[BIO 120.12] Final Exam - Exercises 3-4
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
TRUE
T/F: Endospores are metabolically dormant
FALSE
T/F: Endospores are metabolically vegetative
TRUE
T/F: Endospores function only for protection and survival, but not for metabolism and reproduction
FALSE
T/F: Endospores function for protection, survival, and metabolism, but not for reproduction
FALSE
T/F: Endospores function for protection and reproduction, but not for metabolism
Endospore
Spore that develops within the parent bacterial cell (vegetative cell/sporangium)
TRUE
T/F: Endospores are chemically more complex than the vegetative cell
FALSE
T/F: Vegetative cells are chemically more complex than the endospores
Calcium, Dipicolinic Acid
Endospores are high in what nutrients?
Heat resistant, Thick walled, Highly refractile, Resistant to physical and chemical agents
What are the 4 characteristics of endospores (heat tolerance, thickness, refraction, resistance)
TRUE
T/F: Endospores are resistant to both physical and chemical agents
FALSE
T/F: Endospores are resistant only to physical agents, but may be broken by chemical agents
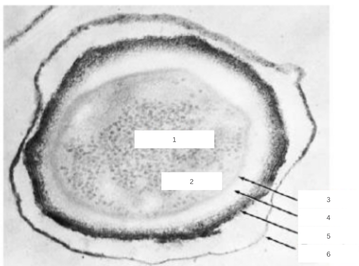
Ribosomes, Nucleoid, Core Wall, Cortex, Spore Coat, Exosporium
What are the parts of the endospore shown?
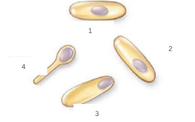
Central, Subterminal, Terminal, Swollen Sporangium
Label the endospore positions in the mother cell
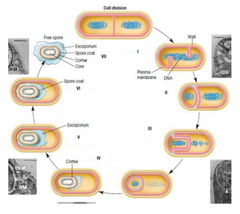
Axial filament formation, Septum formation and forespore development, Engulfment of forespore, Cortex formation, Coat Synthesis, Completion of coat synthesis + Increase in refractility and heat resistance, Lysis of sporangium + spore liberation
What are the 7 stages of endospore formation?
Schaeffer-Fulton Procedure
Endospore staining is alternatively called as?
Prepare smear → Flood with malachite green for 15 minutes → Rinse with distilled water → Cover smear with safranin for 30 seconds → Pour off excess and rinse with distilled → Observe under OIO
What are the steps for endospore staining?
Steaming helps stain permeate endospore
What is the purpose of steaming in some endospore staining procedures?
Cold Method
What method of endospore staining uses no steam?
Reduces exposure to toxic effects of malachite green
What is the purpose of the cold method?
TRUE
T/F: In the endospore staining technique, both vegetative cells and endospores are stained green during the flooding of malachite green
FALSE
T/F: In the endospore staining technique, only vegetative cells are stained green during the flooding of malachite green
TRUE
T/F: In endospore staining technique, water serves as a decolorizer to decolorize vegetative cells
FALSE
T/F: In endospore staining technique, 95% ethanol serves as a decolorizer to decolorize vegetative cells
FALSE
T/F: In endospore staining technique, water serves as a decolorizer to decolorize both vegetative cells and endospores
Safranin
What is the counterstain used in endospore staining?
Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, Clostridium botulinum, Clostridium tetani
What are 4 examples of medically important endospore forming bacteria?
Bacillus anthracis
Endospore forming bacteria that is known to be a bioterrorism agent
TRUE
T/F: Bacillus anthracis infection is often obtained through contact with infected animals
FALSE
T/F: Bacillus anthracis infection is often obtained through fecal-oral route
Bacillus cereus
Endospore forming bacteria that is a common rice contaminant
Log phase or sporulation
When does toxin production of B. cereus occur?
Localized infections, Systemic infections, Food poisoning, Food infection
What are 4 diseases that B. cereus can cause?
Clostridium botulinum
Endospore forming bacteria that can be occasionally found in feces and honey
Clostridium botulinum
A major potential agent for bioterrorism and biologic warfare
Clostridium tetani
Endospore forming bacteria that is known to cause toxemia
4-5 days to 3 weeks
How long can tetanus or toxemia last?
Self propulsion
Motility refers to movement of cells by some form of ___.
Exploit new resources, from unfavorable conditions
What are two benefits of motility?
Swarming
Multicellular surface movement powered by rotating helical flagella
Swimming
Individual movement in liquid powered by rotating flagella
Twitching
Surface movement powered by the extension and retraction of pili
Gliding
Active surface movement that does not require flagella or pili and involves focal adhesion complexes
Sliding
Passive surface translocation powered by growth and facilitated by a surfactant
Surfactant
What facilitates sliding?
Focal adhesion complexes
Gliding is unique as it involves?
Sliding
Spreading by growth
Flagella
Extremely thin, hairlike appendages for locomotion
Electron Microscope
What can be used to see flagella directly?
Swimming
What motility type is flagella helpful in?
Flagella
What bacterial appendage is useful in taxonomic identification of bacteria?
Pilus
Thin (2–10 nm in diameter) filamentous structures made of protein that extend from the surface of a cell
TRUE
T/F: Pili is typically long and only one or a few pili are present on the surface of a cell
FALSE
T/F: Pili is typically long and numerous and surface on the cell
Hanging Drop Technique, Motility Band, Flagella Staining
What are the 3 Tests for Motility
Hanging Drop Technique
Simple method to observe motility
TRUE
T/F: Hanging drop technique involves observations of living microorganisms
FALSE
T/F: Hanging drop technique involves observations of dead microorganisms
Brownian Movement
Vibration of the cell due to collision with water molecules
Brownian Movement
Oscillating and quivering movement
True Motility
Allows the cell to move in different directions
True Motility
Changes in position with respect to neighboring cells
Semi-solid medium
What kind of medium is needed if we want to do a motility band experiment?
TRUE
T/F: Motility band requires a culture medium with low agar concentration
FALSE
T/F: Motility band requires a culture medium with no agar
Allows bacteria to move away from the line of inoculation, Must be able to support growth, Low concentrations of metabolizable substrate
Why do we require a semi solid medium in motility bands?
EDTA
What substance enhances motility through its chelating action?
Zn, Cu
What heavy metals can abolish motility?
Clump on surface, leaving rest of medium clear, Growth spreads out only in one direction, Sharply differentiated edge between the growth and the agar
What are the observations for a non-motile motility band?
Move down from the surface of the medium and disperse throughout the media, Diffuse growth radiating from the stab line, Medium is slightly turbid, Growth throughout the tube
What are the observations for a motile motility band?
Thickness of flagella must be increased
In flagella staining, what must be done to observe flagella in a light microscope?
Mordants like tannic acid and potassium alum
What is used to coat flagella in flagella staining?
Staining with pararosaniline (Leifson method) or basic fuchsin (Gray method)
What are the 2 options for flagella staining?
TRUE
T/F: Flagella staining does not involve heat fixing
FALSE
T/F: As a staining technique, flagella staining involves heat fixing
Flagella is denatured by heat
Why do we not do heat fixing in flagella staining?
Taxis
Ability to sense and respond to stimuli in their environments
Osmotaxis
A response to an ionic strength gradient
Ionic strength gradient
Osmotaxis is a response to what gradient?
O2 gradient
Aerotaxis is a response to what gradient?