3- WBC values
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
purpose of WBC count in dentistry
WBC disorders can influence clinical decision since WBCs are the primary defense against infection
pts w/ life threatening WBC disorders should not receive dental tx w/o physician consult
2 categories of leukocytes (WBCs)
polymorphonucleocytes
mononucleocytes
what are the 2 types of polymorphonucleocytes
agranulocytes: monocytes
granulocytes: neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils
M N B E
what are the 2 types of mononucleocytes
agranulocytes: dendritic cells
granulocytes: mast cells, macrophages, NK cells
D M M N
normal range of circulating WBCs in adults
4400-110,000 μL
what’s ANC
absolute neutrophil count
normal range for ANC (absolute neutrophil count)
1500-7200 cells/mm3
ANC lower than 1500 mm3 indicates
increased risk for infection
ANC lower than 500 mm3 indicates
severe neutropenia → dental tx CANNOT be performed
how do you calculate ANC
WBC count x (neutrophil % + bands %)/100
bands = % of immature neutrophils
leukemia vs. lymphoma
leukemia: originates in bone marrow + spreads through blood
lymphoma: originates in lymph nodes/spleen + spreads through lymphatic system
both affect lymphocytes
2 types of leukemia
myeloproliferative
lymphoproliferative
2 types of myeloproliferative disorders
acute myeloid leukemia: immature malignant myeloid cells
chronic myeloid leukemia: mature malignant myeloid cells
2 types of lymphoproliferative disorders
acute lymphoblastic leukemia: immature malignant lymphoid cells
chronic lymphoblastic leukemia: mature malignant lymphoid cells
2 types of lymphoma
Hodgkin’s: malignant B lymphocytes, primarily in lymph nodes
Non-Hodgkin’s: malignant B or T cells, many types/locations- mostly B cells
Burkitt lymphoma: type of non-Hodgkin’s B cell lymphoma involving bone + lymph nodes
how does Hodgkin’s lymphoma first manifest in the body
painless group of firm, nontender, enlarged lymph nodes
usually located: mediastinal, neck, underarm, groin nodes
symptoms of Hodgkin’s lymphoma
fever
fatigue
weight loss
night sweats
how does non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma first manifest in the body
multifocal enlarged painless lymph nodes
T/F: 20-40% of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma pts develop enlargements outside of lymph nodes
true
symptoms of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma
fever
weight loss
malaise
sweating
tender lymphadenopathy
abdominal/chest pain
what’s the most common lymphoma of childhood
Burkitt lymphoma
3 types of Burkitt lymphoma
endemic
sporadic
immunodeficiency associated
where do enlargements occur in Burkitt lymphoma
mostly at extra-nodal sites (outside of lymph nodes)
describe the tumor growth rate of Burkitt lymphoma
they can double in size every 3 days → airway, alimentary canal, vasculature obstruction
describe the location of enlargements in endemic Burkitt lymphoma
usually in jaw, abdominal organs, kidneys, ovaries, adrenal glands
jaw involvement is common in pts younger than 5
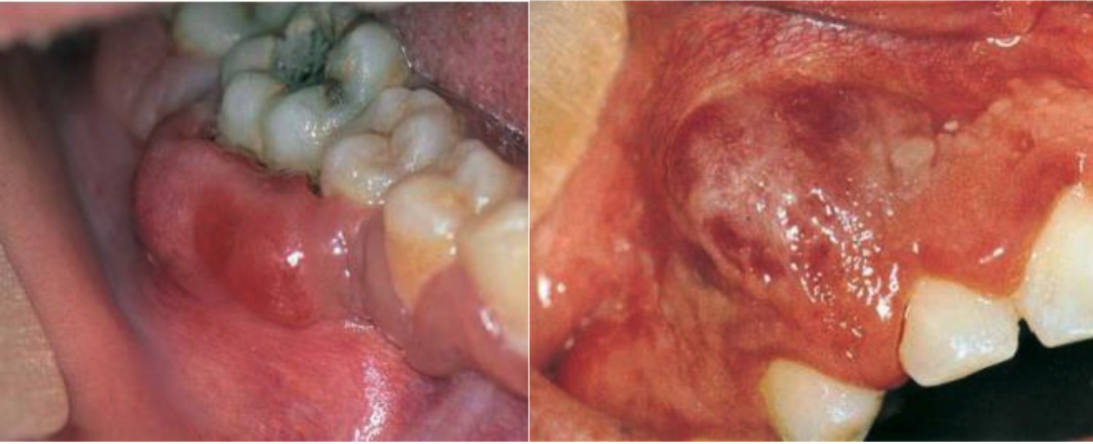
describe the oral manifestation of endemic Burkitt lymphoma
rapidly expanding tumor in posterior of maxilla/mandible w/ 50-70% of cases w/ jaw lesions → displacing adjacent teeth → resulting in mobile + abnormally positioned teeth
symptoms of oral manifestation of endemic Burkitt lymphoma
pain
paresthesia (tingling/numbness)
describe the radiograph of an endemic Burkitt lymphoma of the jaw
the tumor produces an osteolytic lesion w/ poorly demarcated margins, erosion of the cortical plate, + soft tissue involvement
what’s multiple myeloma
malignant plasma cells