Sex, gender, and health (differential morbidity and mortality)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Trivers-Willard hypothesis
Under poor conditions, mothers will have fewer male offspring, better conditions will have more male offspring, increasing the fitness of the mother because in poor conditions males will have few offspring but in good conditions that can have many more
Alternative to the Trivers-Willard hypothesis
Males grow more rapidly which makes them more likely to die in bad conditions, not enough food to support quick growth
SDIM
Sex differences in mortality
Sex at birth ratio (SRB)
The number of males born for every 100 females born in the same period of time
Weak male hypothesis
Idea that males were more biologically vulnerable, almost pathologised maleness
What are the sex ratios/sex differences
Number of males : number of females
Equal is 1, excess females <1.0, excess males >1.0
When did sex-based differential infant mortality being to be noticed?
In the 17th to 18th centuries
Found higher male mortality in infancy and early childhood and more males born, countering female weakness idea
Initially believed to be because of urban development, accidents, or injury
Later, weak male hypothesis
How can known differential mortality be used to measure discrimination against female offspring?
106 (or 102-106) males to every 100 females, so a number of males > 106 indicates sex selection or infanticide
Like estimating how many girls were aborted in South Korea, very high proportion of males
But this varies on country, some have more males or more females and the ratio uses European and American birth rates as the default
Historical, economic, and epidemiological context matters
What is Wells’ extended model to investigate differential mortality and what does it suggest?
Extended from just gestation to the whole early childhood period (age of weaning finished, around 3 or 4 years old although not binary)
Would expect that by that point the sex ratio evened out as males died
Malnutrition and infection signal poor conditions biologically (both work together and influence each other)
Both males and females vulnerable to the process, but males are more vulnerable
Suggested that males were less buffered and that environmental stress will always impact males more early in life as they are less able to recover
What are other biological explanations for the excess in early male mortality common across species?
Chromosomal explanation (XX confers greater genetic capacity in the case there is a defect on one X, there is a backup)
Sex-based differences in response to infection due to immunomodulatory functions of sex steroid hormones
Testosterone has a negative impact vs oestrogen is positive
Supposedly higher Th1 response in females
What are critiques of the biological explanations for excess male mortality? (6)
In the 1980s, Stinson argued there was only weak support that males were less buffered
Sex differences in responses to stress may vary depending on the stressor
Humans live in complex cultural environments, may apply to some but not others, social patterns are important
Disease transmission dynamics and behaviour patterns based on sex
If age can impact mortality for a disease, but social conditions mean males get it more when younger, could look like males are more susceptible
Interactions between culture and the environment
What are proposed reasons for changes in sex-based mortality differences over time?
Rather than being a constant, the expression of biological differences is sensitive to the context of the place and time, and is historically contingent
Excess male mortality may be a product of the western demographic and epidemiological transition, as the male survival disadvantage was uncovered (maybe Omran’s theory should be expanded to include a sex difference in mortality transition?)
Cullen et al. (2015), transition in SDIM as the female survival advantage for non-communicable diseases has emerged with the decrease in infectious disease-related deaths
There is an inverse relationship between the infant mortality rate and excess male infant mortality
What were the hypothesised explanations and conclusions regarding the high infant mortality and skewed sex ratio (129 : 100) in the Agta foragers?
Hypothesis 1 = skewed sex ratio was due to systematic female neglect and infanticide
Hypothesis 2 = a higher sex ratio at birth has evolved as an adaptive response to high extrinsic male mortality in this population
Study showed that the sex ratio was due to a biological response to male-biased juvenile mortality
What were the hypothesised reasons for why males had a higher risk of severe disease and a 1.7x higher risk of death from COVID-19 than females after 30?
Oestrogen was protective but androgen wasn’t
Many immune-related genes are on the X chromosome
Females may also be less susceptible to extreme immune responses
But also gender roles and behaviour
These sex differences also depend on the disease, as the way the virus binds to the cell (which is how they sex difference arises) is specific to viruses, so sex differences depend on what the main cause of death is
According to Johansson (1991), why is a historical perspective essential when looking at demography/differential mortality?
Because the relationship between biology, welfare, and longevity is subject to differential social, cultural, and historical contexts, which can all influence each other
Biology is inconsistent and alone, it can’t explain patterns
According to Johansson (1991), why is context an important determinant?
The relationships between biology, sex-specific behaviour, and relative welfare are very complex and vary based on time and place
Context helps to check the observed patterns are real (confounding factors) and to explain patterns and why they change
Usually multiple factors influence each other, contributing to excess or differential mortality
According to Johansson (1991), what factors may influence each other and contribute to excess or differential mortality?
Different disease environments, same behavioural and cultural patterns will have different biological outcomes
Local biologies, we are shaped by our environment
Immune system is adaptive
People’s choices influencing longevity/mortality are constrained by their context (job, diet, etc)
According to Beltrán-Sánchez et al. (2015), what were the causes of higher adult male mortality?
Adult male mortality was higher due to increased rates of heart disease and smoking-related deaths to a lesser degree
According to Beltrán-Sánchez et al. (2015), what factors contributed to higher rates of heart disease and smoking-related deaths among adult males?
Biological, social, and environmental context
Epidemiological transition
Males were more likely to smoke in most places
Differences in diet and lifestyle, men had a higher-fat diet with more meat
Some biological factors, making men more susceptible to changes in lifestyle, like fat distribution and arterial function
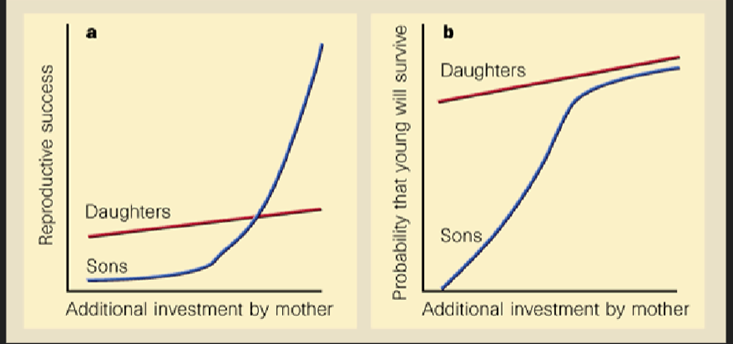
What does this graph show?
The Trivers-Willard hypothesis
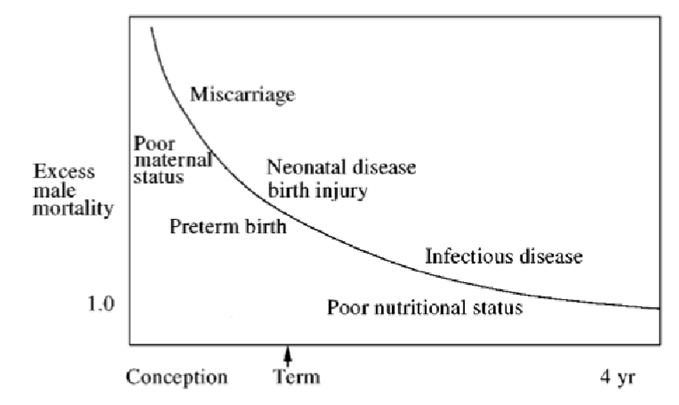
What does this graph show?
Development of the pattern of excess male mortality in early life in relation to different environmental stresses
The cause of malnutrition is given below the curve, and the associated cause of mortality above it
But approximately four years old the sex difference in mortality disappears
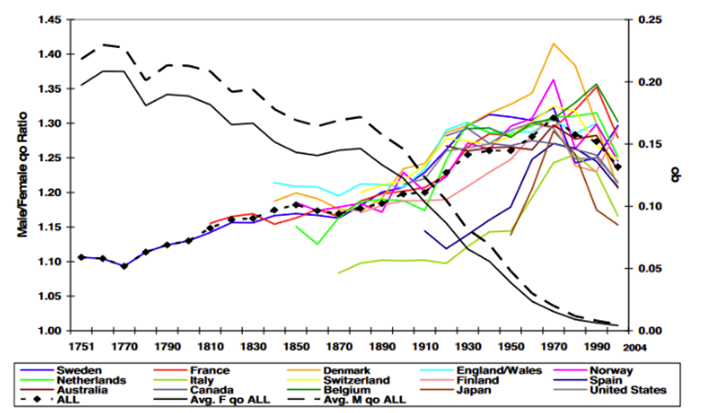
What does this graph show?
The worsening male disadvantage during the major historical decline in infant mortality