Chapter 6 - Ethics, economics and sustainable development
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
ethics
set of moral principles or values used to determine right and wrong
economics
study of how people use scare resources to provide goods and services
Decisions on how to….
to manipulate the environment involve economics, but are also influenced by our own culture and worldview.
Relativists
believe that ethics vary depending on the context of the problems
Universalists
define objective notions of right and wrong that hold across many cultures and contexts. like universal standards like reducing carbon emissions
Ethical standards and principle of utility
Ethical standards are the criteria that help to differentiate right from wrong.
The principle of utility holds that something is right when it produces the greatest practical benefits for the most people.
instrumental value.
If something is valued for the pragmatic beliefs that it brings us
intrinsic value
If something is believed to have a right to exist and its valuable for its own sake
Environmental ethics
The application of ethical standards to the relationship between people and nonhuman entities
Anthropocentrism
human-centered view; nonhuman things are given little or no intrinsic value
costs and benefits of actions are evaluated solely on the positive and negative impacts on people
Biocentrism
Ascribes intrinsic value to both human and nonhuman life. – Biocentrists may oppose clearing a forest, even if it would increase food production for people.
Ecocentrism
judges actions based on their effects on ecological systems, including nonliving elements. – The belief is that preserving systems also preserves their components, including life, water quality, etc.
Two types of views
Utilitarian or instrumental value
value for its usefulness
Intrinsic (inherent) value
something valuable with history
Forest value
can be both intrinsic (habitats…) and instrumental (timber, logging)
environmental ethics
ethical standards relationship between people and nonhuman entities
Ethical considerations
Anthropocentrism - humans are first, no intrinsic value to nature
Biocentrism - intrinsic value to humans and nature, middle ground
Ecocentrism - nature first
Industrial revolution
agricultural economies became industrial ones when machines replaced human and animal labour
Population, resource consumption and pollution increased
Industrial revolution transcendentalism
rejecting materialism and beginning the ideals of preserving nature as a priority to industrial modernization.
John Muir Conservation and Preservation arose in the 20th century
Believer in transcendentalism and promoted preservation ethics. He was ecocentrism and also anthropocentric
Gifford Pinchot Conservation and Preservation arose in the 20th century
Conservation ethic and belvied in anthropogenic in the fact that we need resources but use them wisely
Overview Conservation and Preservation arose in the 20th century
Pinchot - use natural resources wisely - conservation ethic
Muir - protect the natural environment - preservation ethic
These were both opposed to development ethic and did not want economic development as a priority
Enviro justice
ensured that enviro polices and protection apply equally to all
A political group promotes the opening of a wildlife refuge in Alaska to oil drilling, arguing that it would create thousands of jobs for Alaskans and help lower oil prices in the United States. These arguments are examples of what?
anthropocentrism
Which of these individuals would apply a conservation ethic to debates like drilling in Alaska, seeking to promote the “greatest good for the greatest number”?
Gifford Pinchot
Traditional economics is in the box
Natural resources, or ecosystem goods, include fresh water, trees that provide timber, and the energy from the sun, wind, water, and fossil fuels.
Ecological services include air and water purification, soil formation, climate regulation, pollination, and waste recycling.
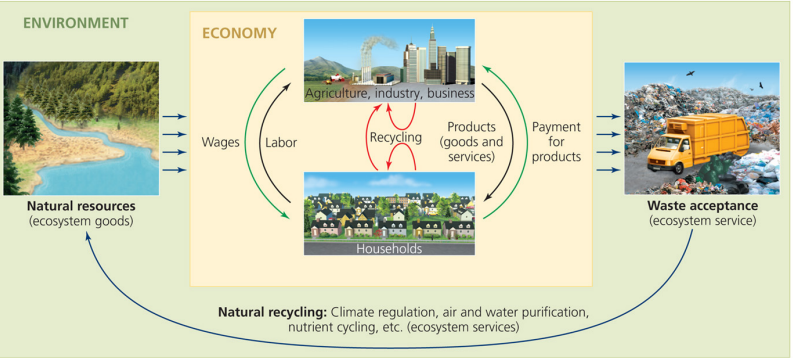
Natural goods
trees, water, sun energy, wind energy, fossil fuels
Natural services
air and water purification, climate regulation, pollination, soil formation
Invisible hand
Adam smith, classical economics, where, under the right conditions, the marketplace will behave as if guided by an “invisible hand” to benefit society.
Neoclassical economics
Conflict of wanting a low prices and seller want high price to find the market equilibrium
Cost benefit analysis
Compare the estimated costs of a proposed action with its benefits
Problems with cost-benefit analyses arise when not all costs and benefits are easily identified.
What is the monetary value of the ecological costs of clearing a forest?
Neoclassical has environmental consequences 4
Neoclassical economics assumes that natural and human resources either are infinite or can be substituted easily when used up, discounting and economic growth is number 1. One takes into account internal costs, not external (like physical heath problems, air and water pollution)
replacing resources, external costs, discounting and economic growth
Monetary benefits…
are more easily quantified than environmental costs
(one tree is able to be quantified, but clearing a whole forest?
Economic growth can occur in two ways
increasing inputs (labour or natural resources)
improving the efficiency of production with better tech or methods
Cornucopians
Assumes that human ingenuity can overcome environmental constraints, allowing indefinite growth
Cassandras
Believe indefinite growth is not possible
The limits to economic growth
Include simulation models to predict how our economies would fare in the future using status quo and sustainable policies.
Cornucopians counter that these models underestimate human ingenuity and the effect of rising prices on resources that become depleted.
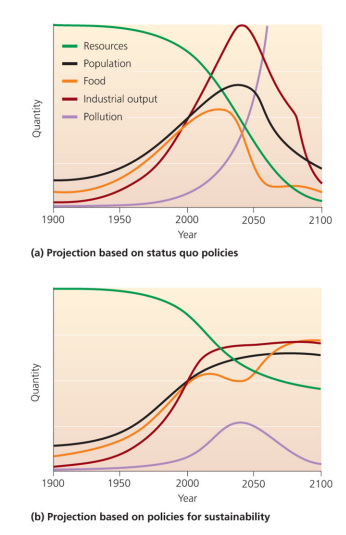
Ecological economics
economies should attain a stability, much like natural populations do in the face of environmental limitations.
Steady-state economics
Mirror ecological systems by neither growing or shrinking and instead establishing a natural equilibrium. intended to mirror natural ecological ecosystems
Issues with classical economics have led to
environmental economics, the use of discounting and lack of accounting for external resources are the biggest problems
Contingent valuation
uses surveys to determine how much people are willing to pay to protect or restore a resoruce
Ways to assign monetary value to ecosystem goods (7)
use value
existence value
option value
aesthetic value
scientific value
educational value
cultural value
GDP
does not account for nonmarket values and includes both desirable and undesirable economic activity. An oil spill could increase GDP because of clean up labour and economic gains but not good for the enviro
GDP alternative
Genuine Progress Indicator GPI
Adds in unpaid positive contributions such as parenting
Negative impacts, such as prime and pollution, are subtracted
The GDP of the US has increased, while the GPI has remained flat
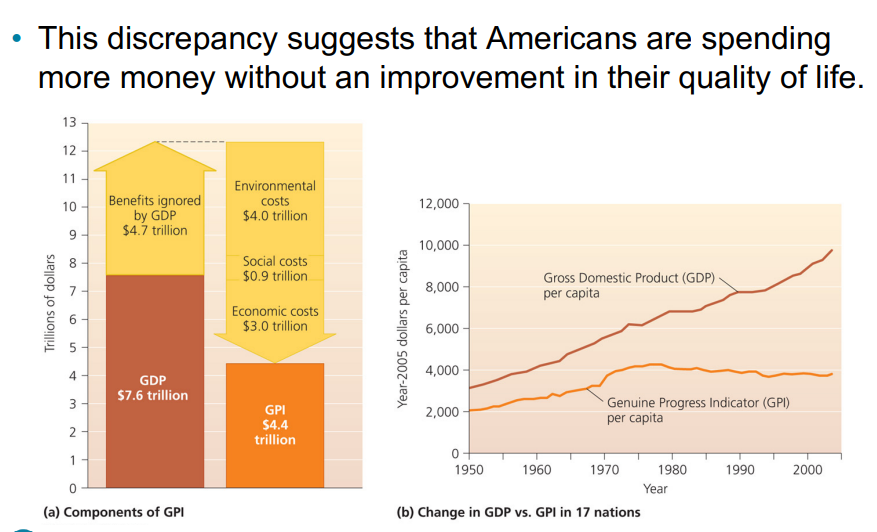
Full cost accounting
includes all costs and benefits. An example of this is GPI
Long term…
Sustainability is a long-term goal
GNH
Gross national happiness
Sustainable enviro
conservation of enviro
preservation of culture
good governed
Happy Planet Index
Based on well-being, life expectancy, ecological footprint
Market failure
Occurs when positive outside forces like ecosystem service and external costs are not considered
Ecolabeling
Advertising sustainable practices on labels to attract more consumers
Socially responsible investing
when investors choose companies that promote sustainability
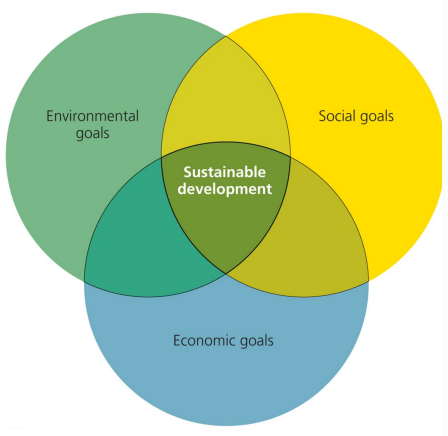
Sustainable development
form of economic progress that maintains resources for the future.
Economic goals
environmental goals/ protection
social goals/equity
Weak vs strong sustainability
Weak sustainability is the idea that natural capital can be depleted as long as human-made capital increases to compensate.
Strong sustainability means that natural capital cannot be allowed to diminish because human capital cannot replace it.
Which of these is not part of traditional economic development, but is part of the triple bottom line?
social equity
Which is not one of the four assumptions of neoclassical economics?
a. Resources are infinite or are interchangeable with other resources.
b. Future consequences are discounted in favor of present day benefits.
c. Constant economic growth is essential for a thriving society.
d. Economic decisions consider external costs that affect others besides the buyer and seller.
d
What is included in the calculation of a country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
The total goods and services produced by a country during a given year