Mitral Regurgitation
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
196 Terms
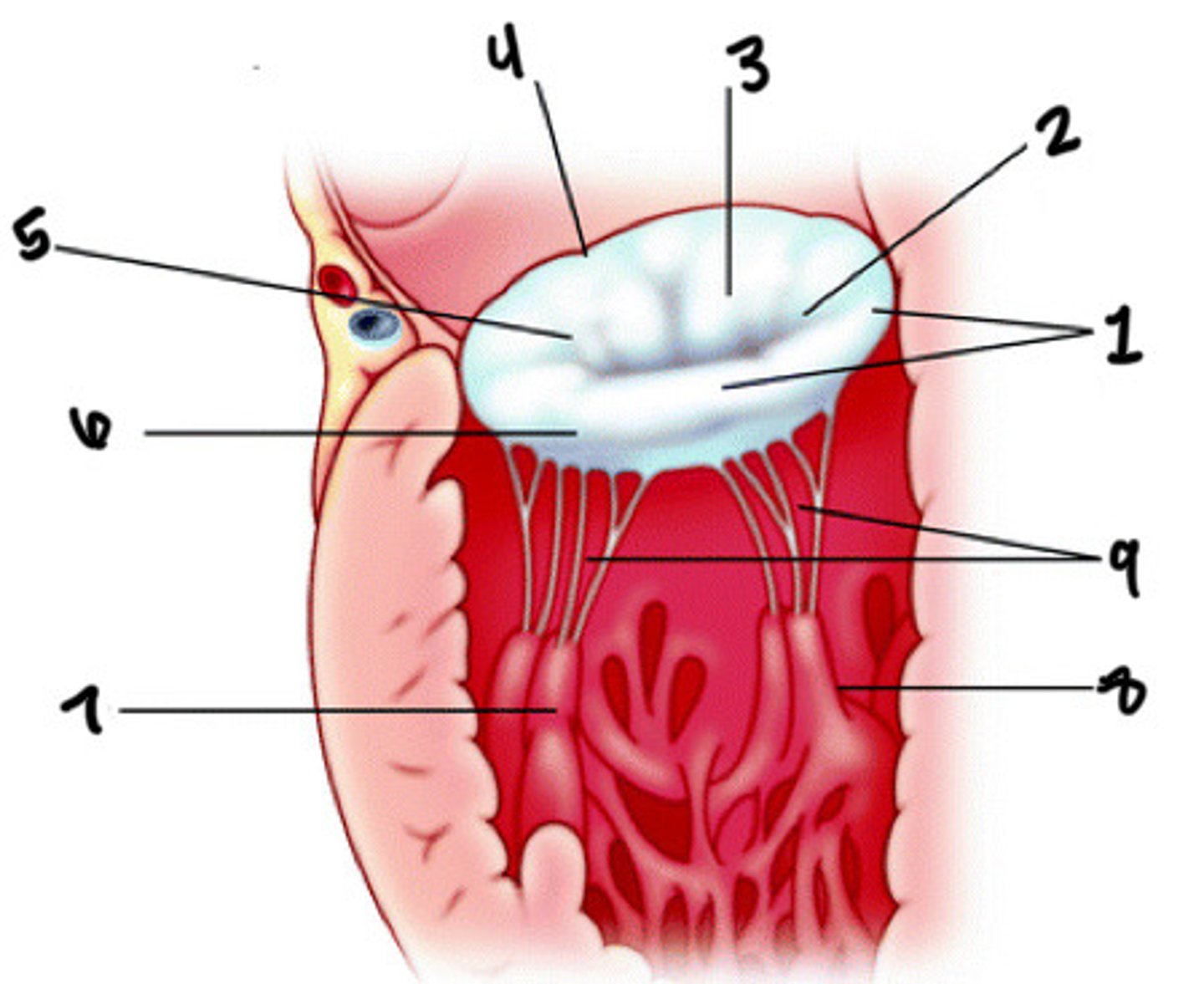
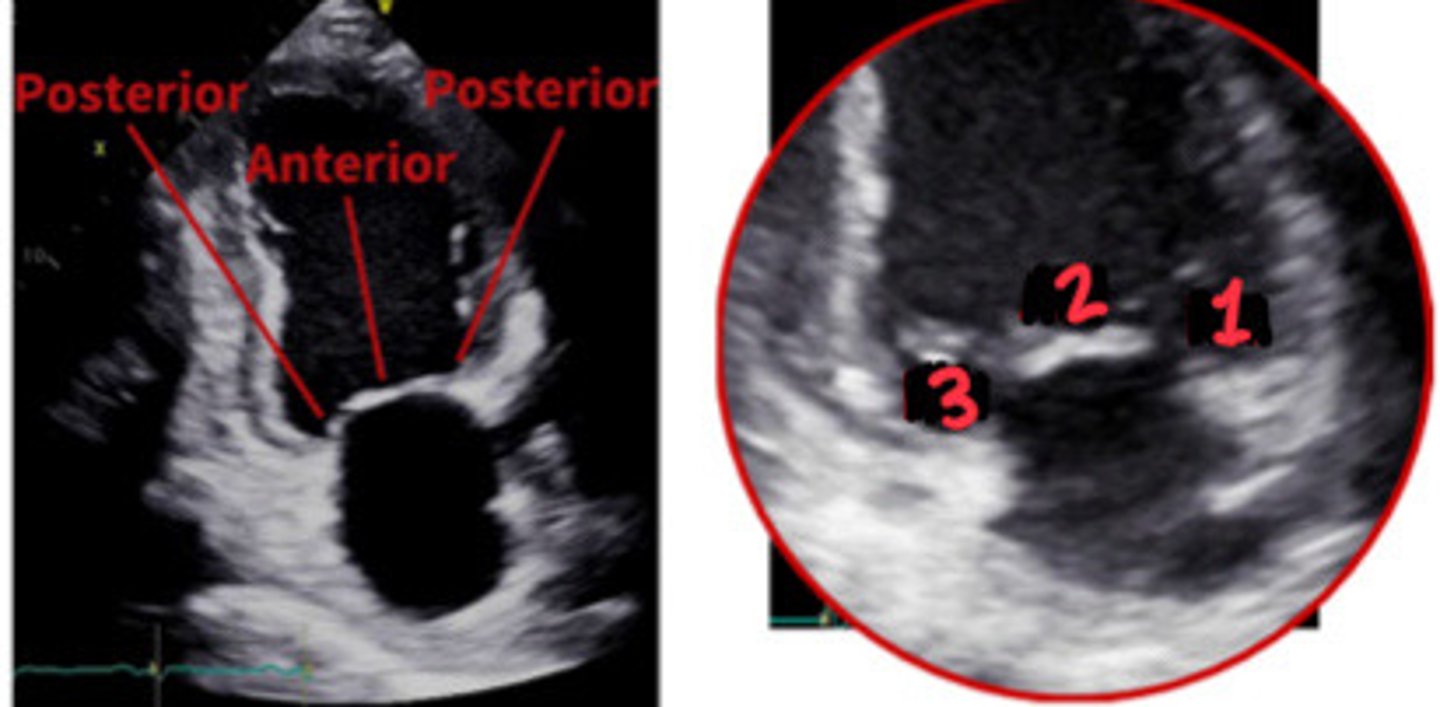
Posterior leaflet
What is 1
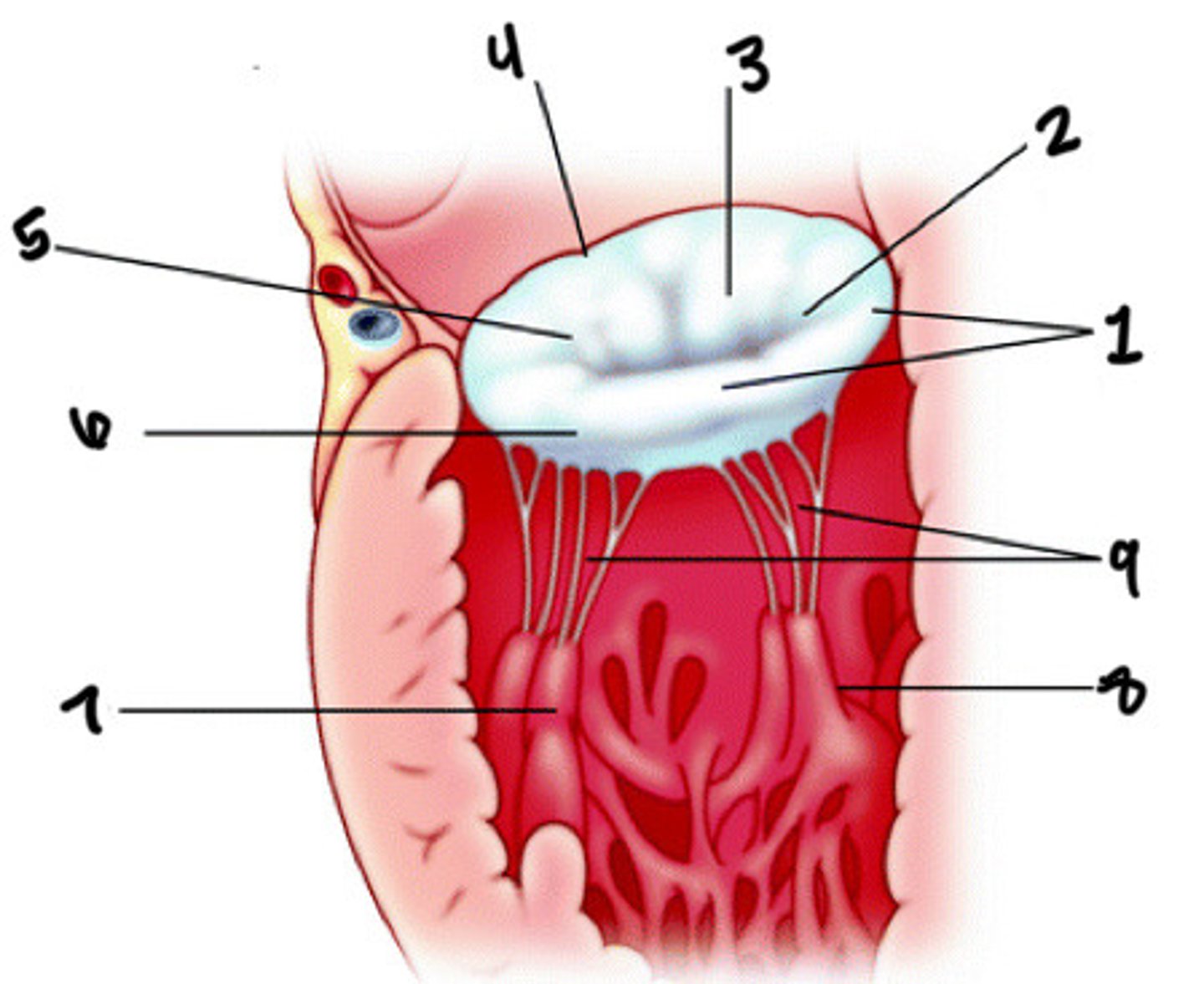
Posteromedial commissures
What is 2
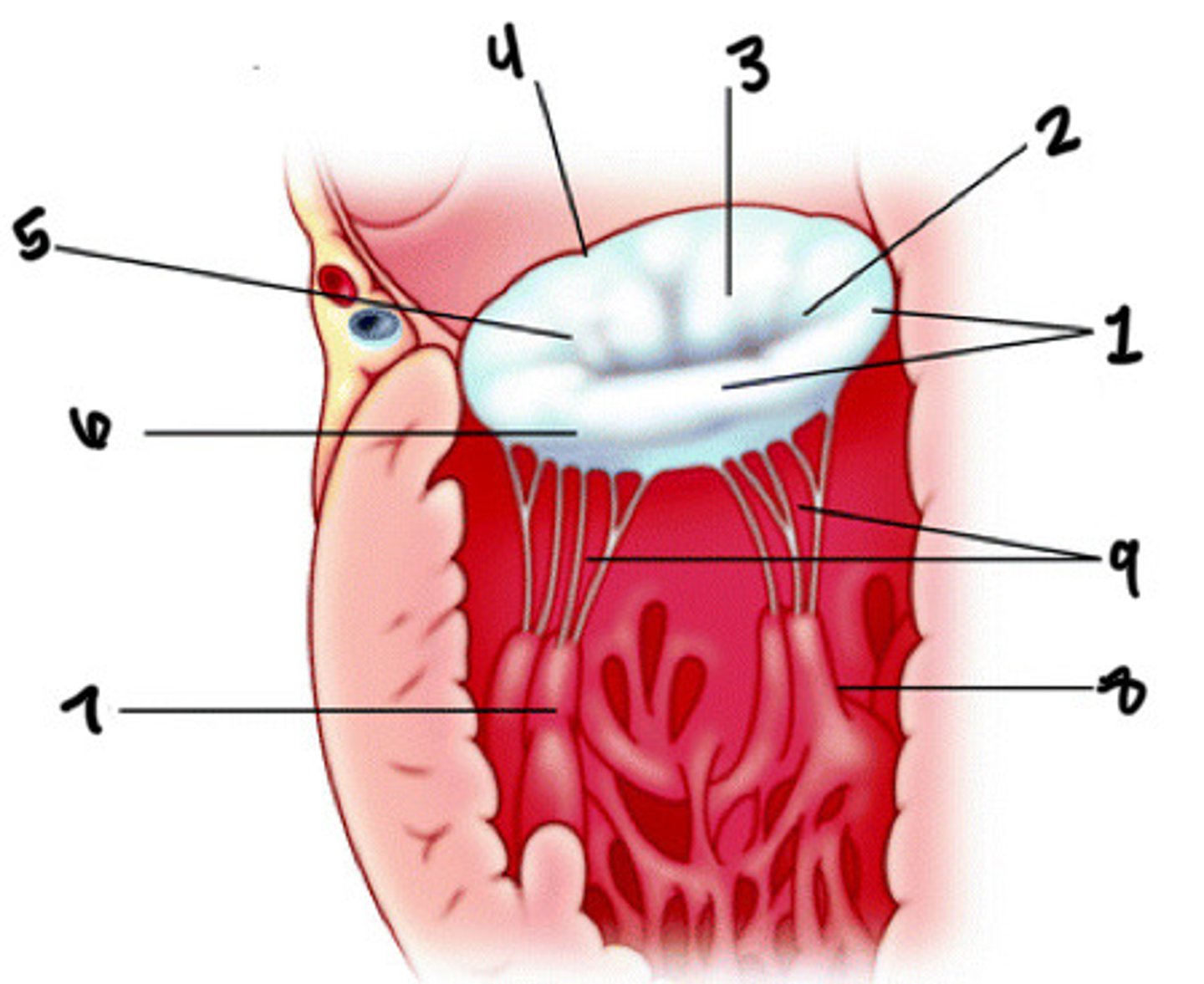
Anterior leaflet
What is 3
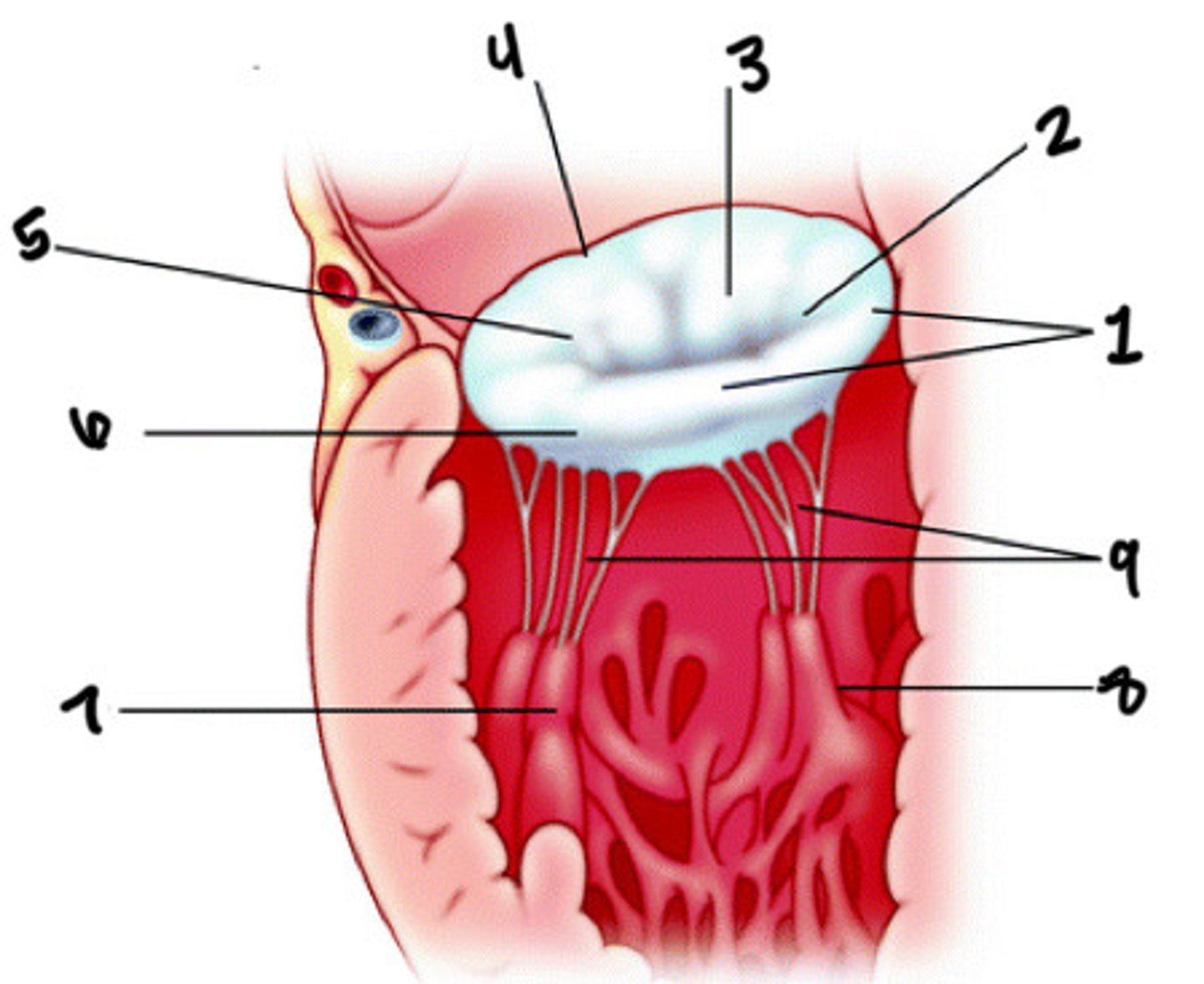
Anterior annulus
What is 4
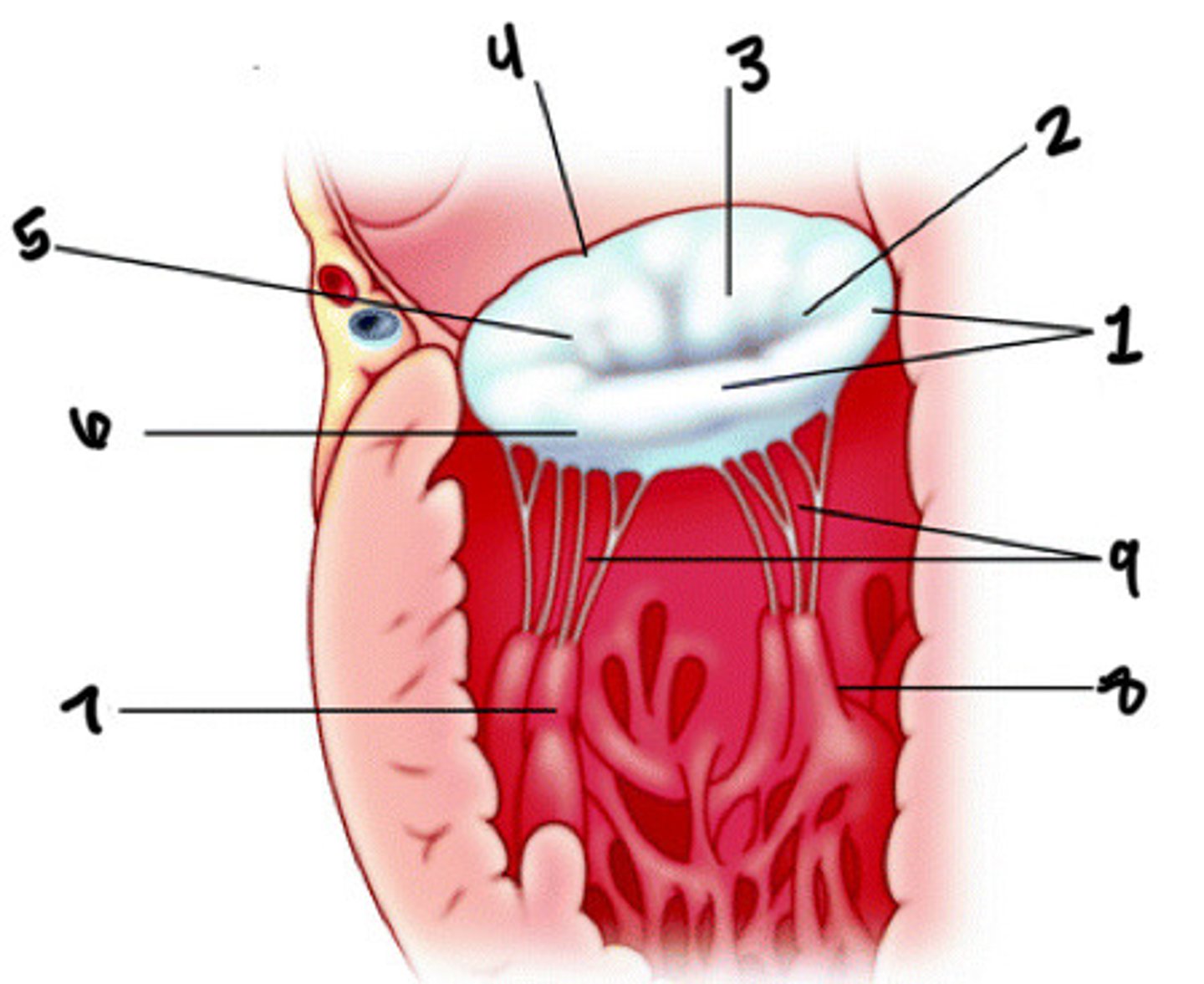
Anterolateral commissure
What is 5
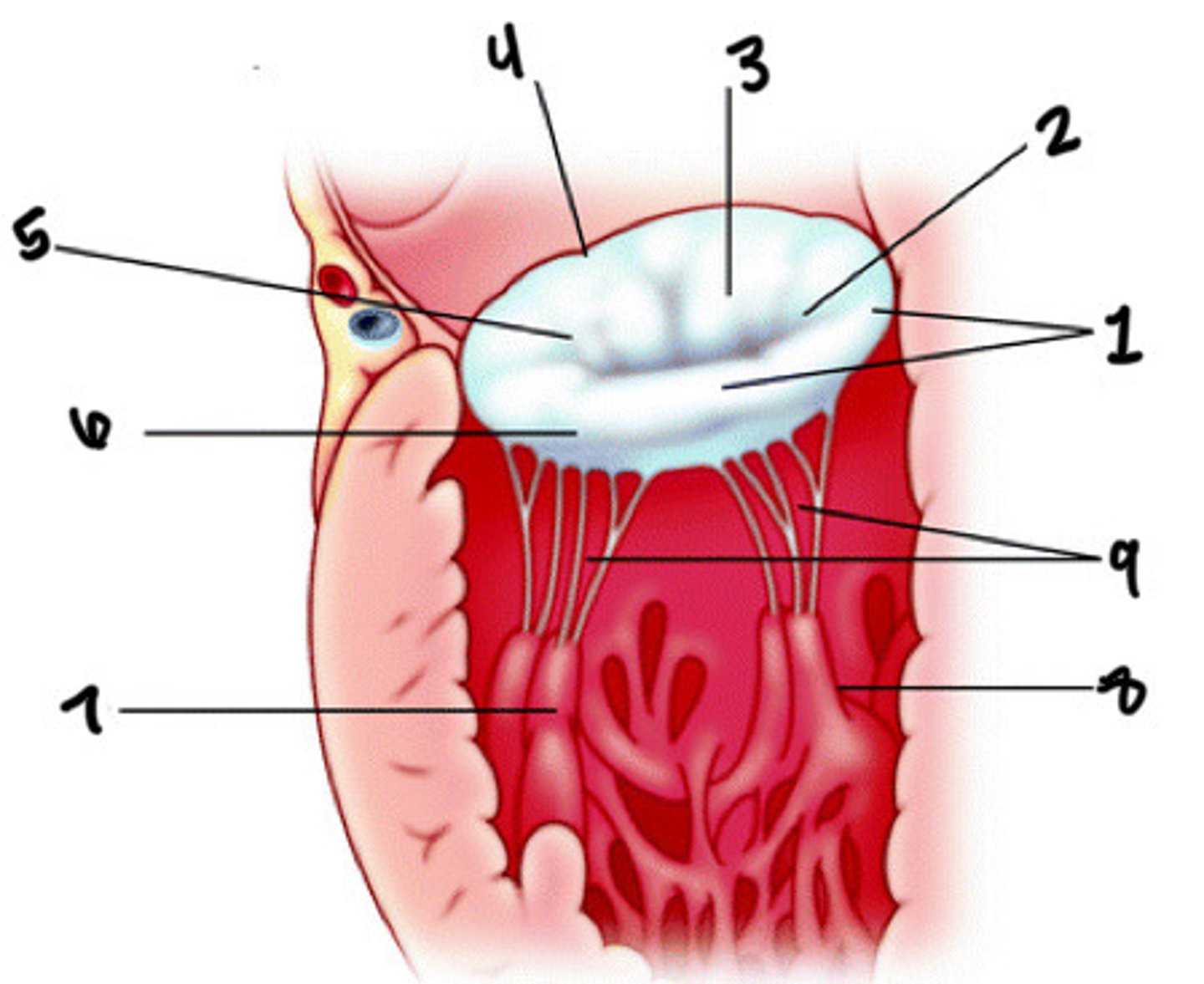
Posterior annulus
What is 6
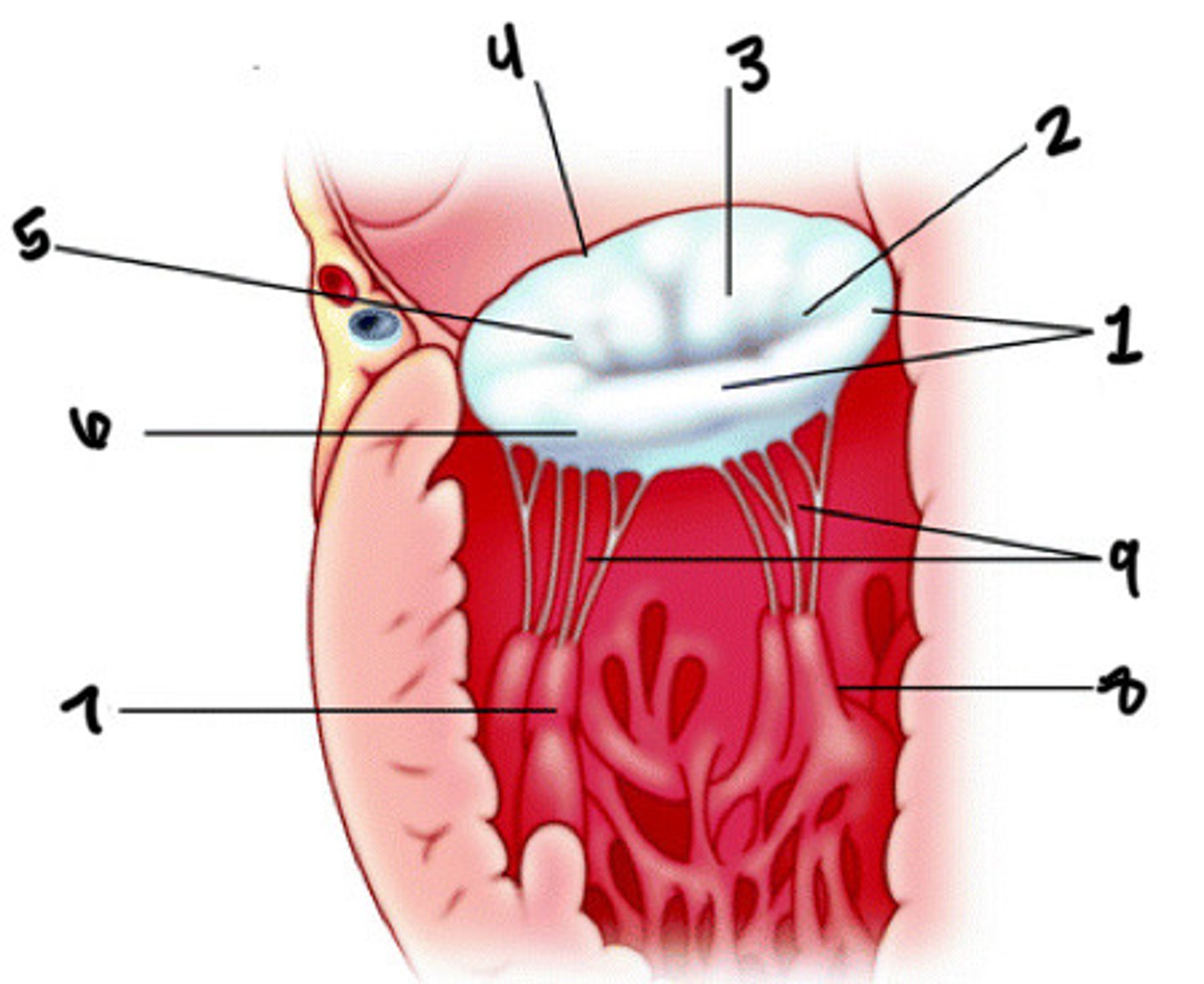
Anterolateral pap muscle
What is 7
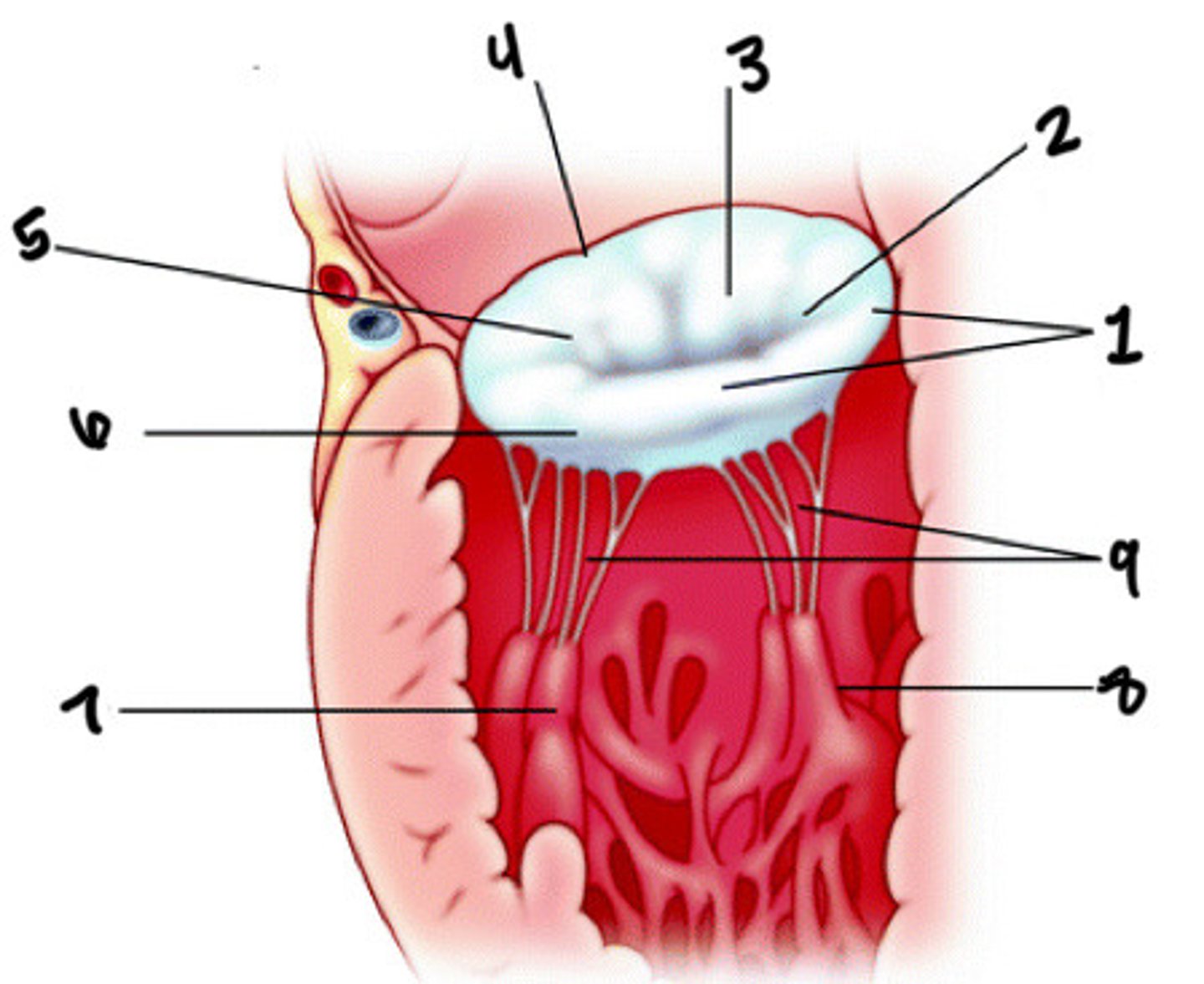
Posteromedial pap muscle
What is 8
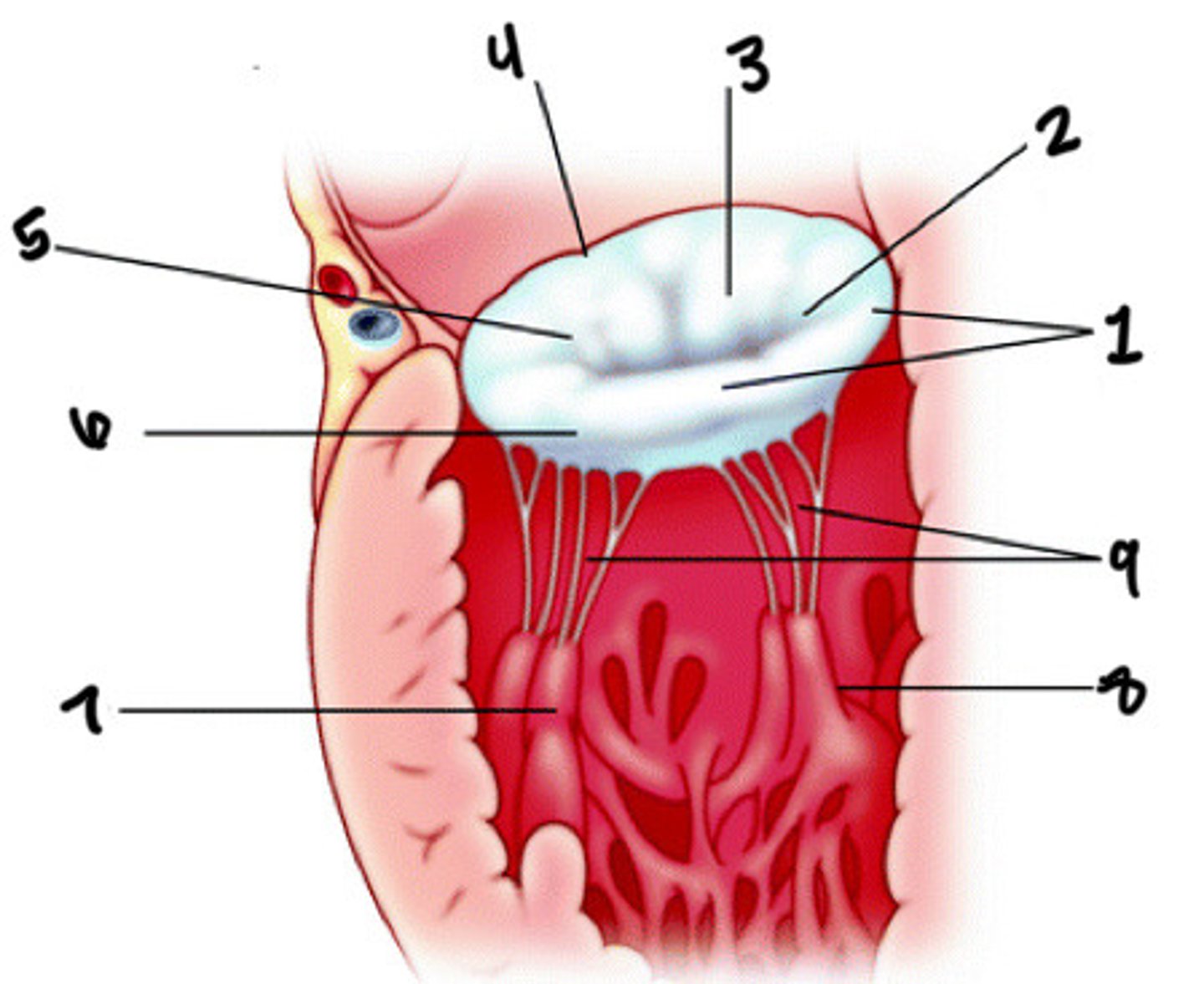
Chordae tendineae
What is 9
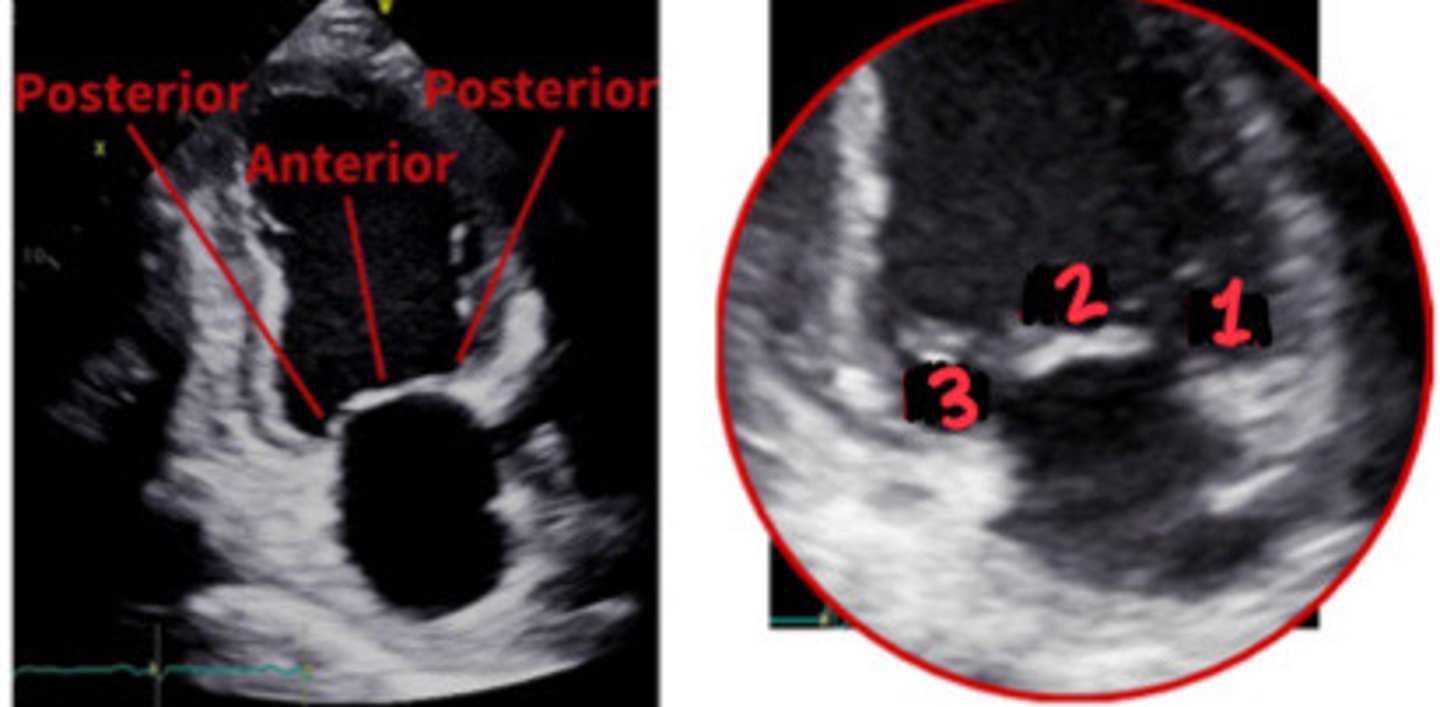
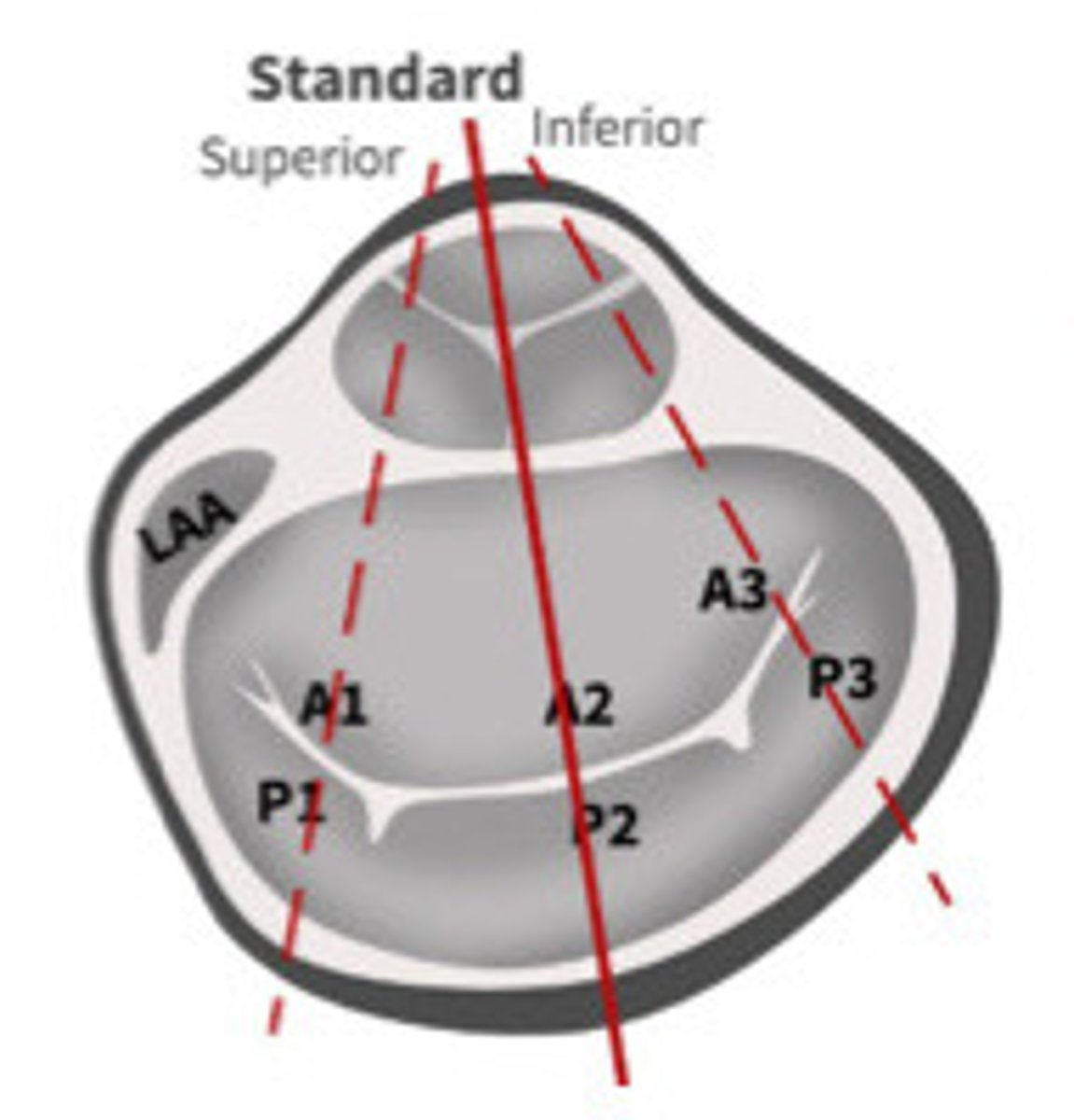
A2
What section of the MV is 1
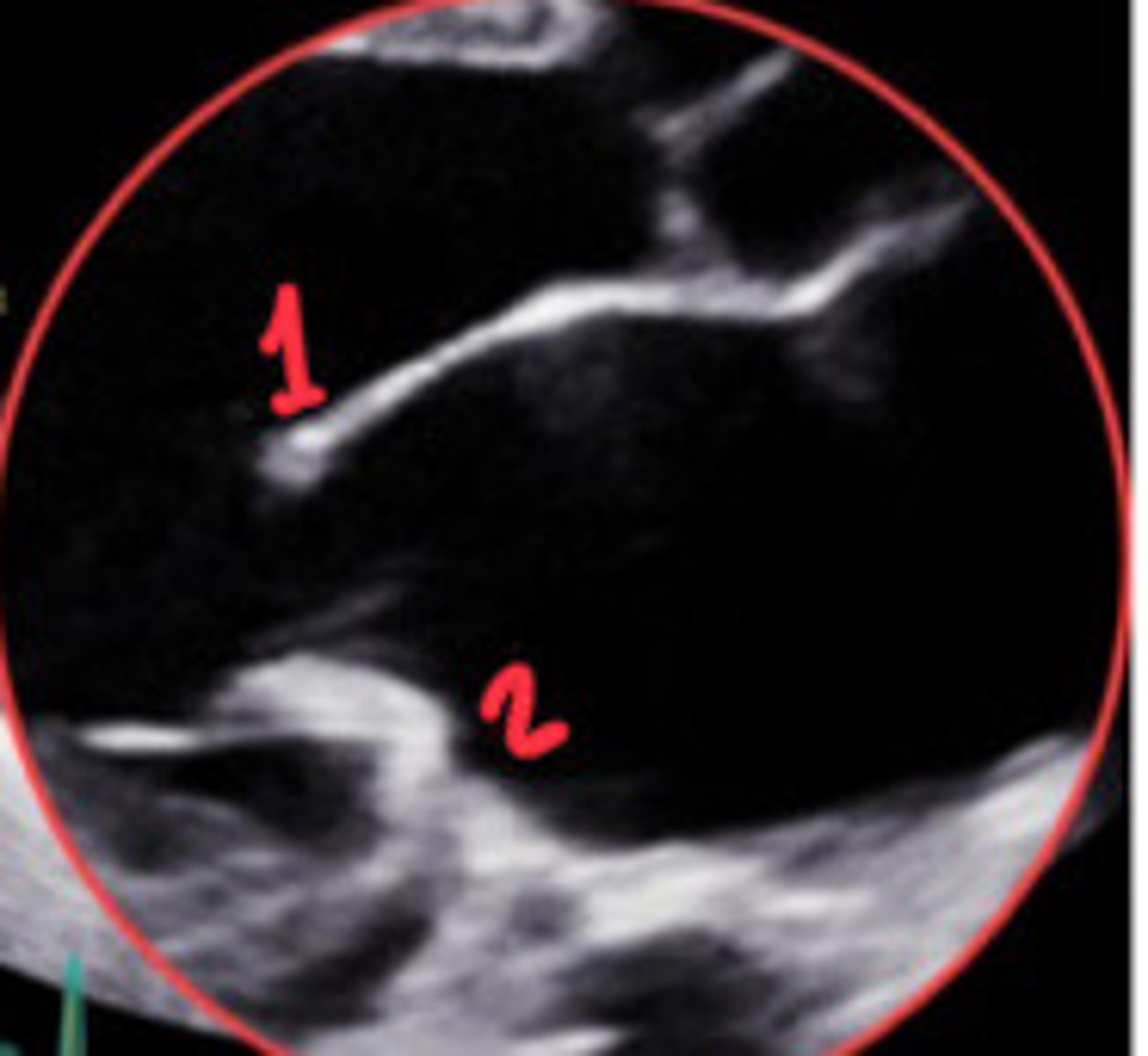
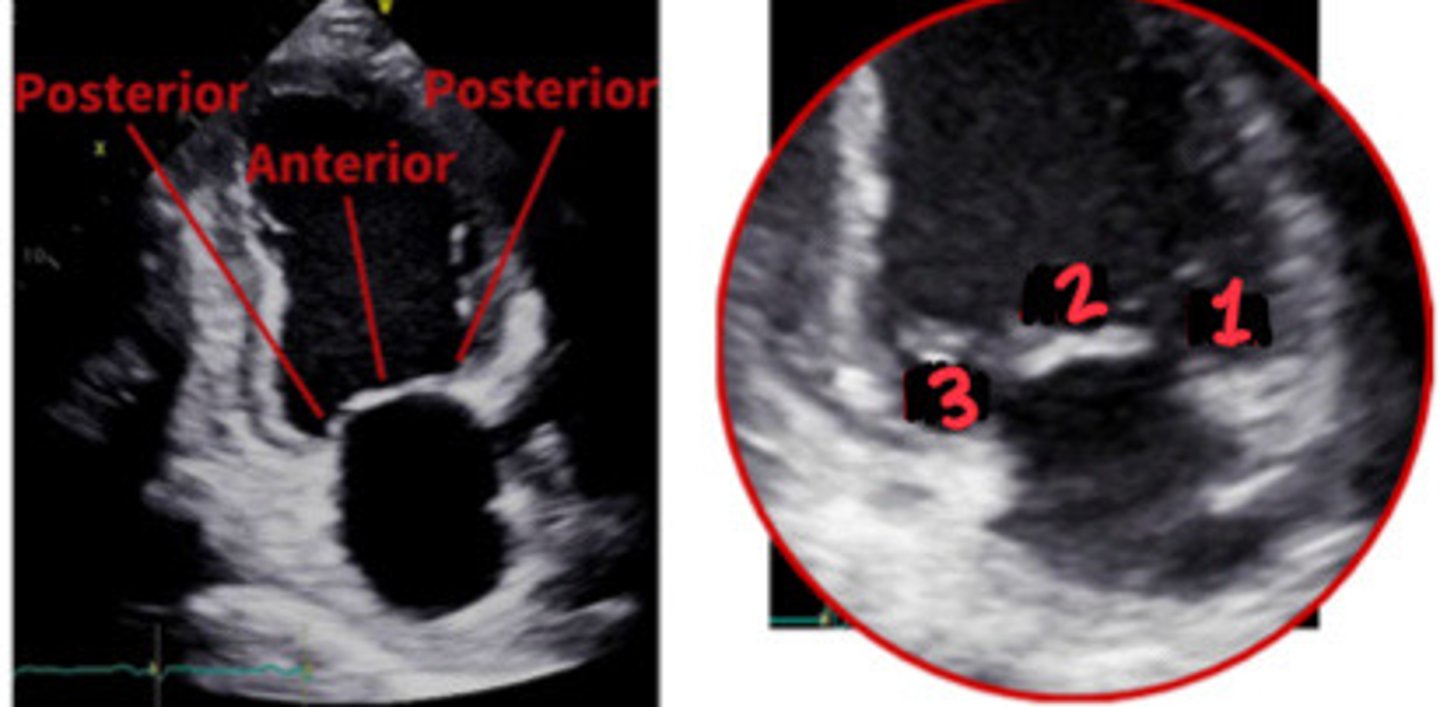
P2
What section of the MV is 2
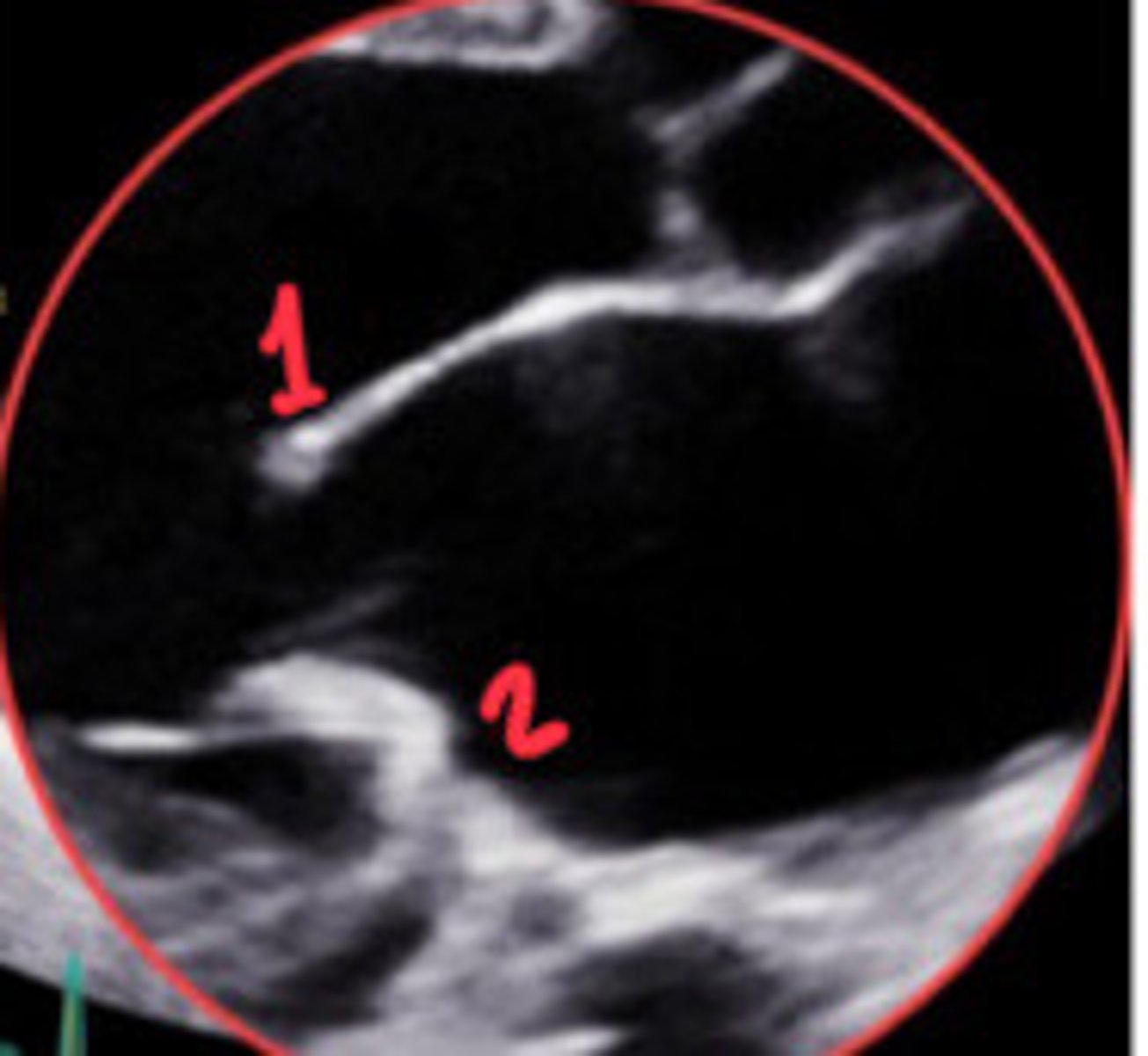
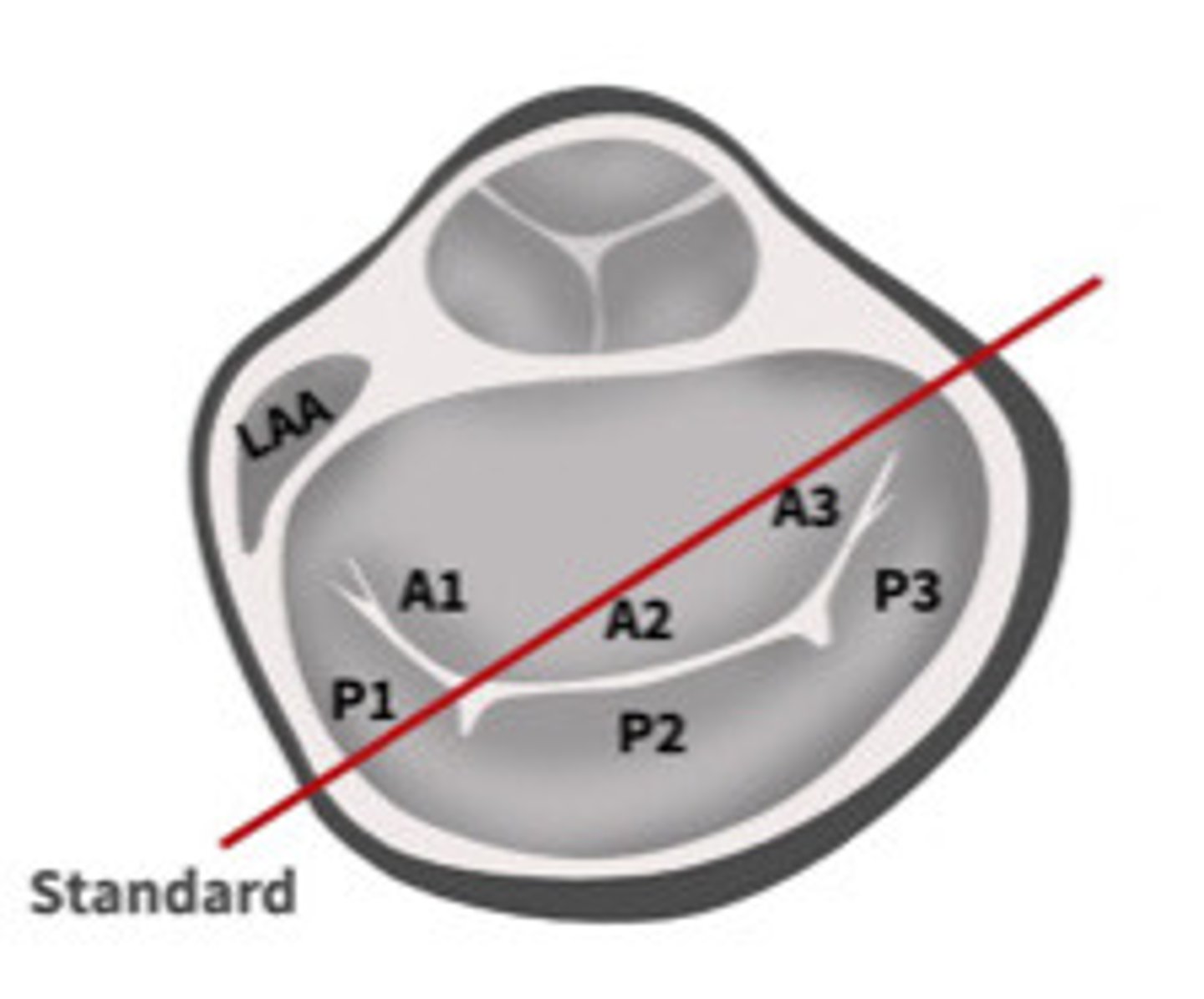
P1
What section of the MV is 1
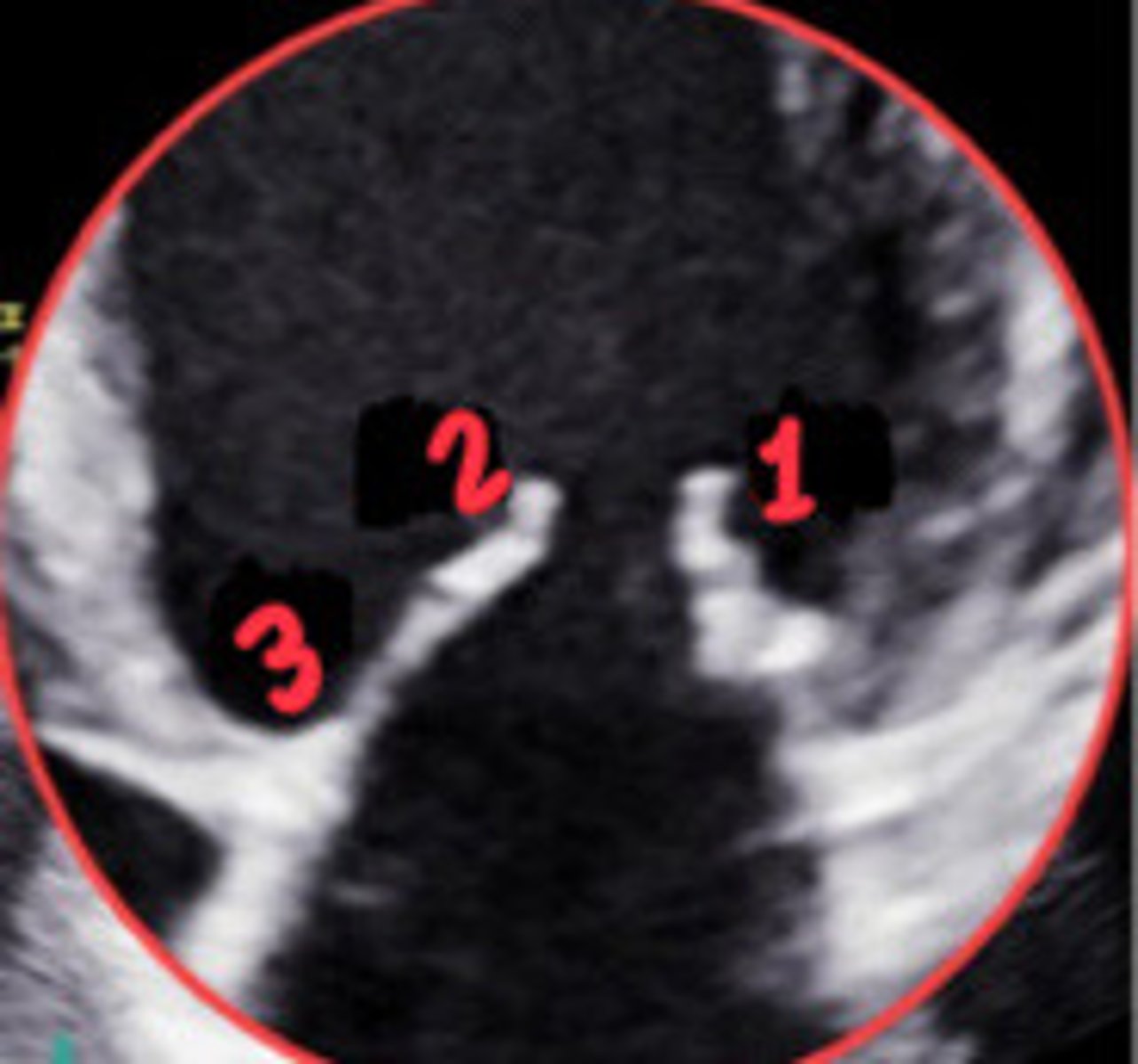
A2
What section of the MV is 2
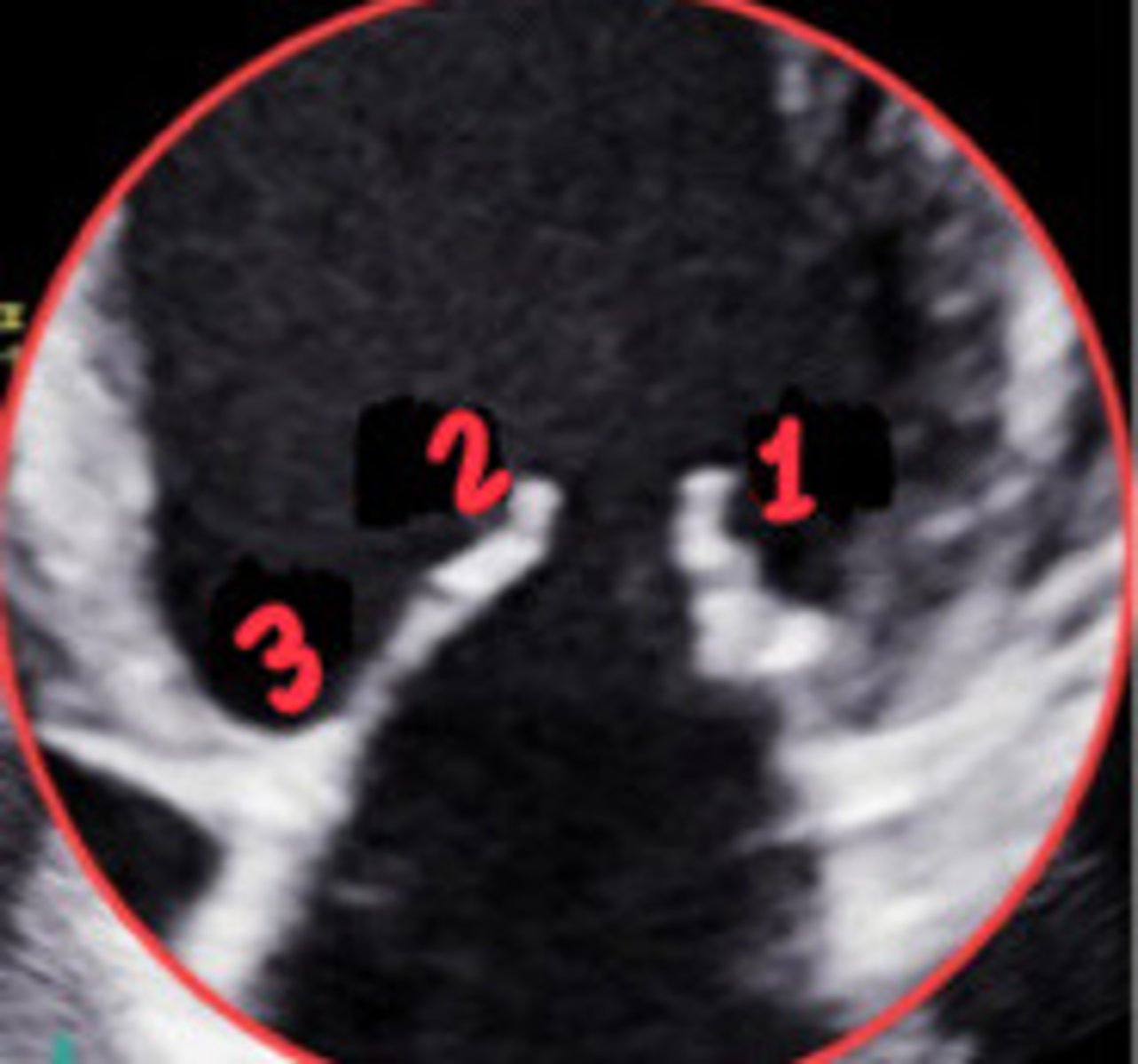
A3
What section of the MV is 3
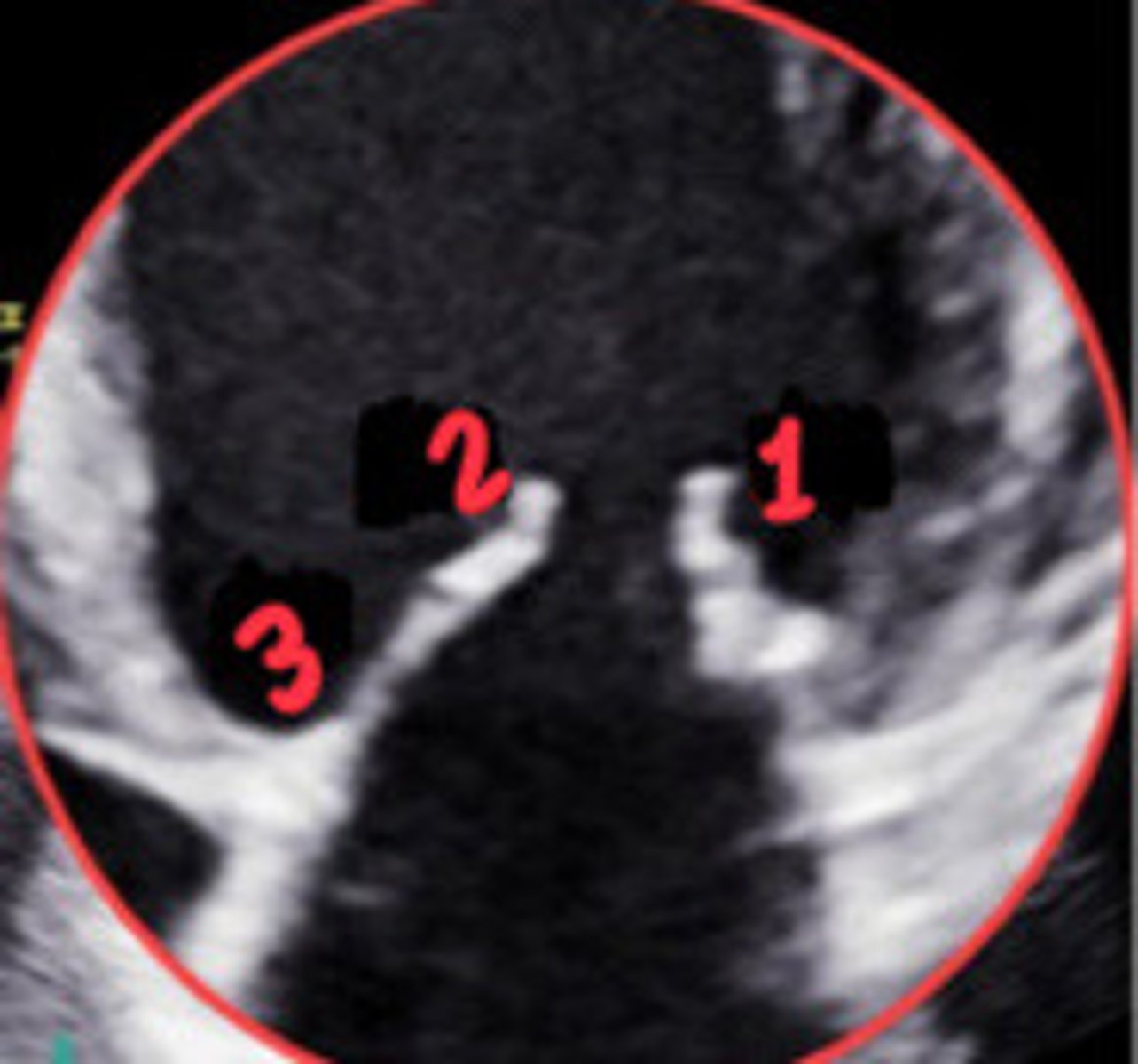
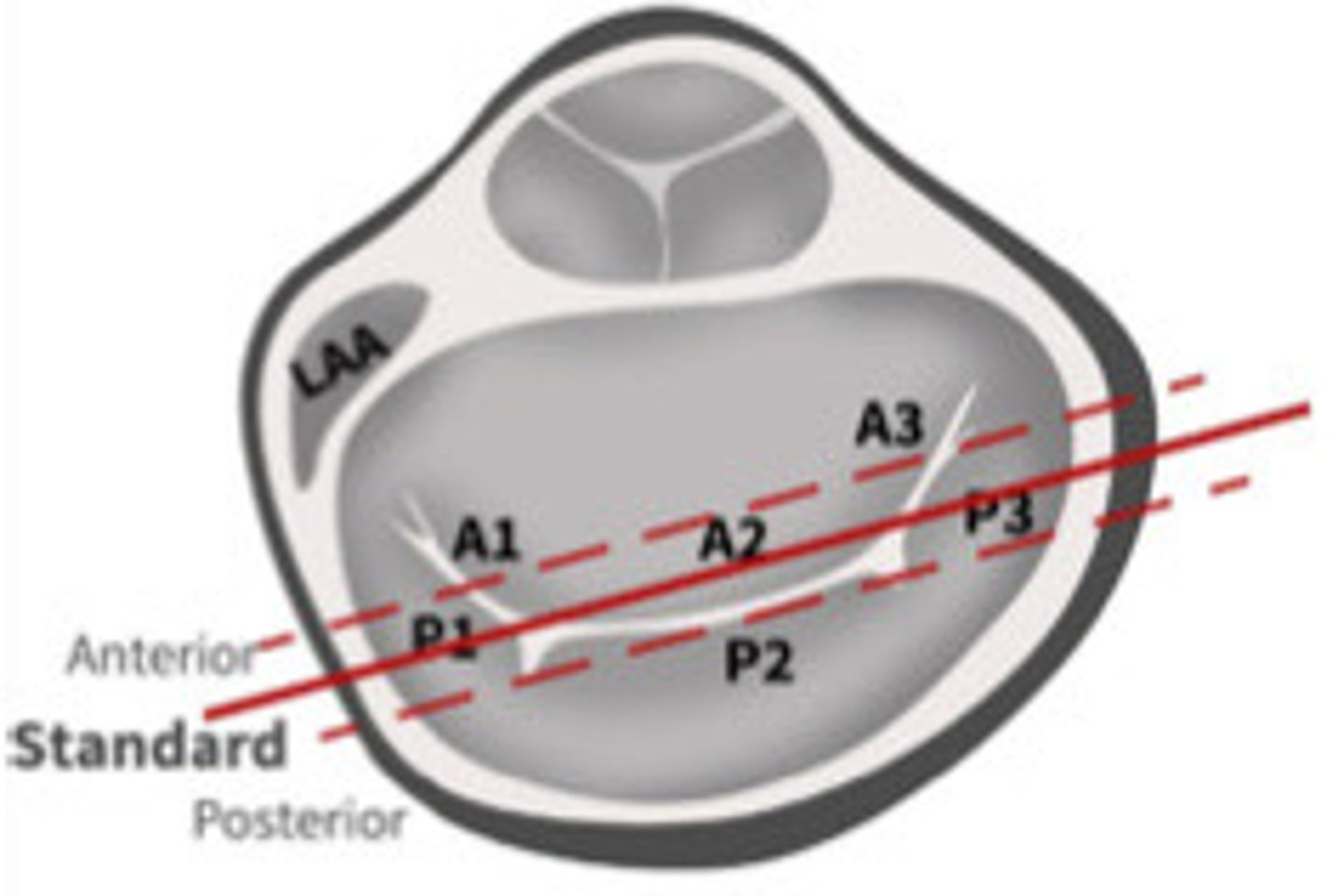
P1
What section of the MV is 1
A2
What section of the MV is 2
P3
What section of the MV is 3
PLAX
What view is represented by the line
A4C
What view is represented by the line
A2C
What view is represented by the line
Backward flow of blood from LV to the LA during systole
Define MR
During systole through both isovolumic periods
When does MR occur
True
T/F: you will see MR throughout IVRT and IVCT
Big LA
What is the first remodeling change that will occur with MR
Eccentric
What type of hypertrophy will result from chronic MR
Increase in LA vol leads to LAE which will accommodate the extra volume at a lower pressure
Describe the changes that happen with chronic compensated MR
Remains increased until many years later when it fails and decreases
What is the LV EF like with chronic compensated MR
Starling's Law
What law predicts that that LV EF will increases from an increase LA vol
Prolonged LVVO damages the muscle fibres in the LV when it fails and EF drops
Describe what chrnoic decompensated MR is
Decreased
In chronic decompensated MR is SV decreased or increased
Increases
In chronic decompensated MR is LVEDP and LAP decreased or increases
Eccentric
What type of hypertrophy do we expect with chronic decompensated MR
False
T/F: EF is still a good marker of systolic function with chronic decompensated MR
Because 30-50% of the SV us going back into the LA
Why is EF not a good marker of systolic function for decompensated MR
Dp/Dt method
What method should we use instead to measure the systolic function with decompensated MR
Acute MI trauma
What are the two main causes of acute MR
Myocardial infarction
What does MI stand for
Torn leaflet, chordae or pap muscle
What are some examples of trauma to the MV apparatus
LVVO
What does accute MR cause
No time to dilate so pressure increases (LAP) which backs up into the pulmonary and then further results in CHF
Describe how acute MR affects the LA
Forward SV decreases (but total SV increases) which results in tachycardia. As well, afterload decreases which increases the EF
Explain how acute MR affects the LV
Tachycardia
What can the changes to the LV from acute MR result in
Dyspnea, CHF symptoms, palpitations
What are the main three signs of MR
Fatigue and low exercise tolerance
What are some other signs of MR
Cardiomegaly and pulmonary venous congestion
What are 2 signs from a chest X-ray that may indicate MR
LVH, a-fib, murmur
What are some other signs of MR
Soft blowing at apex
What murmur is associated with MR
A-fib
What arrhythmia is associated with MR
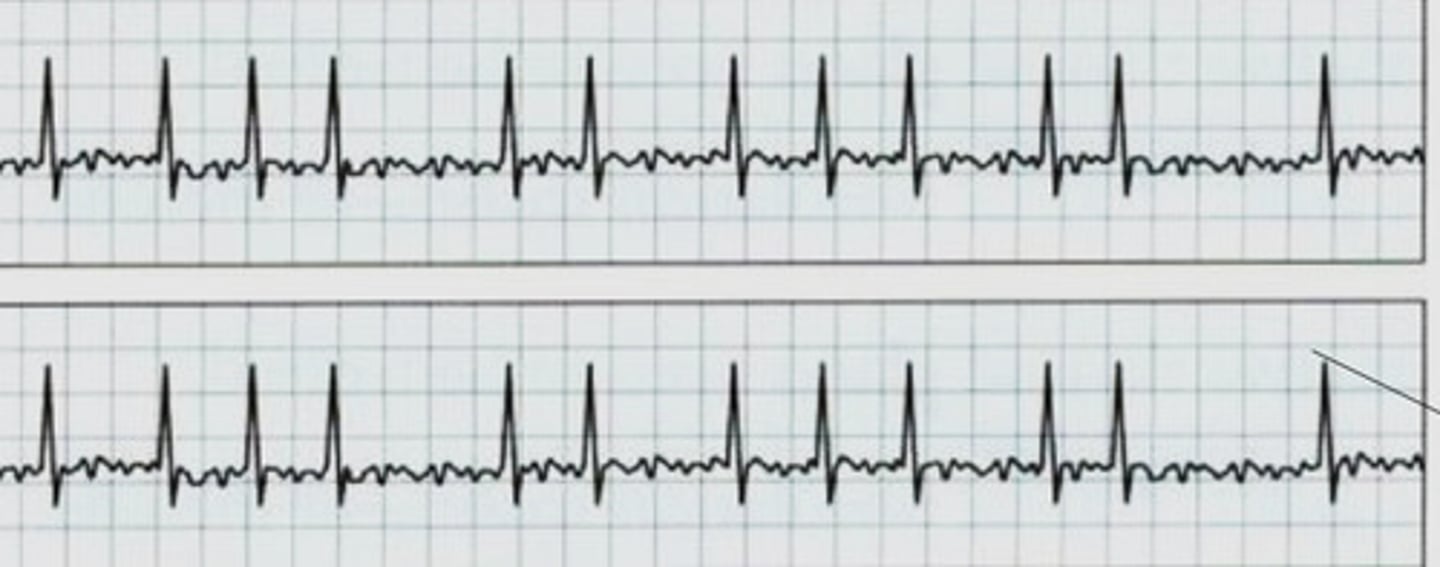
A-fib
What rhythm is this
Assess MV in 2D, determine etiology, assess LA/LV size and systolic function, estimate RVSP, estimate severity of the regurge
What are the 5 main steps in assessing MR
Thickening, movement, valve lesions
What are we looking for when assess the MV in 2D
Myxomatous or rheumatic
What may cause thickening of the MV leaflets
Bowing, prolapse, tenting/doming
What are some abnormal MV movements that can be associated with MR
MAC, endocarditis, thrombus, masses
What are some examples of valve lesions in the MV
Organic
What is another term for primary valve disease
Issues related to MV apparatus, either congenital or acquired
What is organic causes of MR
Functional
What is another term for secondary valve disease
Anything causing annular dilatation
What is functional causes of MR
Cardiomyopathies, CAD/decreases systolic function
What are some examples of functional/secondary MR causes
Prosthetic valves
What is another possible cause of MR
Perfectly aligned
Leaflets of the MV need to be ___________ ________ in order to stop any regurgitation
Malformed, torn, or degenerated
What leaflets abnormalities result in poor coaptation
>100mmHg PG
What is the PG between the LV and LA
Elongated, maldeveloped, or ruptured
What are some chordae tendinae abnormalities that can cause MR
Over 120
How many chordae tendinae's does the MV have
True
T/F: inflammation (rheumatic), calcification and endocarditis may affect the charade tendinae in addition to the valve
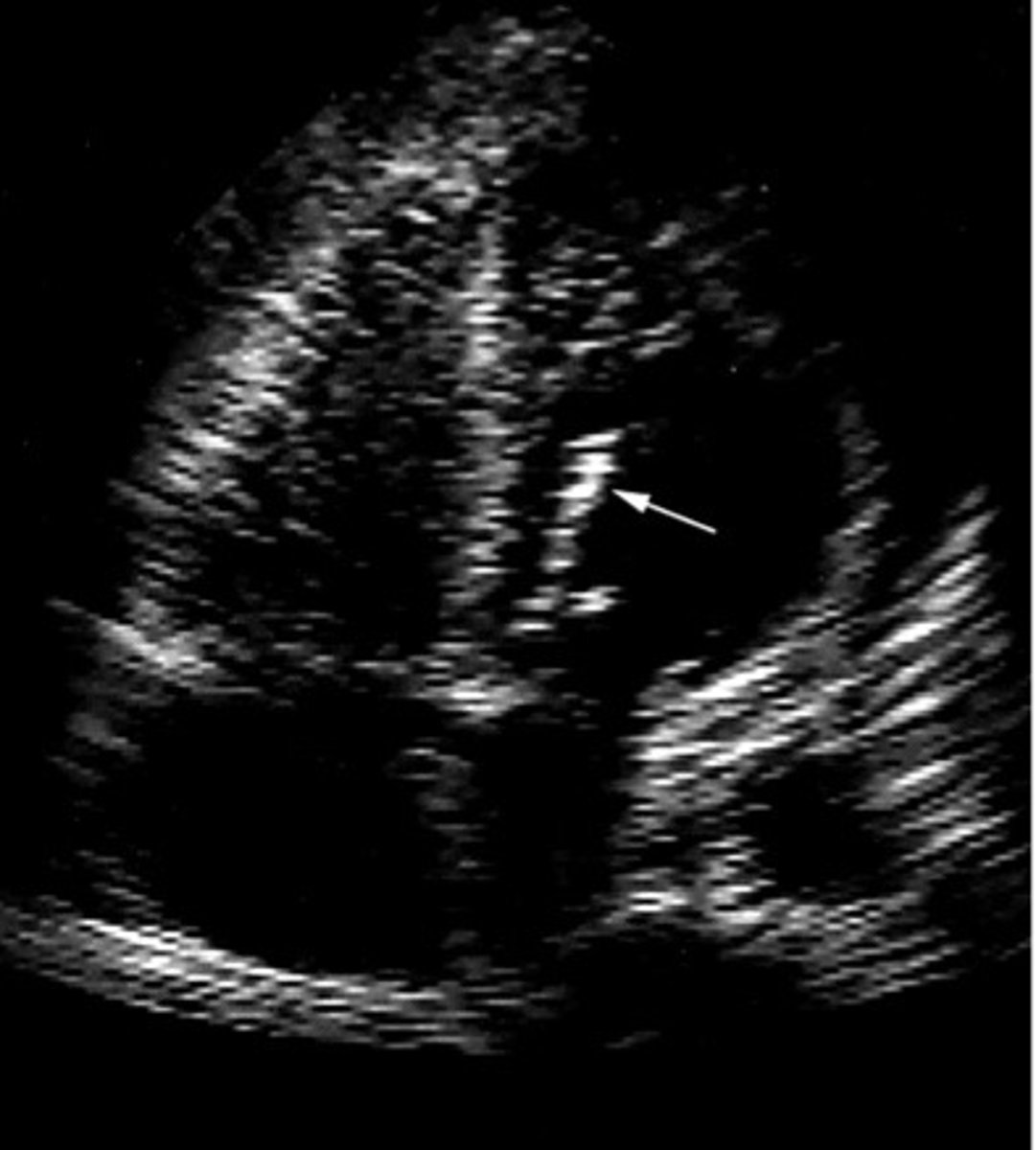
Calcific chordae tendinae
What is represented by this image
MVP, cleft MV, chordal rupture, flail MV, MAC, LV dilatation, Masses
List 7 examples of MR etiology
Mitral valve prolapse
What does MVP stand for
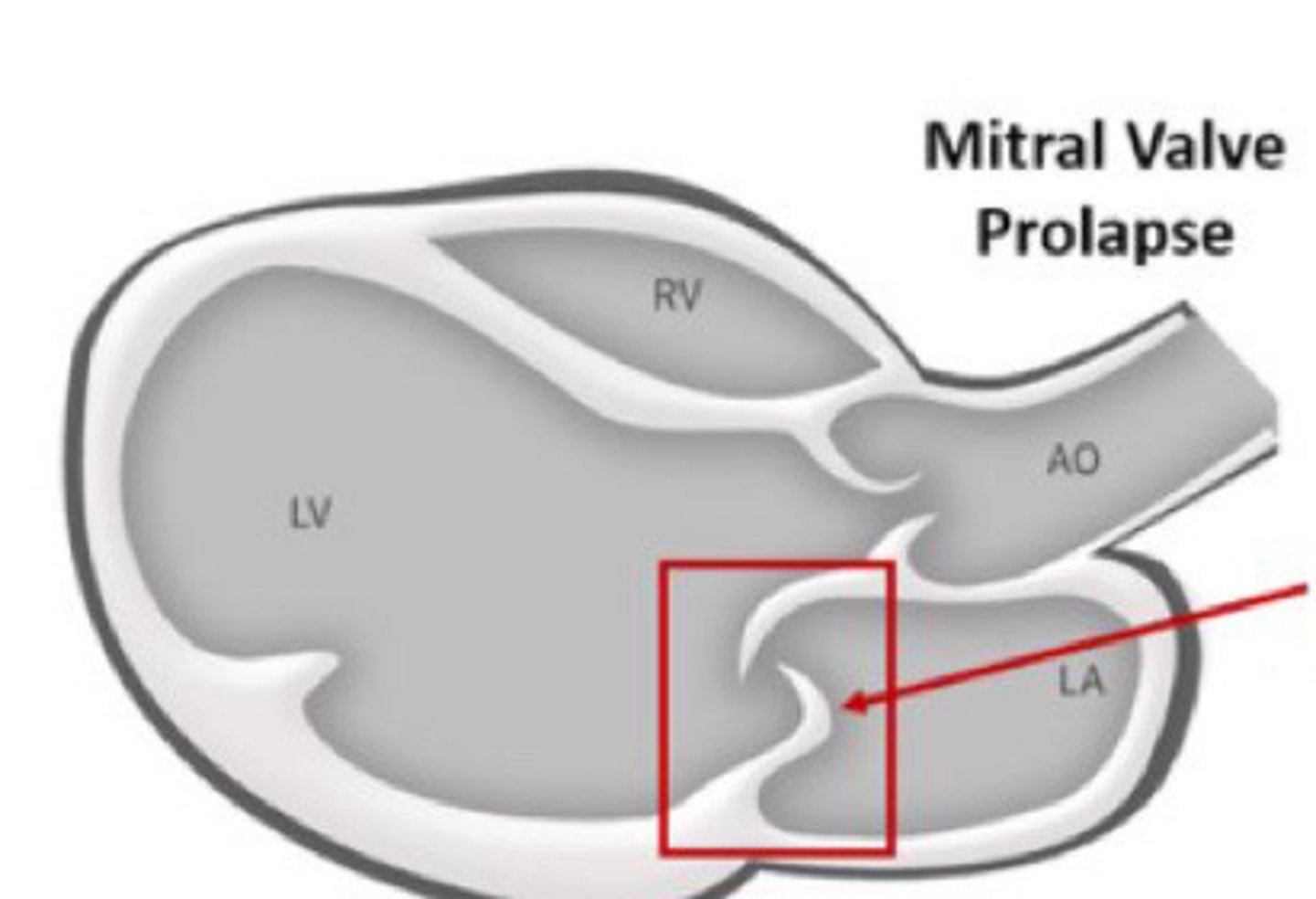
Systolic bowing of the bellow of the MV leaflets in systole into the LA
What is mitral valve prolapse
>2mm
How far into the LA does the belly of the MV have to go into the LA to be considered MVP
The motion of a prolapsed MV bowing into LA
What does this image represent
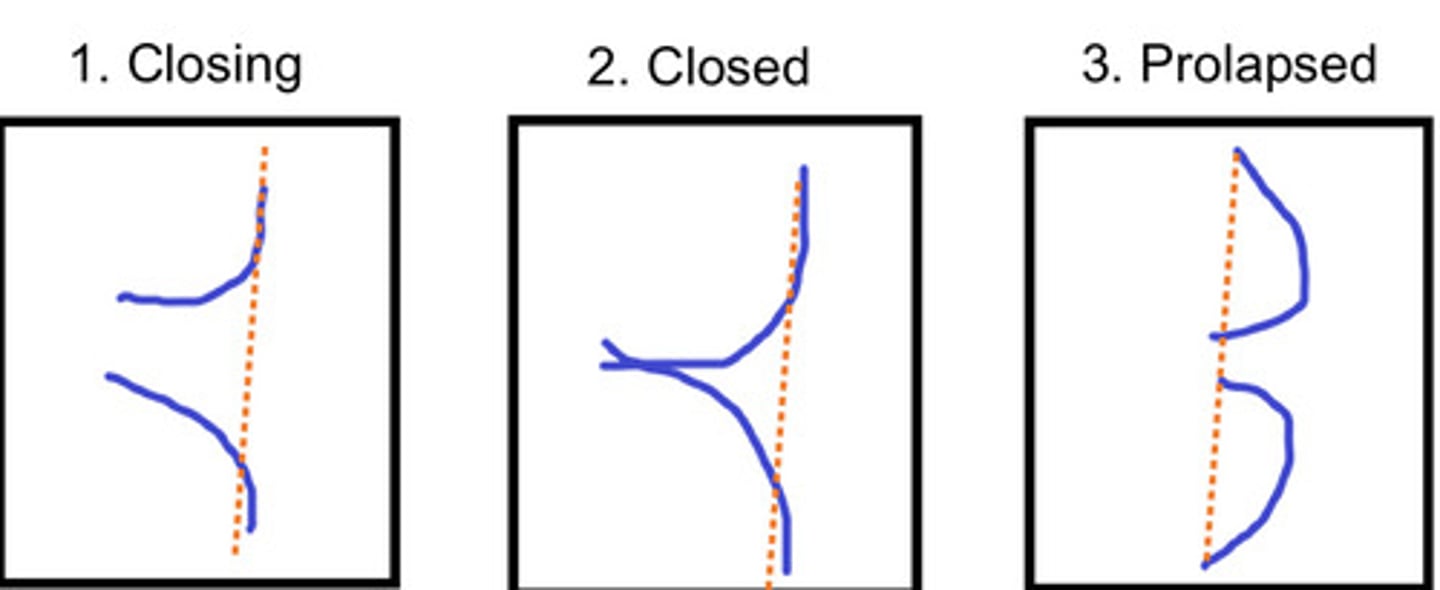
Systole (while closing)
What does MVP occur
Because the leaflet edges no longer coapt
Why does MVP lead to MR
No, if one or both leaflets prolapse it is considered MVP
Does both MV leaflets have to bow back to be considered MVP
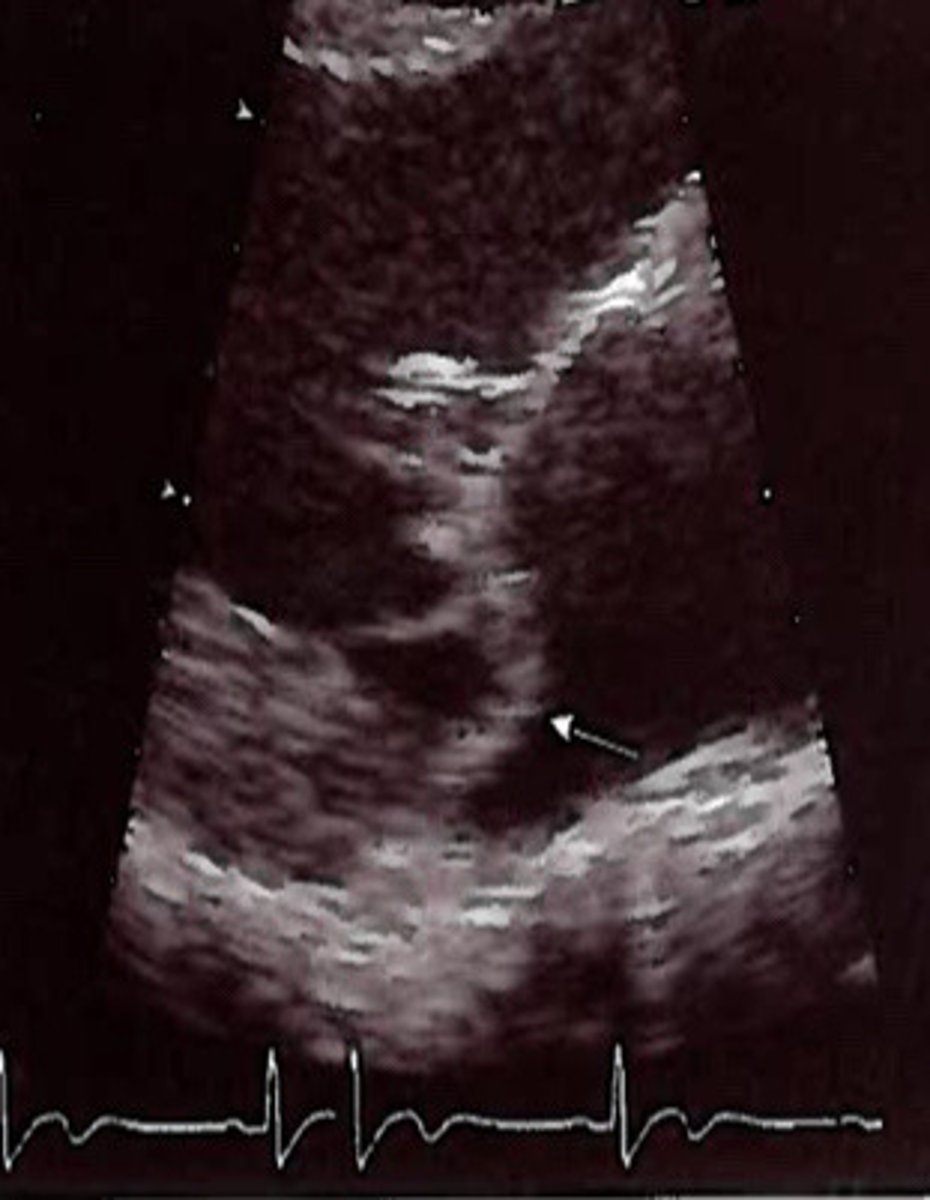
PMVL bowing back into the LA from MVP
What is represented by this image
PMVL bowing back into the LA from MVO
What is represented by this image
Myxomatous
MVP is a type of ___________________ valve disease (thickening)
Mid-systolic click
What murmur may indicate a MVP
Females
Is MVP more common in males or females
3:1
What is the ratio of F:M for MVP
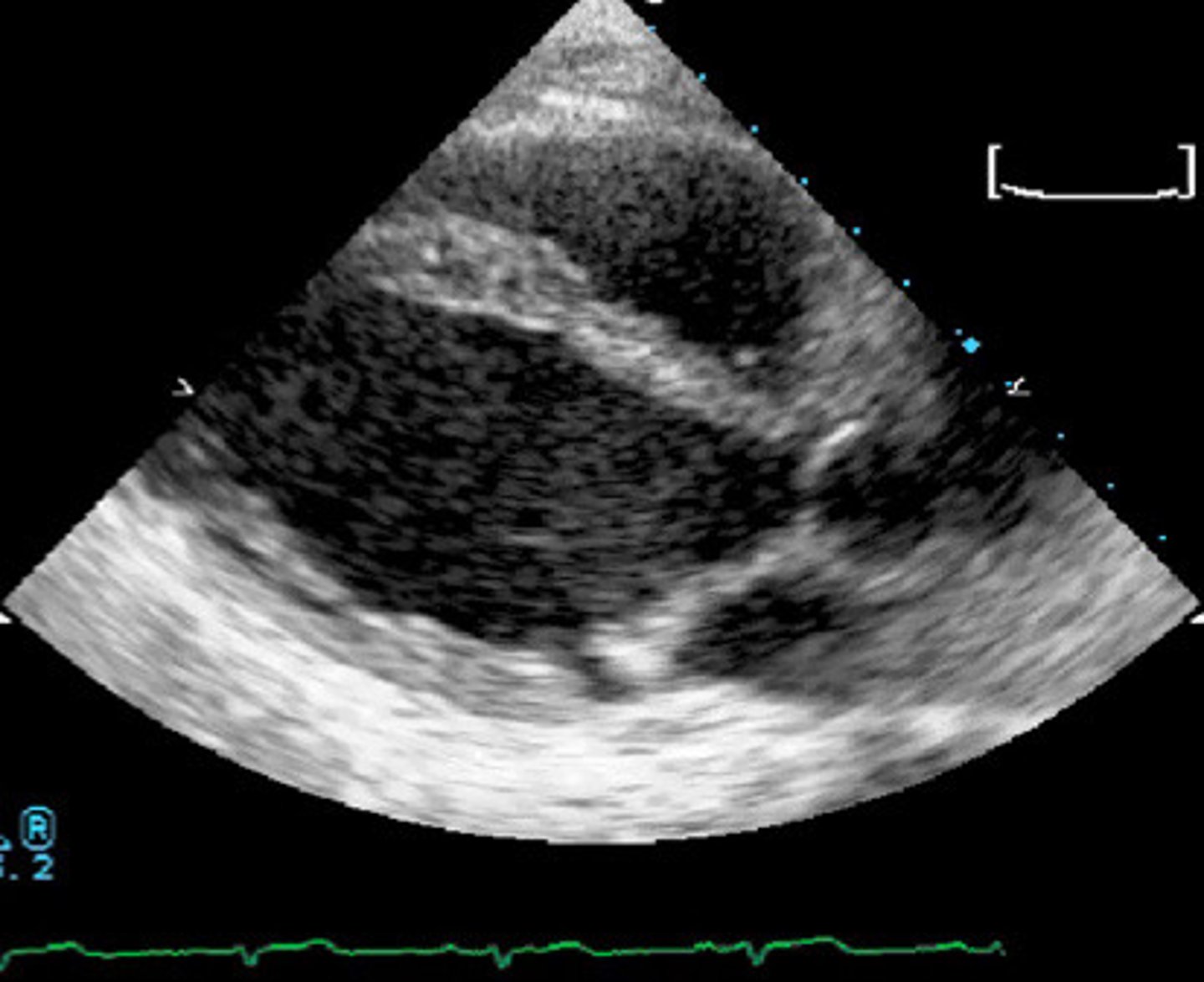
Myxomatous MV with bowing of AMVL
What is represented by this image
Connective tissue disorders
MVP has a genetic association with:
Marian or Ehler-Danilo's Syndrome
What are two examples of connective tissue disorder that may be associated with MVP
Chordal rupture, bacterial endocarditis, arrhythmias, MVP
What are patients with connective tissues disorders prone to
2-5%
What percentage of the general population has a connective tissue disorder
Tall, slender build sometimes with pet us excavatum
Describe the general appearance of someone with a connective tissue disorder
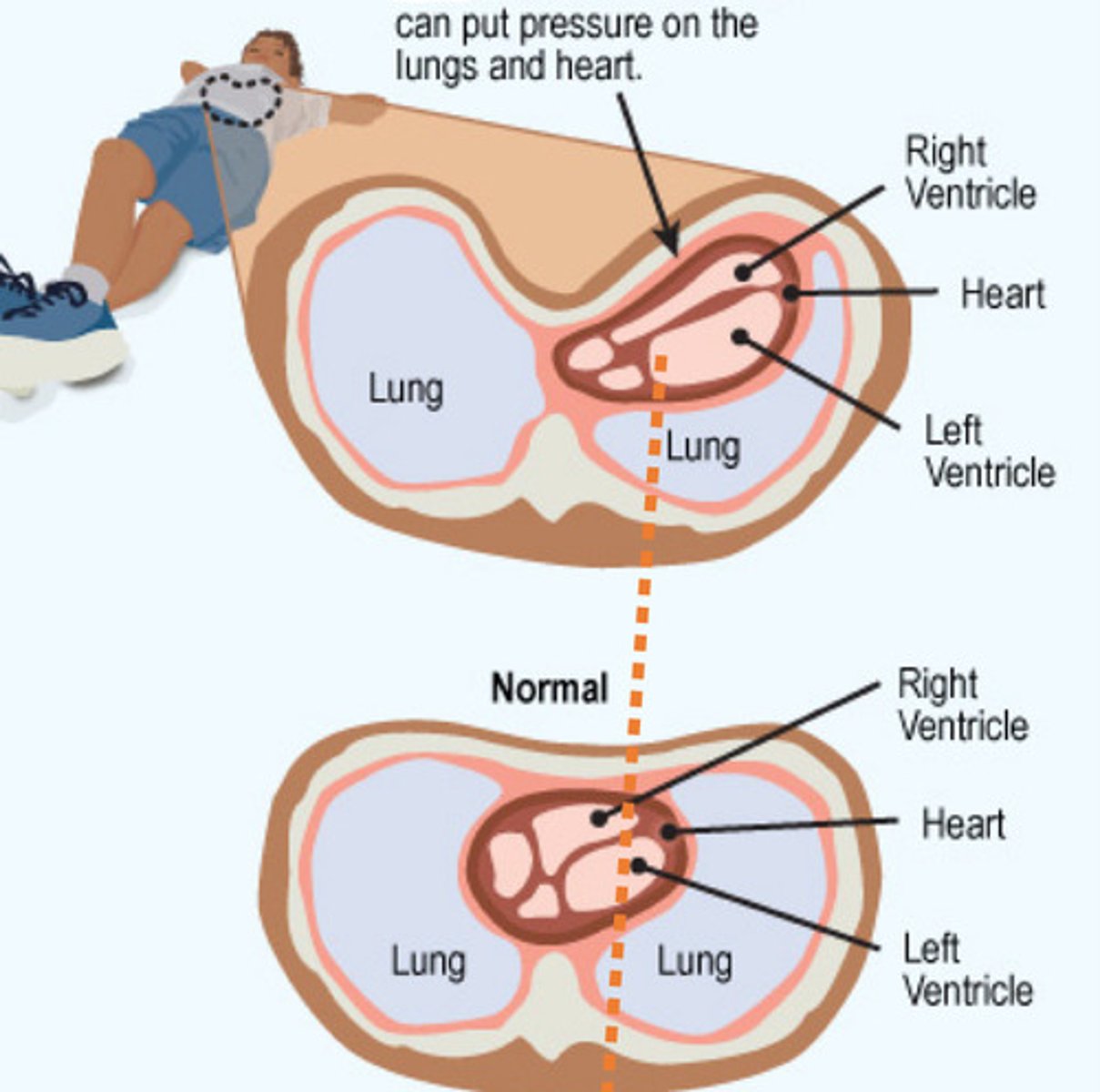
Congenital deformation of the chest wall that causes several ribs and sternum to grow inwardly
What is pectus excavatum
Marfan Syndrome
What is pectus excavatum syndrome associated with
Pectus excavatum
What is demonstrated by this image
True
T/F: patients that have pectus excavatum are very difficult scans for echo
PLAX zoom
What view do we always measure the bowing of the MVP to determine if it is a true MVP
A4C give false +
Why do we not measure the bowing of a MVP in A4C
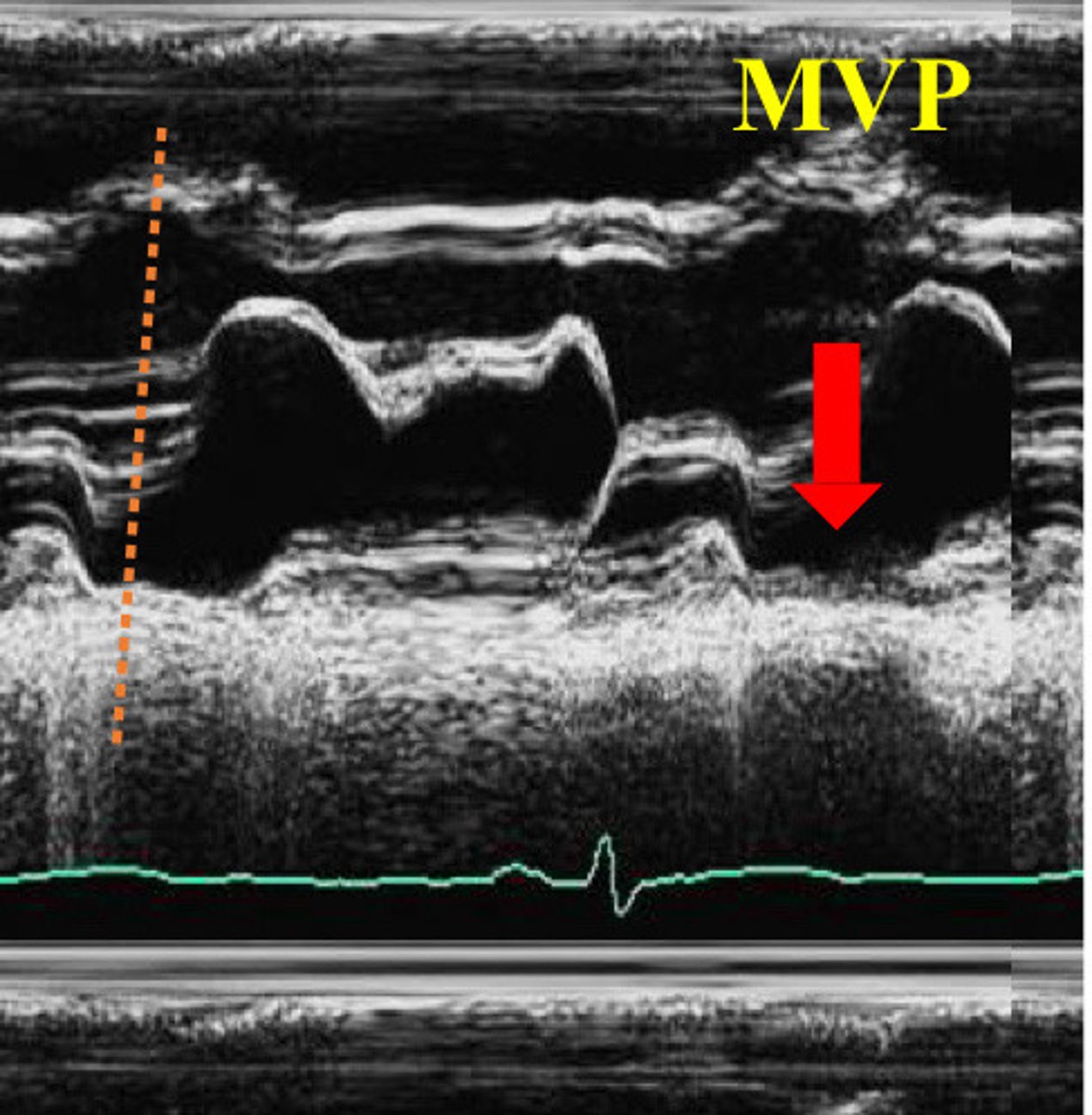
Posterior displacement of the prolapsing leaflet(s) in systole (near end of T wave of ECG)
Describe the findings of this image
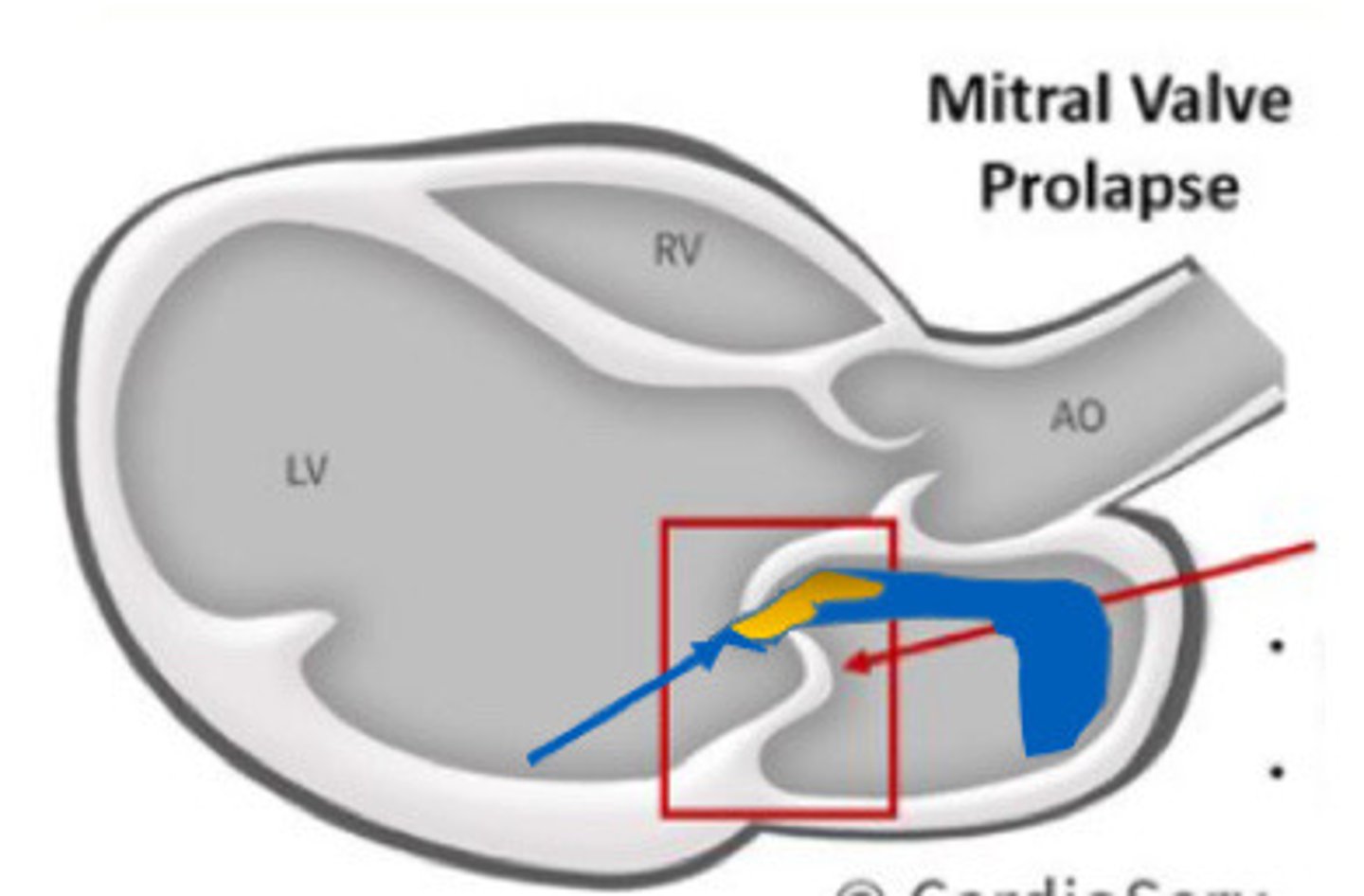
Opposite direction
How will the MR jet be angled if only one MV leaflet is prolapsed
MR jet angled in the opposite direction of the single prolapsed leaflet
What is this image demonstrating
Slit-like defect in one of the MV leaflets
What is a cleft MV
Rare
Is a cleft mitral valve rare or common
AMVL
What leaflets does the cleft usually occur on
Thickened
If a patient has a cleft MV, the MV may also be ___________