Physical Chemistry
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Explain, in terms of bond breaking and bond making, why this reaction (burning a fuel) gives out energy. (3)
m1: breaking bonds is endothermic m2: making bonds is exothermic m3: more energy given out than taken in
A student added a solid to some hydrogen peroxide solution to see if the solid acted as a catalyst. He noticed that a lot of bubbles formed, and that the solid was still present at the end of the reaction.
Outline a method to show that the solid acted as a catalyst and not as a reactant. (2)
m1: weigh solid mass before and after m2: unchanged
Explain, in terms of particles, why the rate of a reaction increases as the concentration of a reactant increases. (2)
m1: more particles collide m2: more frequently
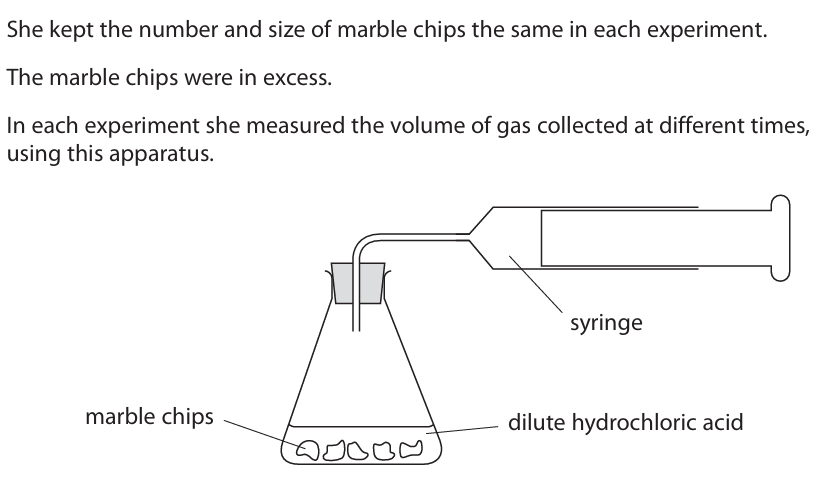
Explain why increasing the concentration has this effect on the rate of reaction (3)
m1: more ions in a given volume m2: collide per second m3: more frequently
The rate of reaction increases as the concentration of the acid increases. Explain this relationship in terms of particles. (3)
m1: more particles in a given volume m2: more collisions between particles
Explain, in terms of particles, why an increase in temperature increases the rate of this reaction. (3)
m1: average kinetic energy in particles increases m2: more successful collisions m3: per second
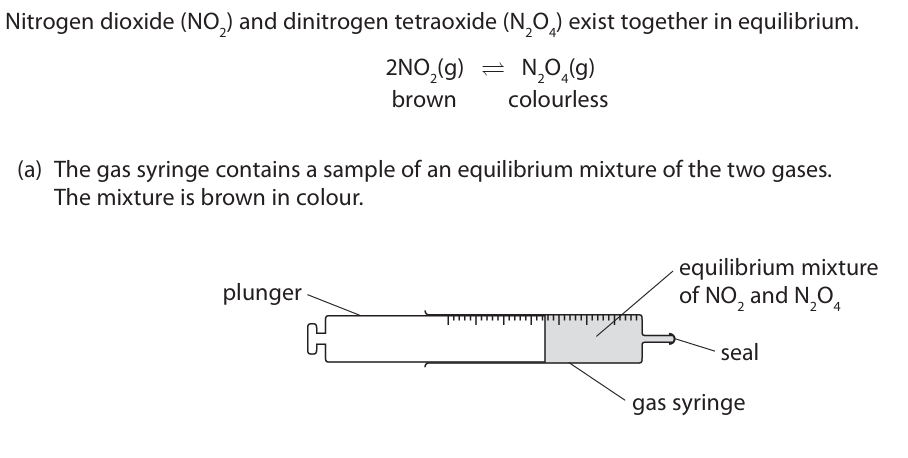
The plunger is pulled out to reduce the pressure of the gaseous mixture. When the equilibrium is reached the mixture is darker in colour.
Explain this observation. (3)
m1: becomes darker because NO2 is formed m2: as equilibrium shifts to the left m3: because there are more molecules