higher biology - unit 2.1: metabolic pathways and their control
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
cell metabolism
all the biochemical reactions that occur within a living cell
metabolic pathways
integrated and controlled pathways of enzyme-catalysed reactions, series of chemical reactions
steps in a metabolic pathway can be...
reversible and irreversible.
alternative pathways
are pathways that exist through substances that allow certain stages controlled by enzymes to be bypassed
two categories of metabolic pathway?
anabolic + catabolic
anabolic
build up of larger molecules from smaller molecules and requires energy
catabolic
break down of larger molecules into smaller molecules and releases energy
membrane proteins
protein pores, protein pumps and enzymes are embedded in membranes
protein pores
channel proteins which span the membrane, allow specific larger molecules to pass through the membrane by diffusion
protein pump
carrier proteins which bind to specific molecules or ions temporarily, enabling them to cross the membrane by active transport
enzymes
catalyse for a specific reaction
how do enzymes control metabolic pathways?
their presence or absence / the regulation of the rate of reaction of key enzymes
activation energy
energy needed to get a reaction started
what do enzymes do to activation energy?
lower it, meaning a quicker reaction
induced fit
the change in shape of the active site of an enzyme so that it binds more snugly to the substrate, induced by entry of the substrate
high affinity
the substate molecules have this for the active site
low affinity
once a reaction is complete, the products have this for the active site
concentration of substrate and product
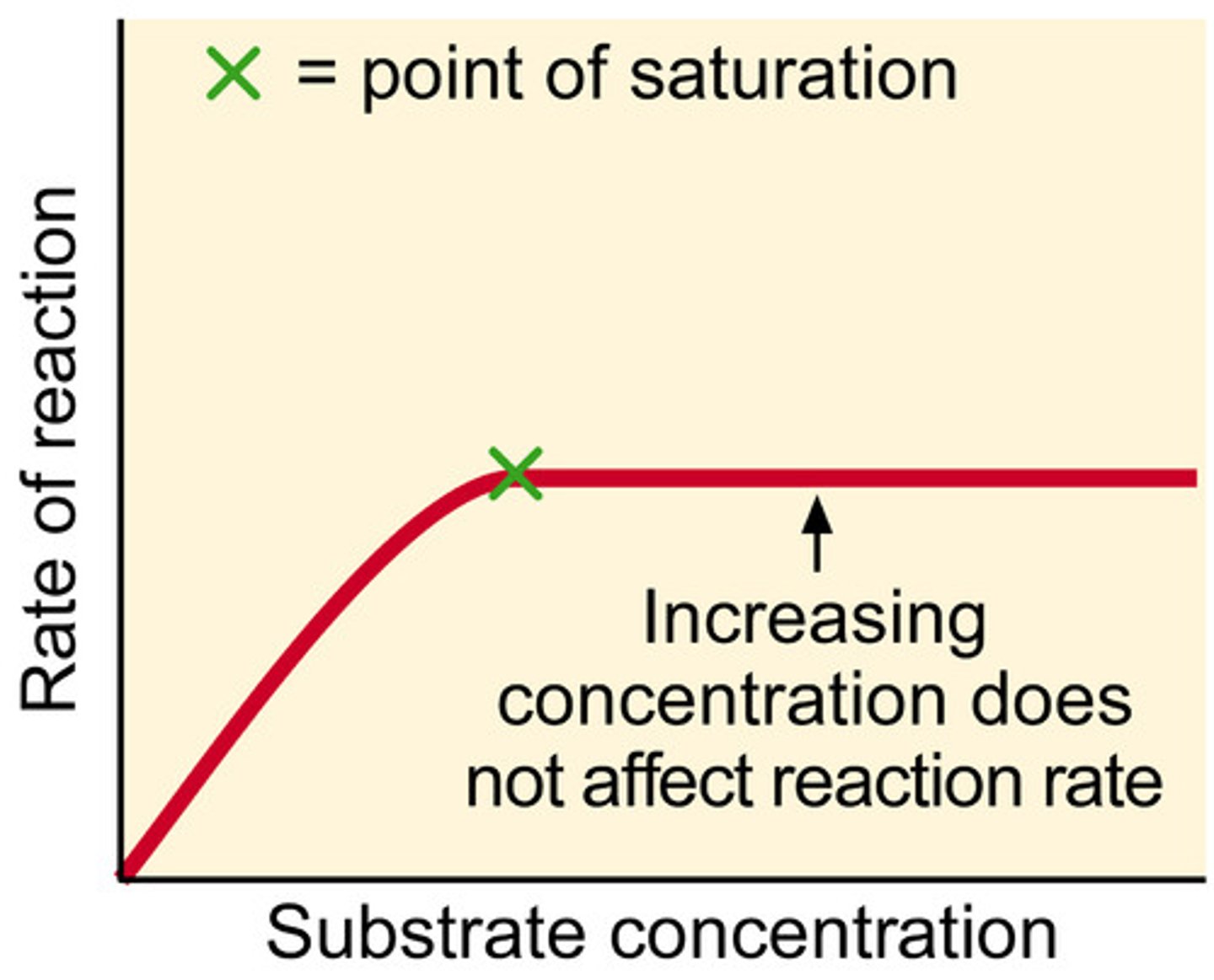
direction of enzyme action
most metabolic reactions are reversible and the presence of a substrate or the removal of a product will drive a sequence of reactions in a particular direction
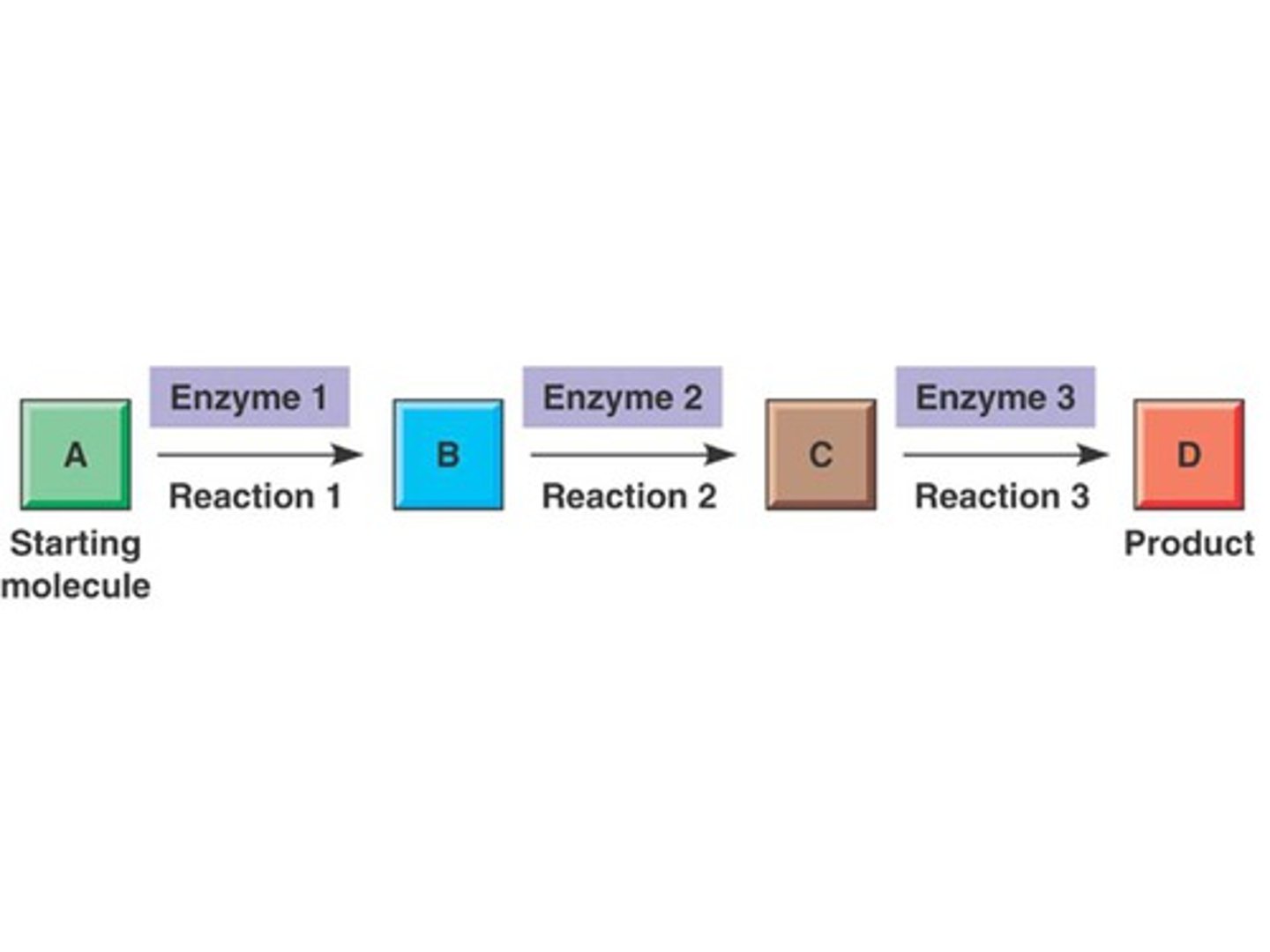
how can metabolic pathways be controlled?
regulating enzyme activity through inhibitors
competitive inhibition
inhibitors bind at the active site and prevent substrates from binding, can be reversed by increasing substate concentration
non-competitive inhibition
inhibitors bind away from the active site, but change the shape of the active site. Cannot be reversed by increasing substrate concentration
feedback inhibition
inhibition occurs when end product reaches a critical concentration. The end product then inhibits an earlier enzyme blocking the pathway and prevents further synthesis of end product