Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Structures
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
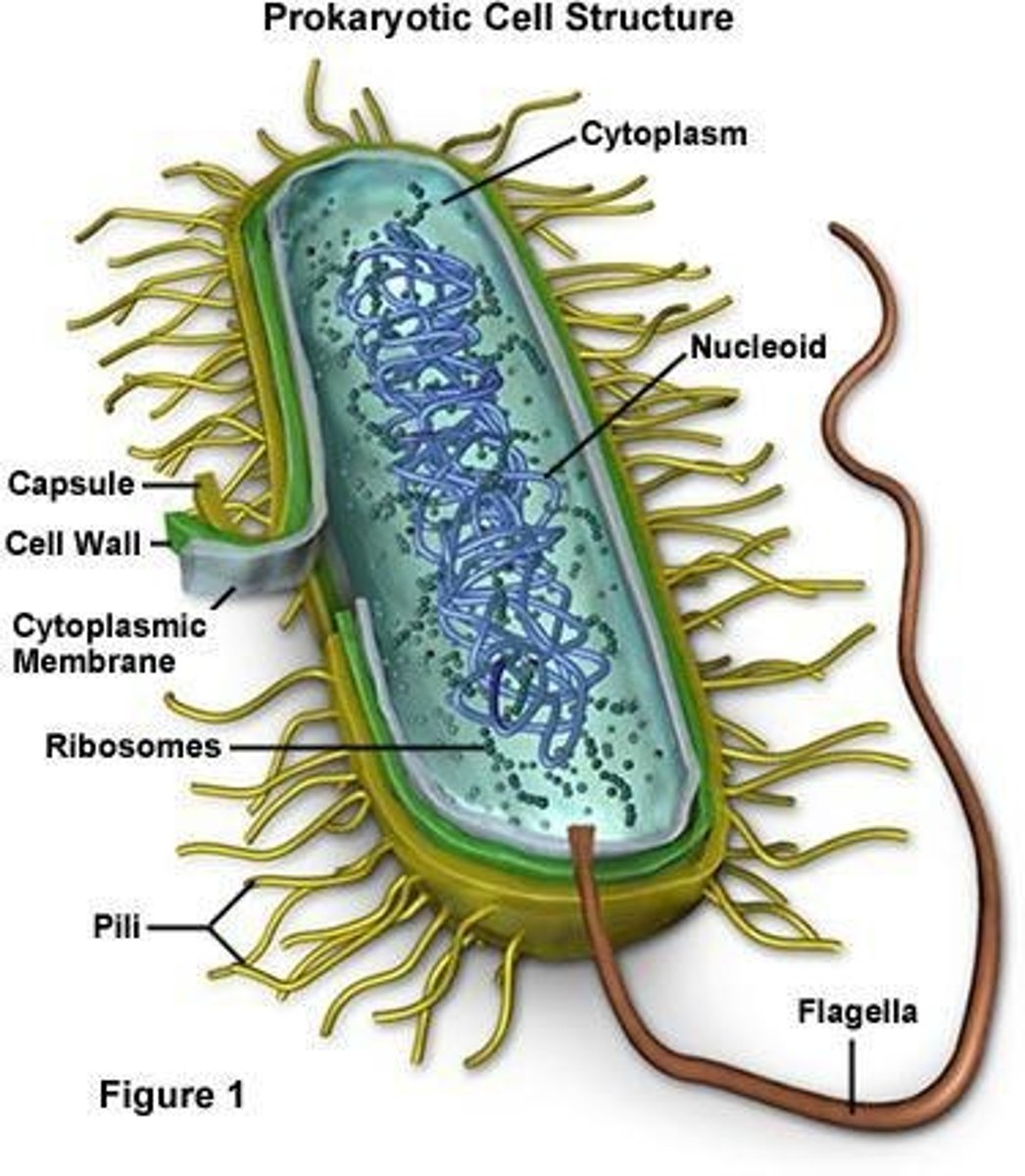
Circular chromosome
Part of the prokaryotic cell where the DNA is found.
Plasmid
Small, separate piece of DNA.
Cell membrane
Innermost covering of the cell made up of phospholipids.
Cell wall
Made up of a special mix of polysaccharides and proteins; antibiotics break it down.
Capsule
Outside of the cell wall, protective covering; not all bacteria have it.
Flagella (sing. Flagellum)
Moves bacteria.
Cytoplasm
Dissolves substances, place for life processes.
Ribosomes
Organelles that make proteins in the cytoplasm.
Fimbriae
These extensions allow bacteria to stick to various surfaces.
Sex pilus
Helps bacteria to exchange DNA with each other.
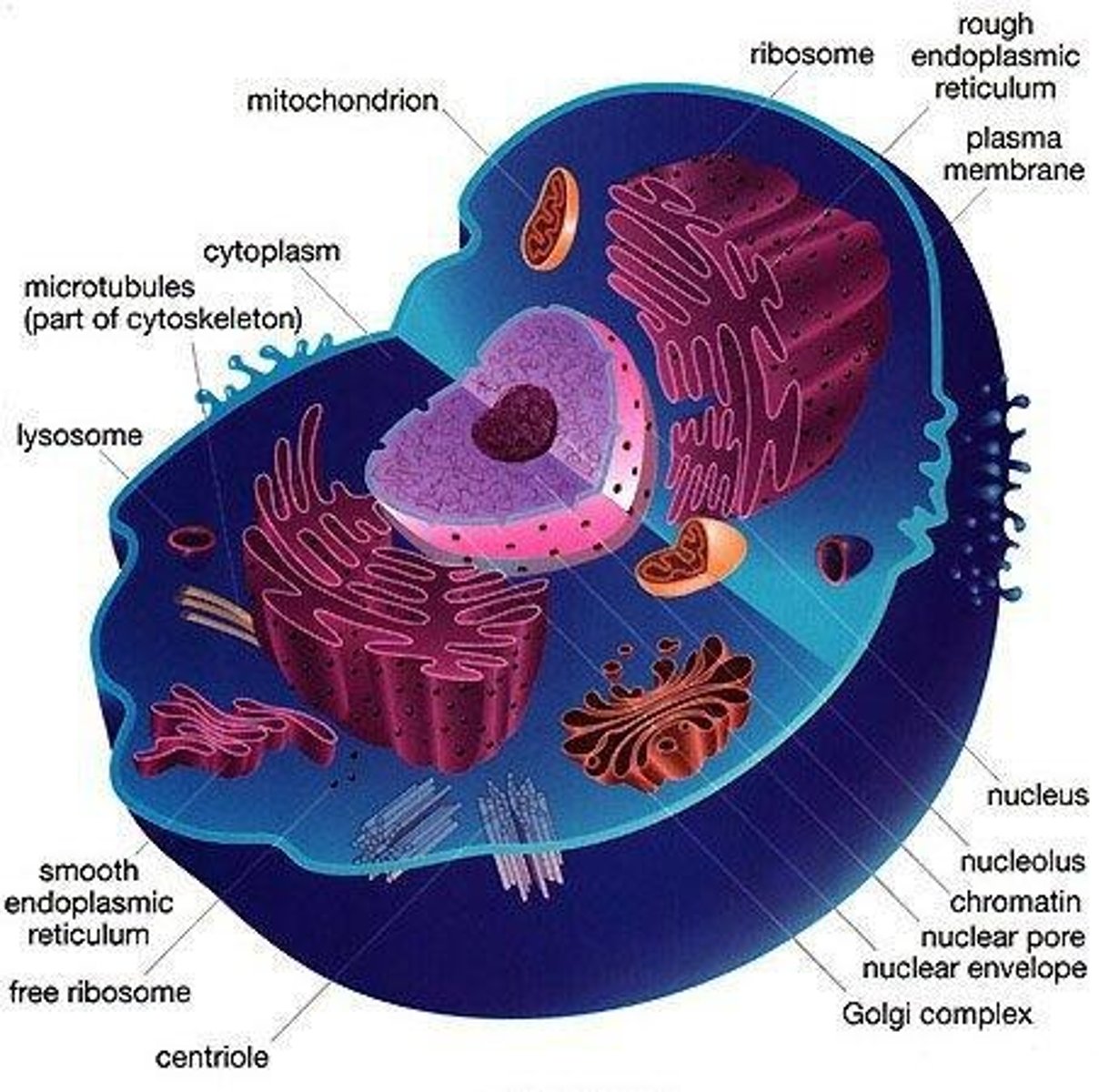
Eukaryotic Cells
Includes Protists, Fungi, Plants, and Animals; have nucleus and organelles surrounded by phospholipid membranes.
Organelles
Structures found inside of the cytoplasm specialized to perform certain functions by creating compartments with unique compositions.
Eukaryotic cells size
Much larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells (10-100 µm).
Nucleus
Contains most of the cell's DNA and proteins in the form of linear chromosomes; responsible for regulating cell functions and storing genetic information.
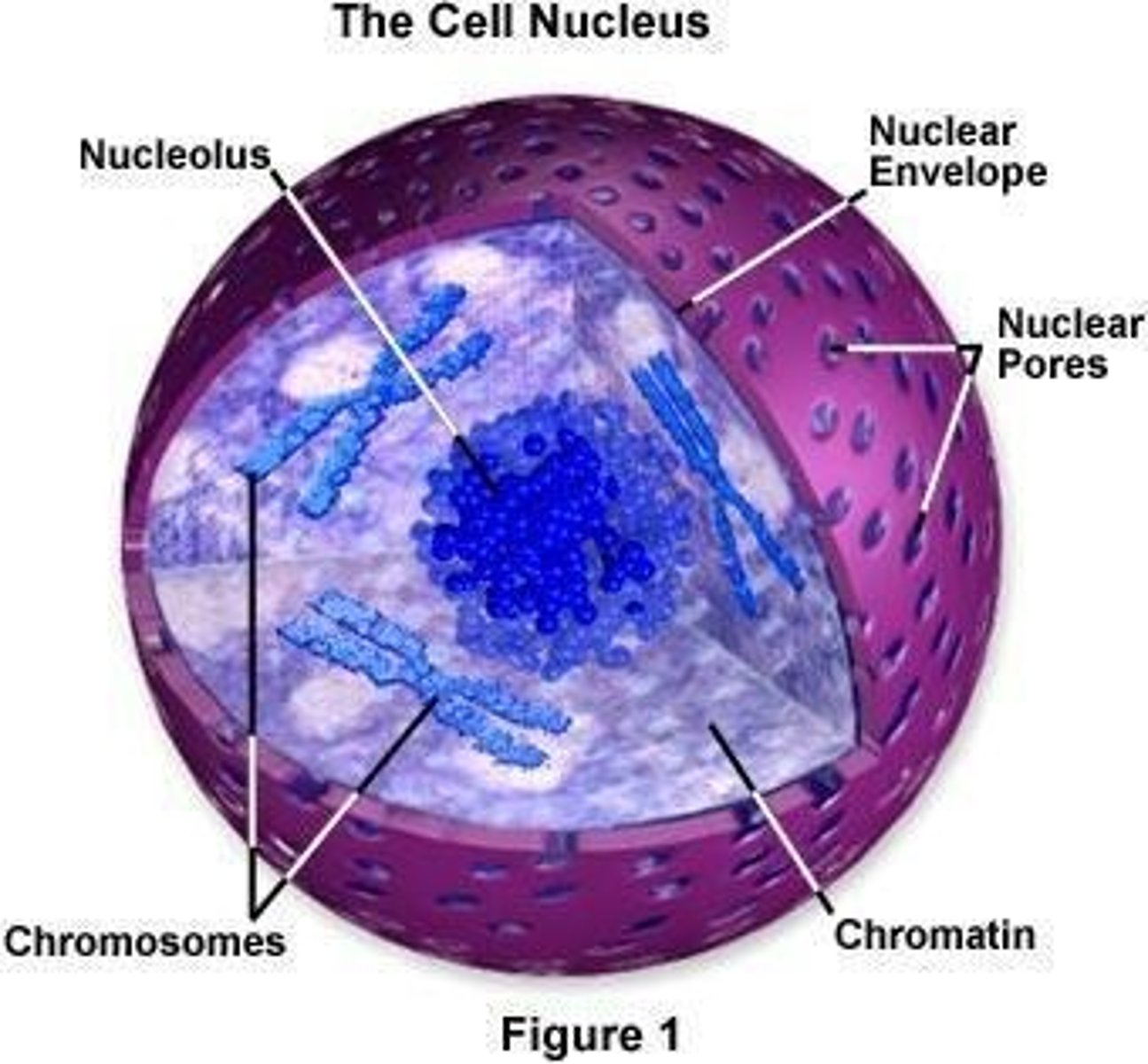
Nuclear envelope
Protects the DNA in the nucleus; nuclear pores allow the exchange of materials.
Rough ER
Comprised of a network of tubes and flattened sacs; site of protein synthesis (consists of ribosomes) and protein folding.
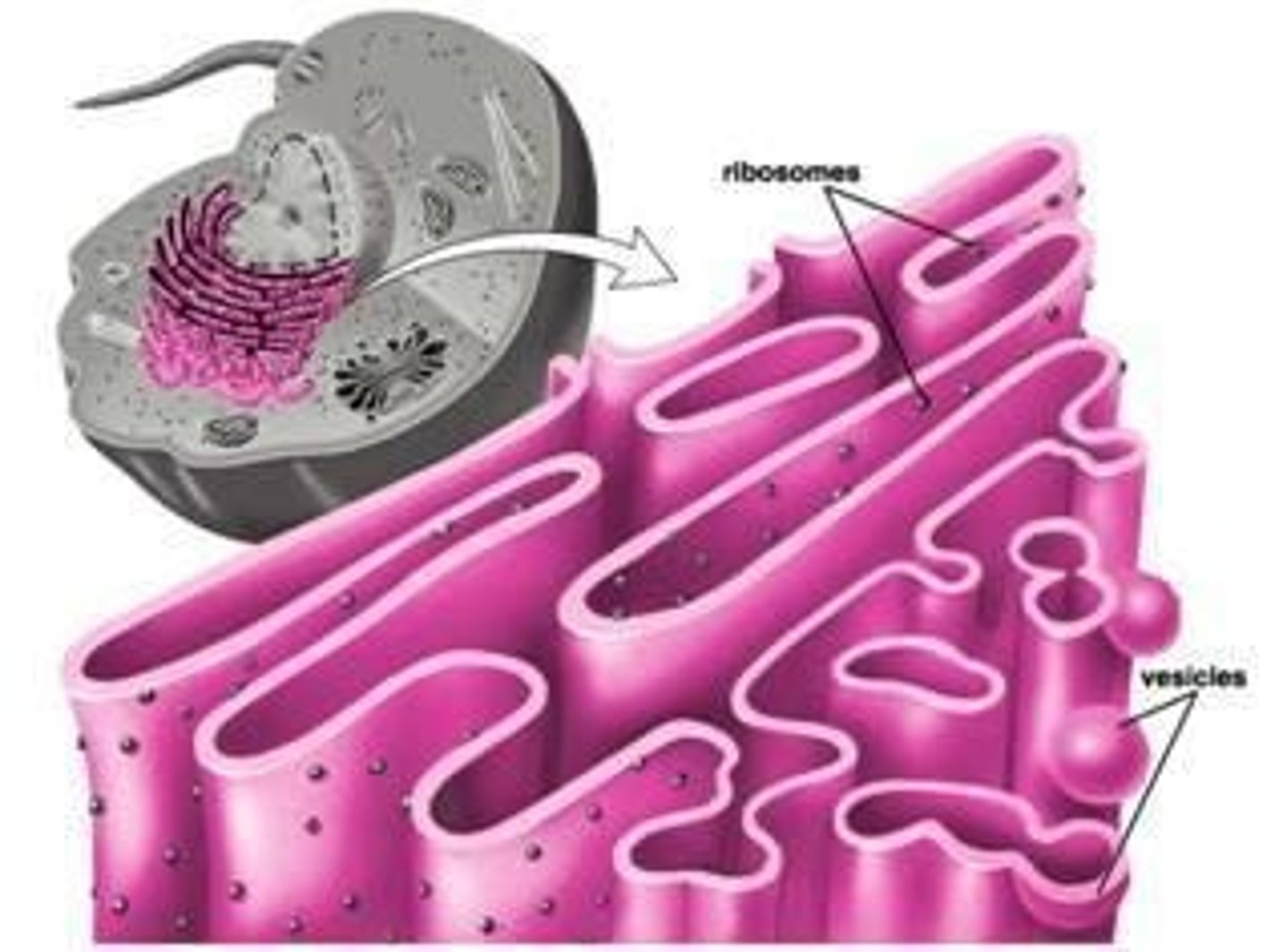
Smooth ER
Folded membrane with no ribosomes on its surface; site of lipid and carbohydrate synthesis and hydrolysis, performs detoxification and stores calcium ions.
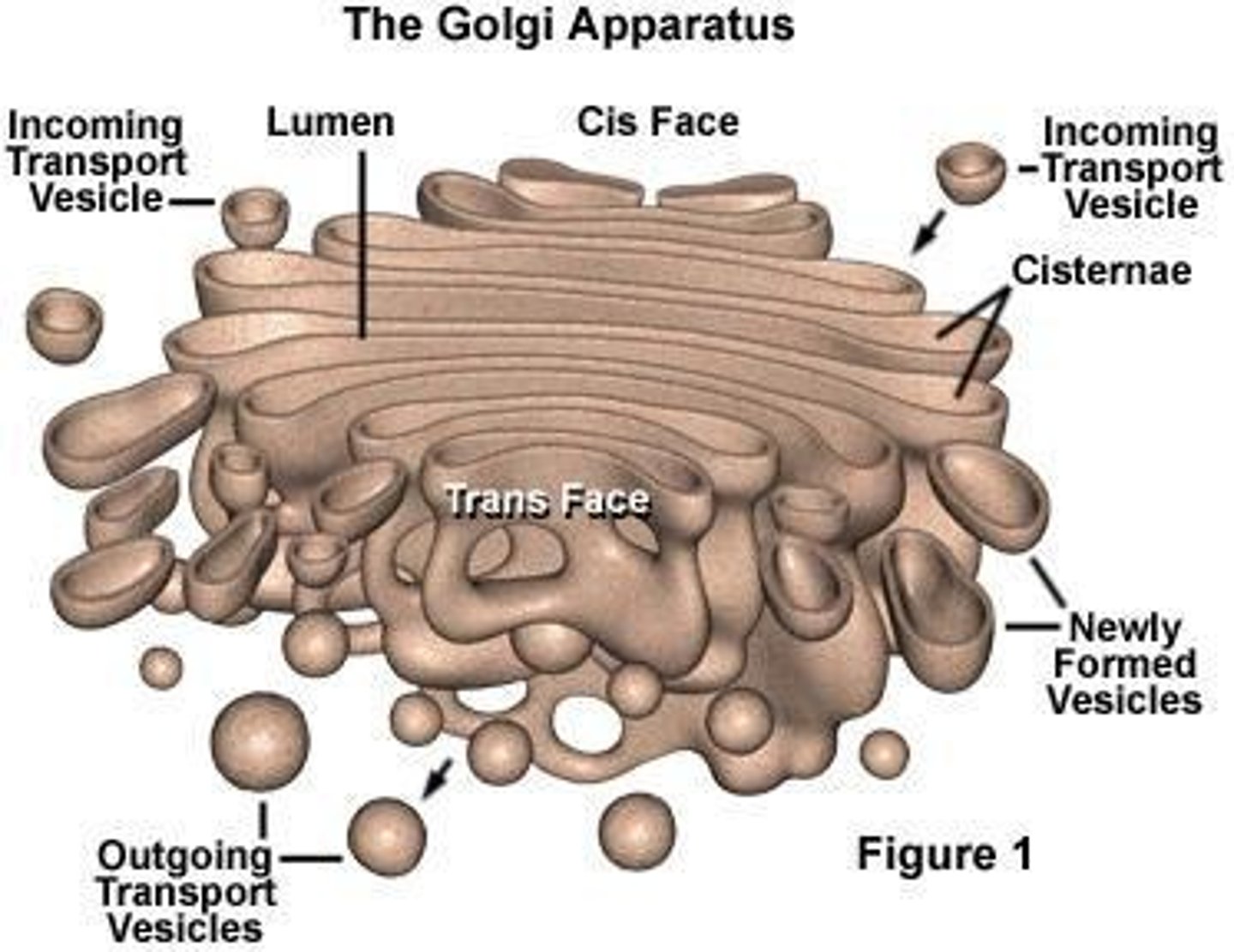
Golgi Apparatus
Connected with ER; modification, storage, and packaging of proteins and other molecules; 'tags' proteins for correct destination.
Lysosomes
Contain hydrolytic enzymes; digestion of nutrients, bacteria, and damaged organelles.
Vacuoles
Small membrane structure in animals, really large in older plant cells; storage of chemicals, cell enlargement and support.
Vesicles
Small membrane bubbles without enzymes; ship materials within and out of the cell.
Chloroplasts
Only found in eukaryotic autotrophs; conversion of light energy to chemical energy of sugars (site of photosynthesis).
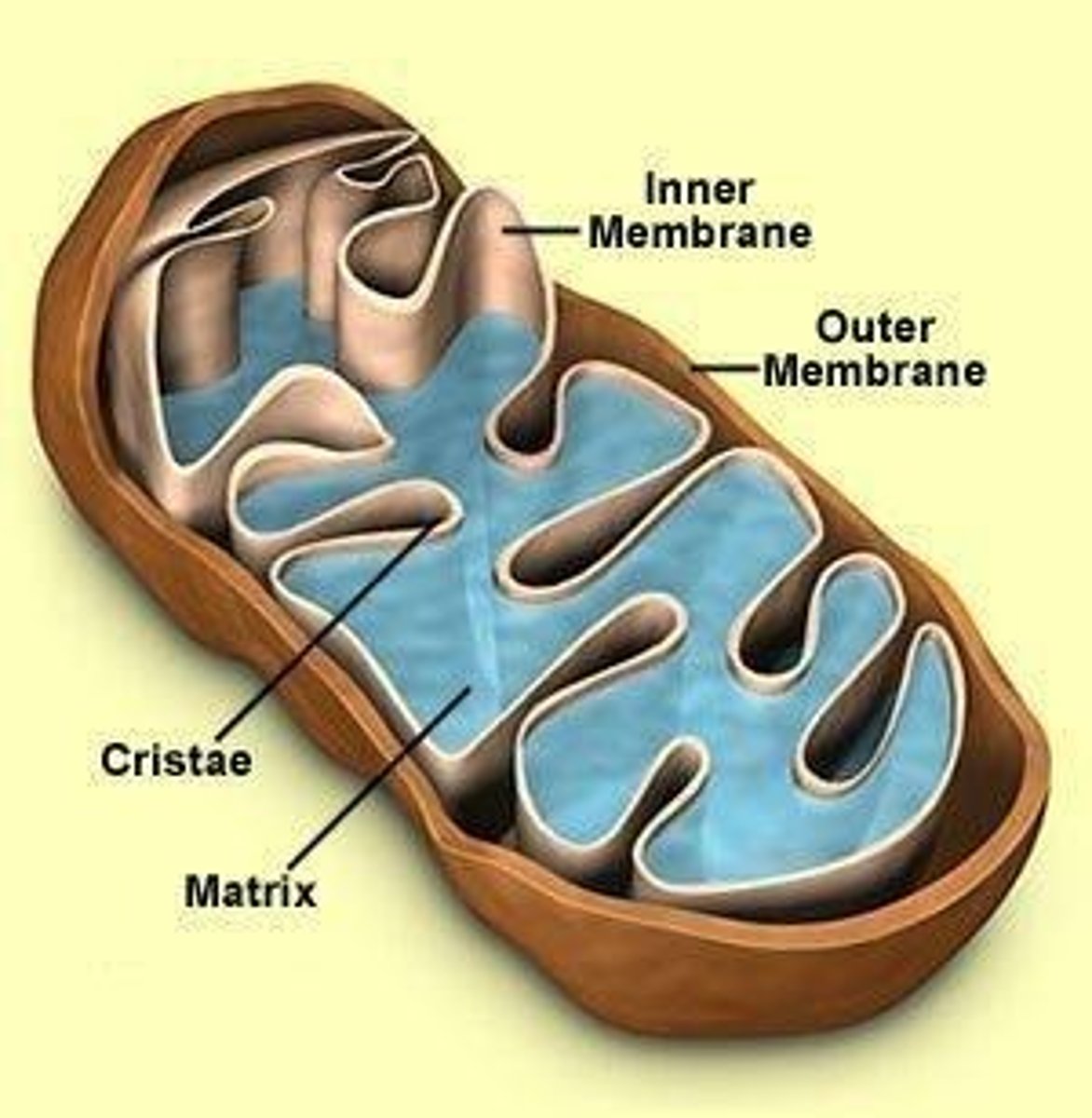
Mitochondria
Found in every eukaryotic cell; conversion of chemical energy of organic matter to chemical energy (parts of cellular respiration).
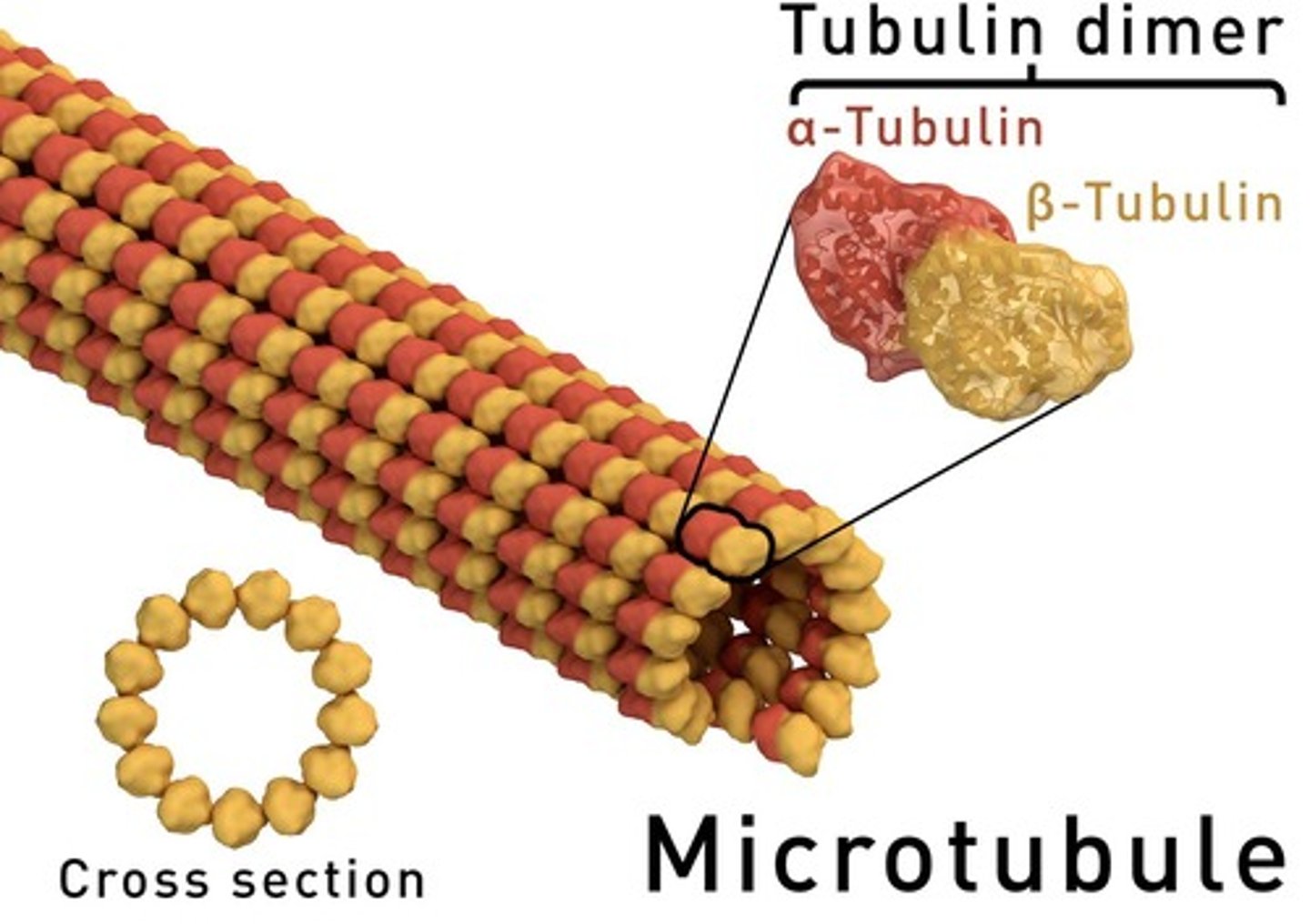
Cytoskeleton
Protein structures of the cell; maintenance of cell shape, anchorage for organelles, movement of organelles within cells.
Centrioles
Important for cell division in animals.
Cilia and flagella
Move the cell or move substances on the cell; not organelles but cell structures.