Lecture 22: Mirrors and Snell's Law
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
23.1-23.5 Giancoli
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
ray model of light
light travels in straight lines, we represent light using rays which are straight lines emanating from each single point on an object, these rays entering the eye makes the image
Law of Reflection
angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence
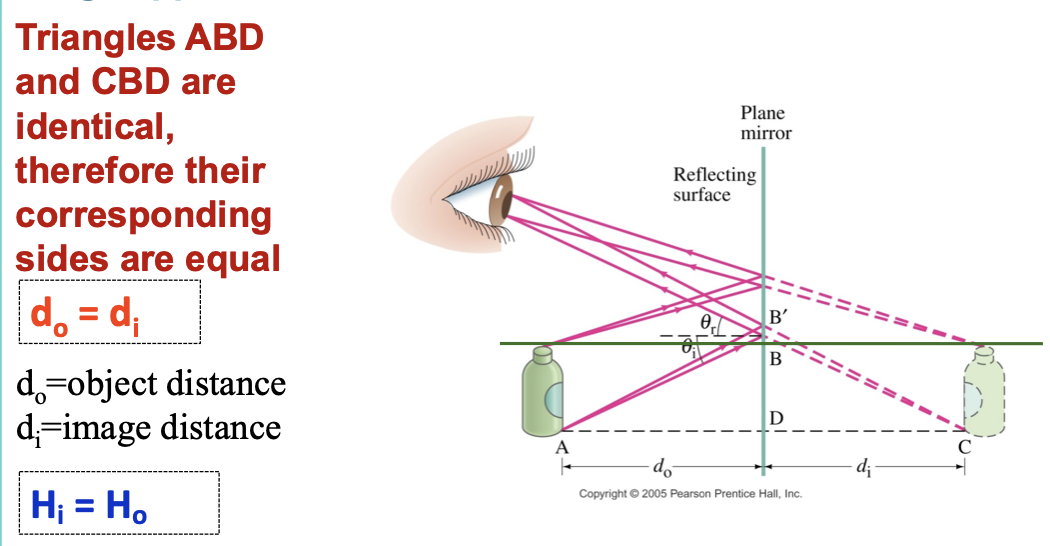
when an object is placed in front of a plane mirror, its image appears to be…
behind the mirror
plane mirror image
Types of images
real image
virtual image
real image
when light rays actually pass through the image location
virtual image
when the light rays do not pass through the image location
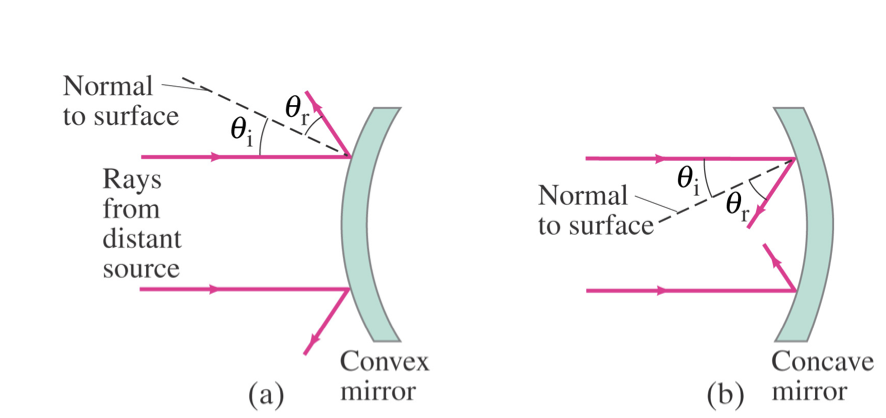
Types of spherical mirrors
convex
concave
concave mirrors: parallel rays after reflection from a mirror converge at a point called…
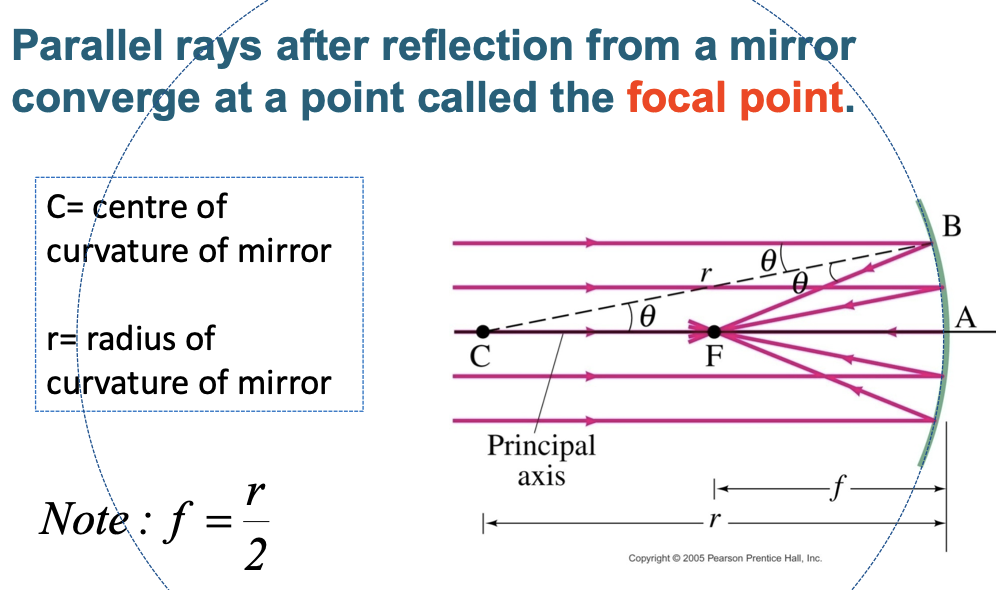
the focal point
mirror equation
relates the object distance, image distance, and focal length of the mirror
1/d0 + 1/di = 1/f
1/distance of object + 1/distance of reflected image = 1/distance to focal point
magnification equation
m = hi/ho = -di/do
hi = height of image
ho = height of the object
di = image distance
do = object distance
NOTE: negative sign indicates that the image is inverted
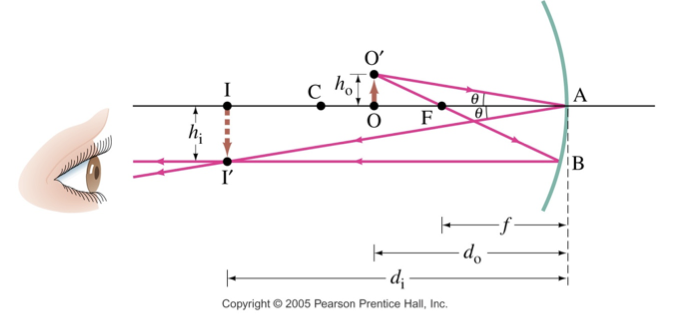
Convex mirrors
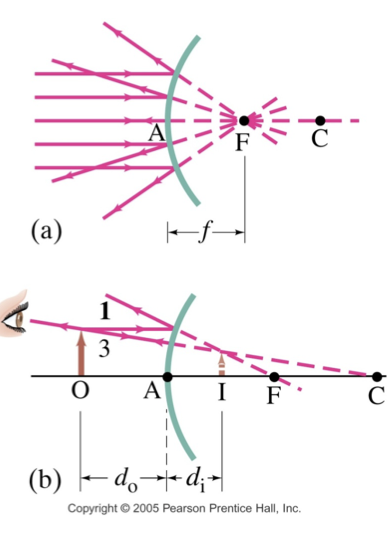
convex and concave mirrors table relating to mirror equation and magnification
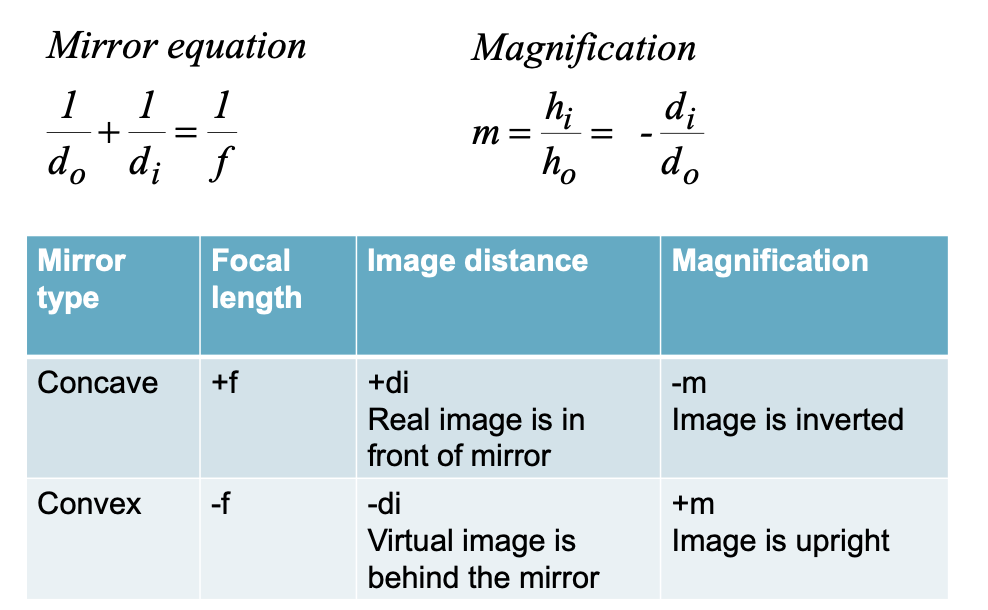
If you look at yourself in a Christmas three ball with a diameter of 9cm when your face is 30 cm away from it, where is your image, is it real of virtual, is it upright or inverted?
real or virtual
to get radius, 9/2 = 4.5 cm
since mirror is convex, focal length will be neg and given by
f = r/2 = 4.5/2 = -2.25
object distance = distance from face to mirror
do = +30 cm
1/do + 1/di = 1/f
1/30 + 1/di = 1/-2.25 —> di = -2.1 cm
since distance is negative, the image is virtual (appears behind the mirror)
magnification
m= ho/hi= −do/di
m = -(2.1/30) = 0.07
therefore image is upright (positive magnification)
image is smaller by 7%
a concave mirror has a radius of 42 cm. an object is laced 84 cm in front of the mirror’s principal axis. Where is the image located?
f = r/2 = 42/2 - 21 cm
1/do + 1/di = 1/f
1/84 + 1/di = 1/21
di = 28
m = hi/ho = -di/do
m = -28/84 = -0.333
a dentist holds a concave mirror of r = 50 mm at a distance of 20 mm from a cavity in a tooth, what is the image of the cavity, what is the size of the image
1/do + 1/di = 1/f
f = d/2 = 50/2 = 25
1/20 + 1/di = 1/25
di = -100 mm
m= -di/do = -(-100/20) = 5
image is virtual
index of refraction
light slows down when traveling through any medium
ratio of the speed of light in vacuum to the speed of light n the medium is called the index of refraction of he medium
n = c/v
c = speed of light in vacuum
v = speed of light in medium
The higher the index of refraction the…
slower light will travel through that material
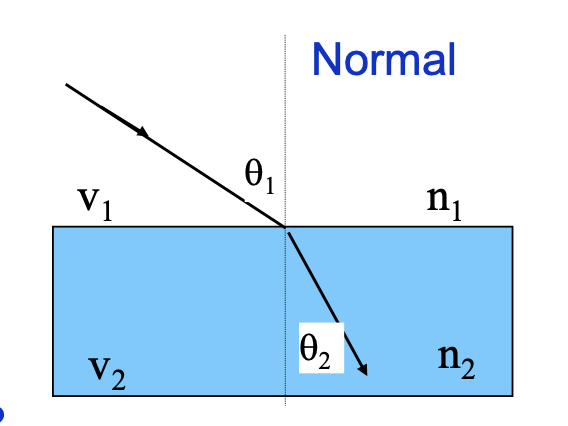
what is refraction
light changes direction when crossing a boundary from one medium to another
refraction formula and theory
the angle of refraction depends on the speed of light in the two mediums (media) and the incident angle
sin theta1/sin theta2 = v1/v2
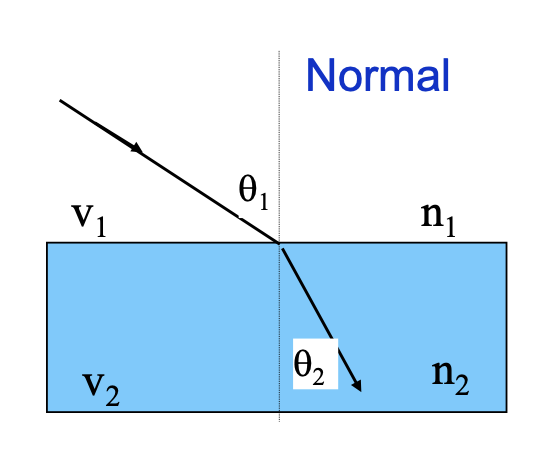
snells law
v = c/n
c = speed of light in vacuum
v = speed of light in medium
n = index of refraction
THEREFORE:
n1 sin(theta1) = n2 sin(theta2) [snell’s law]
n2 > n1 → towards the normal line
n2 < n1 → away from the normal line
a flashlight beam strikes a surface of a pane of glass (n =1.52) at 63 degrees to the normal, what is the angle of refraction
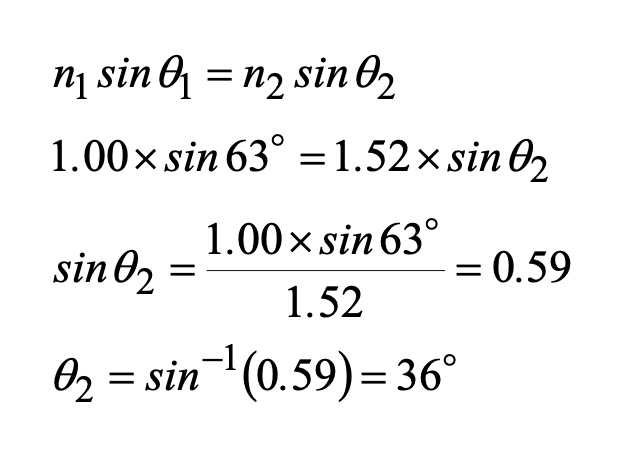
total internal reflection - fiber optics
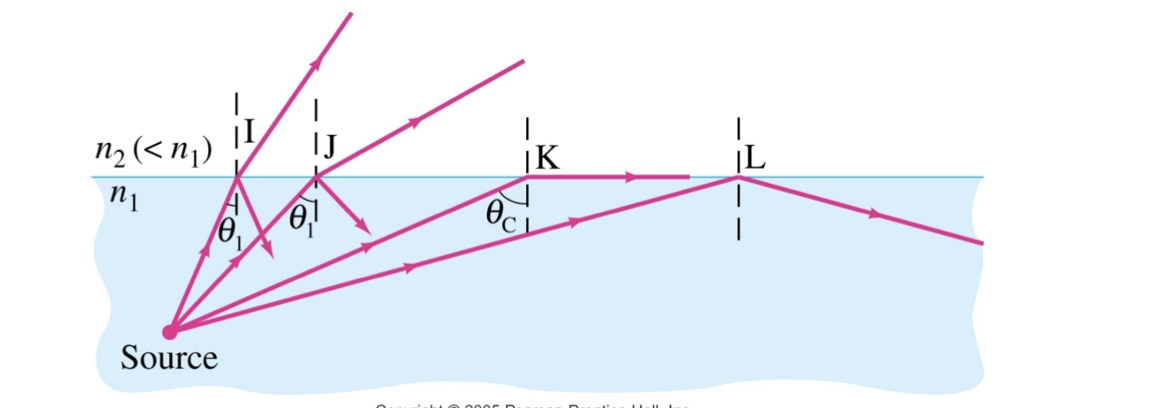
when light passes into a medium whose n2 < n1, then theta-r > theta-i
there is an angle theta-i for which theta-r = 90 degrees
this is called the critical angle theta-c
if theta-i is larger than theta-c, no transmission occurs
this is called total internal reflection
n1 sin theta(1) = n2 sin theta(2)
as theta(1) increases so does theta(2)
at critical angle → theta(2) = 90 degrees
n1sin theta-c = n2 sin90
theta-c = inverse sine(n2/n1)
when theta 1 > theta-c LIGHT IS TOTALLY REFLECTED BACK INTO THE SAME MEDIUM
total internal reflection is the
principle behind fiber optics
Light will be transmitted along the fiber even if it is not
straight
image can be formed using
multiple small fibres