The Struggle with France (military operations)
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Wars between 1689 and 1763
The War of the League of Augsburg (1689-97)
The War of Spanish Succession (1702-13)
The War of Austrian Succession (1740-8)
The Seven Years’ War (1756-63)
Overarching characteristics of wars here
First three began in Europe and were essentially about the balance of power within the continent
Conflict then spread across the Atlantic
Colonists viewed them as overseas wars that they became embroiled in as subjects of the British Crown (clear via names of King William’s War, Queen Anne’s War and King George’s War)
Colonists were eager to defeat French and Spanish neighbours - despised their Catholicism
Features of King William’s and Queen Anne’s Wars
French forces - Native American allies
Carried out savage attacks on frontier areas of New York and New England
Hundreds of colonists killed, tortured and scalped
Colonists - little help from Britain - dependent on militias and Native American allies
1710 - a New England force managed to annex Nova Scotia
Treaty of Utrecht 1713
Gave Britain control of Hudson Bay, Newfoundland and Nova Scotia
France recognised British control over the Iroquois native people - Iroquois were not consulted
Britain gained St Kitts
War of Austrian Succession (1740-48) features
Most of fighting - colonial militia as Britain too absorbed in Europe
Royal Navy stronger than French and Spanish navies - also hard for enemies to send forces to America
English-speaking colonists outnumbered French 15 to 1 - but advantage offset by French alliances with Native Americans
New England colonies bore much of cost
Sailors pressed into Royal Navy, men of military age fighting on land
War of Austrian Succession events (2)
Colonists captured Louisbourg 1745
Annoyed when British gave it back in 1748 Treaty of Aix-La-Chapelle
Who made ‘Join, or Die’ image in 1754? Message?
Benjamin Franklin - English colonies unite to fight French, if do not join together the unit of colonies would ‘die’
Albany Congress - when?
June 1754
Albany Congress - where, what and who?
Called on the colonies from Virginia northward to send delegates to a meeting at Albany to discuss joint Native American policy
Albany Congress - why?
1748 peace was simply a truce - British and French colonists redoubled efforts to control Ohio Valley
Only 500 British troops in America
Board of Trade recognised Native American support would be essential in upcoming struggle against French
Albany Congress - what ended up happening?
Failed to secure an alliance with the Iroquois people (tribe best disposed towards British)
Adopted scheme (Benjamin Franklin’s Plan of Union) for permanent intercolonial confederation - envisaged elected colonial parliament, authority over N.A. affairs and power to levy taxes for army - but colonial assemblies rejected it
Albany Congress - significance (Franklin’s plan)
Franklin’s Plan of Union - envisaged an elected colonial Parliament with authority over Native American affairs and defence and with power to levy taxes (support army)
Colonial assemblies either rejected or ignored
Fort Duquesne - events
1753-4 Virginian planters organised the Ohio Company - secured from British government 200,000 acres in trans-Allegheny region
At same time - French plan building chain of forts between Lake Erie and the Allegheny river - aimed for control over Great Lakes to mouth of Mississippi
Virginian force led by 22-year old George Washington sent to forestall them 1754
Washington found French already in possession of the fork of the Ohio River (modern day Pittsburgh) and constructing Fort Duquesne
Fighting - Washington forced to surrender July 1754 (Battle of Jumonville Glen)
War not declared but Britain sends General Braddock and 2000 troops to America
On way to Fort Duquesne Braddock (unfamiliar with Native American warfare) blundered into French-Native American ambush
Was killed and army routed July 1755 (Battle of the Monongahela)
Next two years - Native American war parties devastated scores of frontier settlements
What happened in 1756?
Britain declared war on France - the Seven Years’ War - or the French-Indian War as it was known in America - developed into a worldwide conflict
Britain ally in Seven Years’ War
Prussia
France ally in Seven Years’ War
Spain, Austria and Russia
Locations of Fighting in 7 Years’ War
Europe, the West Indies, Africa, India, North America
Evidence things going badly for Britain at start of war (1756-7)
French General Montcalm captured Fort Oswego on Lake Ontario in 1756 - strengthens hold on Great Lakes
And Fort William Henry at the southern end of Lake George in 1757
Reasons for British weakness before 1756
Unaccustomed to remote/hostile environment
Red uniforms easy targets
Conflicts failed
Lost forts - Oswego
Guerrilla warfare - used to set-piece battles
Failed to gain N.A. support as French offered greater rewards and allowed pillaging
Colonial troops not good, often did not serve beyond their short enlistment period, could desert
Civil administrators in charge lacked military expertise to handle forces
Star of war who was British commander-in-chief, and what was he unable to do?
Earl of Loudon - inability to induce the ethnically and religiously divided colonists to unite in their own defence
Who formed a ministry with the Duke of Newcastle in 1757 and was largely responsible for British victory in the 7 Years’ War?
William Pitt - British Secretary of State during Seven Years’ War
Pitt’s leadership in 7 Years’ War
Sent 25,000 troops to America under the command of Jeffrey Amherst and James Wolfe
Established a global strategy - priority given to defeating French in America and Caribbean
Deployed most aggressive of commanders in America - men he appointed prepared to launch offensives
Developed three-pronged strategy to attack Louisbourg, Ticonderoga and Quebec and retake Fort Duquesne
Support of colonists - more colonial volunteers and support
Ensured crown paid for equipping and provisioning of militias and reimbursed colonial assemblies
War became seen as shared endeavour Britain and colonists - crown helped by deploying 45,000 troops by 1758
Militia Act 1757 - established local militias to protect Britain from possible French invasion, giving him more front line soldiers
Finance in 7 Years’ War (Pitt)
Pitt paid ally, Frederick the Great of Prussia, to attack French forces in Europe - strategy worked brilliantly, meant that even before naval superiority was ensured, France was unable to send reinforcements to North America
Pitt reimbursed 2/5 of military expenditures made by colonial legislatures - saddled colonists and Britons with public debt to finance the wars
Annual expense of £18 million
Role of the Navy 7 Years’ War
Won control of Atlantic and devastated French shipping - reducing reinforcements and supplies reaching New France
Huge British Fleet captures Louisbourg 1758
Native Americans in 7 Years’ War
Cultivated their friendship to be used successfully against French - commented by Amherst that French were afraid of them
Support much easier to gain once Britain secured Naval superiority after Battle of Quiberon Bay in 1759
Britain supplied them with goods
Colonists involvement in 7 Years’ War
Pitt’s reversal of rule where British officers took precedence over colonial officers - war support increased
More involvement of colonial troops and supplies in wars
Colonial troops contributed to building roads and forts
Gained support of colonial legislatures
French weaknesses in 7 Years’ War
Deserted by Native Americans
Loss of trade to forts due to British naval dominance
Small in number, depended on supplies from France (inhabited less fertile regions - big issue as supplies couldn’t reach New France)
Natives took to British
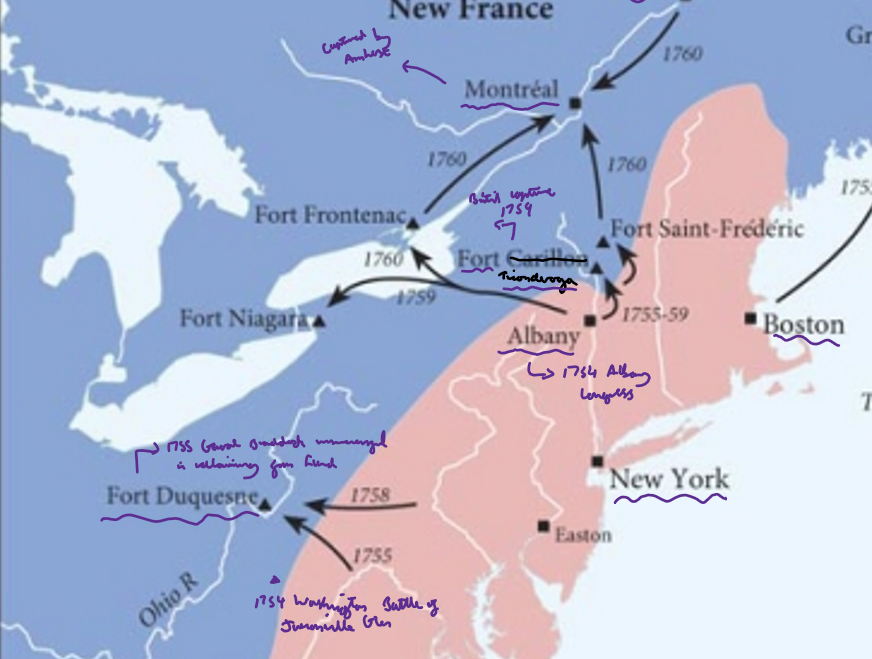
Key events 1758
1758 British forces captured Louisbourg, then cut link between Canada and Mississippi Valley by taking Fort Frontenac on Lake Ontario
November 1758 French abandoned Fort Duquesne - advancing British force rebuilt fort and renamed it Fort Pitt
Elsewhere, Robert Clive won series of victories in India while Frederick the Great defeated armies of France, Russia and Austria in Europe
Key events (victories) 1759
Battle of Quiberon Bay 1759 - Admiral Hawke smashed a French fleet at Quiberon Bay (France, southeast of Brest) - prevented France from sending reinforcements to Canada
British troops won major victory at Minden in Germany
Britain captured Gaudeloupe in Caribbean
1759 Britain three-pronged strategy Canada
One force captured strategically important Fort Niagara,
Advancing up Lake Champlain, General Amherst captured Fort Ticonderoga
General Wolfe led a 10,000 strong expedition up the St Lawrence River - aimed to capture Quebec, eventually defeated the French commander Montcalm on the Plains of Abraham 12 September 1759 (Battle of Quebec/Plains of Abraham) - Wolfe died but ensured capture of Quebec, effectively destroyed French power in Canada
1760 what happened
Amherst took Montreal
1763 Peace of Paris
Britain received Canada and all French possessions east of Mississippi
Britain acquired most of France’s Caribbean Islands
Britain got Florida from Spain
France ceded Louisiana to Spain