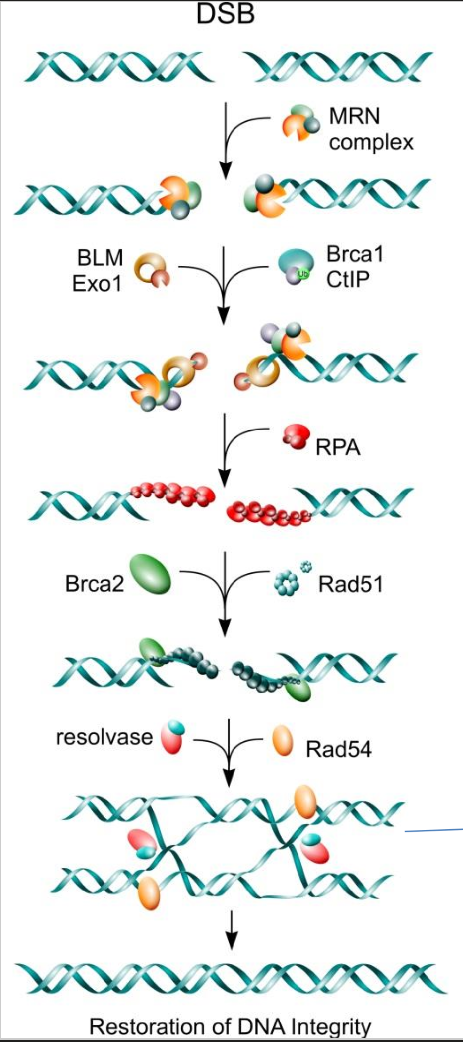
HR Step 3 - forming of Holliday Structure
BRCA2 and Rad 51 remove the RPA coating
resolvase and Rad 54 then allow for strand invasion leading to a holliday structure
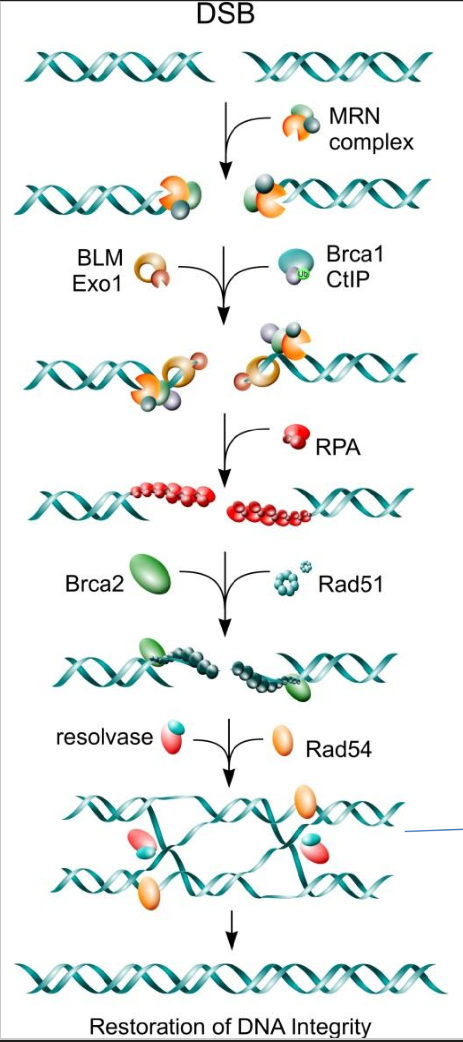
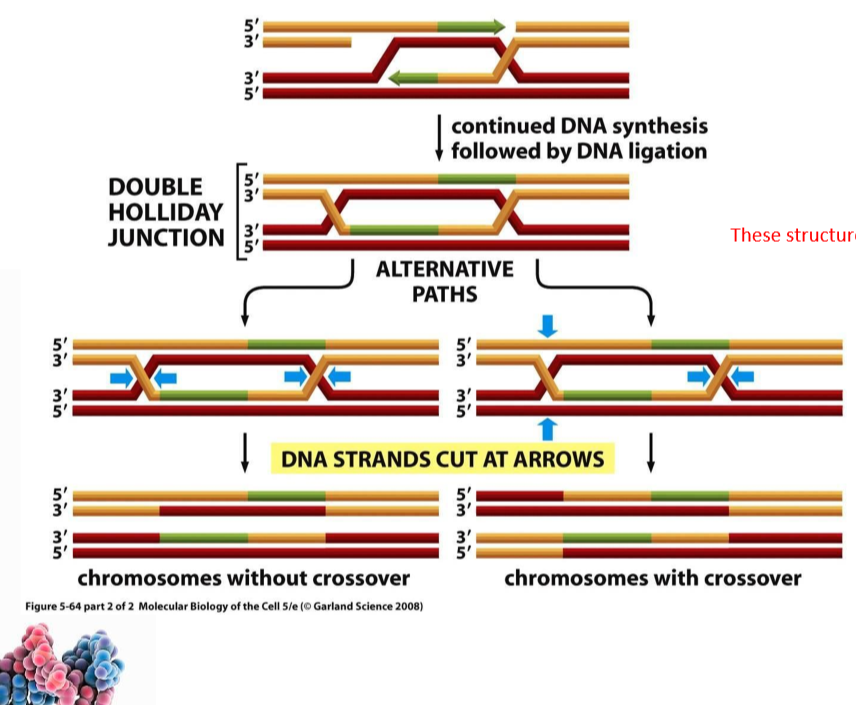
HR Step 4 - Resolution of Holliday structure
holliday structure is cleaved, resulting in corrected DNA
When is NHEJ dominant over HR?
G1
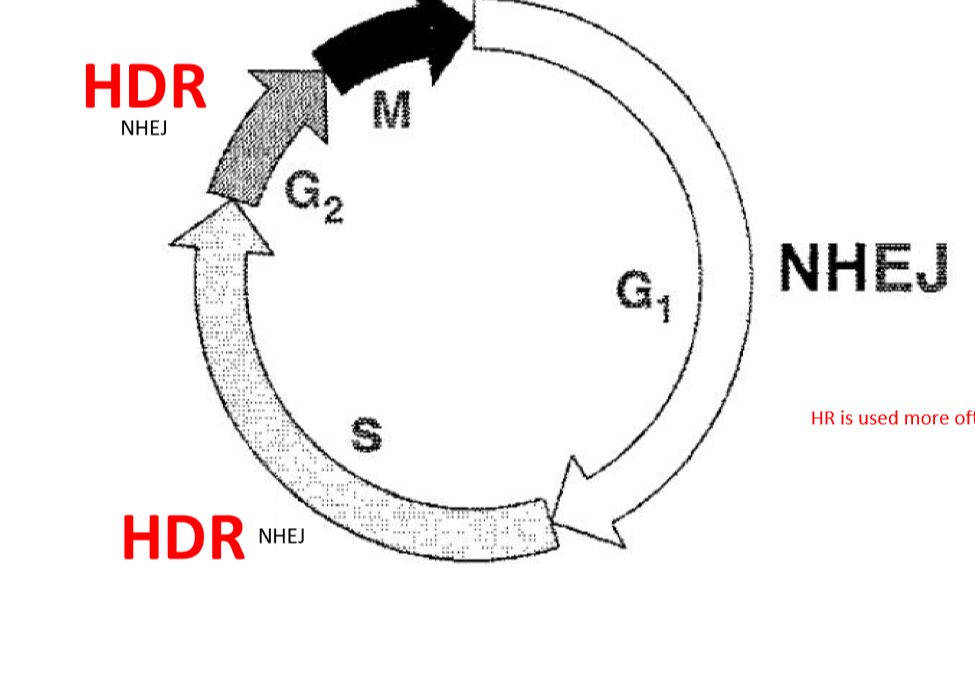
When is HR dominant over NHEJ?
HR dominates in Mid-S to G2 phase
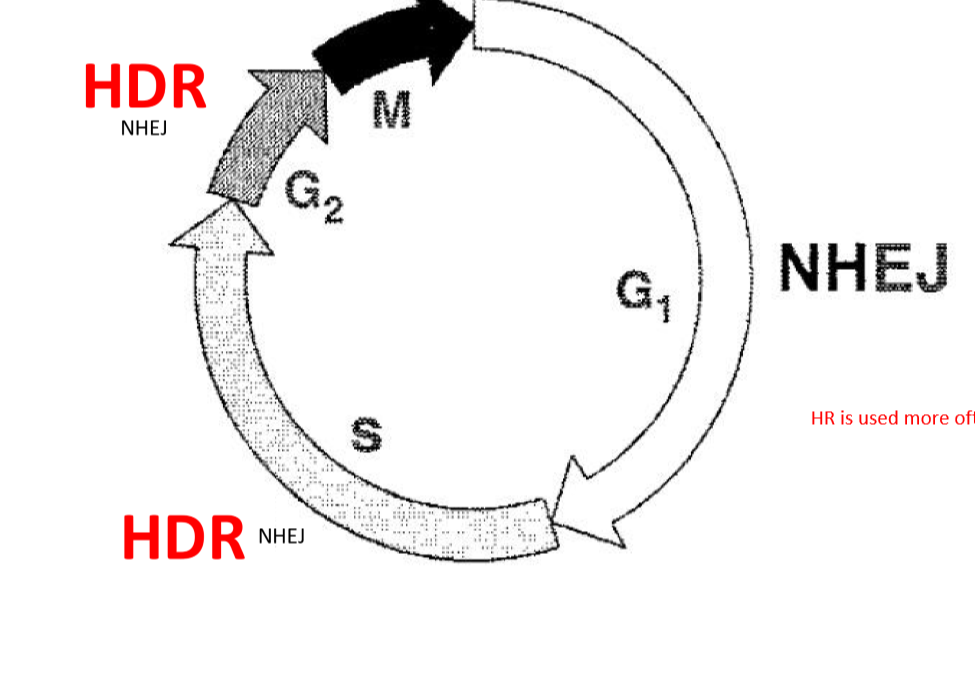
are NHEJ and HR mutually exclusive?
no, theoretically NHEJ can happen in S and G2 but it is not common
What is step that determines that HR will be done over NHEJ
if part of the DNA is resected, it must do HR
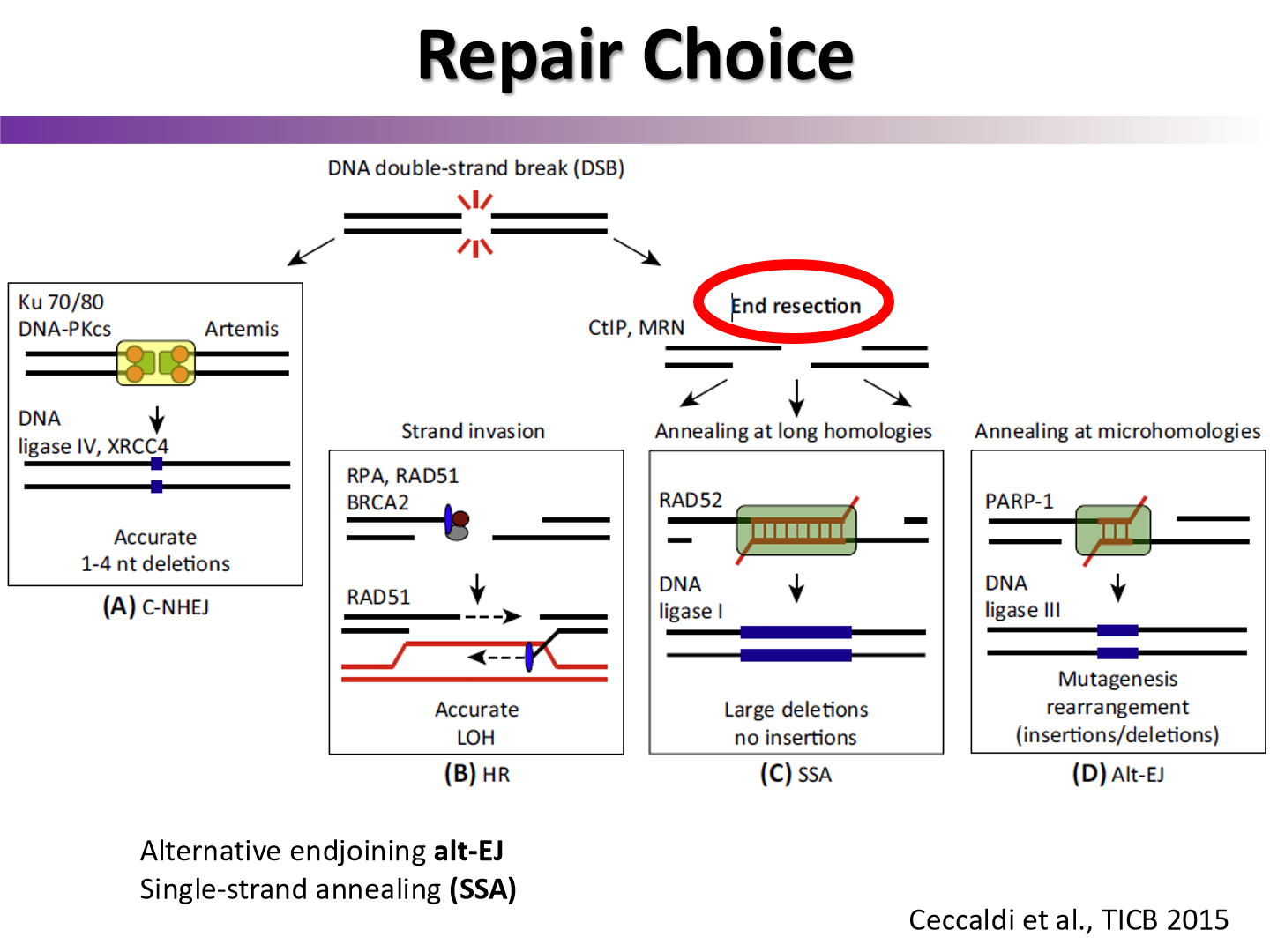
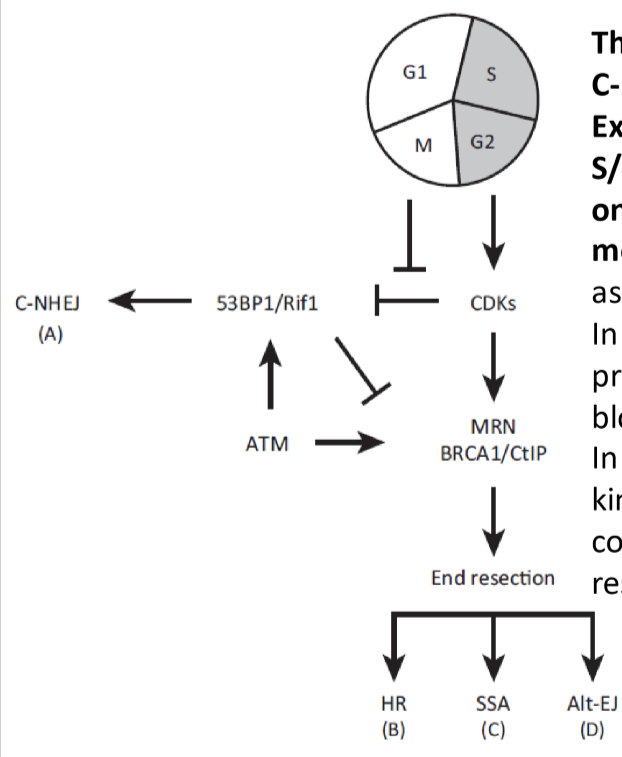
what controls the competition between NHEJ and HR?
cell cycle controls
end resection is stimulated by CDK activity, which mediates phosphorylation of substrates
what gene mutaton causes ataxia telangectasia
ATM
What gene mutaton causes Nijmegen breakage syndrome
NBS1
What gene mutaton causes AT- like disorder?
MRE11
What gene mutaton causes RAD50 deficiency?
Rad50
What gene mutatons may cause SCID?
Artemis
Ligase IV
XLF
What gene mutaton causes fanconi anemia
FANC2, BRCA2
What gene mutaton causes familial breast, ovarian carcinoma syndrom? (Angelina Jolie gene)
BRCA1 and 2
What gene mutaton causes Li-Fraumeni syndrome
p53, CHK2