MacroTheory- Chapter 10 (HW based flashcards)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
The main difference between the classical IS-LM model and the Keynesian IS-LM model is that
In the classical model, prices are assumed to adjust quickly to restore equilibrium, while in the Keynesian model, prices are slow to adjust to restore equilibrium.
The main components that any theory of the business cycle must contain or describe are
A specification of the types of shocks affecting the economy and a model of the macroeconomy that explains how the economy responds to such shocks.
In the real business cycle theory, the primary source of cyclical fluctuations is
productivity shocks
The model of the macroeconomy that is used in the real business cycle theory is
The classical IS-LM model that assumes that prices adjust quickly to restore equilibrium
The real business cycle theory can successfully explain all of the following major facts of the business cycle EXCEPT:
Identifying the productivity shocks that have caused business cycle fluctuations.
In terms of Solow’s Residual the most common measure of productivity shocks is
Strongly procyclical
Which of the following does not cause a change in the Solow Residual?
A change in expectations
What are the factors that could cause a change in the Solow residual ?
A change in the capital utilization rate
A change in the total factor productivity
A change in the labor utilization rate
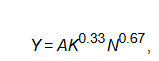
The growth rate of Solow’s residual
is equal to growth rate in productivity as measured by the parameter A
The discovery of a new technology increases the expected future marginal product of capital- how does this affect the FE line and LM curve?
The FE line and LM curve will not shift due to the new technology.
How does the discovery of a new technology that increases the MPKf affect the IS curve and AD curve? (In the classic model with no misperceptions)
The IS curve and AD curve will both shift up and to the right.
What would be the effects on general equilibrium in the economy due to an increase MPKf ?
Employment is unchanged
Output is unchanged
The price level increases
The real interest rate increases
Consumption decreases
Investment increases
Under the misperceptions theory, an increase in MPKf causes all of the following in general equilibrium except that
The SRAS and LRAS curve do not shift, the AD curve shifts up and to the right and the price level increases but output remains unchanged at the full employment level
Under misperceptions theory, an increase in MPKf causes all of the following in general equilibrium
-Producers misperceive the change in the price level as a change in relative prices and increase in labor demand and output
-Both the price level and output increase
-the SRAS and LRAS curve do not shift, the AD curve shifts up and to the right and the economy moves along the SRAS curve
The recognition lag means that
it takes time for policymakers to realize that a policy change is needed
Fiscal policy may not be effective because of the time it takes for policymakers to enact a change in the policy, which is known as the
Legislative Lag
In the classical model, a temporary decrease in government purchases causes people to ___ their labor supply because the current or future taxes are expected to ___
decrease, decrease
In the classical model in general equilibrium, a temporary decrease in government purchases leads to a ___ in output and ____ in employment
decrease, increase
In the classical model, a temporary decrease in government purchases causes the IS curve and the FE line to shift to the left. In general equilibrium, if the IS curve shifts to the left more than the FE line does, the real interest rate will be ___ before the shock.
lower than
In the classical model, a temporary decrease in government purchases causes the IS curve and the FE line to shift to the left. In general equilibrium, if the IS curve shifts to the left more than the FE line does, the price level will be ___ before the shock
lower than
In the classical model, money is neutral. This seems to be inconsistent with the business cycle fact that:
Money is a leading, procyclical variable
In order to explain the link between money growth and economic expansion, real business cycle theorists use the concept of:
reverse causation, in which money supply increases in projection of economic expansion
Which of the following historical facts of monetary policy indicates that reverse causation alone cannot explain the entire relationship between money and output?
Monetary changes have often had an independent origin; they have not been simply a reflection of changes in economic activity.
According to the misperceptions theory, producers are unable to determine whether an increase in prices is an increase in relative prices or an increase in the general price level. This inability generates:
An upward sloping short run aggregate supply curve.
The misperceptions theory concludes that:
in the short run, anticipated money changes are neutral and unanticipated monetary changes are not neutral
Under the rational expectations hypothesis..
a central bank cannot surprise the public systematically, and hence cannot use monetary policy to stabilize output .
In the misperceptions theory, unanticipated changes in the money supply aren’t neutral in the short run because….
producers are fooled into producing more or less output based on the unanticipated changes in prices.
According to the misperceptions theory, what effect does an increase in the price level have on the amount of output supplied by producers?
it fools producers of goods into producing more
Does it matter whether the increase in the price level was expected, for an increase in price level to increase output?
The change in prices must be unexpected