1.2.5 Compression
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Perceptual music shaping
Refers to the process of removing inaudible sounds in order to make a file size smaller.
e.g.
Noises at frequencies that humans cannot hear
Quiet sounds that cannot be heard over louder sounds
Compression
a method or protocol for using fewer bits to represent the original information
Lossy Compression
Reduction of file size by removing certain, redundant information from the file
The eliminated data is unrecoverable.
Tries to recreate an file without the omitted data
Much smaller file sizes but there will be some loss of quality
Lossy benefits
Means the decompressed file is not identical to the original...
...the difference is unlikely to be noticed by humans
Lossy will decrease the file size ...
... so it can be sent via e-mail/sent quickly/uses less bandwidth
Lossy Image Compression
A compression algorithm is used
Permanently deleting some data // file cannot be restored to original
Colour depth / colour palette can be reduced
Resolution can be reduced // number of pixels can be reduced
Lossy text compression
File is compressed some detail / data / quality / is lost...
... would make the text file unreadable / lose meaning or comprehension
Lossless compression
Every bit of the original data can be recovered from the compressed file.
the uncompressed image will be the same as the original with no loss of data
Works by looking for patterns in the data
Larger compressed file sizes than lossy
e.g. Run-length encoding
Lossless image compression
A compression algorithm is used
No data is removed in the compression process
An index/dictionary of pixels is created
The number of times a pixel is repeated in a row is stored
Run length encoding
Reasons to Compress data
Download/buffering times decrease
Smaller files = fewer packets = faster transmission time
Reduces traffic over the Internet
Less chance of collisions or transmission errors
Data allowances do not run out as quickly = Saves money
Voice can be transmitted fast enough to keep up with speech in a video
Saves spending more money on data storage e.g. hard drives, cloud etc
Faster to back-up data
Run Length Encoding (RLE)
Lossless compression technique
Summarises consecutive patterns of the same data
Works well with image and sound data where data could be repeated many times
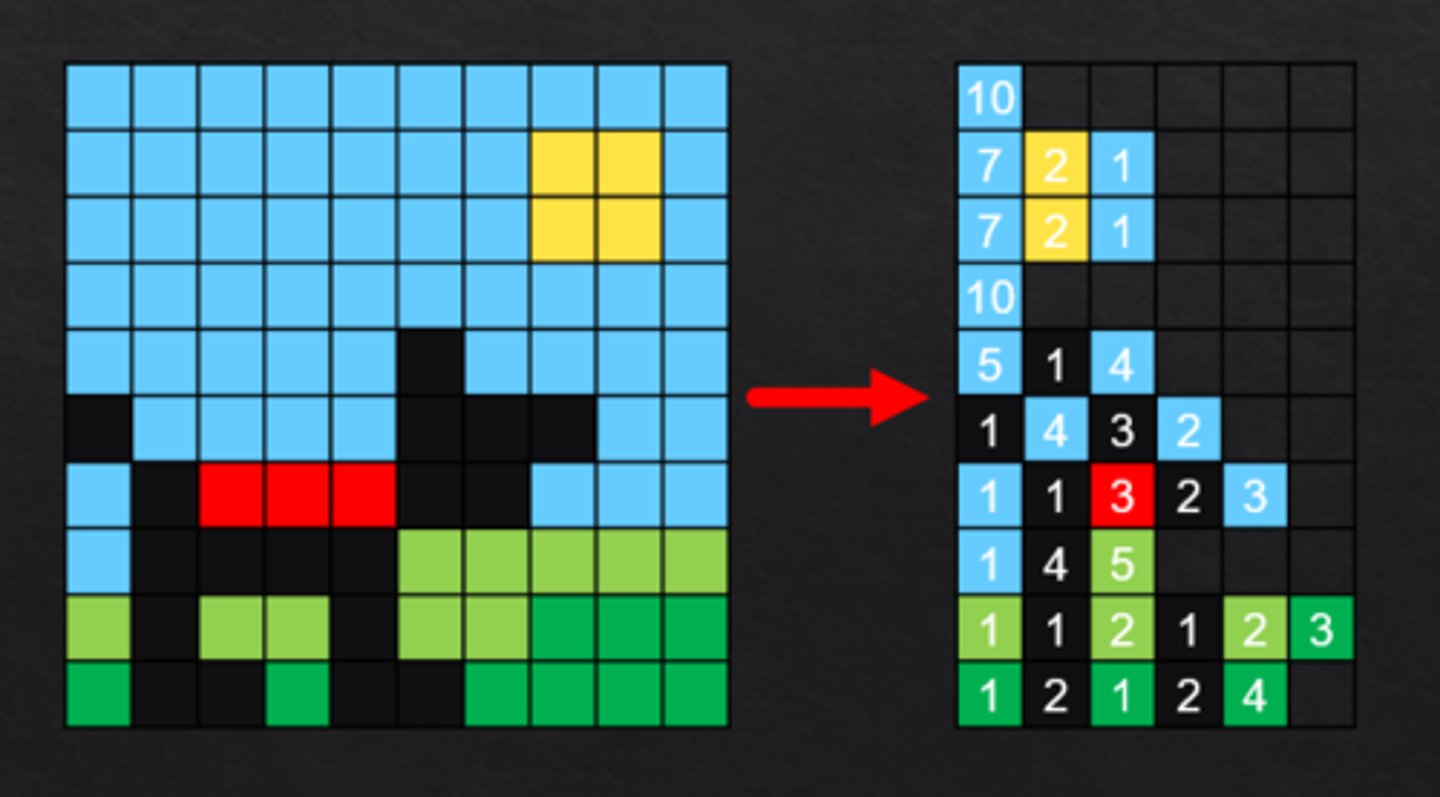
RLE of sound
Sound recordings can have many thousands of samples taken every second
The same sound or note played for a fraction of a second could result in hundreds of identical samples
RLE records one example of the sample and how many times it consecutively repeats

JPEG
A commonly used file format that uses lossy compression for digital photography
MP3
Lossy compressed audio file format