ap biology | cell communication + cell cycle
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
ligand
a chemical signal that triggers a specific cellular response
three main steps of signal transduction
reception, transduction, response
autocrine signaling
the cell that secreted the ligand binds to a receptor + triggers a response on the same cell
juxtacrine signaling
direct contact between the cell sending the ligand and the cell receiving the ligand
paracrine signaling
ligand travels a short distance
effects cells in the immediate area
endocrine signaling
ligands (hormones) travel a long distance between the sending and receiving cells
ligands that travel a long distance are
hormones
hydrophilic ligands ___ cross the phospholipid bilayer
cannot
hydrophilic ligands bind to the
cell membrane receptors
target cells
cells that respond to the presence of the ligand
hydrophobic ligands bind to
intracellular receptors in the cytosol
reception
ligand binds to a specific receptor on or in the target cell
(receptor must be specific to the ligand)
receptor changes shape upon binding
transduction
series of chemical reactions that help the cell choose the appropriate response
possible components of transduction
signal amplification
kinases
phosphatases
secondary messengers
signal amplification
a series of chemical reactions where one molecules activates multiple molecules, amplifying the cell’s response to a signal
kinases
enzyme that transfer phosphate groups to other molecules (activates those molecules)
phosphatases
enzymes that remove phosphate groups from other molecules (inactivates those molecules)
secondary messangers
other molecules that relay signals
produced by enzymes
adenylyl cyclase
producesthe secondary messenger cyclic AMP (cAMP) from ATP
response
final stage of signal transduction and ultimate result generated by the ligand
signal transduction pathways
series of chemical reactions that mediate the sensing and processing of stimuli
feedback mechanisms
help living organisms respond to changes in the environment while maintaining homeostasis
homeostasis
the maintenance of an organism’s stable stae
negative feedback
returns a system to its original condition
cell signaling causes a person to release sweat when they become to hot, which helps them cool back down. what kind of feedback mechanism is this?
negative
the pancreas releases insulin when blood levels are too high. insulin is a ligand that triggers a series of chemical reactions upon binding that causes cells to absorb glucose from the blood. what kind of feedback mechanism is this?
negative
the pancreas releases glucagon when blood levels are too low. insulin is a ligand that triggers a series of chemical reactions upon binding that causes liver cells to break down glycogen into glucose, releasing glucose into the blood. what kind of feedback mechanism is this?
negative
positive feedback
magnifies cell processes
the hormone oxytocin stimulates contraction of the uterine muscle in labor interaction during childbirth. the contractions triggers production of even more oxytocin, which increases the contracts of the uterine muscles further. what kind of feedback mechanism is this?
positive
positive feedback ____ deviation from homeostasis
increases
negative feedback ___ deviation from homeostasis
decreases
three phases of the cell cycle
interphase
mitosis
cytokinesis
what are the stages of interphase?
g1, s, g2
what is stage g0?
the stage nondividing cells enter after leaving the cell cycle
what’s the longest phase of the cell cycle?
interphase
what happens during interphase?
the cell grows so that it has enough material to divide between two daughter cells
(replicates dna)
what happens during g1?
the cell grows and prepares for dna replication
some cell organelles are replicated
what happens during the s (synthesis) stage?
dna is replicated
contains double the dna but the same amount of chromosomes
each chromosome ; one chromatid → two identical chromatids held together by one centromere
what happens during the g2 stage?
the cell continues to grow and prepares the materials needed for mitosis
stages of mitosis
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
what happens during mitosis?
two identical daughter cells are created from one parent cell
what happens during prophase?
nuclear membrane dissolves
chromosomes condense + become visible
spindle fibers begin to form
what happens during metaphase?
the spindle fibers have fully attached to the centromeres of each chromosome
chromosomes align at the “equator” of the cell
what is the center of the mitotic spindle called?
metaphase plate
what happens during anaphase?
each chromosome splits at its centromere as opposing spindle fibers begin to shorten
the identical chromatids are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell
what happens during telophase?
two new nuclear membranes form
each of the nuclei now contain the same number of chromosomes + the same genetic information as the parent cell
cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm, a long with all of its cellular contents, between the two daughter cells
how does cytokinesis occur in animal cells?
a cleavage furrow forms which partitions the cytosol and its contents between the two new cells
how does cytokinsis occur in plant cells?
a cell plate is built within the dividing cell, providing new cell wall material for each daughter cell
when may cell stop dividing?
when they reach their fully differentiated state or when environmental conditions are not favorable for continued growth
how is progress during the cell cycle regulated?
checkpoints
where are the checkpoints of the cell cycles located?
g1 checkpoint
s checkpoint
g2 checkpoint
m (metaphase/spindle) checkpoint
some checkpoints are controlled by the interactions between
cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases
cyclin-dependent kinases are present at ____ levels throughout the cell cycle
constant
the levels of cycling proteins __ during the cell cycle
vary
when does the amount of cycling proteins reach it’s maximum?
just before mitosis starts
mitosis-promoting factor (MPF)
formed when cycling are bound to cyclin-dependent kinases
triggers the start of mitosis
somatic (body) cells
all of the cells in an organism that are not involved with sexual reproduction
density-dependent inhibition
may occur in somatic cells
when the density of cells is too high, they will stop dividing
anchorage dependence
may occur in somatic cells
cells need to be attached to a surface in order to divide
are cancer cells regulated by density-dependent inhibition or anchorage dependence?
no
proto-oncogenes
propel cell division at a specific rate
oncogenes
mutated proto-oncogenes that promote abnormally high rates of cell division
causes the formation of tuomrs
tumor suppressor genes
code for proteins that detect mutations in cells that may cause tumors to develop
what happens to a tumor suppressor gene if there is a single mutation in one allele?
the unmutated tumor suppressor allele will still continue to function
apoptosis
programmed cell death

what stage of the cell cycle is this?
interphase

what stage of the cell cycle is this?
prophase
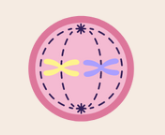
what stage of the cell cycle is this?
metaphase
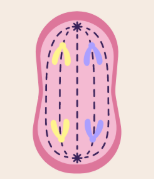
what stage of the cell cycle is this?
anaphase
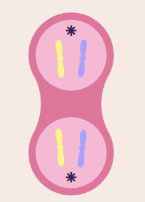
what stage of the cell cycle is this?
telophase

what stage of the cell cycle is this?
cytokinesis